
Windows Vista networking technologies
Encyclopedia
Windows Vista
and Windows Server 2008 contain a new networking stack, named Next Generation TCP/IP stack, that improves on the previous stack in several ways. It includes native implementation of IPv6, as well as complete overhaul of IPv4. The new TCP/IP stack uses a new method to store configuration settings that enables more dynamic control and does not require a computer restart after settings are changed. The new stack, implemented as a dual stack model, is based on a strong host model and features an infrastructure to enable more modular components that can be dynamically inserted and removed.
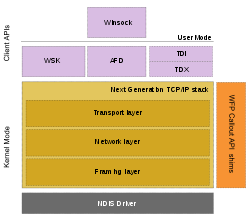 The Next Generation TCP/IP stack connects to NICs via a Network Driver Interface Specification
The Next Generation TCP/IP stack connects to NICs via a Network Driver Interface Specification
(NDIS) driver. The network stack, implemented in
, Network
and Data link
layers of the TCP/IP model. The Transport layer includes implementations for TCP
, UDP
and unformatted RAW protocols
. At the Network layer, IPv4
and IPv6
protocols are implemented in a dual-stack architecture. And the Data link layer (also called Framing layer) implements 802.3, 802.1, PPP
, Loopback
and tunnelling protocols. Each layer can accommodate Windows Filtering Platform
(WFP) shims, which allows packets at that layer to be introspected and also host the WFP Callout API. The networking API is exposed via three components:
Winsock
: A user mode API for abstracting network communication using sockets
and ports
. Datagram socket
s are used for UDP
, whereas Stream socket
s are for TCP
. While Winsock
is a user mode library, it uses a kernel mode driver, called Ancillary Function Driver (AFD) to implement certain functionality.
Winsock Kernel (WSK): A kernel-mode API providing the same socket-and-port abstraction as Winsock
, while exposing other features such as Asynchronous I/O
using I/O request packets.
Transport Driver Interface (TDI): A kernel-mode API which can be used for legacy protocols like NetBIOS
. It includes a component, known as TDX to map the TDI functionality to the network stack.
 The user interface for configuring, troubleshooting and working with network connections has changed significantly from prior versions of Windows as well. Users can make use of the new "Network and Sharing Center" to see the status of their network connections, and to access every aspect of configuration. A single icon in the notification area (system tray) represents connectivity through all network adapters, whether wired or wireless. The network can be browsed using Network Explorer, which replaces Windows XP's
The user interface for configuring, troubleshooting and working with network connections has changed significantly from prior versions of Windows as well. Users can make use of the new "Network and Sharing Center" to see the status of their network connections, and to access every aspect of configuration. A single icon in the notification area (system tray) represents connectivity through all network adapters, whether wired or wireless. The network can be browsed using Network Explorer, which replaces Windows XP's
"My Network Places". Network Explorer items can be a shared device such as a scanner, or a file share. The Network Location Awareness (NLA) service uniquely identifies each network and exposes the network's attributes and connectivity type so that applications can determine the optimal network configuration. However, applications have to use the NLA APIs explicitly to be aware of the network connectivity changes, and adapt accordingly. Windows Vista uses the Link Layer Topology Discovery
(LLTD) protocol to graphically present how different devices are connected over a network, as a Network Map. In addition, the Network Map uses LLTD to determine connectivity information and media type (wired or wireless), so that the map is topologically accurate. The ability to know network topology is important for diagnosing and solving networking problems, and for streaming content over a network connection. Any device can implement LLTD to appear on the Network Map with an icon representing the device, allowing users one-click access to the device's user interface. When LLTD is invoked, it provides metadata about the device that contains static or state information, such as the MAC address
, IPv4/IPv6 address, signal strength
etc.
. When a network is first connected to, Windows Vista prompts to choose the correct network type. On subsequents connections to the network, the service is used to gain information on which network is connected to and automatically switch to the network configuration for the connected network. Windows Vista introduces a concept of network profiles. For each network, the system stores the IP address
, DNS server, Proxy server
and other network features specific to the network in that network's profile. So when that network is subsequently connected to, the settings need not be reconfigured, the ones saved in its profile are used. In the case of mobile machines, the network profiles are chosen automatically based on what networks are available. Each profile is part of either a Public, Private or Domain network.
(IP) layer architecture in which the IPv4
and IPv6
implementations share common Transport
and Framing
layers. Windows Vista provides a GUI
for configuration of both IPv4 and IPv6 properties. IPv6
is now supported by all networking components and services. The Windows Vista DNS client can use IPv6 transport. Internet Explorer in Windows Vista and other applications that use WinINet (Windows Mail, file sharing) support literal IPv6 addresses (RFC 2732). Windows Firewall and the IPsec Policies snap-in support IPv6 addresses as permissible character strings. In IPv6 mode, Windows Vista can use the Link Local Multicast Name Resolution
(LLMNR) protocol, as described in RFC 4795, to resolve names of local hosts on a network which does not have a DNS server running. This service is useful for networks without a central managing server, and for ad-hoc wireless networks
. IPv6 can also be used over PPP
-based dial-up and PPPoE connections. Windows Vista can also act as a client/server for file sharing or DCOM over IPv6. Support for DHCPv6
, which can be used with IPv6, is also included. IPv6 can even be used when full native IPv6 connectivity is not available, using Teredo tunneling
; this can even traverse most IPv4 symmetric Network Address Translation
s (NATs) as well. Full support for multicast
is also included, via the MLDv2
and SSM
protocols. The IPv6 interface ID is randomly generated for permanent autoconfigured IPv6 addresses to prevent determining the MAC address based on known company IDs of NIC manufacturers.
