Wulfhere of Mercia
Encyclopedia
Wulfhere was King of Mercia from the end of the 650s until 675. He was the first Christian king of all of Mercia
, though it is not known when or how he converted from Anglo-Saxon paganism. His accession marked the end of Oswiu of Northumbria
's overlordship of southern England, and Wulfhere extended his influence over much of that region. His campaigns against the West Saxons led to Mercian control
of much of the Thames valley
. He conquered the Isle of Wight
and the Meon
valley and gave them to King Æthelwealh of the South Saxons. He also had influence in Surrey
, Essex
, and Kent
. He married Eormenhild
, the daughter of King Eorcenberht of Kent
.
Wulfhere's father, Penda
, was killed in 655 at the Battle of Winwaed, fighting against Oswiu of Northumbria
. Penda's son Peada
became king under Oswiu's overlordship but was murdered a year later. Wulfhere came to the throne when Mercian nobles organized a revolt against Northumbria
n rule in 658 and drove out Oswiu's governors.
By 670, when Oswiu died, Wulfhere was the most powerful king in southern Britain. He was effectively the overlord of Britain south of the Humber
from the early 660s, although not overlord of Northumbria as his father had been. In 674, he challenged Oswiu's son Ecgfrith of Northumbria
, but was defeated. He died, probably of disease, in 675. Wulfhere was succeeded as King of Mercia by his brother, Æthelred. Stephen of Ripon's Life of Wilfrid
describes Wulfhere as "a man of proud mind, and insatiable will".
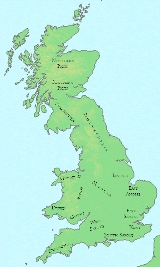
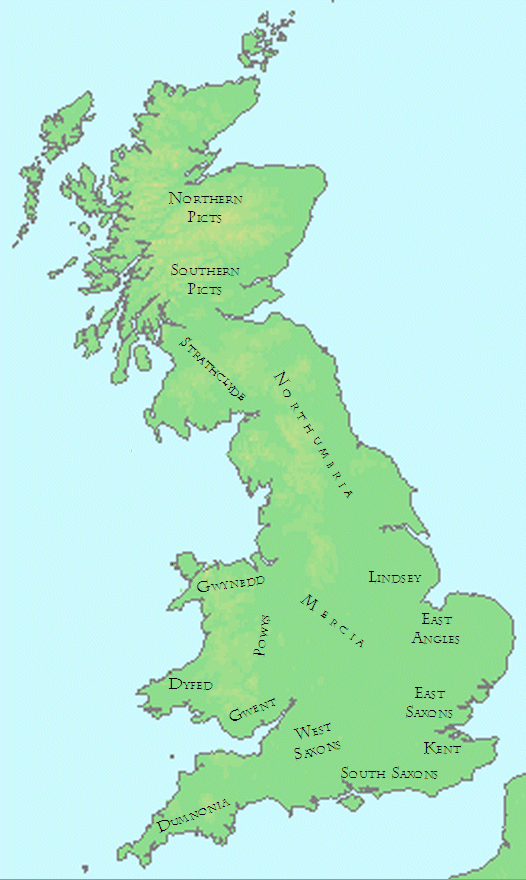 England in the early 7th century was ruled almost entirely by the Anglo-Saxon peoples
England in the early 7th century was ruled almost entirely by the Anglo-Saxon peoples
who had come to Britain from northwestern Europe, starting in the early 5th century. The monk Bede
, who wrote in the 8th century, considered the Mercians to be descended from the Angles
, one of the invading groups; the Saxons
and Jutes
settled in the south of Britain, while the Angles settled in the north. Little is known about the origins of the kingdom of Mercia
, in what is now the English midlands, but according to genealogies preserved in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
and the Anglian collection
the early kings were descended from Icel; the dynasty is therefore known as the Iclingas. The earliest Mercian king about whom definite historical information has survived is Penda of Mercia
, Wulfhere's father.
According to Bede's Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum
, a history of the English church, there were seven early Anglo-Saxon rulers who held imperium, or overlordship, over the other kingdoms. The fifth of these was Edwin of Northumbria
, who was killed at the battle of Hatfield Chase
by a combined force including Cadwallon
, a British king of Gwynedd
, and Penda. At the time of this victory, Penda was probably not yet king of Mercia. His children included two future kings of Mercia: Wulfhere and Æthelred.
After Edwin's death, Northumbria briefly fell apart into its two constituent kingdoms. Within a year Oswald
killed Cadwallon and reunited the kingdoms, and subsequently re-established Northumbrian hegemony over the south of England. However, on 5 August 642, Penda killed Oswald at the battle of Maserfield
, probably at Oswestry
in the northwest midlands. Penda is not recorded as overlord of the other southern Anglo-Saxon kings, but he became the most powerful of the Anglo-Saxon kings after he defeated Oswald. On Oswald's death, Northumbria was divided again: Oswald's son Oswiu
succeeded to the throne of Bernicia
, and Osric's
son Oswine
to Deira, the southern of the two kingdoms.
The main source for this period is Bede's History, completed in about 731. Despite its focus on the history of the church, this work also provides valuable information about the early pagan kingdoms. For other kingdoms than his native Northumbria, such as Wessex and Kent, Bede had an informant within the ecclesiastical establishment who supplied him with additional information. This does not seem to have been the case with Mercia, about which Bede is less informative than about other kingdoms. Further sources for this period include the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
, compiled at the end of the 9th century in Wessex
. The Chronicle's anonymous scribe appears to have incorporated much information recorded in earlier periods.
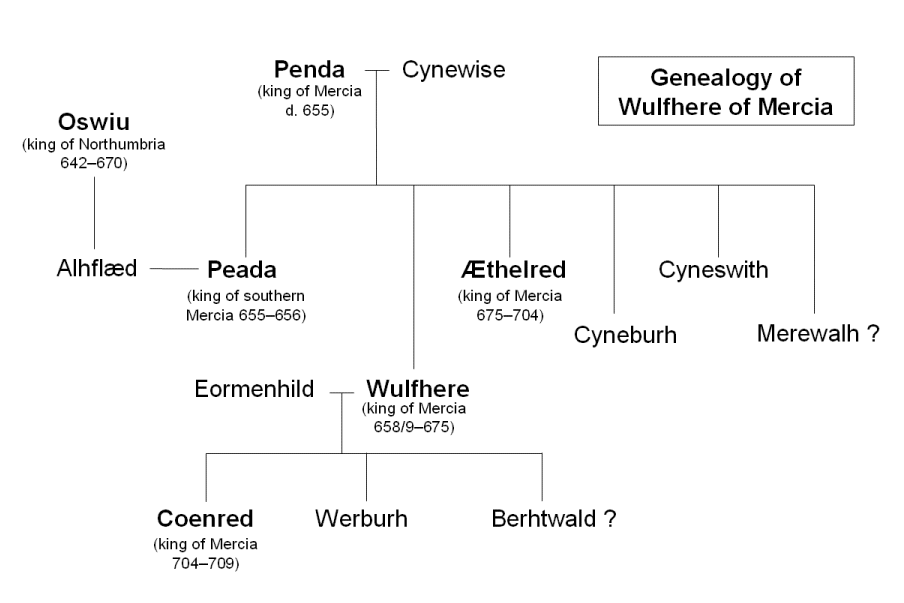 Wulfhere was the son of Penda of Mercia. Penda's queen, Cynewise, is named by Bede, who does not mention her children; no other wives of Penda are known and so it is likely but not certain that she was Wulfhere's mother. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle gives Penda's age as fifty in 626, and credits him with a thirty-year reign, but this would put Penda at eighty years old at the time of his death, which is generally thought unlikely as two of his sons (Wulfhere and Æthelred) are recorded as being young when he was killed. It is thought at least as likely that Penda was 50 years old at his death, rather than at his accession. Wulfhere's date of birth is unknown, but Bede describes him as a youth at the time of his accession in 658, so it is likely he was in his middle teens at that time; Penda would then have been in his thirties at the time Wulfhere was born.
