
Volcher Coiter
Encyclopedia
Volcher Coiter (1534, Groningen - 2 June 1576, Brienne-le-Château
) was a Dutch
anatomist who established the study of comparative osteology
and first described cerebrospinal meningitis
.
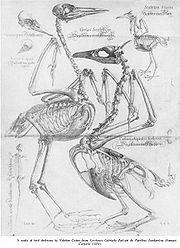 Coiter was born in Groningen. He studied in Italy
Coiter was born in Groningen. He studied in Italy
and France
and was a pupil of Ulisse Aldrovandi
, Gabriele Falloppio
, Bartolomeo Eustachi
and Guillaume Rondelet
. He became city physician of Nuremberg
in 1569. He took part in the French Wars of Religion as field surgeon to Count Palatine Johann Casimir. He died in Champagne
during the German forces' return march.
His works included Externarum et Internarum Principalium Humani Corporis Partium Tabulae (1573) and De Avium Sceletis et Praecipius Musculis (1575). His work included detailed anatomical studies of birds as well as a classification of the birds based on structure and habits. He produced an early dichotomous classification key.
Brienne-le-Château
Brienne-le-Château is a commune in the Aube department in north-central France. It is located from the right bank of the Aube River and 26 m. northeast of Troyes....
) was a Dutch
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
anatomist who established the study of comparative osteology
Osteology
Osteology is the scientific study of bones. A subdiscipline of anatomy, anthropology, and archeology, osteology is a detailed study of the structure of bones, skeletal elements, teeth, morphology, function, disease, pathology, the process of ossification , the resistance and hardness of bones , etc...
and first described cerebrospinal meningitis
Meningitis
Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known collectively as the meninges. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms, and less commonly by certain drugs...
.

Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
and France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and was a pupil of Ulisse Aldrovandi
Ulisse Aldrovandi
Ulisse Aldrovandi was an Italian naturalist, the moving force behind Bologna's botanical garden, one of the first in Europe. Carolus Linnaeus and the comte de Buffon reckoned him the father of natural history studies...
, Gabriele Falloppio
Gabriele Falloppio
Gabriele Falloppio , often known by his Latin name Fallopius, was one of the most important anatomists and physicians of the sixteenth century....
, Bartolomeo Eustachi
Bartolomeo Eustachi
Bartolomeo Eustachi , also known by his Latin name of Eustachius, was one of the founders of the science of human anatomy.-Life:...
and Guillaume Rondelet
Guillaume Rondelet
Guillaume Rondelet , known also as Rondeletus , was Regus Professor of medicine at the University of Montpellier in southern France and Chancellor of the University between 1556 and his death in 1566. He achieved renown as an anatomist and a naturalist with a particular interest in botany and zoology...
. He became city physician of Nuremberg
Nuremberg
Nuremberg[p] is a city in the German state of Bavaria, in the administrative region of Middle Franconia. Situated on the Pegnitz river and the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal, it is located about north of Munich and is Franconia's largest city. The population is 505,664...
in 1569. He took part in the French Wars of Religion as field surgeon to Count Palatine Johann Casimir. He died in Champagne
Champagne, France
Champagne is a historic province in the northeast of France, now best known for the sparkling white wine that bears its name.Formerly ruled by the counts of Champagne, its western edge is about 100 miles east of Paris. The cities of Troyes, Reims, and Épernay are the commercial centers of the area...
during the German forces' return march.
His works included Externarum et Internarum Principalium Humani Corporis Partium Tabulae (1573) and De Avium Sceletis et Praecipius Musculis (1575). His work included detailed anatomical studies of birds as well as a classification of the birds based on structure and habits. He produced an early dichotomous classification key.

