
Voiceless velar lateral fricative
Encyclopedia
The voiceless velar lateral fricative is a very rare speech sound. As one element of an affricate, it is found for example in Zulu
and Xhosa
. However, a simple fricative has only been reported from a few languages in the Caucasus
and New Guinea
.
Archi
, a Northeast Caucasian language
of Dagestan
, has four velar lateral fricatives which are voiceless: plain [ʟ̝̊], labialized
[ʟ̝̊ʷ], fortis
[ʟ̝̊ː], and labialized fortis [ʟ̝̊ːʷ]. Although clearly fricatives
, these are further forward than velar
s in most languages, and might better be called prevelar. Archi also has a voiced fricative
, as well as a voiceless
and several ejective
lateral velar affricates, but no alveolar
lateral fricatives or affricates.
In New Guinea, the Melpa
and Nii languages have a voiceless velar lateral fricative, which they write with a double-bar L l. This sound also appears in syllable coda
position as an allophone
of the voiced velar lateral fricative
in Kuman
.
The IPA
has no separate symbol for these sounds, but it can be transcribed as a devoiced raised velar lateral approximant, [ʟ̝̊], in which the devoicing ring diacritic is placed above the letter to avoid clashing with the raising diacritic
. Furthermore, the "belt" of the voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
on the symbol of the corresponding lateral approximant forms the basis for occasional ad hoc symbols for the other voiceless lateral fricatives:
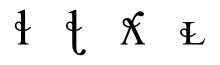
Indeed, SIL International
has added these symbols to the Private Use Areas of their Charis
and Doulos
fonts, as U+F268 ().
Zulu language
Zulu is the language of the Zulu people with about 10 million speakers, the vast majority of whom live in South Africa. Zulu is the most widely spoken home language in South Africa as well as being understood by over 50% of the population...
and Xhosa
Xhosa language
Xhosa is one of the official languages of South Africa. Xhosa is spoken by approximately 7.9 million people, or about 18% of the South African population. Like most Bantu languages, Xhosa is a tonal language, that is, the same sequence of consonants and vowels can have different meanings when said...
. However, a simple fricative has only been reported from a few languages in the Caucasus
Caucasus
The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea...
and New Guinea
New Guinea
New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago...
.
Archi
Archi language
Archi is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken by the 1,200 Archis in the village of Archib, southern Dagestan, Russia and the six surrounding smaller villages...
, a Northeast Caucasian language
Northeast Caucasian languages
The Northeast Caucasian languages constitute a language family spoken in the Russian republics of Dagestan, Chechnya, Ingushetia, northern Azerbaijan, and in northeastern Georgia, as well as in diaspora populations in Russia, Turkey, and the Middle East...
of Dagestan
Dagestan
The Republic of Dagestan is a federal subject of Russia, located in the North Caucasus region. Its capital and the largest city is Makhachkala, located at the center of Dagestan on the Caspian Sea...
, has four velar lateral fricatives which are voiceless: plain [ʟ̝̊], labialized
Labialisation
Labialization is a secondary articulatory feature of sounds in some languages. Labialized sounds involve the lips while the remainder of the oral cavity produces another sound. The term is normally restricted to consonants. When vowels involve the lips, they are called rounded.The most common...
[ʟ̝̊ʷ], fortis
Fortis and lenis
In linguistics, fortis and lenis are terms generally used to refer to groups of consonants that are produced with greater and lesser energy, respectively, such as in energy applied, articulation, etc....
[ʟ̝̊ː], and labialized fortis [ʟ̝̊ːʷ]. Although clearly fricatives
Fricative consonant
Fricatives are consonants produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate, in the case of German , the final consonant of Bach; or...
, these are further forward than velar
Velar consonant
Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth, known also as the velum)....
s in most languages, and might better be called prevelar. Archi also has a voiced fricative
Voiced velar lateral fricative
The voiced velar lateral fricative is a very rare speech sound that can be found in Archi, a Northeast Caucasian language of Dagestan, in which it is clearly a fricative, although further forward than velars in most languages, and might better be called prevelar...
, as well as a voiceless
Voiceless velar lateral affricate
The voiceless velar lateral affricate is an uncommon speech sound found as a phoneme in the Caucasus and as an allophone in several languages of eastern and southern Africa....
and several ejective
Ejective velar lateral affricate
The velar lateral ejective affricate is a rare type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ....
lateral velar affricates, but no alveolar
Alveolar consonant
Alveolar consonants are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli of the superior teeth...
lateral fricatives or affricates.
In New Guinea, the Melpa
Melpa language
Melpa is a Papuan language spoken by about 130,000 people predominantly in Mount Hagen and the surrounding district of Western Highlands Province, Papua New Guinea....
and Nii languages have a voiceless velar lateral fricative, which they write with a double-bar L l. This sound also appears in syllable coda
Syllable coda
In phonology, a syllable coda comprises the consonant sounds of a syllable that follow the nucleus, which is usually a vowel. The combination of a nucleus and a coda is called a rime. Some syllables consist only of a nucleus with no coda...
position as an allophone
Allophone
In phonology, an allophone is one of a set of multiple possible spoken sounds used to pronounce a single phoneme. For example, and are allophones for the phoneme in the English language...
of the voiced velar lateral fricative
Voiced velar lateral fricative
The voiced velar lateral fricative is a very rare speech sound that can be found in Archi, a Northeast Caucasian language of Dagestan, in which it is clearly a fricative, although further forward than velars in most languages, and might better be called prevelar...
in Kuman
Kuman language (New Guinea)
Kuman is a language of Simbu Province, Papua New Guinea. , it was spoken by about 80,000 people, 10,000 of which were monolinguals. In 2000 the number of speakers increased to 115,000.-References:...
.
The IPA
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
has no separate symbol for these sounds, but it can be transcribed as a devoiced raised velar lateral approximant, [ʟ̝̊], in which the devoicing ring diacritic is placed above the letter to avoid clashing with the raising diacritic
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
. Furthermore, the "belt" of the voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
Voiceless alveolar lateral fricative
The voiceless alveolar lateral fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents voiceless dental, alveolar, and postalveolar fricatives is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is K...
on the symbol of the corresponding lateral approximant forms the basis for occasional ad hoc symbols for the other voiceless lateral fricatives:
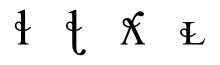
Indeed, SIL International
SIL International
SIL International is a U.S.-based, worldwide, Christian non-profit organization, whose main purpose is to study, develop and document languages, especially those that are lesser-known, in order to expand linguistic knowledge, promote literacy, translate the Christian Bible into local languages,...
has added these symbols to the Private Use Areas of their Charis
Charis SIL
Charis SIL is a glyphic serif typeface developed by SIL International. It is based on Bitstream Charter, one of the first fonts designed for laser printers...
and Doulos
Doulos SIL
Doulos SIL is a serif typeface developed by SIL International, very similar to Times or Times New Roman. Unlike Times New Roman, Doulos only has a single face, Regular...
fonts, as U+F268 ().