is built into the network stack itself as a new set of APIs called Native Wifi, and does not emulate wired connections, as was the case with previous versions of Windows. This allows implementation of wireless-specific features such as larger frame sizes and optimized error recovery procedures. Native Wifi is exposed by Auto Configuration Module (ACM) which replaces Windows XP's Wireless Zero Configuration
. The ACM is extensible, so developers can incorporate additional wireless functionality (such as automatic wireless roaming) and override the automatic configuration and connection logic without affecting the built-in framework. It is easier to find wireless networks in range and tell which networks are open and which are closed. Hidden wireless networks, which do not advertise their name (SSID
) are better supported. Security for wireless networks is improved with improved support for newer wireless standards like 802.11i
. EAP-TLS is the default authentication mode. Connections are made at the most secure connection level supported by the wireless access point. WPA2 can be used even in ad-hoc mode. Windows Vista also provides a Fast Roaming service that will allow users to move from one access point to another without loss of connectivity. Preauthentication with the new wireless access point
can be used to retain the connectivity. Wireless networks are managed from either the Connect to a network dialog box within the GUI or the netsh wlan command from the shell. Settings for wireless networks can also be configured using Group policy
.
Windows Vista enhances security when joining a domain over a wireless network. It can use Single Sign On
to use the same credentials to join a wireless network as well as the domain housed within the network. In this case, the same RADIUS
server is used for both PEAP
authentication for joining the network and MS-CHAP v2
authentication to log in to the domain. A bootstrap wireless profile can also be created on the wireless client, which first authenticates the computer to the wireless network and joins the network. At this stage, the machine still does not have any access to the domain resources. The machine will run a script, stored either on the system or on USB thumb drive, which authenticates it to the domain. Authentication can be done either by using username and password combination or security certificates from a Public key infrastructure
(PKI) vendor such as VeriSign
.
standard. It implements a native code API, Web Services for Devices (WSDAPI) to support Devices Profile for Web Services
(DPWS) and also a managed code implementation in WCF
. DPWS enables simpler device discoverability like UPnP and describes available services to those clients. Function Discovery is a new technology that serves as an abstraction layer between applications and devices, allowing applications to discover devices by referencing the device's function, rather than by its bus type or the nature of its connection. Plug and Play Extensions (PnP-X) allow network-connected devices to appear as local devices inside Windows connected physically. UPnP
support has also been enhanced to include integration with PnP-X and Function Discovery.
) to reduce the amount of data to be retransmitted in case a portion of the data sent was not received correctly, and Forward RTO-Recovery
(F-RTO) to prevent unnecessary retransmission of TCP segments when round trip time
increases. It also includes Neighbour Unreachability Detection capability in both IPv4 and IPv6, which tracks the accessibility of neighboring nodes. This allows faster error recovery, in case a neighboring node fails. NDIS
6.0 introduced in Windows Vista supports offloading IPv6 traffic and checksum calculations for IPv6, improved manageability, scalability and performance with reduced complexity for NDIS miniports, and simpler models for writing Lightweight Filter Drivers (LWF). LWF drivers are a combination of NDIS intermediate drivers and a miniport driver that eliminate the need to write a separate protocol and miniport and have a bypass mode to examine only selected control and data paths. The TCP/IP stack also provides fail-back support for default gateway changes by periodically attempting to send TCP traffic through a previously detected unavailable gateway. This can provide faster throughput by sending traffic through the primary default gateway on the subnet.
Another significant change that aims to improve network throughput is the automatic resizing of TCP Receive window. The receive window (RWIN) specifies how much data a host is prepared to receive, and is limited by, among other things, the available buffer space. In other words, it is a measure of how much data the remote transmitter can send before requiring an acknowledgement for the outstanding data. When the receive window is too small, the remote transmitter will frequently find that it has hit the limit of how much outstanding data it can transmit, even though there is enough bandwidth available to transmit more data. This leads to incomplete link utilization. So using a larger RWIN size boosts throughput in such situations; an auto-adjusting RWIN tries to keep the throughput rate as high as is permissible by the bandwidth of the link. Receive window auto tuning functionality continually monitors the bandwidth and the latency of TCP connections individually and optimize the receive window for each connection. The window size is increased in high-bandwidth (~5 Mbit/s+) or high-latency
(>10ms) situations.
Traditional TCP implementations uses the TCP Slow Start
algorithm to detect how fast it can transmit without choking the receiver (or intermediate nodes). In a nutshell, it specifies that transmission should start at a slow rate, by transmitting a few packets. This number is controlled by the Congestion window
– which specifies the number of outstanding packets that has been transmitted but for which an acknowledgement of receipt from the receiver has not yet been received. As acknowledgements are received, the congestion window is expanded, one TCP segment at a time till an acknowledgement fails to arrive. Then the sender assumes that with the congestion window size of that instant, the network gets congested. However, a high bandwidth network can sustain a quite large congestion window without choking up. The slow start algorithm can take quite some time to reach that threshold – leaving the network under-utilized for a significant time.