Wulfhere was the son of Penda of Mercia. Penda's queen, Cynewise, is named by Bede, who does not mention her children; no other wives of Penda are known and so it is likely but not certain that she was Wulfhere's mother. The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle gives Penda's age as fifty in 626, and credits him with a thirty-year reign, but this would put Penda at eighty years old at the time of his death, which is generally thought unlikely as two of his sons (Wulfhere and Æthelred) are recorded as being young when he was killed. It is thought at least as likely that Penda was 50 years old at his death, rather than at his accession. Wulfhere's date of birth is unknown, but Bede describes him as a youth at the time of his accession in 658, so it is likely he was in his middle teens at that time; Penda would then have been in his thirties at the time Wulfhere was born.
Nothing is known of Wulfhere's childhood. He had two brothers, Peada and Æthelred, and two sisters, Cyneburh and Cyneswith; it is also possible that Merewalh
, king of the Magonsæte, was Wulfhere's brother. He married Eormenhild of Kent; no date is recorded for the marriage and there is no record of any children in the earliest sources, though Coenred, who was king of Mercia from 704 to 709, is recorded in John of Worcester
's 12th century chronicle as Wulfhere's son. Another possible child is Berhtwald, a subking who is recorded as a nephew of Æthelred, and a third child, Werburh, is recorded in an 11th century manuscript as a daughter of Wulfhere. An 11th-century history of St. Peter's Monastery
in Gloucester
names two other women, Eadburh and Eafe, as queens of Wulfhere, but neither claim is plausible.
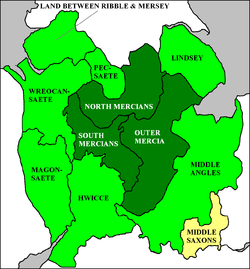 In 655 Penda besieged Oswiu of Northumbria at Iudeu, the location of which is unknown but which may have been Stirling
In 655 Penda besieged Oswiu of Northumbria at Iudeu, the location of which is unknown but which may have been Stirling
, in Scotland. Penda took Oswiu's son, Ecgfrith
, as hostage, and Oswiu paid tribute, in the form of treasure, to secure Penda's departure. On the way back to Mercia, Oswiu overtook Penda and on 15 November 655 Oswiu and Penda fought on the banks of the (unidentified) river Winwaed. Penda was killed and beheaded by Oswiu, who divided Mercia into northern and southern halves. The northern portion was kept under direct Northumbrian control; the southern kingdom was given to Penda's son Peada, who had married Oswiu's daughter Ealhflæd ca 653.
Peada did not remain king long. He was murdered at Easter
in 656, perhaps with the connivance of his wife, Oswiu's daughter. Oswiu then ruled all Mercia himself. Bede lists Oswiu as the seventh and last king to hold imperium (or bretwalda
in the language of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle) over the other Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. Overlordship was a common relationship between kingdoms at this time, often taking the form of a lesser king under the domination of a stronger one. Oswiu went further than this, however, and installed his own governors in Mercia after the deaths of Penda and Peada. This attempt to establish close control of Mercia failed in 658 when three Mercian leaders, Immin, Eafa and Eadbert, rebelled against the Northumbrians. Bede reports that they had kept Wulfhere in hiding, and when the revolt succeeded Wulfhere became king. It has been suggested that the Mercian revolt succeeded because Oswiu may have been occupied with fighting in Pictland, in northern Britain. His nephew the Pictish
king Talorgan
, son of Eanfrith
, had died in 657.
How much direct control Oswiu exerted over the southern kingdoms during his imperium is unclear. Bede describes Oswiu's friendship and influence over Sigeberht
of the East Saxons, but generally the pattern in the southeast is of more local domination, with Oswiu's influence unlikely to have been particularly strong. Wulfhere appears to have taken over Oswiu's position in many instances. Bede does not list him as one of the rulers who exercised imperium, but modern historians consider that the rise to primacy of the kingdom of Mercia began in his reign. He seems to have been the effective overlord of Britain south of the Humber
from the early 660s, though not overlord of Northumbria as his father had been.
A document called the Tribal Hidage
may date from Wulfhere's reign. Drawn up before many smaller groups of peoples were absorbed into the larger kingdoms, such as Mercia, it records the peoples of Anglo-Saxon England, along with an assessment in hides
, a unit of land. The Tribal Hidage is difficult to date precisely; it may have been written down in Wulfhere's reign, but other suggested origins include the reign of Offa of Mercia
, or Edwin
or Oswiu of Northumbria.
, but the incoming Anglo-Saxons practiced their indigenous religion (Anglo-Saxon paganism) and the church in Great Britain was limited to the surviving British kingdoms in Scotland and Wales, and the kingdom of Dumnonia
in the southwest of England. Missionaries from Rome began converting
the Anglo-Saxons to Christianity at the end of the 6th century, and this process was well under way in Penda's reign, though Penda himself remained pagan throughout his life. Records survive of the baptism of other kings at this time—Cynegils of Wessex
was baptized in about 640, for example, and Edwin of Northumbria was converted in the mid 620s. However, later kings, such as Cædwalla of Wessex, who ruled in the 680s, are recorded as pagan at their accession.
Bede
writes that after Wulfhere became king: "Free under their own king, they [the Mercians] gave willing allegiance to Christ their true king, so that they might win his eternal kingdom in heaven". While Wulfhere's father had refused to convert to Christianity, and Peada had apparently converted in order to marry Oswiu's daughter, the date and the circumstances of Wulfhere's conversion are unknown. It has been suggested that he adopted Christianity as part of a settlement with Oswiu. Bede records that two years before Penda's death, his son Peada converted to Christianity, influenced partly by Oswiu's son Ealhfrith
, who had married Peada's sister Cyneburh. Peada brought a Christian mission into Mercia, and it is possible that this was when Wulfhere became a Christian. Wulfhere's marriage to Eormenhild of Kent
would have brought Mercia into close contact with the Christian kingdoms of Kent and Merovingian Gaul
, which were connected by kinship and trade. The political and economic benefits of the marriage may therefore also have been a factor in Wulfhere's Christianization of his kingdom.
Wulfhere's relationship with Bishop Wilfrid
is recorded in Stephen of Ripon's Life of Wilfrid. During the years 667–9, while Wilfrid was at Ripon
, Wulfhere frequently invited him to come to Mercia when there was need of the services of a bishop. According to Stephen, Wulfhere rewarded Wilfrid with "many tracts of land", in which Wilfrid "soon established minsters for servants of God".
According to the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
, Wulfhere endowed a major monastery at Medeshamstede
, in modern Peterborough. The monastery had initially been endowed by Peada; for the dedication of Wulfhere's gift both Archbishop Deusdedit
(died 664), and Bishop Jaruman
(held office from 663), were present. The endowment was signed by Wulfhere and Oswiu, and by Sigehere
and Sæbbi
, the Kings of Essex.
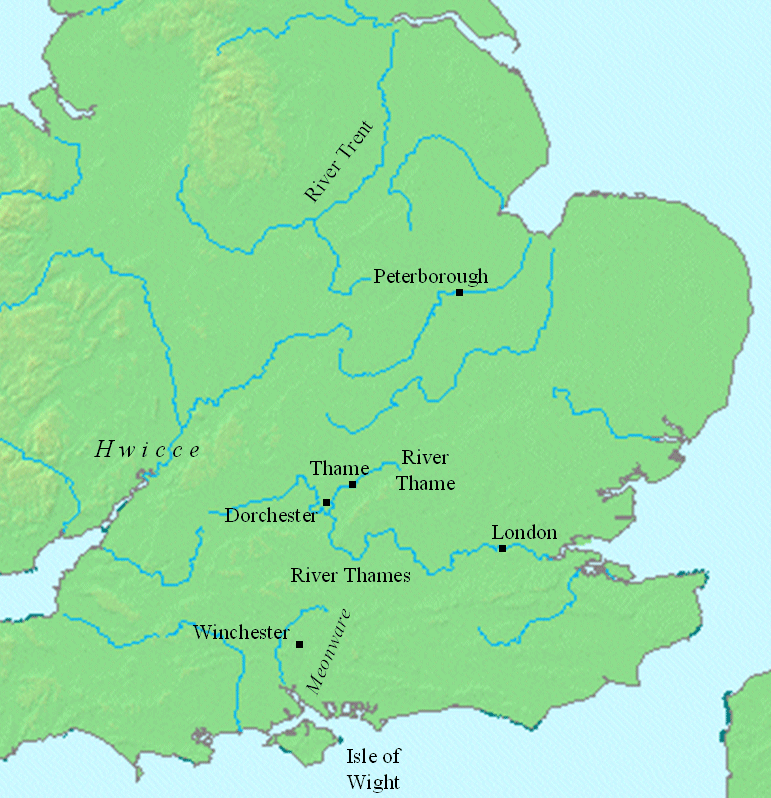 In 661, Wulfhere is recorded in the Chronicle as harrying Ashdown, in West Saxon territory. The Gewisse, thought to be the original group from which the West Saxons came, appear to have originally settled in the upper Thames
In 661, Wulfhere is recorded in the Chronicle as harrying Ashdown, in West Saxon territory. The Gewisse, thought to be the original group from which the West Saxons came, appear to have originally settled in the upper Thames
valley, and what records survive of the 6th century show them active in that region. The Mercian resurgence under Wulfhere placed them under severe pressure. Also in the early 660s, the West Saxon see of Dorchester, in the same area, was divided, and a new bishopric set up at Winchester
. This decision was probably a reaction to the advance of the Mercians into the traditional heartland of the West Saxons, leaving Dorchester dangerously close to the border. Within a few years, the Dorchester see was abandoned; the exact date is not known, but it was probably in the mid 660s.
