Wihtred of Kent
Encyclopedia
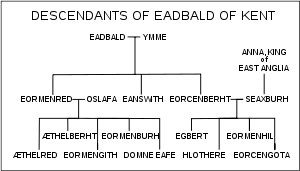
Wihtred was king of Kent
from about 690 or 691 until his death. He was a son of Ecgberht I
and a brother of Eadric
. Wihtred acceded to the throne after a confused period in the 680s, which included a brief conquest of Kent by Cædwalla of Wessex and subsequent dynastic conflicts. His immediate predecessor was Oswine of Kent
, who was probably descended from Eadbald of Kent
, though not through the same line as Wihtred. Shortly after the start of his reign, Wihtred issued a code of laws—the Law of Wihtred
—that has been preserved in a manuscript known as the Textus Roffensis
. The laws pay a great deal of attention to the rights of the Church, including punishment for irregular marriages and for pagan worship. Wihtred's long reign had few incidents recorded in the annals of the day. He was succeeded in 725 by his sons, Æthelberht II
, Eadberht I
, and Ælfric.
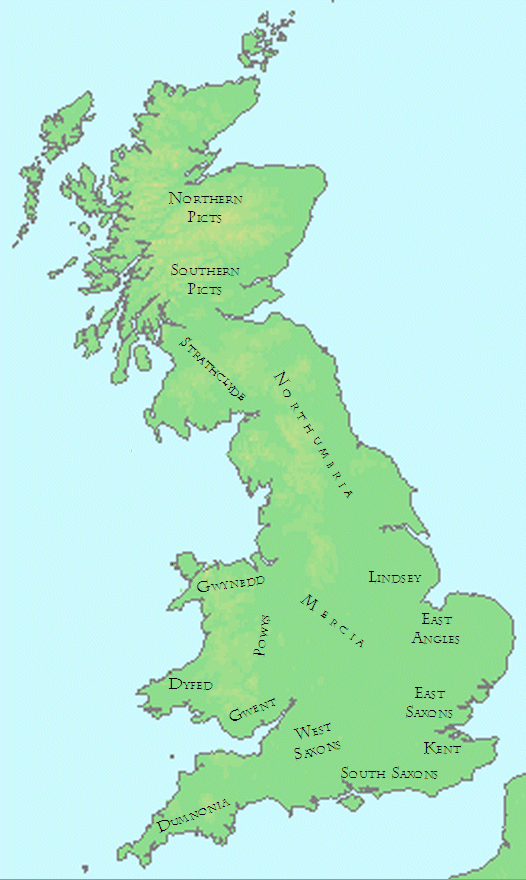 The dominant force in late seventh-century politics south of the River Humber was Wulfhere of Mercia
The dominant force in late seventh-century politics south of the River Humber was Wulfhere of Mercia
, who reigned from the late 650s to 675. The king of Kent for much of this time was Ecgberht
, who died in 673. Ecgberht's sons, Eadric
and Wihtred, were probably no more than infants of two or three years old when their father died, and Wulfhere was their uncle by virtue of his marriage to Eormenhild, Ecgberht's sister. Hlothhere
, Ecgberht's brother, became king of Kent, but not until about a year later, in 674, and it may be that Wulfhere opposed the accession of Hlothhere and was the effective ruler of Kent during this year-long interregnum.
Eadric raised an army against his uncle and Hlothhere died of wounds sustained in battle in February 685 or possibly 686. Eadric died the following year, and according to Bede
, whose Ecclesiastical History of the English People is one of the primary sources for this period, the kingdom fell apart into disorder. Cædwalla of Wessex invaded in 686 and established his brother Mul
as king there; Cædwalla may have ruled Kent directly for a period when Mul was killed in 687. When Cædwalla departed for Rome in 688, Oswine
, who was probably supported by Æthelred of Mercia, took the throne for a time. Oswine lost power in 690, but Swæfheard
(son of Sebbi
, the king of Essex), who had been a king in Kent for a year or two, remained. There is clear evidence that both Swæfheard and Oswine were kings at the same time, as each witnessed the other's charters. It seems that Oswine was king of east Kent, which was usually the position of the dominant king, while Swæfheard was king of west Kent.
