
Weston cell
Encyclopedia
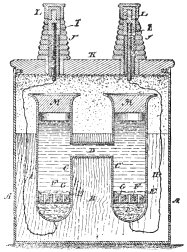
The Weston cell, invented by Edward Weston
Edward Weston (chemist)
Edward Weston was an English-born American chemist noted for his achievements in electroplating and his development of the electrochemical cell, named the Weston cell, for the voltage standard...
in 1893, is a wet-chemical cell that produces a highly stable voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
suitable as a laboratory standard for calibration
Calibration
Calibration is a comparison between measurements – one of known magnitude or correctness made or set with one device and another measurement made in as similar a way as possible with a second device....
of voltmeter
Voltmeter
A voltmeter is an instrument used for measuring electrical potential difference between two points in an electric circuit. Analog voltmeters move a pointer across a scale in proportion to the voltage of the circuit; digital voltmeters give a numerical display of voltage by use of an analog to...
s. It was adopted as the International Standard for EMF
Electromotive force
In physics, electromotive force, emf , or electromotance refers to voltage generated by a battery or by the magnetic force according to Faraday's Law, which states that a time varying magnetic field will induce an electric current.It is important to note that the electromotive "force" is not a...
between 1911 and 1990.
Chemistry
The anodeAnode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
is an amalgam
Amalgam (chemistry)
An amalgam is a substance formed by the reaction of mercury with another metal. Almost all metals can form amalgams with mercury, notable exceptions being iron and platinum. Silver-mercury amalgams are important in dentistry, and gold-mercury amalgam is used in the extraction of gold from ore.The...
of cadmium
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low...
with mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
, the cathode
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
is of pure mercury, the electrolyte
Electrolyte
In chemistry, an electrolyte is any substance containing free ions that make the substance electrically conductive. The most typical electrolyte is an ionic solution, but molten electrolytes and solid electrolytes are also possible....
is a solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
of cadmium sulfate octahydrate
Cadmium sulfate
Cadmium sulfate is the name of a series of related inorganic compounds with the formula CdSO4.xH2O. The most common form is the monohydrate CdSO4.H2O, but two other forms are known CdSO4.8/3H2O and the anhydrous salt...
and the depolarizer
Depolarizer
A depolarizer or depolariser, in electrochemistry, according to an IUPAC definition, is a synonym of electroactive substance, i.e., a substance which changes its oxidation state, or partakes in a formation or breaking of chemical bonds, in a charge-transfer step of an electrochemical reaction.In...
is a paste of mercurous sulfate.
As shown in the illustration, the cell is set up in an H-shaped glass vessel with the cadmium amalgam in one leg and the pure mercury in the other. Electrical connections to the cadmium amalgam and the mercury are made by platinum
Platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal...
wires fused through the lower ends of the legs.
Characteristics
The original design was a saturated cadmium cell producing a convenient 1.018638 VoltVolt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
reference and had the advantage of having a lower temperature coefficient
Temperature coefficient
The temperature coefficient is the relative change of a physical property when the temperature is changed by 1 K.In the following formula, let R be the physical property to be measured and T be the temperature at which the property is measured. T0 is the reference temperature, and ΔT is the...
than the previously used Clark cell
Clark cell
The Clark cell, invented by English engineer Josiah Latimer Clark in 1873, is a wet-chemical cell that produces a highly stable voltage usable as a laboratory standard.-Chemistry:...
. (Reference cells must be applied in such a way that no current is drawn from them.)
The temperature coefficient can be reduced by shifting to an unsaturated design, the predominant type today. However, an unsaturated cell's output decreases by some 80 microvolts per year, which is compensated by periodic calibration against a saturated cell.
Dr. F.A. Wolff, NBS Researcher and 1st Chair of the Washington AIEE Section contributed significant research to the
studies of the Weston Cell.
Literature
- Practical Electricity by W. E. Ayrton and T. Mather, published by Cassell and Company, London, 1911, pp 198–203, "Voltaic cell"
- Standard Cells, Their Construction, Maintenance, and Characteristics by Walter J. Hamer, National Bureau of Standards Monograph 84, January 15, 1965.