In addition to the attack on Ashdown, Wulfhere raided the Isle of Wight
in 661. He subsequently gave both the island and the territory of the Meonware, which lay along the river Meon
, on the mainland north of the Isle of Wight, to his godson King Æthelwealh of the South Saxons. It seems likely that the ruling dynasty on the island found these arrangements acceptable to some degree, since the West Saxons, under Cædwalla, exterminated the whole family when they launched their own attack on the island in 686. After the conquest of the Isle of Wight, Wulfhere ordered the priest Eoppa to provide baptism to the inhabitants. According to the Chronicle, this was the first time Christian baptism had reached the island.
In the early 670s, Cenwealh of Wessex died, and perhaps as a result of the stress caused by Wulfhere's military activity the West Saxon kingdom fragmented and came to be ruled by underkings, according to Bede. Eventually these underkings were defeated and the kingdom reunited, probably by Cædwalla but possibly by Centwine
. A decade after Wulfhere's death, the West Saxons under Cædwalla began an aggressive expansion to the east, reversing much of the Mercian advance.
In addition to being Wulfhere's godson, King Æthelwealh of the South Saxons had a connection to the Mercians via marriage. His wife was Queen Eafe, the daughter of Eanfrith of the Hwicce
, a tribe whose territory lay to the southwest of Mercia. The Hwicce had their own royal family, but it appears that at this date they were already subordinate to Wulfhere: the marriage between Æthelwealh and Eafe may well have taken place at Wulfhere's court, since it is known Æthelwealh was converted there. The kingdom of the Hwicce is sometimes regarded as a creation of Penda's, but it is equally likely that the kingdom existed independently of Mercia, and that Penda and Wulfhere's increasing influence in the area represented an extension of Mercian power rather than the creation of a separate entity.
, who reigned for fifty years. Almost nothing is known of Mercian relations with East Anglia
during this time; East Anglia had previously been dominated by Northumbria, but there is no evidence that this continued after Wulfhere's accession. Swithhelm
of the East Saxons also died in 664; he was succeeded by his two sons, Sigehere
and Sæbbi
, and Bede describes their accession as "rulers ... under Wulfhere, king of the Mercians". A plague the same year caused Sigehere and his people to recant their Christianity, and according to Bede, Wulfhere sent Jaruman, the bishop of Lichfield
, to reconvert the East Saxons. Jaruman was not the first bishop of Lichfield; Bede mentions a predecessor, Trumhere, but nothing is known about Trumhere's activities or who appointed him.
It is apparent from these events that Oswiu's influence in the south had waned by this time, if not before, and that Wulfhere now dominated the area. This becomes even clearer in the next few years, as some time between 665 and 668 Wulfhere sold the see of London
to Wine
, who had been expelled from his West Saxon bishopric by Cenwealh. London fell within the East Saxons' territory in that period. From the archaeological evidence, it appears to be about this time that the Middle Saxon settlement in London began to expand significantly; the centre of Anglo-Saxon London was not at the old Roman centre, but about a mile west of that, near what is now the location of the Strand
. Wulfhere may have been in control of the city when this expansion began.
was the king of Kent at Wulfhere's accession, and the two families became connected when Wulfhere married Eorcenberht's daughter Eormenhild. In 664 Eorcenberht's son Egbert
succeeded to the Kentish throne. The situation in Kent at Egbert's death in 673 is not clearly recorded. It appears that a year passed before Hlothhere
, Egbert's brother, became king. Wulfhere may have had an interest in the succession, as through his marriage to Eormenhild he was the uncle of Egbert's two sons, Eadric
and Wihtred
. It has been speculated that Wulfhere acted as the effective ruler of Kent in the interregnum between Egbert's death and Hlothhere's accession. Another Mercian connection to Kent was through Merewalh
, the king of the Magonsæte, and hence a subking under Wulfhere. Merewalh, who may have been Wulfhere's brother, was married to Hlothhere's sister, Eormenburh.
Surrey
is not recorded as ever having been an independent kingdom, but was at least a province that was under the control of different neighbours at different times. It was ruled by Egbert until the early 670s, when a charter shows Wulfhere confirming a grant made to Bishop Eorcenwald by Frithuwold, a sub-king in Surrey, which may have extended north into modern Buckinghamshire
. Frithuwold himself was probably married to Wilburh, Wulfhere's sister. The charter, made from Thame
, is dated between 673 and 675, and it was probably Egbert's death that triggered Wulfhere's intervention. A witness named Frithuric is recorded on a charter in the reign of Wulfhere's successor, Æthelred, making a grant to the monastery of Peterborough, and the alliteration common in Anglo-Saxon dynasties has led to speculation that the two men may have both come from a Middle Anglian
dynasty, with Wulfhere perhaps having placed Frithuwold on the throne of Surrey. The charter is witnessed by three other subkings, named Osric, Wigheard, and Æthelwold; their kingdoms are not identified but the charter mentions Sonning, a province in what is now eastern Berkshire
, and it may be that one of these subkings was a ruler of the Sunningas, the people of that province. This would in turn imply Wulfhere's domination of that province by that time.
Wulfhere's influence among the Lindesfara, whose territory, Lindsey
, lay in what is now Lincolnshire
, is known from information about episcopal authority. At least one of the Mercian bishops of Lichfield is known to have exercised authority there: Wynfrith, who became bishop on Chad's
death in 672. In addition it is known that Wulfhere gave land at Barrow upon Humber
, in Lindsey, to Chad, for a monastery. It is possible that Chad also had authority there as bishop, probably no later than 669. It may be that the political basis for Mercian episcopal control of the Lindesfara was laid early in Wulfhere's reign, under Trumhere and Jaruman, the two bishops who preceded Chad.
says that Wulfhere "stirred up all the southern nations against [Northumbria]". Bede does not report the fighting, nor is it mentioned in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, but according to Stephen, Ecgfrith defeated Wulfhere, forcing him to surrender Lindsey, and to pay tribute.
Wulfhere survived the defeat, but evidently lost some degree of control over the south as a result; in 675, Æscwine, one of the kings of the West Saxons, fought him at Biedanheafde. It is not known where this battle was, or who was the victor. Henry of Huntingdon
, a 12th-century historian who had access to versions of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle now lost, believed that Mercians had been the victors in a "terrible battle", and remarks upon Wulfhere having inherited "the valour of his father and grandfather". Kirby, however, presumes Æscwine was sufficiently successful to break Wulfhere's hold over Wessex.
Wulfhere died later in 675. The cause of death, according to Henry of Huntingdon, was disease. He would have been in his mid-thirties. His widow, Eormenhild, is thought to have later become the abbess of Ely
. Æthelred, Wulfhere's brother, succeeded to the throne, and reigned for nearly thirty years. Æthelred recovered Lindsey from the Northumbrians a few years after his accession, but was generally unable to maintain the domination of the south achieved by Wulfhere.
Mercia
Mercia was one of the kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was centred on the valley of the River Trent and its tributaries in the region now known as the English Midlands...