The new TCP/IP stack also supports Explicit Congestion Notification
(ECN) to keep throughput hit due to network congestion as low as possible. Without ECN, a TCP message segment is dropped by some router when its buffer is full. Hosts get no notice of building congestion until packets start being dropped. The sender detects the segment did not reach the destination; but due to lack of feedback from the congested router, it has no information on the extent of reduction in transmission rate it needs to make. Standard TCP implementations detect this drop when they time out waiting for acknowledgement from the receiver. The sender then reduces the size of its congestion window
, which is the limit on the amount of data in flight at any time. Multiple packet drops can even result in a reset of the congestion window, to TCP's Maximum Segment Size
, and a TCP Slow Start
. Exponential back-off and only additive increase produce stable network behaviour, letting routers recover from congestion. However, the dropping of packets has noticeable impacts on time-sensitive streams like streaming media, because it takes time for the drop to be noticed and retransmitted. With ECN support enabled, the router sets two bits in the data packets that indicate to the receiver it is experiencing congestion (but not yet fully choked). The receiver in turn lets the sender know that a router is facing congestion and then the sender lowers its transmission rate by some amount. If the router is still congested, it will set the bits again, and eventually the sender will slow down even more. The advantage of this approach is that the router does not get full enough to drop packets, and thus the sender does not have to lower the transmission rate significantly to cause serious delays in time-sensitive streams; nor does it risk severe under-utilization of bandwidth. Without ECN, the only way routers can tell hosts anything is by dropping packets. ECN is like Random Early Drop
, except that the packets are marked instead of dropped. The only caveat is that both sender and receiver, as well as all intermediate routers, have to be ECN-friendly. Any router along the way can prevent the use of ECN if it considers ECN-marked packets invalid and drops them (or more typically the whole connection setup fails because of a piece of network equipment that drops connection setup packets with ECN flags set). Routers that don't know about ECN can still drop packets normally, but there is some ECN-hostile network equipment on the Internet. For this reason, ECN is disabled by default. It can be enabled via the
In previous versions of Windows, all processing needed to receive or transfer data over one network interface was done by a single processor, even in a multi processor system. With supported network interface adapters, Windows Vista can distribute the job of traffic processing in network communication among multiple processors. This feature is called Receive Side Scaling. Windows Vista also supports network cards with TCP Offload Engine
, that have certain hardware-accelerated TCP/IP-related functionality. Windows Vista uses its TCP Chimney Offload system to offload to such cards framing, routing, error-correction and acknowledgement and retransmission jobs required in TCP. However, for application compatibility, only TCP data transfer functionality is offloaded to the NIC, not TCP connection setup. This will remove some load from the CPU. Traffic processing in both IPv4 and IPv6 can be offloaded. Windows Vista also supports NetDMA, which uses the DMA engine to allow processors to be freed from the hassles of moving data between network card data buffers and application buffers. It requires specific hardware DMA architectures, such as Intel I/O Acceleration to be enabled.
, meant to improve networking performance in all applications. It is not enabled by default in the pre-Service Pack 1 version of Windows Vista, but enabled in SP1 and Windows Server 2008. It uses a different algorithm to modify the congestion window – borrowing from TCP Vegas
and TCP New Reno. For every acknowledgement received, it increases the congestion window more aggressively, thus reaching the peak throughput much faster, increasing overall throughput.
(QoS) functionality to prioritize network traffic. Quality of Service can be used to manage network usage by specific applications or users, by throttling the bandwidth available to them, or it can be used to limit bandwidth usage by other applications when high priority applications, such as real time conferencing applications, are being run, to ensure they get the bandwidth they need. Traffic throttling can also be used to prevent large data transfer operations from using up all the available bandwidth. QoS policies can be confined by application executable name, folder path, source and destination IPv4 or IPv6 addresses, source and destination TCP or UDP ports or a range of ports. In Windows Vista, QoS policies can be applied to any application at the Network Layer
, thus eliminating the need to rewrite applications using QoS APIs to be QoS-aware. QoS policies can either be set on a per-machine basis or set by Active Directory
Group policy
objects which ensures that all Windows Vista clients connected to the Active Directory
container (a domain, a site or an organizational unit) will enforce the policy settings.
Windows Vista supports the Wireless Multimedia
(WMM) profile classes for QoS in wireless networks as certified by the Wi-Fi Alliance
: BG (for background data), BE (for Best Effort
non real time data), VI (for real time videos) and VO (for real time voice data). When both the wireless access point as well as the wireless NIC supports the WMM profiles, Windows Vista can provide preferential treatment to the data sent.
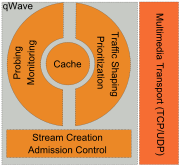 Windows Vista includes a specialized QoS API called qWave (Quality Windows Audio/Video Experience), which is a pre-configured Quality of Service module for time dependent multimedia data, such as audio or video streams. qWave uses different packet priority schemes for real-time flows (such as multimedia packets) and best-effort flows (such as file downloads or e-mails) to ensure that real-time data gets as little delays as possible, while providing a high quality channel for other data packets.