 Wihtred emerged from this disarray and became king in the early 690s. Bede describes his accession by saying that he was the "rightful" king, and that he "freed the nation from foreign invasion by his devotion and diligence". Oswine was also of the royal family, and arguably had a claim to the throne; hence it has been suggested that Bede's comments here are strongly partisan. Bede's correspondent on Kentish affairs was Albinus, abbot of the monastery of St. Peter and St. Paul (subsequently renamed St. Augustine's
Wihtred emerged from this disarray and became king in the early 690s. Bede describes his accession by saying that he was the "rightful" king, and that he "freed the nation from foreign invasion by his devotion and diligence". Oswine was also of the royal family, and arguably had a claim to the throne; hence it has been suggested that Bede's comments here are strongly partisan. Bede's correspondent on Kentish affairs was Albinus, abbot of the monastery of St. Peter and St. Paul (subsequently renamed St. Augustine's
) in Canterbury, and these views can almost certainly be ascribed to the Church establishment there.
Two charters provide evidence of Wihtred's date of accession. One, dated April 697, indicates Wihtred was then in the sixth year of his rule, so his accession can be dated to some time between April 691 and April 692. Another, dated 17 July 694, is in his fourth regnal year, giving a possible range of July 690 to July 691. The overlap in date ranges gives April to July of 691 as the likely date of his accession. Another estimate of the date of Wihtred's accession can be made from the duration of his reign, given by Bede as thirty four and a half years. He died on 23 April 725, which would imply an accession date in late 690.
Initially Wihtred ruled alongside Swæfheard. Bede's report of the election of Beorhtwald
as Archbishop of Canterbury
in July 692 mentions that Swæfheard and Wihtred were the kings of Kent, but Swæfheard is not heard of after this date. It appears that by 694 Wihtred was the sole ruler of Kent, though it may also be that his son Æthelberht
was a junior king in west Kent during Wihtred's reign. Wihtred is thought to have had three wives. His first was called Cynegyth, but a charter of 696 names Æthelburh as the royal consort and co-donor of an estate: the former spouse must have died or been dismissed after a short time. Near the end of his reign, a new partner, Wærburh, attested with Wihtred the proceedings of the synod at Bapchild
circa 716.
It was also in 694 that Wihtred made peace with the West Saxon
king Ine
. Ine's predecessor, Cædwalla, had invaded Kent and installed his brother Mul
as king, but the Kentishmen had subsequently revolted and burned Mul. Wihtred agreed compensation for the killing, but the amount paid to Ine is uncertain. Most manuscripts of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
record "thirty thousand", and some specify thirty thousand pounds. If the pounds are equal to sceat
tas, then this amount is the equal of a king's wergild—that is, the legal valuation of a man's life, according to his rank. It seems likely that Wihtred ceded some border territory to Ine as part of this settlement.
 The earliest Anglo-Saxon law code to survive, which may date from 602 or 603, is that of Æthelberht of Kent, whose reign ended in 616. In the 670s or 680s, a code was issued in the names of Hlothhere
The earliest Anglo-Saxon law code to survive, which may date from 602 or 603, is that of Æthelberht of Kent, whose reign ended in 616. In the 670s or 680s, a code was issued in the names of Hlothhere
and Eadric of Kent
. The next kings to issue laws were Ine of Wessex and Wihtred.
The dating of Wihtred’s and Ine’s laws is somewhat uncertain, but there is reason to believe that Wihtred’s laws were issued on 6 September 695, while Ine’s laws were written in 694 or shortly before. Ine had recently agreed peaceful terms with Wihtred over compensation for the death of Mul, and there are indications that the two rulers collaborated to some degree in producing their laws. In addition to the coincidence of timing, there is one clause that appears in almost identical form in both codes. Another sign of collaboration is that Wihtred’s laws use gesith, a West Saxon term for noble, in place of the Kentish term eorlcund. It is possible that Ine and Wihtred issued the law codes as an act of prestige, to re-establish authority after periods of disruption in both kingdoms.
Wihtred's laws were issued at "Berghamstyde"; it is not known for certain where this was, but the best candidate is Bearsted
, near Maidstone
. The laws are primarily concerned with religious affairs; only the last four of its twenty-eight chapters do not deal with ecclesiastical affairs. The first clause of the code gives the Church freedom from taxation. Subsequent clauses specify penalties for irregular marriages, heathen worship, work on the sabbath, and breaking fasts, among other things; and also define how members of each class of society—such as the king, bishops, priests, ceorls, and esnes—can clear themselves by giving an oath. In addition to the focus of the laws themselves, the introduction makes clear the importance of the Church in the legislative process. Bertwald, the Archbishop of Canterbury, was present at the assembly which devised the decrees, and so was Gefmund, the Bishop of Rochester; and "every order of the Church of that nation spoke in unanimity with the loyal people".
