Vinyl polymer
Encyclopedia

Polymer
A polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units. These subunits are typically connected by covalent chemical bonds...
s derived from vinyl
Vinyl
A vinyl compound is any organic compound that contains a vinyl group ,which are derivatives of ethene, CH2=CH2, with one hydrogen atom replaced with some other group...
monomer
Monomer
A monomer is an atom or a small molecule that may bind chemically to other monomers to form a polymer; the term "monomeric protein" may also be used to describe one of the proteins making up a multiprotein complex...
s. Their backbone is an extended alkane chain, made by polymerizing an alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
group (C=C) into a chain (..-C-C-C-C-..). In popular usage, "vinyl" refers only to polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Vinyl polymers are the most common type of plastic:
- Polymerized simple alkenes: polyethylenePolyethylenePolyethylene or polythene is the most widely used plastic, with an annual production of approximately 80 million metric tons...
from ethene, polypropylenePolypropylenePolypropylene , also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications including packaging, textiles , stationery, plastic parts and reusable containers of various types, laboratory equipment, loudspeakers, automotive components, and polymer banknotes...
from propene and polybutadienePolybutadienePolybutadiene is a synthetic rubber that is a polymer formed from the polymerization process of the monomer 1,3-butadiene.It has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tires, which consumes about 70% of the production...
from butadiene. - PolystyrenePolystyrenePolystyrene ) also known as Thermocole, abbreviated following ISO Standard PS, is an aromatic polymer made from the monomer styrene, a liquid hydrocarbon that is manufactured from petroleum by the chemical industry...
is made from styrene or "vinyl benzene". - Polyvinyl chloridePolyvinyl chloridePolyvinyl chloride, commonly abbreviated PVC, is a thermoplastic polymer. It is a vinyl polymer constructed of repeating vinyl groups having one hydrogen replaced by chloride. Polyvinyl chloride is the third most widely produced plastic, after polyethylene and polypropylene. PVC is widely used in...
(PVC) is made by polymerizationPolymerizationIn polymer chemistry, polymerization is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form three-dimensional networks or polymer chains...
of the monomerMonomerA monomer is an atom or a small molecule that may bind chemically to other monomers to form a polymer; the term "monomeric protein" may also be used to describe one of the proteins making up a multiprotein complex...
vinyl chlorideVinyl chlorideVinyl chloride is the organochloride with the formula H2C:CHCl. It is also called vinyl chloride monomer, VCM or chloroethene. This colorless compound is an important industrial chemical chiefly used to produce the polymer polyvinyl chloride . At ambient pressure and temperature, vinyl chloride...
(chloroethene) CH2=CHCl - Polyvinyl acetatePolyvinyl acetatePolyvinyl acetate, PVA, PVAc, poly, is a rubbery synthetic polymer with the formula n. It belongs to the polyvinyl esters family with the general formula -[RCOOCHCH2]-...
(PVAc) is made by polymerization of vinyl acetateVinyl acetateVinyl acetate is an organic compound with the formula CH3COOCH=CH2. A colorless liquid with a pungent odor, it is the precursor to polyvinyl acetate, an important polymer in industry.-Production:...
. In a water suspension, this is used as a glue. - Polyvinyl alcoholPolyvinyl alcoholPolyvinyl alcohol is a water-soluble synthetic polymer .-Properties:...
(PVA) is produced by hydrolysisHydrolysisHydrolysis is a chemical reaction during which molecules of water are split into hydrogen cations and hydroxide anions in the process of a chemical mechanism. It is the type of reaction that is used to break down certain polymers, especially those made by condensation polymerization...
of polyvinyl acetatePolyvinyl acetatePolyvinyl acetate, PVA, PVAc, poly, is a rubbery synthetic polymer with the formula n. It belongs to the polyvinyl esters family with the general formula -[RCOOCHCH2]-...
. (Not by polymerization of the monomer vinyl alcohol or ethenolEthenolVinyl alcohol, also called ethenol , is an alcohol. It is not to be confused with the drinking alcohol, ethanol. With the formula 2CHH, vinyl alcohol is an isomer of acetaldehyde and ethylene oxide...