Windows Vista includes a specialized QoS API called qWave (Quality Windows Audio/Video Experience), which is a pre-configured Quality of Service module for time dependent multimedia data, such as audio or video streams. qWave uses different packet priority schemes for real-time flows (such as multimedia packets) and best-effort flows (such as file downloads or e-mails) to ensure that real-time data gets as little delays as possible, while providing a high quality channel for other data packets.
qWave is intended to ensure real-time transport of multimedia networks within a wireless network. qWave supports multiple simultaneous multimedia as well as data streams. qWave does not depend solely on bandwidth reservation schemes, as provided by RSVP
for providing QoS
guarantees, as the bandwidth in a wireless network fluctuates constantly. As a result, it also uses continuous bandwidth monitoring to implement service guarantees.
Applications have to explicitly use the qWave API
s to use the service. When the multimedia application requests qWave to initiate a new media stream, qWave tries to reserve bandwidth using RSVP
. At the same time, it uses QoS probes to make sure the network has enough bandwidth to support the stream. If the conditions are met, the stream is allowed, and prioritized so that other applications do not eat into its share of bandwidth. However, environmental factors can affect the reception of the wireless signals, which can reduce the bandwidth, even if no other stream is allowed to access the reserved bandwidth. Due to this, qWave continuously monitors the available bandwidth, and if it decreases, the application is informed, creating a feedback loop, so that it can adapt the stream to fit into the lower bandwidth range. If more bandwidth is available, qWave automatically reserves it and informs the application of the improvement.
For probing the quality of the network, probe packets are sent to the source and statistics (such as round trip time, loss, latency jitter etc.) of their path analyzed and the results are cached. The probe is repeated after specific time intervals to update the cache. Whenever the stream is requested, the cache is looked up. qWave also serializes creation of multiple simultaneous streams, even across devices, so that probes sent for one stream are not interfered by others. qWave uses client side buffers to keep transmission rate within range of the slowest part in the network, so that the access point buffers are not overwhelmed, thus reducing packet loss.
qWave works best if both the source and sink (client) of the multimedia stream are qWave aware. Also, the wireless access point
(AP) needs to be QoS
-enabled, supporting bandwidth reservation. It can also work without QoS-aware APs; however, since qWave cannot reserve bandwidth in this case, its has to depend on the application to adapt the stream based on the available bandwidth, which not only will be affected by network conditions, but other data in the network as well. qWave is also available for other devices as a part of the Windows Rally
technologies.
(AES) is included in the network stack itself. Direct support for SSL
connections in new Winsock
API allows socket applications to directly control security of their traffic over a network (such as providing security policy and requirements for traffic, querying security settings) rather than having to add extra code to support a secure connection. Computers running Windows Vista can be a part of logically isolated networks within an Active Directory
domain. Only the computers which are in the same logical network partition will be able to access the resources in the domain. Even though other systems may be physically on the same network, unless they are in the same logical partition, they won't be able to access partitioned resources. A system may be part of multiple network partitions.
Windows Vista also includes an Extensible Authentication Protocol
Host (EAPHost) framework that provides extensibility for authentication methods for commonly used protected network access technologies such as 802.1X
and PPP. It allows networking vendors to develop and easily install new authentication methods known as EAP methods.
A planned feature in the new TCP/IP suite known as "Routing Compartments", utilized a per-user routing table
, thus compartmentalizing the network according to the user's needs, so that data from one segment would not go into another. This feature however was removed before the release of Windows Vista, and is slated to be included possibly in a future release of Windows.
(NAP), which makes sure that computers connecting to a network conform to a required level of system health as has been set by the administrator of the network. With NAP enabled on a network, when a Windows Vista computer attempts to join a network, it is verified that the computer is up-to-date with security updates, virus signatures and other factors, including configuration of IPsec
and 802.1x authentication settings, specified by the network administrator. It will be granted full access to the network only when the criteria is met, failing which it may be either denied access to the network or granted limited access only to certain resources. It may optionally be granted access to servers which will provide it with the latest updates. Once the updates are installed, the computer is granted access to the network. However, Windows Vista can only be a NAP client, i.e., a client computer which connects to a NAP enabled network. Health policy and verification servers have to be running Windows Server 2008.
accounts.
Prior to Windows Vista, setting up and maintaining IPsec policy configuration in many scenarios required setting up a set of rules for protection and another set of rules for traffic exemptions. IPsec nodes in Windows Vista communicate while simultaneously negotiating protected communications and if a response is received and negotiation completes, subsequent communications are protected. This eliminates the need to set up IPsec filters for exemptions for the set of hosts that do not or cannot support IPsec, allows setting up required incoming protected initiated communication and optional outgoing communication. IPsec also allows securing traffic between domain controllers and member computers, while still allowing clear text for domain joins and other communication types. IPsec protected domain joins are allowed if using NTLM
v2 and if both, the domain controllers and member computers are running Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista respectively.