The privileges given to the Church are notable: in addition to the freedom from taxation, the oath of a bishop is "incontrovertible", which places it at the same level as the oath of a king, and the Church receives the same level of compensation for violence done to dependents as does the king. This has led one historian to describe the Church's power, less than a century after the original Roman mission landed in Kent, as "all but co-ordinate with the king himself in the Kentish state", and it has also been described as presupposing "a frightening degree of royal power". However, the presence of clauses that provide penalties for any of Wihtred's subjects who "sacrifice to devils" makes it clear that although Christianity was dominant, the older pagan beliefs of the population had by no means died out completely.
Clause 21 of the code specifies that a ceorl must find three men of his own class to be his "oath-helpers". An oath-helper would swear an oath on behalf of an accused man, to clear him from the suspicion of the crime. The laws of Ine were more stringent than this, requiring that a high-ranking person must be found to be an oath-helper for everyone, no matter what class they were from. The two laws taken together imply a significant weakening of an earlier state in which a man's kin were legally responsible for him.
, Eadberht I
, and Ælfric. The chronology of the reigns following Wihtred is unclear, although there is evidence of both an Æthelbert and at least one Eadbert in the following years. After Wihtred's death, and the departure of Ine of Wessex for Rome the following year, Æthelbald of Mercia became the dominant power in the south of England.
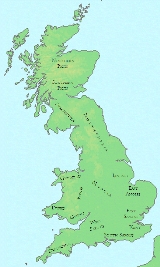
Kingdom of Kent
The Kingdom of Kent was a Jutish colony and later independent kingdom in what is now south east England. It was founded at an unknown date in the 5th century by Jutes, members of a Germanic people from continental Europe, some of whom settled in Britain after the withdrawal of the Romans...
from about 690 or 691 until his death. He was a son of Ecgberht I
Ecgberht of Kent
Ecgberht was a King of Kent who ruled from 664 to 673, succeeding his father Eorcenberht s:Ecclesiastical History of the English People/Book 4#1....
and a brother of Eadric
Eadric of Kent
Eadric was a King of Kent . He was the son of Ecgberht I.Eadric was for a time co-ruler alongside his uncle Hlothhere, and a code of laws issued in both their names has survived. However, Eadric eventually revolted and defeated Hlothhere with the aid of the South Saxons...
. Wihtred acceded to the throne after a confused period in the 680s, which included a brief conquest of Kent by Cædwalla of Wessex and subsequent dynastic conflicts. His immediate predecessor was Oswine of Kent
Oswine of Kent
Oswine, King of Kent, jointly with Swæfberht and Swæfheard.Oswine is known from three charters: one is dated July 689 and apparently witnessed by Swæfberht ; another is dated 26 January 690, witnessed by Swæfheard, and implies Oswine's descent from Eormenred; and in third , which is undated, but...
, who was probably descended from Eadbald of Kent
Eadbald of Kent
Eadbald was King of Kent from 616 until his death in 640. He was the son of King Æthelberht and his wife Bertha, a daughter of the Merovingian king Charibert. Æthelberht made Kent the dominant force in England during his reign and became the first Anglo-Saxon king to convert to Christianity from...
, though not through the same line as Wihtred. Shortly after the start of his reign, Wihtred issued a code of laws—the Law of Wihtred
Law of Wihtred
The Law of Wihtred is an early English legal text attributed to the Kentish king Wihtred . It is believed to date to the final decade of the 7th century and is the last of three Kentish legal texts, following the Law of Æthelberht and the Law of Hlothhere and Eadric...
—that has been preserved in a manuscript known as the Textus Roffensis
Textus Roffensis
The Textus Roffensis, or in full, Textus de Ecclesia Roffensi per Ernulphum episcopum , refers to a manuscript in which two originally separate manuscripts written about the same time, between 1122 and 1124, are bound together...
. The laws pay a great deal of attention to the rights of the Church, including punishment for irregular marriages and for pagan worship. Wihtred's long reign had few incidents recorded in the annals of the day. He was succeeded in 725 by his sons, Æthelberht II
Æthelbert II of Kent
Æthelbert II was king of Kent. Upon the death of his father Wihtred s:Ecclesiastical History of the English People/Book 5#23, the kingdom was ruled by his three sons, Æthelbert II, Eadberht I and Ælfric. Æthelbert seems to have outlived both of his brothers and later reigned jointly with his...