, though it is not known when or how he converted from Anglo-Saxon paganism. His accession marked the end of Oswiu of Northumbria
Oswiu of Northumbria
Oswiu , also known as Oswy or Oswig , was a King of Bernicia. His father, Æthelfrith of Bernicia, was killed in battle, fighting against Rædwald, King of the East Angles and Edwin of Deira at the River Idle in 616...
's overlordship of southern England, and Wulfhere extended his influence over much of that region. His campaigns against the West Saxons led to Mercian control
Mercian Supremacy
The Mercian Supremacy is a term commonly used to describe that period of English history between AD 600 and 900, in which the Kingdom of Mercia dominated the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy...
of much of the Thames valley
Thames Valley
The Thames Valley Region is a loose term for the English counties and towns roughly following the course of the River Thames as it flows from Oxfordshire in the west to London in the east. It includes parts of Buckinghamshire, Berkshire, North Hampshire, Surrey and west London...
. He conquered the Isle of Wight
Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight is a county and the largest island of England, located in the English Channel, on average about 2–4 miles off the south coast of the county of Hampshire, separated from the mainland by a strait called the Solent...
and the Meon
River Meon
The River Meon is a river that flows through an area of Hampshire in southern England known as the Meon Valley, it flows generally southwards from the South Downs to the Solent. For most of its route it is a chalk stream, with a length of 21 miles .The River Meon rises approximately...
valley and gave them to King Æthelwealh of the South Saxons. He also had influence in Surrey
Surrey
Surrey is a county in the South East of England and is one of the Home Counties. The county borders Greater London, Kent, East Sussex, West Sussex, Hampshire and Berkshire. The historic county town is Guildford. Surrey County Council sits at Kingston upon Thames, although this has been part of...
, Essex
Kingdom of Essex
The Kingdom of Essex or Kingdom of the East Saxons was one of the seven traditional kingdoms of the so-called Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was founded in the 6th century and covered the territory later occupied by the counties of Essex, Hertfordshire, Middlesex and Kent. Kings of Essex were...
, and Kent
Kingdom of Kent
The Kingdom of Kent was a Jutish colony and later independent kingdom in what is now south east England. It was founded at an unknown date in the 5th century by Jutes, members of a Germanic people from continental Europe, some of whom settled in Britain after the withdrawal of the Romans...
. He married Eormenhild
Ermenilda of Ely
Saint Eormenhild is a seventh-century Anglo-Saxon saint. Later hagiography makes her the daughter of King Eorcenberht of Kent and St. Seaxburh of Ely, and wife to Wulfhere of Mercia, with whom she had a daughter, St. Wærburh, and a son, Coenred...
, the daughter of King Eorcenberht of Kent
Eorcenberht of Kent
Eorcenberht of Kent was king of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Kent from 640 until his death, succeeding his father Eadbald....
.
Wulfhere's father, Penda
Penda of Mercia
Penda was a 7th-century King of Mercia, the Anglo-Saxon kingdom in what is today the English Midlands. A pagan at a time when Christianity was taking hold in many of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, Penda took over the Severn Valley in 628 following the Battle of Cirencester before participating in the...
, was killed in 655 at the Battle of Winwaed, fighting against Oswiu of Northumbria
Oswiu of Northumbria
Oswiu , also known as Oswy or Oswig , was a King of Bernicia. His father, Æthelfrith of Bernicia, was killed in battle, fighting against Rædwald, King of the East Angles and Edwin of Deira at the River Idle in 616...
. Penda's son Peada
Peada of Mercia
Peada , a son of Penda, was briefly King of southern Mercia after his father's death in November 655 until his own death in the spring of the next year.In about the year 653 Peada was made king of the Middle Angles by his father...
became king under Oswiu's overlordship but was murdered a year later. Wulfhere came to the throne when Mercian nobles organized a revolt against Northumbria
Northumbria
Northumbria was a medieval kingdom of the Angles, in what is now Northern England and South-East Scotland, becoming subsequently an earldom in a united Anglo-Saxon kingdom of England. The name reflects the approximate southern limit to the kingdom's territory, the Humber Estuary.Northumbria was...
n rule in 658 and drove out Oswiu's governors.
By 670, when Oswiu died, Wulfhere was the most powerful king in southern Britain. He was effectively the overlord of Britain south of the Humber
Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal River Ouse and the tidal River Trent. From here to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between the East Riding of Yorkshire on the north bank...
from the early 660s, although not overlord of Northumbria as his father had been. In 674, he challenged Oswiu's son Ecgfrith of Northumbria
Ecgfrith of Northumbria
King Ecgfrith was the King of Northumbria from 670 until his death. He ruled over Northumbria when it was at the height of its power, but his reign ended with a disastrous defeat in which he lost his life.-Early life:...
, but was defeated. He died, probably of disease, in 675. Wulfhere was succeeded as King of Mercia by his brother, Æthelred. Stephen of Ripon's Life of Wilfrid
Wilfrid
Wilfrid was an English bishop and saint. Born a Northumbrian noble, he entered religious life as a teenager and studied at Lindisfarne, at Canterbury, in Gaul, and at Rome; he returned to Northumbria in about 660, and became the abbot of a newly founded monastery at Ripon...
describes Wulfhere as "a man of proud mind, and insatiable will".
Mercia in the seventh century

Anglo-Saxons
Anglo-Saxon is a term used by historians to designate the Germanic tribes who invaded and settled the south and east of Great Britain beginning in the early 5th century AD, and the period from their creation of the English nation to the Norman conquest. The Anglo-Saxon Era denotes the period of...
who had come to Britain from northwestern Europe, starting in the early 5th century. The monk Bede
Bede
Bede , also referred to as Saint Bede or the Venerable Bede , was a monk at the Northumbrian monastery of Saint Peter at Monkwearmouth, today part of Sunderland, England, and of its companion monastery, Saint Paul's, in modern Jarrow , both in the Kingdom of Northumbria...
, who wrote in the 8th century, considered the Mercians to be descended from the Angles
Angles
The Angles is a modern English term for a Germanic people who took their name from the ancestral cultural region of Angeln, a district located in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany...
, one of the invading groups; the Saxons
Saxons
The Saxons were a confederation of Germanic tribes originating on the North German plain. The Saxons earliest known area of settlement is Northern Albingia, an area approximately that of modern Holstein...
and Jutes
Jutes
The Jutes, Iuti, or Iutæ were a Germanic people who, according to Bede, were one of the three most powerful Germanic peoples of their time, the other two being the Saxons and the Angles...
settled in the south of Britain, while the Angles settled in the north. Little is known about the origins of the kingdom of Mercia
Mercia
Mercia was one of the kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was centred on the valley of the River Trent and its tributaries in the region now known as the English Midlands...
, in what is now the English midlands, but according to genealogies preserved in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle is a collection of annals in Old English chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the Chronicle was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alfred the Great...
and the Anglian collection
Anglian collection
The Anglian collection is a collection of Anglo-Saxon royal genealogies and regnal lists. These survive in four manuscripts; two of which now reside in the British Library...
the early kings were descended from Icel; the dynasty is therefore known as the Iclingas. The earliest Mercian king about whom definite historical information has survived is Penda of Mercia
Penda of Mercia
Penda was a 7th-century King of Mercia, the Anglo-Saxon kingdom in what is today the English Midlands. A pagan at a time when Christianity was taking hold in many of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, Penda took over the Severn Valley in 628 following the Battle of Cirencester before participating in the...
, Wulfhere's father.
According to Bede's Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum
Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum
The Historia ecclesiastica gentis Anglorum is a work in Latin by Bede on the history of the Christian Churches in England, and of England generally; its main focus is on the conflict between Roman and Celtic Christianity.It is considered to be one of the most important original references on...
, a history of the English church, there were seven early Anglo-Saxon rulers who held imperium, or overlordship, over the other kingdoms. The fifth of these was Edwin of Northumbria
Edwin of Northumbria
Edwin , also known as Eadwine or Æduini, was the King of Deira and Bernicia – which later became known as Northumbria – from about 616 until his death. He converted to Christianity and was baptised in 627; after he fell at the Battle of Hatfield Chase, he was venerated as a saint.Edwin was the son...