IPsec fully supports IPv6, AuthIP
(which allows for a second authentication), integration with NAP
for authenticating with a health certificate, Network Diagnostics Framework support for failed IPsec negotiation, new IPsec performance counters, and improved detection of cluster node failure and faster renegotiation of security associations. There is support for stronger algorithms for main mode negotiation (stronger DH algorithms and Suite B) and data integrity and encryption (AES with CBC, AES-GMAC, SHA-256, AES-GCM).
(MIB)-II and better system event logging and tracing. The Vista TCP/IP stack also supports ESTATS which defines extended performance statistics for TCP and can help in determining the cause of network performance bottlenecks. Windows Vista can inform the user of most causes of network transmission failure, such as incorrect IP address
, incorrect DNS and default gateway settings, gateway failure, port in use or blocked, receiver not ready, DHCP service not running, NetBIOS over TCP/IP name resolution failure etc. Transmission errors are also exhaustively logged, which can be analyzed to better find the cause of error. Windows Vista has a greater awareness of the network topology the host computer is in, using technologies such as Universal Plug and Play
. With this new network awareness technology, Windows Vista can provide help to the user in fixing network issues or simply provide a graphical view of the perceived network configuration.
, which allows external applications to access and hook into the packet processing pipeline of the networking subsystem. WFP allows incoming and outgoing packets to be filtered, analyzed or modified at several layers of the TCP/IP protocol stack. Because WFP has an inbuilt filtering engine, applications need not write any custom engine, they just need to provide the custom logic for the engine to use. WFP includes a Base Filtering Engine which implements the filter requests. The packets are then processed using the Generic Filtering Engine, which also includes a Callout Module, where applications providing the custom processing logic can be hooked up. WFP can be put to uses such as inspecting packets for malware, selective packet restriction, such as in firewalls, or providing custom encryption systems, among others. Upon its initial release WFP was plagued with bugs including memory leaks and race conditions.
communication and includes implementation of peer-to-peer
protocols out-of-the-box. It also includes a new version of the Peer Name Resolution Protocol
(PNRPv2), which is faster and more scalable. Windows Vista also includes a peer-to-peer
API for name resolution and secure Group creation. Peer-to-peer networking functionality can be accessed from the Winsock
API as well. The peer-to-peer networking subsystem can also discover other people running the same service in the local subnet, using a feature dubbed People Near Me and integrate with Windows Contacts to store their information. This facility can be used to develop ad-hoc collaborative applications, such as Windows Meeting Space
. Peer-to-peer networking settings are configurable through netsh p2p and Group Policy
.
A feature called Windows Internet Computer Names (WICN) based on PNRP allows any computer connected to an IPv6 network to get a unique domain name. If the computer is connected to the Internet, users can easily specify a secured or unsecured host name for their computer from a console command and their computer can be easily accessible from any remote computer, without requiring to register a domain name and configuring a dynamic DNS. Windows Internet Computer Names can be used in any application that accepts an IP address or DNS name. PNRP performs all the domain name resolution at the peer-to-peer level.
PNRP also allows creating an overlay network
called a Graph. Each peer in the overlay network corresponds to a node in the graph. Nodes are resolved to addresses using PNRP
. All the nodes in a graph share book-keeping information responsible for the functioning of the network as a whole. For example, in a distributed resource management network, which node has what resource needs to be shared. Such information is shared as Records, which are flooded to all the peers in a graph. Each peer stores the Record to a local database. A Record consists of a header and a body. The body contains data specific to the application that is using the API; the header contains metadata to describe the data in the body as name-value pairs serialized using XML
, in addition to author and version information. It can also contain an index of the body data, for fast searching. A node can connect to other nodes directly as well, for communication that need not be shared with the entire Graph. The API also allows creation of a secure overlay network
called a Group, consisting of all or a subset of nodes in a Graph. A Group can be shared by multiple applications, unlike a Graph. All peers in a Group must be identifiable by a unique named, registered using PNRP
, and have a digital signature
certificate termed as Group Member Certificate (GMC). All Records exchanged are digitally signed. Peers must be invited into a Group. The invitation contains the GMC that enables it to join the group.
Another planned feature in Windows Vista would have taken advantage of peer-to-peer
technology to provide a new type of domain-like networking setup known as a Castle, but this did not make it into the release version. Castle would have made it possible to have an identification service, which provides user authentication, for all members on the network, without a centralized server. It would have allowed user credentials to propagate across the peer-to-peer network, making them more suitable for a home network. This feature eventually materialized in Windows 7 as HomeGroup.
(BITS) 3.0 has a new feature called Neighbor Casting which supports peer-to-peer file transfers within a domain
. This facilitates peer caching, allows users to download and serve content (such as WSUS
updates) from peers on the same subnet, receive notification when a file is downloaded, access the temporary file while the download is in progress, and control HTTP redirects. This saves bandwidth on the network and reduces performance load on the server. BITS 3.0 also uses Internet Gateway Device Protocol counters to more accurately calculate available bandwidth.
s support and Event Tracing. WinHTTP, the client API for server-based applications and services
supports IPv6, AutoProxy
, HTTP/1.1 chunked transfer encoding
, larger data uploads, SSL and client certificates, server and proxy authentication, automatic handling of redirects and keep-alive connections and HTTP/1.0 protocol, including support for keep-alive (persistent) connections and session cookies. Winsock
has been updated with new APIs and support for Event Tracing. Winsock Layered Service Provider
support has been enhanced with logged installations and removals, a new API for reliably installing LSPs, a command to reliably remove LSPs, facilities to categorize LSPs and to remove most LSPs from the processing path for system critical services and support for Network Diagnostics Framework.