, Eadberht I
Eadbert I of Kent
Eadberht I was king of Kent from 725 to 748. After his father, Wihtred of Kent died, he inherited the kingdom of Kent along with his two brothers Æðelberht II and Ælfric. Æðelberht II seems to have been the eldest and more dominant brother. Eadberht I died in 748, according to the Anglo-Saxon...
, and Ælfric.
Kent in the late seventh century

Wulfhere of Mercia
Wulfhere was King of Mercia from the end of the 650s until 675. He was the first Christian king of all of Mercia, though it is not known when or how he converted from Anglo-Saxon paganism. His accession marked the end of Oswiu of Northumbria's overlordship of southern England, and Wulfhere...
, who reigned from the late 650s to 675. The king of Kent for much of this time was Ecgberht
Ecgberht of Kent
Ecgberht was a King of Kent who ruled from 664 to 673, succeeding his father Eorcenberht s:Ecclesiastical History of the English People/Book 4#1....
, who died in 673. Ecgberht's sons, Eadric
Eadric of Kent
Eadric was a King of Kent . He was the son of Ecgberht I.Eadric was for a time co-ruler alongside his uncle Hlothhere, and a code of laws issued in both their names has survived. However, Eadric eventually revolted and defeated Hlothhere with the aid of the South Saxons...
and Wihtred, were probably no more than infants of two or three years old when their father died, and Wulfhere was their uncle by virtue of his marriage to Eormenhild, Ecgberht's sister. Hlothhere
Hlothhere of Kent
Hlothhere was a King of Kent who ruled from 673 to 685.He succeeded his brother Ecgberht I in 673. He must have come into conflict with Mercia, since in 676 the Mercian king Æthelred invaded Kent and caused great destruction; according to Bede, even churches and monasteries were not spared, and...
, Ecgberht's brother, became king of Kent, but not until about a year later, in 674, and it may be that Wulfhere opposed the accession of Hlothhere and was the effective ruler of Kent during this year-long interregnum.
Eadric raised an army against his uncle and Hlothhere died of wounds sustained in battle in February 685 or possibly 686. Eadric died the following year, and according to Bede
Bede
Bede , also referred to as Saint Bede or the Venerable Bede , was a monk at the Northumbrian monastery of Saint Peter at Monkwearmouth, today part of Sunderland, England, and of its companion monastery, Saint Paul's, in modern Jarrow , both in the Kingdom of Northumbria...
, whose Ecclesiastical History of the English People is one of the primary sources for this period, the kingdom fell apart into disorder. Cædwalla of Wessex invaded in 686 and established his brother Mul
Mul of Kent
Mul may have briefly ruled as king of Kent following its conquest by his brother, Caedwalla of Wessex, in 686. Mul's father was Coenberht, making him a member of the House of Wessex The name Mul is very unusual and it has been postulated that it derives from the Latin mulus meaning mule, a word...
as king there; Cædwalla may have ruled Kent directly for a period when Mul was killed in 687. When Cædwalla departed for Rome in 688, Oswine
Oswine of Kent
Oswine, King of Kent, jointly with Swæfberht and Swæfheard.Oswine is known from three charters: one is dated July 689 and apparently witnessed by Swæfberht ; another is dated 26 January 690, witnessed by Swæfheard, and implies Oswine's descent from Eormenred; and in third , which is undated, but...
, who was probably supported by Æthelred of Mercia, took the throne for a time. Oswine lost power in 690, but Swæfheard
Swæfheard
Swæfheard was a king of Kent, reigning jointly with Oswine, Wihtred, and possibly Swæfberht.Swæfheard’s charter dated 1 March 689, in the second year of his reign, identifies his father as Sæbbi, King of Essex . He witnessed two charters of Oswine , one of which is dated 27 January 690...
(son of Sebbi
Sebbi of Essex
Sebbi was the joint King of Essex from 664 to 683 along with his brother, Sighere. After Sighere died, Sebbi became sole ruler of Essex until 694....
, the king of Essex), who had been a king in Kent for a year or two, remained. There is clear evidence that both Swæfheard and Oswine were kings at the same time, as each witnessed the other's charters. It seems that Oswine was king of east Kent, which was usually the position of the dominant king, while Swæfheard was king of west Kent.
Accession and reign

St Augustine's Abbey
St Augustine's Abbey was a Benedictine abbey in Canterbury, Kent, England.-Early history:In 597 Saint Augustine arrived in England, having been sent by Pope Gregory I, on what might nowadays be called a revival mission. The King of Kent at this time was Æthelberht, who happened to be married to a...