, who was killed at the battle of Hatfield Chase
Battle of Hatfield Chase
The Battle of Hatfield Chase was fought on October 12, 633 at Hatfield Chase near Doncaster, Yorkshire, in Anglo-Saxon England between the Northumbrians under Edwin and an alliance of the Welsh of Gwynedd under Cadwallon ap Cadfan and the Mercians under Penda. The site was a marshy area about 8...
by a combined force including Cadwallon
Cadwallon ap Cadfan
Cadwallon ap Cadfan was the King of Gwynedd from around 625 until his death in battle. The son and successor of Cadfan ap Iago, he is best remembered as the King of the Britons who invaded and conquered Northumbria, defeating and killing its king, Edwin, prior to his own death in battle against...
, a British king of Gwynedd
Gwynedd
Gwynedd is a county in north-west Wales, named after the old Kingdom of Gwynedd. Although the second biggest in terms of geographical area, it is also one of the most sparsely populated...
, and Penda. At the time of this victory, Penda was probably not yet king of Mercia. His children included two future kings of Mercia: Wulfhere and Æthelred.
After Edwin's death, Northumbria briefly fell apart into its two constituent kingdoms. Within a year Oswald
Oswald of Northumbria
Oswald was King of Northumbria from 634 until his death, and is now venerated as a Christian saint.Oswald was the son of Æthelfrith of Bernicia and came to rule after spending a period in exile; after defeating the British ruler Cadwallon ap Cadfan, Oswald brought the two Northumbrian kingdoms of...
killed Cadwallon and reunited the kingdoms, and subsequently re-established Northumbrian hegemony over the south of England. However, on 5 August 642, Penda killed Oswald at the battle of Maserfield
Battle of Maserfield
The Battle of Maserfield , Welsh: "Maes Cogwy", was fought on August 5, 641 or 642, between the Anglo-Saxon kings Oswald of Northumbria and Penda of Mercia, ending in Oswald's defeat, death, and dismemberment...
, probably at Oswestry
Oswestry
Oswestry is a town and civil parish in Shropshire, England, close to the Welsh border. It is at the junction of the A5, A483, and A495 roads....
in the northwest midlands. Penda is not recorded as overlord of the other southern Anglo-Saxon kings, but he became the most powerful of the Anglo-Saxon kings after he defeated Oswald. On Oswald's death, Northumbria was divided again: Oswald's son Oswiu
Oswiu of Northumbria
Oswiu , also known as Oswy or Oswig , was a King of Bernicia. His father, Æthelfrith of Bernicia, was killed in battle, fighting against Rædwald, King of the East Angles and Edwin of Deira at the River Idle in 616...
succeeded to the throne of Bernicia
Bernicia
Bernicia was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom established by Anglian settlers of the 6th century in what is now southeastern Scotland and North East England....
, and Osric's
Osric of Deira
Osric was a King of Deira in northern England. He was a cousin of king Edwin of Northumbria, being the son of Edwin's uncle Aelfric...
son Oswine
Oswine of Deira
Oswine was a King of Deira in northern England. He succeeded King Oswald of Northumbria, probably around the year 644, after Oswald's death at the Battle of Maserfield. Oswine was the son of Osric....
to Deira, the southern of the two kingdoms.
The main source for this period is Bede's History, completed in about 731. Despite its focus on the history of the church, this work also provides valuable information about the early pagan kingdoms. For other kingdoms than his native Northumbria, such as Wessex and Kent, Bede had an informant within the ecclesiastical establishment who supplied him with additional information. This does not seem to have been the case with Mercia, about which Bede is less informative than about other kingdoms. Further sources for this period include the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle is a collection of annals in Old English chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the Chronicle was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alfred the Great...
, compiled at the end of the 9th century in Wessex
Wessex
The Kingdom of Wessex or Kingdom of the West Saxons was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the West Saxons, in South West England, from the 6th century, until the emergence of a united English state in the 10th century, under the Wessex dynasty. It was to be an earldom after Canute the Great's conquest...
. The Chronicle's anonymous scribe appears to have incorporated much information recorded in earlier periods.
Ancestry

Nothing is known of Wulfhere's childhood. He had two brothers, Peada and Æthelred, and two sisters, Cyneburh and Cyneswith; it is also possible that Merewalh
Merewalh
Merewalh Merewalh Merewalh (sometimes given as Merwal or Merewald was a sub-king of the Magonsæte, a western cadet kingdom of Mercia thought to have been located in Herefordshire and Shropshire...
, king of the Magonsæte, was Wulfhere's brother. He married Eormenhild of Kent; no date is recorded for the marriage and there is no record of any children in the earliest sources, though Coenred, who was king of Mercia from 704 to 709, is recorded in John of Worcester
John of Worcester
John of Worcester was an English monk and chronicler. He is usually held to be the author of the Chronicon ex chronicis.-Chronicon ex chronicis:...
's 12th century chronicle as Wulfhere's son. Another possible child is Berhtwald, a subking who is recorded as a nephew of Æthelred, and a third child, Werburh, is recorded in an 11th century manuscript as a daughter of Wulfhere. An 11th-century history of St. Peter's Monastery
Gloucester Cathedral
Gloucester Cathedral, or the Cathedral Church of St Peter and the Holy and Indivisible Trinity, in Gloucester, England, stands in the north of the city near the river. It originated in 678 or 679 with the foundation of an abbey dedicated to Saint Peter .-Foundations:The foundations of the present...
in Gloucester
Gloucester
Gloucester is a city, district and county town of Gloucestershire in the South West region of England. Gloucester lies close to the Welsh border, and on the River Severn, approximately north-east of Bristol, and south-southwest of Birmingham....
names two other women, Eadburh and Eafe, as queens of Wulfhere, but neither claim is plausible.
Accession and overlordship

Stirling
Stirling is a city and former ancient burgh in Scotland, and is at the heart of the wider Stirling council area. The city is clustered around a large fortress and medieval old-town beside the River Forth...
, in Scotland. Penda took Oswiu's son, Ecgfrith
Ecgfrith of Northumbria
King Ecgfrith was the King of Northumbria from 670 until his death. He ruled over Northumbria when it was at the height of its power, but his reign ended with a disastrous defeat in which he lost his life.-Early life:...
, as hostage, and Oswiu paid tribute, in the form of treasure, to secure Penda's departure. On the way back to Mercia, Oswiu overtook Penda and on 15 November 655 Oswiu and Penda fought on the banks of the (unidentified) river Winwaed. Penda was killed and beheaded by Oswiu, who divided Mercia into northern and southern halves. The northern portion was kept under direct Northumbrian control; the southern kingdom was given to Penda's son Peada, who had married Oswiu's daughter Ealhflæd ca 653.
Peada did not remain king long. He was murdered at Easter
Easter
Easter is the central feast in the Christian liturgical year. According to the Canonical gospels, Jesus rose from the dead on the third day after his crucifixion. His resurrection is celebrated on Easter Day or Easter Sunday...
in 656, perhaps with the connivance of his wife, Oswiu's daughter. Oswiu then ruled all Mercia himself. Bede lists Oswiu as the seventh and last king to hold imperium (or bretwalda
Bretwalda
Bretwalda is an Old English word, the first record of which comes from the late 9th century Anglo-Saxon Chronicle. It is given to some of the rulers of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms from the 5th century onwards who had achieved overlordship of some or all of the other Anglo-Saxon kingdoms...
in the language of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle) over the other Anglo-Saxon kingdoms. Overlordship was a common relationship between kingdoms at this time, often taking the form of a lesser king under the domination of a stronger one. Oswiu went further than this, however, and installed his own governors in Mercia after the deaths of Penda and Peada. This attempt to establish close control of Mercia failed in 658 when three Mercian leaders, Immin, Eafa and Eadbert, rebelled against the Northumbrians. Bede reports that they had kept Wulfhere in hiding, and when the revolt succeeded Wulfhere became king. It has been suggested that the Mercian revolt succeeded because Oswiu may have been occupied with fighting in Pictland, in northern Britain. His nephew the Pictish
Picts
The Picts were a group of Late Iron Age and Early Mediaeval people living in what is now eastern and northern Scotland. There is an association with the distribution of brochs, place names beginning 'Pit-', for instance Pitlochry, and Pictish stones. They are recorded from before the Roman conquest...
king Talorgan
Talorcan of the Picts
Talorcan mac Enfret was a King of the Picts . He was the son of Eanfrith of Bernicia, who had fled into exile among the Picts after his father, Æthelfrith of Northumbria, was killed around the year 616...