Kernel (WSK) is a new transport-independent kernel-mode Network Programming Interface (NPI) for that provides TDI client developers with a sockets-like programming model similar to those supported in user-mode Winsock
. While most of the same sockets
programming concepts exist as in user-mode Winsock such as socket, creation, bind, connect, accept, send and receive, Winsock Kernel is a completely new programming interface with unique characteristics such as asynchronous I/O
that uses IRPs and event callbacks to enhance performance. TDI is supported in Windows Vista for backward compatibility.
(SMB) protocol has been introduced with Windows Vista. A significant improvement over SMB support in prior versions of Windows is the ability to compound multiple actions into a single request, which significantly reduces the number of round-trips
the client needs to make to the server, improving performance as a result. SMB1 also has a compounding mechanism (known as AndX) to compound multiple actions, but is rarely used by Microsoft clients. Larger buffer sizes are supported, also increasing performance with large file transfers. The notion of "durable file handles" is introduced, which allow a connection to an SMB server to survive brief network outages, such as with a wireless network, without having to construct a new session. Support for symbolic links is included as well. In SMB 1, various sizes in the protocol are 16 bits. Many have been changed to 32 or 64 bit, and in the case of file handles to 16 bytes.
SMB2 reduces the 'chattiness' of the protocol by reducing the number of commands and subcommands to 19 from over 100. It has mechanisms for pipelining, that is, sending additional requests before the response to a previous request arrives. Other improvements include caching of file properties, improved message signing with HMAC SHA-256 hashing algorithm and better scalability by increasing number of users, shares and open files per server among others.
Windows Vista and later operating systems use SMB 2.0 when communicating with other machines running Windows Vista or later. SMB 1.0 continues in use for connections to any previous version of Windows, or to Samba. Samba 3.6 also includes support for SMB 2.0.
SMB 2 has two big benefits to Microsoft. The first is clear intellectual property ownership. SMB 1 was originally designed by IBM and was shipped on a wide variety of non-Windows operating systems such as SCO Xenix, OS/2 and DEC VMS (Pathworks). It was partially standardised by X/Open
and also had draft standards for IETF which lapsed. (See http://ubiqx.org/cifs/Intro.html for historical detail).
The second benefit is a clean break. Microsoft's SMB1 code has to work with a huge variety of SMB clients and servers. A large number of items in the protocol are optional (such as short and long filenames), there are many infolevels for commands (selecting what structure is returned to a particular request), Unicode
was a later addition etc. With SMB2 there is significantly reduced compatibility testing (currently only other Windows Vista clients and servers). Additionally the code is a lot less complex since there is far less variability (e.g. there is no need to worry about having Unicode and non-Unicode code paths as SMB2 requires Unicode support).
Bluetooth
stack is improved with support for more hardware IDs, EDR performance improvements, Adaptive frequency hopping for Wi-Fi co-existence, and Synchronous Connection Oriented (SCO) protocol support which is needed for audio profiles. The Windows Vista Bluetooth stack supports a kernel mode device driver interface
besides the user-mode programming interface, which enables third-parties to add support for additional Bluetooth Profiles such as SCO, SDP, and L2CAP. This was lacking in the Windows XP Service Pack 2 built-in Bluetooth stack, which had to be entirely replaced by a third-party stack for additional profile support. It also provides RFCOMM support using sockets besides virtual COM ports. KB942567 called Windows Vista Feature Pack for Wireless adds Bluetooth 2.1+EDR support and remote wake from S3 or S4 support for self-powered Bluetooth modules. This feature pack while initially only available to OEMs, was eventually included in Windows Vista Service Pack 2.
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
and Windows Server 2008 contain a new networking stack, named Next Generation TCP/IP stack, that improves on the previous stack in several ways. It includes native implementation of IPv6, as well as complete overhaul of IPv4. The new TCP/IP stack uses a new method to store configuration settings that enables more dynamic control and does not require a computer restart after settings are changed. The new stack, implemented as a dual stack model, is based on a strong host model and features an infrastructure to enable more modular components that can be dynamically inserted and removed.
Architecture

Network Driver Interface Specification
The Network Driver Interface Specification is an application programming interface for network interface cards . It was jointly developed by Microsoft and 3Com Corporation, and is mostly used in Microsoft Windows, but the open-source NDISwrapper and Project Evil driver wrapper projects allow...
(NDIS) driver. The network stack, implemented in
tcpip.sys implements the TransportTransport layer
In computer networking, the transport layer or layer 4 provides end-to-end communication services for applications within a layered architecture of network components and protocols...
, Network
Network layer
The network layer is layer 3 of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking.The network layer is responsible for packet forwarding including routing through intermediate routers, whereas the data link layer is responsible for media access control, flow control and error checking.The network...
and Data link
Data link layer
The data link layer is layer 2 of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. It corresponds to, or is part of the link layer of the TCP/IP reference model....
layers of the TCP/IP model. The Transport layer includes implementations for TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
The Transmission Control Protocol is one of the core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite. TCP is one of the two original components of the suite, complementing the Internet Protocol , and therefore the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP...