) in Canterbury, and these views can almost certainly be ascribed to the Church establishment there.
Two charters provide evidence of Wihtred's date of accession. One, dated April 697, indicates Wihtred was then in the sixth year of his rule, so his accession can be dated to some time between April 691 and April 692. Another, dated 17 July 694, is in his fourth regnal year, giving a possible range of July 690 to July 691. The overlap in date ranges gives April to July of 691 as the likely date of his accession. Another estimate of the date of Wihtred's accession can be made from the duration of his reign, given by Bede as thirty four and a half years. He died on 23 April 725, which would imply an accession date in late 690.
Initially Wihtred ruled alongside Swæfheard. Bede's report of the election of Beorhtwald
Bertwald
Berhtwald was the ninth Archbishop of Canterbury in England. The medieval writer Bede claims that he served as the Abbot of Glastonbury, and documentary evidence names Berhtwald as abbot at Reculver before his election as archbishop...
as Archbishop of Canterbury
Archbishop of Canterbury
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and principal leader of the Church of England, the symbolic head of the worldwide Anglican Communion, and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. In his role as head of the Anglican Communion, the archbishop leads the third largest group...
in July 692 mentions that Swæfheard and Wihtred were the kings of Kent, but Swæfheard is not heard of after this date. It appears that by 694 Wihtred was the sole ruler of Kent, though it may also be that his son Æthelberht
Æthelbert II of Kent
Æthelbert II was king of Kent. Upon the death of his father Wihtred s:Ecclesiastical History of the English People/Book 5#23, the kingdom was ruled by his three sons, Æthelbert II, Eadberht I and Ælfric. Æthelbert seems to have outlived both of his brothers and later reigned jointly with his...
was a junior king in west Kent during Wihtred's reign. Wihtred is thought to have had three wives. His first was called Cynegyth, but a charter of 696 names Æthelburh as the royal consort and co-donor of an estate: the former spouse must have died or been dismissed after a short time. Near the end of his reign, a new partner, Wærburh, attested with Wihtred the proceedings of the synod at Bapchild
Synod of Baccanceld
The Synod of Baccanceld was held in 694 in Bapchild, Kent.This meeting was rather a witenagemot, or Anglo-Saxon Parliament or Royal Council , rather than an ecclesiastical synod, as it was presided over by Wihtred, King of Kent...
circa 716.
It was also in 694 that Wihtred made peace with the West Saxon
Wessex
The Kingdom of Wessex or Kingdom of the West Saxons was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the West Saxons, in South West England, from the 6th century, until the emergence of a united English state in the 10th century, under the Wessex dynasty. It was to be an earldom after Canute the Great's conquest...
king Ine
Ine of Wessex
Ine was King of Wessex from 688 to 726. He was unable to retain the territorial gains of his predecessor, Cædwalla, who had brought much of southern England under his control and expanded West Saxon territory substantially...
. Ine's predecessor, Cædwalla, had invaded Kent and installed his brother Mul
Mul of Kent
Mul may have briefly ruled as king of Kent following its conquest by his brother, Caedwalla of Wessex, in 686. Mul's father was Coenberht, making him a member of the House of Wessex The name Mul is very unusual and it has been postulated that it derives from the Latin mulus meaning mule, a word...
as king, but the Kentishmen had subsequently revolted and burned Mul. Wihtred agreed compensation for the killing, but the amount paid to Ine is uncertain. Most manuscripts of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle is a collection of annals in Old English chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the Chronicle was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alfred the Great...
record "thirty thousand", and some specify thirty thousand pounds. If the pounds are equal to sceat
Sceat
Sceattas were small, thick silver coins minted in England, Frisia and Jutland during the Anglo-Saxon period.-History:Their name derives from an Old English word meaning 'wealth', which has been applied to these coins since the seventeenth century, based on interpretations of the law-code of King...
tas, then this amount is the equal of a king's wergild—that is, the legal valuation of a man's life, according to his rank. It seems likely that Wihtred ceded some border territory to Ine as part of this settlement.