, son of Eanfrith
Eanfrith of Bernicia
Eanfrith was briefly King of Bernicia from 633 to 634. He was the son of Æthelfrith, a Bernician king who had also ruled Deira to the south before being killed in battle around 616 against Raedwald of East Anglia, who had given refuge to Edwin, an exiled prince of Deira.Edwin became king of...
, had died in 657.
How much direct control Oswiu exerted over the southern kingdoms during his imperium is unclear. Bede describes Oswiu's friendship and influence over Sigeberht
Sigeberht II of Essex
Sigeberht II, nicknamed the Good or the Blessed , was King of the East Saxons , in succession to his relative Sigeberht I the Little...
of the East Saxons, but generally the pattern in the southeast is of more local domination, with Oswiu's influence unlikely to have been particularly strong. Wulfhere appears to have taken over Oswiu's position in many instances. Bede does not list him as one of the rulers who exercised imperium, but modern historians consider that the rise to primacy of the kingdom of Mercia began in his reign. He seems to have been the effective overlord of Britain south of the Humber
Humber
The Humber is a large tidal estuary on the east coast of Northern England. It is formed at Trent Falls, Faxfleet, by the confluence of the tidal River Ouse and the tidal River Trent. From here to the North Sea, it forms part of the boundary between the East Riding of Yorkshire on the north bank...
from the early 660s, though not overlord of Northumbria as his father had been.
A document called the Tribal Hidage
Tribal Hidage
Image:Tribal Hidage 2.svg|thumb|400px|alt=insert description of map here|The tribes of the Tribal Hidage. Where an appropriate article exists, it can be found by clicking on the name.rect 275 75 375 100 Elmetrect 375 100 450 150 Hatfield Chase...
may date from Wulfhere's reign. Drawn up before many smaller groups of peoples were absorbed into the larger kingdoms, such as Mercia, it records the peoples of Anglo-Saxon England, along with an assessment in hides
Hide (unit)
The hide was originally an amount of land sufficient to support a household, but later in Anglo-Saxon England became a unit used in assessing land for liability to "geld", or land tax. The geld would be collected at a stated rate per hide...
, a unit of land. The Tribal Hidage is difficult to date precisely; it may have been written down in Wulfhere's reign, but other suggested origins include the reign of Offa of Mercia
Offa of Mercia
Offa was the King of Mercia from 757 until his death in July 796. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa, Offa came to the throne after a period of civil war following the assassination of Æthelbald after defeating the other claimant Beornred. In the early years of Offa's reign it is likely...
, or Edwin
Edwin of Northumbria
Edwin , also known as Eadwine or Æduini, was the King of Deira and Bernicia – which later became known as Northumbria – from about 616 until his death. He converted to Christianity and was baptised in 627; after he fell at the Battle of Hatfield Chase, he was venerated as a saint.Edwin was the son...
or Oswiu of Northumbria.
A convert king
Britain had been Christianized under the RomansRoman Britain
Roman Britain was the part of the island of Great Britain controlled by the Roman Empire from AD 43 until ca. AD 410.The Romans referred to the imperial province as Britannia, which eventually comprised all of the island of Great Britain south of the fluid frontier with Caledonia...
, but the incoming Anglo-Saxons practiced their indigenous religion (Anglo-Saxon paganism) and the church in Great Britain was limited to the surviving British kingdoms in Scotland and Wales, and the kingdom of Dumnonia
Dumnonia
Dumnonia is the Latinised name for the Brythonic kingdom in sub-Roman Britain between the late 4th and late 8th centuries, located in the farther parts of the south-west peninsula of Great Britain...
in the southwest of England. Missionaries from Rome began converting
Christianization
The historical phenomenon of Christianization is the conversion of individuals to Christianity or the conversion of entire peoples at once...
the Anglo-Saxons to Christianity at the end of the 6th century, and this process was well under way in Penda's reign, though Penda himself remained pagan throughout his life. Records survive of the baptism of other kings at this time—Cynegils of Wessex
Cynegils of Wessex
Cynegils was King of Wessex from c. 611 to c. 643.Cynegils is traditionally considered to have been King of Wessex, but the familiar kingdoms of the so-called Heptarchy had not yet formed from the patchwork of smaller kingdoms in his lifetime...
was baptized in about 640, for example, and Edwin of Northumbria was converted in the mid 620s. However, later kings, such as Cædwalla of Wessex, who ruled in the 680s, are recorded as pagan at their accession.
Bede
Bede
Bede , also referred to as Saint Bede or the Venerable Bede , was a monk at the Northumbrian monastery of Saint Peter at Monkwearmouth, today part of Sunderland, England, and of its companion monastery, Saint Paul's, in modern Jarrow , both in the Kingdom of Northumbria...
writes that after Wulfhere became king: "Free under their own king, they [the Mercians] gave willing allegiance to Christ their true king, so that they might win his eternal kingdom in heaven". While Wulfhere's father had refused to convert to Christianity, and Peada had apparently converted in order to marry Oswiu's daughter, the date and the circumstances of Wulfhere's conversion are unknown. It has been suggested that he adopted Christianity as part of a settlement with Oswiu. Bede records that two years before Penda's death, his son Peada converted to Christianity, influenced partly by Oswiu's son Ealhfrith
Alchfrith of Deira
Alhfrith or Ealhfrith was a son of King Oswiu of Northumbria and Rieinmelth of Rheged.In around 655 Alhfrith was appointed by his father as sub-king of Deira, the southern part of the Northumbrian kingdom. He replaced his cousin Æthelwold, who had supported Oswiu's enemy Penda of Mercia in the...
, who had married Peada's sister Cyneburh. Peada brought a Christian mission into Mercia, and it is possible that this was when Wulfhere became a Christian. Wulfhere's marriage to Eormenhild of Kent
Kingdom of Kent
The Kingdom of Kent was a Jutish colony and later independent kingdom in what is now south east England. It was founded at an unknown date in the 5th century by Jutes, members of a Germanic people from continental Europe, some of whom settled in Britain after the withdrawal of the Romans...
would have brought Mercia into close contact with the Christian kingdoms of Kent and Merovingian Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
, which were connected by kinship and trade. The political and economic benefits of the marriage may therefore also have been a factor in Wulfhere's Christianization of his kingdom.
Wulfhere's relationship with Bishop Wilfrid
Wilfrid
Wilfrid was an English bishop and saint. Born a Northumbrian noble, he entered religious life as a teenager and studied at Lindisfarne, at Canterbury, in Gaul, and at Rome; he returned to Northumbria in about 660, and became the abbot of a newly founded monastery at Ripon...
is recorded in Stephen of Ripon's Life of Wilfrid. During the years 667–9, while Wilfrid was at Ripon
Ripon
Ripon is a cathedral city, market town and successor parish in the Borough of Harrogate, North Yorkshire, England, located at the confluence of two streams of the River Ure in the form of the Laver and Skell. The city is noted for its main feature the Ripon Cathedral which is architecturally...
, Wulfhere frequently invited him to come to Mercia when there was need of the services of a bishop. According to Stephen, Wulfhere rewarded Wilfrid with "many tracts of land", in which Wilfrid "soon established minsters for servants of God".
According to the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle is a collection of annals in Old English chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the Chronicle was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alfred the Great...
, Wulfhere endowed a major monastery at Medeshamstede
Medeshamstede
Medeshamstede was the name of Peterborough in the Anglo-Saxon period. It was the site of a monastery founded around the middle of the 7th century, which was an important feature in the kingdom of Mercia from the outset. Little is known of its founder and first abbot, Sexwulf, though he was himself...
, in modern Peterborough. The monastery had initially been endowed by Peada; for the dedication of Wulfhere's gift both Archbishop Deusdedit
Deusdedit of Canterbury
Deusdedit , perhaps originally named Frithona, Frithuwine or Frithonas, was a medieval Archbishop of Canterbury, the first native-born holder of the see of Canterbury. By birth an Anglo-Saxon, he became archbishop in 655 and held the office for more than nine years until his death, probably from...
