
W Ursae Majoris variable
Encyclopedia
A W Ursae Majoris variable is a type of eclipsing binary variable star
. These stars are close binaries, whose surfaces are in contact with one another. They are termed contact binaries
because the two stars touch and they essentially share material in their outer layers. Through the neck between the two stars mass and heat is transferred between the components. The latter one equalizes the temperatures of the two stars.
W Ursae Majoris variables are the most common variable stars in the present day Universe. About 1 percent of all stars belong to this group.
The class is divided into two subclasses: A-type and W-type (L. Binnendijk, Veroeffentlichungen der Remeis-Sternwarte zu Bamberg, Nr. 40., p. 36, 1965) A-type W UMa binaries are composed of two stars both hotter than the Sun, having spectral types
A or F, and periods
of 0.4 to 0.8 day. The W-types have cooler spectral types of G or K and shorter periods of 0.22 to 0.4 day. The difference between the surface temperatures of the components is less than several hundred kelvin
s. A new subclass was introduced in 1978: B-type. The B-types have larger surface temperature difference. In 2004 the H (high mass ratio) systems were discovered by Sz. Csizmadia and P. Klagyivik (Astronomy and Astrophysics
, Vol. 426, pp. 1001-1005 (2004)). The H-types have a higher mass ratio than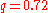 (
(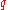 = (secondary's mass)/(primary's mass)) and they have extra angular momentum
= (secondary's mass)/(primary's mass)) and they have extra angular momentum
.
Their light curves differ from those of classical eclipsing binaries, undergoing a constant ellipsoidal variation rather than discrete eclipse
s. This is because the stars are in physical contact and thus constantly eclipse one another, and also because the stars are gravitationally distorted by one another. The depths of the brightness minima are usually equal because both stars have nearly equal luminosities
.
W Ursae Majoris
is the prototype of this class.
Variable star
A star is classified as variable if its apparent magnitude as seen from Earth changes over time, whether the changes are due to variations in the star's actual luminosity, or to variations in the amount of the star's light that is blocked from reaching Earth...
. These stars are close binaries, whose surfaces are in contact with one another. They are termed contact binaries
Contact binary
In astronomy, a contact binary is a binary star system whose component stars are so close that they touch each other or have merged to share their gaseous envelopes. A binary system whose stars share an envelope may also be called an overcontact binary...
because the two stars touch and they essentially share material in their outer layers. Through the neck between the two stars mass and heat is transferred between the components. The latter one equalizes the temperatures of the two stars.
W Ursae Majoris variables are the most common variable stars in the present day Universe. About 1 percent of all stars belong to this group.
The class is divided into two subclasses: A-type and W-type (L. Binnendijk, Veroeffentlichungen der Remeis-Sternwarte zu Bamberg, Nr. 40., p. 36, 1965) A-type W UMa binaries are composed of two stars both hotter than the Sun, having spectral types
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is a classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. The spectral class of a star is a designated class of a star describing the ionization of its chromosphere, what atomic excitations are most prominent in the light, giving an objective measure...
A or F, and periods
Orbital period
The orbital period is the time taken for a given object to make one complete orbit about another object.When mentioned without further qualification in astronomy this refers to the sidereal period of an astronomical object, which is calculated with respect to the stars.There are several kinds of...
of 0.4 to 0.8 day. The W-types have cooler spectral types of G or K and shorter periods of 0.22 to 0.4 day. The difference between the surface temperatures of the components is less than several hundred kelvin
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s. A new subclass was introduced in 1978: B-type. The B-types have larger surface temperature difference. In 2004 the H (high mass ratio) systems were discovered by Sz. Csizmadia and P. Klagyivik (Astronomy and Astrophysics
Astronomy and Astrophysics
* Astronomy and Astrophysics has a 2010 impact factor of 4.410.-See also:*The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review*Advanced Satellite for Cosmology and Astrophysics*Astronomy & Geophysics*Astronomical Journal*Astrophysical Journal...
, Vol. 426, pp. 1001-1005 (2004)). The H-types have a higher mass ratio than
 (
(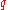 = (secondary's mass)/(primary's mass)) and they have extra angular momentum
= (secondary's mass)/(primary's mass)) and they have extra angular momentumAngular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
.
Their light curves differ from those of classical eclipsing binaries, undergoing a constant ellipsoidal variation rather than discrete eclipse
Eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event that occurs when an astronomical object is temporarily obscured, either by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer...
s. This is because the stars are in physical contact and thus constantly eclipse one another, and also because the stars are gravitationally distorted by one another. The depths of the brightness minima are usually equal because both stars have nearly equal luminosities
Luminosity
Luminosity is a measurement of brightness.-In photometry and color imaging:In photometry, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance, which is the density of luminous intensity in a given direction. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre.The luminosity function...
.
W Ursae Majoris
W Ursae Majoris
W Ursae Majoris is a variable star in the constellation Ursa Major. It is an eclipsing contact binary whose two component stars share a common outer layer, and is the prototype of a class of contact binary variables known as W Ursae Majoris variables...
is the prototype of this class.