, UDP
User Datagram Protocol
The User Datagram Protocol is one of the core members of the Internet Protocol Suite, the set of network protocols used for the Internet. With UDP, computer applications can send messages, in this case referred to as datagrams, to other hosts on an Internet Protocol network without requiring...
and unformatted RAW protocols
Communications protocol
A communications protocol is a system of digital message formats and rules for exchanging those messages in or between computing systems and in telecommunications...
. At the Network layer, IPv4
IPv4
Internet Protocol version 4 is the fourth revision in the development of the Internet Protocol and the first version of the protocol to be widely deployed. Together with IPv6, it is at the core of standards-based internetworking methods of the Internet...
and IPv6
IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6 is a version of the Internet Protocol . It is designed to succeed the Internet Protocol version 4...
protocols are implemented in a dual-stack architecture. And the Data link layer (also called Framing layer) implements 802.3, 802.1, PPP
Point-to-Point Protocol
In networking, the Point-to-Point Protocol is a data link protocol commonly used in establishing a direct connection between two networking nodes...
, Loopback
Loopback
Loopback describes ways of routing electronic signals, digital data streams, or flows of items from their originating facility back to the source without intentional processing or modification...
and tunnelling protocols. Each layer can accommodate Windows Filtering Platform
Windows Filtering Platform
Windows Filtering Platform is a set of system services and an application programming interface introduced with Windows Vista that allows applications to tie into the packet processing and filtering pipeline of the new network stack. It provides features such as integrated communication and it can...
(WFP) shims, which allows packets at that layer to be introspected and also host the WFP Callout API. The networking API is exposed via three components:
Winsock
Winsock
In computing, the Windows Sockets API , which was later shortened to Winsock, is a technical specification that defines how Windows network software should access network services, especially TCP/IP. It defines a standard interface between a Windows TCP/IP client application and the underlying...
: A user mode API for abstracting network communication using sockets
Internet socket
In computer networking, an Internet socket or network socket is an endpoint of a bidirectional inter-process communication flow across an Internet Protocol-based computer network, such as the Internet....
and ports
TCP and UDP port
In computer networking, a port is an application-specific or process-specific software construct serving as a communications endpoint in a computer's host operating system. A port is associated with an IP address of the host, as well as the type of protocol used for communication...
. Datagram socket
Datagram socket
A datagram socket is a type of connectionless Internet socket, which is the sending or receiving point for packet delivery services. Each packet sent or received on a datagram socket is individually addressed and routed...
s are used for UDP
User Datagram Protocol
The User Datagram Protocol is one of the core members of the Internet Protocol Suite, the set of network protocols used for the Internet. With UDP, computer applications can send messages, in this case referred to as datagrams, to other hosts on an Internet Protocol network without requiring...
, whereas Stream socket
Stream socket
In computer networking, a stream socket is a type of internet socket which provides a connection-oriented, sequenced, and unduplicated flow of data without record boundaries, with well-defined mechanisms for creating and destroying connections and for detecting errors.This internet socket type...
s are for TCP
Transmission Control Protocol
The Transmission Control Protocol is one of the core protocols of the Internet Protocol Suite. TCP is one of the two original components of the suite, complementing the Internet Protocol , and therefore the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP...
. While Winsock
Winsock
In computing, the Windows Sockets API , which was later shortened to Winsock, is a technical specification that defines how Windows network software should access network services, especially TCP/IP. It defines a standard interface between a Windows TCP/IP client application and the underlying...
is a user mode library, it uses a kernel mode driver, called Ancillary Function Driver (AFD) to implement certain functionality.
Winsock Kernel (WSK): A kernel-mode API providing the same socket-and-port abstraction as Winsock
Winsock
In computing, the Windows Sockets API , which was later shortened to Winsock, is a technical specification that defines how Windows network software should access network services, especially TCP/IP. It defines a standard interface between a Windows TCP/IP client application and the underlying...
, while exposing other features such as Asynchronous I/O
Asynchronous I/O
Asynchronous I/O, or non-blocking I/O, is a form of input/output processing that permits other processing to continue before the transmission has finished....
using I/O request packets.
Transport Driver Interface (TDI): A kernel-mode API which can be used for legacy protocols like NetBIOS
NetBIOS
NetBIOS is an acronym for Network Basic Input/Output System. It provides services related to the session layer of the OSI model allowing applications on separate computers to communicate over a local area network. As strictly an API, NetBIOS is not a networking protocol...
. It includes a component, known as TDX to map the TDI functionality to the network stack.
User interface

Windows XP
Windows XP is an operating system produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops and media centers. First released to computer manufacturers on August 24, 2001, it is the second most popular version of Windows, based on installed user base...