(died 664), and Bishop Jaruman
Jaruman
Jaruman was the fourth Bishop of Mercia. He fought against apostasy outside his diocese. He served as bishop in the time of King Wulfhere of Mercia, on whose behalf he undertook several missions to Saxon tribes which had lapsed into paganism...
(held office from 663), were present. The endowment was signed by Wulfhere and Oswiu, and by Sigehere
Sighere of Essex
Sighere was the joint king of the Kingdom of Essex along with his brother Sebbi from 664 to 683. He was outlived by Sebbi, who became the sole ruler of Essex after his death. Sighere and Sebbi were cousins of their predecessor Swithelm. While Sighere returned to paganism, Sebbi remained...
and Sæbbi
Sebbi of Essex
Sebbi was the joint King of Essex from 664 to 683 along with his brother, Sighere. After Sighere died, Sebbi became sole ruler of Essex until 694....
, the Kings of Essex.
West Saxons, South Saxons and Hwicce

River Thames
The River Thames flows through southern England. It is the longest river entirely in England and the second longest in the United Kingdom. While it is best known because its lower reaches flow through central London, the river flows alongside several other towns and cities, including Oxford,...
valley, and what records survive of the 6th century show them active in that region. The Mercian resurgence under Wulfhere placed them under severe pressure. Also in the early 660s, the West Saxon see of Dorchester, in the same area, was divided, and a new bishopric set up at Winchester
Winchester
Winchester is a historic cathedral city and former capital city of England. It is the county town of Hampshire, in South East England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government district, and is located at the western end of the South Downs, along the course of...
. This decision was probably a reaction to the advance of the Mercians into the traditional heartland of the West Saxons, leaving Dorchester dangerously close to the border. Within a few years, the Dorchester see was abandoned; the exact date is not known, but it was probably in the mid 660s.
In addition to the attack on Ashdown, Wulfhere raided the Isle of Wight
Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight is a county and the largest island of England, located in the English Channel, on average about 2–4 miles off the south coast of the county of Hampshire, separated from the mainland by a strait called the Solent...
in 661. He subsequently gave both the island and the territory of the Meonware, which lay along the river Meon
River Meon
The River Meon is a river that flows through an area of Hampshire in southern England known as the Meon Valley, it flows generally southwards from the South Downs to the Solent. For most of its route it is a chalk stream, with a length of 21 miles .The River Meon rises approximately...
, on the mainland north of the Isle of Wight, to his godson King Æthelwealh of the South Saxons. It seems likely that the ruling dynasty on the island found these arrangements acceptable to some degree, since the West Saxons, under Cædwalla, exterminated the whole family when they launched their own attack on the island in 686. After the conquest of the Isle of Wight, Wulfhere ordered the priest Eoppa to provide baptism to the inhabitants. According to the Chronicle, this was the first time Christian baptism had reached the island.
In the early 670s, Cenwealh of Wessex died, and perhaps as a result of the stress caused by Wulfhere's military activity the West Saxon kingdom fragmented and came to be ruled by underkings, according to Bede. Eventually these underkings were defeated and the kingdom reunited, probably by Cædwalla but possibly by Centwine
Centwine of Wessex
Centwine was King of Wessex from circa 676 to 685 or 686, although he was perhaps not the only king of the West Saxons at the time.The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle reports that Centwine became king circa 676, succeeding Æscwine...
. A decade after Wulfhere's death, the West Saxons under Cædwalla began an aggressive expansion to the east, reversing much of the Mercian advance.
In addition to being Wulfhere's godson, King Æthelwealh of the South Saxons had a connection to the Mercians via marriage. His wife was Queen Eafe, the daughter of Eanfrith of the Hwicce
Hwicce
The Hwicce were one of the peoples of Anglo-Saxon England. The exact boundaries of their kingdom are uncertain, though it is likely that they coincided with those of the old Diocese of Worcester, founded in 679–80, the early bishops of which bore the title Episcopus Hwicciorum...
, a tribe whose territory lay to the southwest of Mercia. The Hwicce had their own royal family, but it appears that at this date they were already subordinate to Wulfhere: the marriage between Æthelwealh and Eafe may well have taken place at Wulfhere's court, since it is known Æthelwealh was converted there. The kingdom of the Hwicce is sometimes regarded as a creation of Penda's, but it is equally likely that the kingdom existed independently of Mercia, and that Penda and Wulfhere's increasing influence in the area represented an extension of Mercian power rather than the creation of a separate entity.
East Anglia and the East Saxons
In 664, Æthelwald of East Anglia died, and was succeeded by EaldwulfEaldwulf of East Anglia
Ealdwulf or Aldwulf was an obscure King of East Anglia who reigned from 663 to around 713.Ealdwulf's reign of forty-nine years was extraordinary in length: only Ethelbald of Mercia's and Offa of Mercia's reigns are comparable...
, who reigned for fifty years. Almost nothing is known of Mercian relations with East Anglia
Kingdom of the East Angles
The Kingdom of East Anglia, also known as the Kingdom of the East Angles , was a small independent Anglo-Saxon kingdom that comprised what are now the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk and perhaps the eastern part of the Fens...
during this time; East Anglia had previously been dominated by Northumbria, but there is no evidence that this continued after Wulfhere's accession. Swithhelm
Swithelm of Essex
Swithelm was King of Essex from 660 to 664.Swithelm succeeded King Sigeberht II after he, along with his brother Swithfrith, murdered him. They accused him of being too friendly toward Christians. In 662, however, he was persuaded to convert to Christianity by Aethelwald, king of East Anglia. ...
of the East Saxons also died in 664; he was succeeded by his two sons, Sigehere
Sighere of Essex
Sighere was the joint king of the Kingdom of Essex along with his brother Sebbi from 664 to 683. He was outlived by Sebbi, who became the sole ruler of Essex after his death. Sighere and Sebbi were cousins of their predecessor Swithelm. While Sighere returned to paganism, Sebbi remained...
and Sæbbi
Sebbi of Essex
Sebbi was the joint King of Essex from 664 to 683 along with his brother, Sighere. After Sighere died, Sebbi became sole ruler of Essex until 694....
, and Bede describes their accession as "rulers ... under Wulfhere, king of the Mercians". A plague the same year caused Sigehere and his people to recant their Christianity, and according to Bede, Wulfhere sent Jaruman, the bishop of Lichfield
Lichfield
Lichfield is a cathedral city, civil parish and district in Staffordshire, England. One of eight civil parishes with city status in England, Lichfield is situated roughly north of Birmingham...
, to reconvert the East Saxons. Jaruman was not the first bishop of Lichfield; Bede mentions a predecessor, Trumhere, but nothing is known about Trumhere's activities or who appointed him.
It is apparent from these events that Oswiu's influence in the south had waned by this time, if not before, and that Wulfhere now dominated the area. This becomes even clearer in the next few years, as some time between 665 and 668 Wulfhere sold the see of London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
to Wine
Wine (bishop)
Wine was a medieval Bishop of London and the first Bishop of Winchester.Wine was consecrated the first bishop of Winchester in 660 and possibly translated to Dorchester around 663...
, who had been expelled from his West Saxon bishopric by Cenwealh. London fell within the East Saxons' territory in that period. From the archaeological evidence, it appears to be about this time that the Middle Saxon settlement in London began to expand significantly; the centre of Anglo-Saxon London was not at the old Roman centre, but about a mile west of that, near what is now the location of the Strand
Strand, London
Strand is a street in the City of Westminster, London, England. The street is just over three-quarters of a mile long. It currently starts at Trafalgar Square and runs east to join Fleet Street at Temple Bar, which marks the boundary of the City of London at this point, though its historical length...
. Wulfhere may have been in control of the city when this expansion began.
Kent, Surrey and Lindsey
EorcenberhtEorcenberht of Kent
Eorcenberht of Kent was king of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Kent from 640 until his death, succeeding his father Eadbald....
was the king of Kent at Wulfhere's accession, and the two families became connected when Wulfhere married Eorcenberht's daughter Eormenhild. In 664 Eorcenberht's son Egbert
Ecgberht of Kent
Ecgberht was a King of Kent who ruled from 664 to 673, succeeding his father Eorcenberht s:Ecclesiastical History of the English People/Book 4#1....
succeeded to the Kentish throne. The situation in Kent at Egbert's death in 673 is not clearly recorded. It appears that a year passed before Hlothhere
Hlothhere of Kent
Hlothhere was a King of Kent who ruled from 673 to 685.He succeeded his brother Ecgberht I in 673. He must have come into conflict with Mercia, since in 676 the Mercian king Æthelred invaded Kent and caused great destruction; according to Bede, even churches and monasteries were not spared, and...