, which is an unfavored keto-enol tautomerTautomerTautomers are isomers of organic compounds that readily interconvert by a chemical reaction called tautomerization. This reaction commonly results in the formal migration of a hydrogen atom or proton, accompanied by a switch of a single bond and adjacent double bond...
of acetaldehydeAcetaldehydeAcetaldehyde is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CHO or MeCHO. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale industrially. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants as part...
.) - PolyacrylonitrilePolyacrylonitrilePolyacrylonitrile is a synthetic, semicrystalline organic polymer resin, with the linear formula n. Though it is thermoplastic, it does not melt under normal conditions. It degrades before melting. It melts above 300 degrees Celsius only if the heating rates are 50 degrees per minute or above...
is prepared from acrylonitrileAcrylonitrileAcrylonitrile is the chemical compound with the formula C3H3N. This pungent-smelling colorless liquid often appears yellow due to impurities. It is an important monomer for the manufacture of useful plastics. In terms of its molecular structure, it consists of a vinyl group linked to a nitrile...
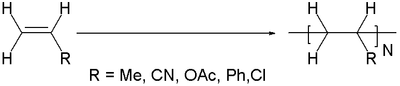
Other vinyl monomers with a 1,2-substitution pattern do as a general rule not polymerize due to steric hindrance it is thermodynamically still favorable. As an exception it was found that the monomer fumaronitrile (related to fumaric acid
Fumaric acid
Fumaric acid or trans-butenedioic acid is the chemical compound with the formula HO2CCH=CHCO2H. This white crystalline compound is one of two isomeric unsaturated dicarboxylic acids, the other being maleic acid. In fumaric acid the carboxylic acid groups are trans and in maleic acid they are cis...
and also to acrylonitrile
Acrylonitrile
Acrylonitrile is the chemical compound with the formula C3H3N. This pungent-smelling colorless liquid often appears yellow due to impurities. It is an important monomer for the manufacture of useful plastics. In terms of its molecular structure, it consists of a vinyl group linked to a nitrile...
but with an extra nitrile group) does polymerize but only in a very special way
- .
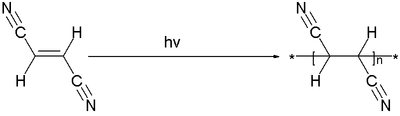
Vinyl polymers are produced catalytically; titanium
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color....
-centered Ziegler-Natta catalyst
Ziegler-Natta catalyst
A Ziegler–Natta catalyst is a catalyst used in the synthesis of polymers of 1-alkenes . Three types of Ziegler–Natta catalysts are currently employed:* Solid and supported catalysts based on titanium compounds...
is the main modern commercial catalyst.
A very thin film of monomer was prepared in a vacuum chamber
Vacuum chamber
A vacuum chamber is a rigid enclosure from which air and other gases are removed by a vacuum pump. The resulting low pressure, commonly referred to as a vacuum, allows researchers to conduct physical experiments or to test mechanical devices which must operate in outer space...
on a tantalum
Tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as tantalium, the name comes from Tantalus, a character in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a rare, hard, blue-gray, lustrous transition metal that is highly corrosion resistant. It is part of the refractory...
substrate at -173°C and then photopolymerized. Due to the poor penetration depth of the radiation, thin polymer films with thickness several micrometre
Micrometre
A micrometer , is by definition 1×10-6 of a meter .In plain English, it means one-millionth of a meter . Its unit symbol in the International System of Units is μm...
s were obtained nevertheless with degree of polymerization
Degree of polymerization
The degree of polymerization, or DP, is usually defined as the number of monomeric units in a macromolecule or polymer or oligomer molecule.For a homopolymer, there is only one type of monomeric unit andthe number-average degree of polymerization is given by...
in the 10,000 range. The polymerization is able to take place because the monomer molecules in the film are completely disorganized (isotropic) and therefore there is always a possibility for two monomers to react which they do not have in the crystalline phase.