Laws

Hlothhere of Kent
Hlothhere was a King of Kent who ruled from 673 to 685.He succeeded his brother Ecgberht I in 673. He must have come into conflict with Mercia, since in 676 the Mercian king Æthelred invaded Kent and caused great destruction; according to Bede, even churches and monasteries were not spared, and...
and Eadric of Kent
Eadric of Kent
Eadric was a King of Kent . He was the son of Ecgberht I.Eadric was for a time co-ruler alongside his uncle Hlothhere, and a code of laws issued in both their names has survived. However, Eadric eventually revolted and defeated Hlothhere with the aid of the South Saxons...
. The next kings to issue laws were Ine of Wessex and Wihtred.
The dating of Wihtred’s and Ine’s laws is somewhat uncertain, but there is reason to believe that Wihtred’s laws were issued on 6 September 695, while Ine’s laws were written in 694 or shortly before. Ine had recently agreed peaceful terms with Wihtred over compensation for the death of Mul, and there are indications that the two rulers collaborated to some degree in producing their laws. In addition to the coincidence of timing, there is one clause that appears in almost identical form in both codes. Another sign of collaboration is that Wihtred’s laws use gesith, a West Saxon term for noble, in place of the Kentish term eorlcund. It is possible that Ine and Wihtred issued the law codes as an act of prestige, to re-establish authority after periods of disruption in both kingdoms.
Wihtred's laws were issued at "Berghamstyde"; it is not known for certain where this was, but the best candidate is Bearsted
Bearsted
Bearsted is an ancient village and civil parish in mid-Kent, three miles to the east of Maidstone. The original village site was on the north bank of the River Len, a tributary of the River Medway, and at the foot of the North Downs....
, near Maidstone
Maidstone
Maidstone is the county town of Kent, England, south-east of London. The River Medway runs through the centre of the town linking Maidstone to Rochester and the Thames Estuary. Historically, the river was a source and route for much of the town's trade. Maidstone was the centre of the agricultural...
. The laws are primarily concerned with religious affairs; only the last four of its twenty-eight chapters do not deal with ecclesiastical affairs. The first clause of the code gives the Church freedom from taxation. Subsequent clauses specify penalties for irregular marriages, heathen worship, work on the sabbath, and breaking fasts, among other things; and also define how members of each class of society—such as the king, bishops, priests, ceorls, and esnes—can clear themselves by giving an oath. In addition to the focus of the laws themselves, the introduction makes clear the importance of the Church in the legislative process. Bertwald, the Archbishop of Canterbury, was present at the assembly which devised the decrees, and so was Gefmund, the Bishop of Rochester; and "every order of the Church of that nation spoke in unanimity with the loyal people".
The privileges given to the Church are notable: in addition to the freedom from taxation, the oath of a bishop is "incontrovertible", which places it at the same level as the oath of a king, and the Church receives the same level of compensation for violence done to dependents as does the king. This has led one historian to describe the Church's power, less than a century after the original Roman mission landed in Kent, as "all but co-ordinate with the king himself in the Kentish state", and it has also been described as presupposing "a frightening degree of royal power". However, the presence of clauses that provide penalties for any of Wihtred's subjects who "sacrifice to devils" makes it clear that although Christianity was dominant, the older pagan beliefs of the population had by no means died out completely.
Clause 21 of the code specifies that a ceorl must find three men of his own class to be his "oath-helpers". An oath-helper would swear an oath on behalf of an accused man, to clear him from the suspicion of the crime. The laws of Ine were more stringent than this, requiring that a high-ranking person must be found to be an oath-helper for everyone, no matter what class they were from. The two laws taken together imply a significant weakening of an earlier state in which a man's kin were legally responsible for him.
Death and succession
On his death, Wihtred left Kent to his three sons: Æthelberht IIÆthelbert II of Kent
Æthelbert II was king of Kent. Upon the death of his father Wihtred s:Ecclesiastical History of the English People/Book 5#23, the kingdom was ruled by his three sons, Æthelbert II, Eadberht I and Ælfric. Æthelbert seems to have outlived both of his brothers and later reigned jointly with his...
, Eadberht I
Eadbert I of Kent
Eadberht I was king of Kent from 725 to 748. After his father, Wihtred of Kent died, he inherited the kingdom of Kent along with his two brothers Æðelberht II and Ælfric. Æðelberht II seems to have been the eldest and more dominant brother. Eadberht I died in 748, according to the Anglo-Saxon...
, and Ælfric. The chronology of the reigns following Wihtred is unclear, although there is evidence of both an Æthelbert and at least one Eadbert in the following years. After Wihtred's death, and the departure of Ine of Wessex for Rome the following year, Æthelbald of Mercia became the dominant power in the south of England.