, Egbert's brother, became king. Wulfhere may have had an interest in the succession, as through his marriage to Eormenhild he was the uncle of Egbert's two sons, Eadric
Eadric of Kent
Eadric was a King of Kent . He was the son of Ecgberht I.Eadric was for a time co-ruler alongside his uncle Hlothhere, and a code of laws issued in both their names has survived. However, Eadric eventually revolted and defeated Hlothhere with the aid of the South Saxons...
and Wihtred
Wihtred of Kent
Wihtred was king of Kent from about 690 or 691 until his death. He was a son of Ecgberht I and a brother of Eadric. Wihtred acceded to the throne after a confused period in the 680s, which included a brief conquest of Kent by Cædwalla of Wessex and subsequent dynastic conflicts...
. It has been speculated that Wulfhere acted as the effective ruler of Kent in the interregnum between Egbert's death and Hlothhere's accession. Another Mercian connection to Kent was through Merewalh
Merewalh
Merewalh Merewalh Merewalh (sometimes given as Merwal or Merewald was a sub-king of the Magonsæte, a western cadet kingdom of Mercia thought to have been located in Herefordshire and Shropshire...
, the king of the Magonsæte, and hence a subking under Wulfhere. Merewalh, who may have been Wulfhere's brother, was married to Hlothhere's sister, Eormenburh.
Surrey
Surrey
Surrey is a county in the South East of England and is one of the Home Counties. The county borders Greater London, Kent, East Sussex, West Sussex, Hampshire and Berkshire. The historic county town is Guildford. Surrey County Council sits at Kingston upon Thames, although this has been part of...
is not recorded as ever having been an independent kingdom, but was at least a province that was under the control of different neighbours at different times. It was ruled by Egbert until the early 670s, when a charter shows Wulfhere confirming a grant made to Bishop Eorcenwald by Frithuwold, a sub-king in Surrey, which may have extended north into modern Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire
Buckinghamshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan home county in South East England. The county town is Aylesbury, the largest town in the ceremonial county is Milton Keynes and largest town in the non-metropolitan county is High Wycombe....
. Frithuwold himself was probably married to Wilburh, Wulfhere's sister. The charter, made from Thame
Thame
Thame is a town and civil parish in Oxfordshire, about southwest of the Buckinghamshire town of Aylesbury. It derives its toponym from the River Thame which flows past the north side of the town....
, is dated between 673 and 675, and it was probably Egbert's death that triggered Wulfhere's intervention. A witness named Frithuric is recorded on a charter in the reign of Wulfhere's successor, Æthelred, making a grant to the monastery of Peterborough, and the alliteration common in Anglo-Saxon dynasties has led to speculation that the two men may have both come from a Middle Anglian
Middle Angles
The Middle Angles were an important ethnic or cultural group within the larger kingdom of Mercia in England in the Anglo-Saxon period.-Origins and territory:...
dynasty, with Wulfhere perhaps having placed Frithuwold on the throne of Surrey. The charter is witnessed by three other subkings, named Osric, Wigheard, and Æthelwold; their kingdoms are not identified but the charter mentions Sonning, a province in what is now eastern Berkshire
Berkshire
Berkshire is a historic county in the South of England. It is also often referred to as the Royal County of Berkshire because of the presence of the royal residence of Windsor Castle in the county; this usage, which dates to the 19th century at least, was recognised by the Queen in 1957, and...
, and it may be that one of these subkings was a ruler of the Sunningas, the people of that province. This would in turn imply Wulfhere's domination of that province by that time.
Wulfhere's influence among the Lindesfara, whose territory, Lindsey
Kingdom of Lindsey
Lindsey or Linnuis is the name of a petty Anglo-Saxon kingdom, absorbed into Northumbria in the 7th century.It lay between the Humber and the Wash, forming its inland boundaries from the course of the Witham and Trent rivers , and the Foss Dyke between...
, lay in what is now Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire
Lincolnshire is a county in the east of England. It borders Norfolk to the south east, Cambridgeshire to the south, Rutland to the south west, Leicestershire and Nottinghamshire to the west, South Yorkshire to the north west, and the East Riding of Yorkshire to the north. It also borders...
, is known from information about episcopal authority. At least one of the Mercian bishops of Lichfield is known to have exercised authority there: Wynfrith, who became bishop on Chad's
Chad of Mercia
Chad was a prominent 7th century Anglo-Saxon churchman, who became abbot of several monasteries, Bishop of the Northumbrians and subsequently Bishop of the Mercians and Lindsey People. He was later canonized as a saint. He was the brother of Cedd, also a saint...
death in 672. In addition it is known that Wulfhere gave land at Barrow upon Humber
Barrow upon Humber
Barrow upon Humber is a village and civil parish in North Lincolnshire, England. Many of the buildings in the centre of the village are of 18th and 19th century origin. There are several buildings of note including Down Hall, Barrow Hall, Forester's Hall and West Cote Farm. There are two public...
, in Lindsey, to Chad, for a monastery. It is possible that Chad also had authority there as bishop, probably no later than 669. It may be that the political basis for Mercian episcopal control of the Lindesfara was laid early in Wulfhere's reign, under Trumhere and Jaruman, the two bishops who preceded Chad.
Defeat and death
When Wulfhere attacked Oswiu's son Ecgfrith in 674, he did so from a position of strength. Stephen of Ripon's Life of WilfridWilfrid
Wilfrid was an English bishop and saint. Born a Northumbrian noble, he entered religious life as a teenager and studied at Lindisfarne, at Canterbury, in Gaul, and at Rome; he returned to Northumbria in about 660, and became the abbot of a newly founded monastery at Ripon...
says that Wulfhere "stirred up all the southern nations against [Northumbria]". Bede does not report the fighting, nor is it mentioned in the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, but according to Stephen, Ecgfrith defeated Wulfhere, forcing him to surrender Lindsey, and to pay tribute.
Wulfhere survived the defeat, but evidently lost some degree of control over the south as a result; in 675, Æscwine, one of the kings of the West Saxons, fought him at Biedanheafde. It is not known where this battle was, or who was the victor. Henry of Huntingdon
Henry of Huntingdon
Henry of Huntingdon , the son of a canon in the diocese of Lincoln, was a 12th century English historian, the author of a history of England, Historia anglorum, "the most important Anglo-Norman historian to emerge from the secular clergy". He served as archdeacon of Huntingdon...
, a 12th-century historian who had access to versions of the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle now lost, believed that Mercians had been the victors in a "terrible battle", and remarks upon Wulfhere having inherited "the valour of his father and grandfather". Kirby, however, presumes Æscwine was sufficiently successful to break Wulfhere's hold over Wessex.
Wulfhere died later in 675. The cause of death, according to Henry of Huntingdon, was disease. He would have been in his mid-thirties. His widow, Eormenhild, is thought to have later become the abbess of Ely
Ely, Cambridgeshire
Ely is a cathedral city in Cambridgeshire, England, 14 miles north-northeast of Cambridge and about by road from London. It is built on a Lower Greensand island, which at a maximum elevation of is the highest land in the Fens...
. Æthelred, Wulfhere's brother, succeeded to the throne, and reigned for nearly thirty years. Æthelred recovered Lindsey from the Northumbrians a few years after his accession, but was generally unable to maintain the domination of the south achieved by Wulfhere.
Primary sources
- BedeBedeBede , also referred to as Saint Bede or the Venerable Bede , was a monk at the Northumbrian monastery of Saint Peter at Monkwearmouth, today part of Sunderland, England, and of its companion monastery, Saint Paul's, in modern Jarrow , both in the Kingdom of Northumbria...
, Ecclesiastical History of the English People. (c. 731 A.D.) Translated by Leo Sherley-Price, revised R.E. Latham, ed. D.H. Farmer. London: Penguin, 1990. ISBN 0-14-044565-X