"My Network Places". Network Explorer items can be a shared device such as a scanner, or a file share. The Network Location Awareness (NLA) service uniquely identifies each network and exposes the network's attributes and connectivity type so that applications can determine the optimal network configuration. However, applications have to use the NLA APIs explicitly to be aware of the network connectivity changes, and adapt accordingly. Windows Vista uses the Link Layer Topology Discovery
Link Layer Topology Discovery
Link Layer Topology Discovery is a proprietary Link Layer protocol for network topology discovery and quality of service diagnostics. Microsoft developed it as part of the Windows Rally set of technologies...
(LLTD) protocol to graphically present how different devices are connected over a network, as a Network Map. In addition, the Network Map uses LLTD to determine connectivity information and media type (wired or wireless), so that the map is topologically accurate. The ability to know network topology is important for diagnosing and solving networking problems, and for streaming content over a network connection. Any device can implement LLTD to appear on the Network Map with an icon representing the device, allowing users one-click access to the device's user interface. When LLTD is invoked, it provides metadata about the device that contains static or state information, such as the MAC address
MAC address
A Media Access Control address is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment. MAC addresses are used for numerous network technologies and most IEEE 802 network technologies, including Ethernet...
, IPv4/IPv6 address, signal strength
Signal strength
In telecommunications, particularly in radio, signal strength refers to the magnitude of the electric field at a reference point that is a significant distance from the transmitting antenna. It may also be referred to as received signal level or field strength. Typically, it is expressed in...
etc.
Network classification by location
Windows Vista classifies the networks it connects to as either Public, Private or Domain and uses Network Location Awareness to switch between network types. Different network types have different firewall policies. An open network such as a public wireless network is classified as Public and is the most restrictive of all network settings. In this mode other computers on the network are not trusted and external access to the computer, including sharing of files and printers, is disabled. A home network is classified as Private, and it enables file sharing between computers. If the computer is joined to a domain, the network is classified as a Domain network; in such a network the policies are set by the domain controllerDomain controller
On Windows Server Systems, a domain controller is a server that responds to security authentication requests within the Windows Server domain...
. When a network is first connected to, Windows Vista prompts to choose the correct network type. On subsequents connections to the network, the service is used to gain information on which network is connected to and automatically switch to the network configuration for the connected network. Windows Vista introduces a concept of network profiles. For each network, the system stores the IP address
IP address
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing...
, DNS server, Proxy server
Proxy server
In computer networks, a proxy server is a server that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from other servers. A client connects to the proxy server, requesting some service, such as a file, connection, web page, or other resource available from a different server...
and other network features specific to the network in that network's profile. So when that network is subsequently connected to, the settings need not be reconfigured, the ones saved in its profile are used. In the case of mobile machines, the network profiles are chosen automatically based on what networks are available. Each profile is part of either a Public, Private or Domain network.
Internet Protocol v6
The Windows Vista networking stack supports the dual Internet ProtocolInternet Protocol
The Internet Protocol is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite...
(IP) layer architecture in which the IPv4
IPv4
Internet Protocol version 4 is the fourth revision in the development of the Internet Protocol and the first version of the protocol to be widely deployed. Together with IPv6, it is at the core of standards-based internetworking methods of the Internet...
and IPv6
IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6 is a version of the Internet Protocol . It is designed to succeed the Internet Protocol version 4...
implementations share common Transport
Transport layer
In computer networking, the transport layer or layer 4 provides end-to-end communication services for applications within a layered architecture of network components and protocols...
and Framing
Data link layer
The data link layer is layer 2 of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. It corresponds to, or is part of the link layer of the TCP/IP reference model....
layers. Windows Vista provides a GUI
Graphical user interface
In computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
for configuration of both IPv4 and IPv6 properties. IPv6
IPv6
Internet Protocol version 6 is a version of the Internet Protocol . It is designed to succeed the Internet Protocol version 4...
is now supported by all networking components and services. The Windows Vista DNS client can use IPv6 transport. Internet Explorer in Windows Vista and other applications that use WinINet (Windows Mail, file sharing) support literal IPv6 addresses (RFC 2732). Windows Firewall and the IPsec Policies snap-in support IPv6 addresses as permissible character strings. In IPv6 mode, Windows Vista can use the Link Local Multicast Name Resolution
Link-local Multicast Name Resolution
The Link Local Multicast Name Resolution is a protocol based on the Domain Name System packet format that allows both IPv4 and IPv6 hosts to perform name resolution for hosts on the same local link...
(LLMNR) protocol, as described in RFC 4795, to resolve names of local hosts on a network which does not have a DNS server running. This service is useful for networks without a central managing server, and for ad-hoc wireless networks
Wireless ad-hoc network
A wireless ad-hoc network is a decentralized type of wireless network. The network is ad hoc because it does not rely on a preexisting infrastructure, such as routers in wired networks or access points in managed wireless networks...
. IPv6 can also be used over PPP
Point-to-Point Protocol
In networking, the Point-to-Point Protocol is a data link protocol commonly used in establishing a direct connection between two networking nodes...
-based dial-up and PPPoE connections. Windows Vista can also act as a client/server for file sharing or DCOM over IPv6. Support for DHCPv6
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a network configuration protocol for hosts on Internet Protocol networks. Computers that are connected to IP networks must be configured before they can communicate with other hosts. The most essential information needed is an IP address, and a default...
, which can be used with IPv6, is also included. IPv6 can even be used when full native IPv6 connectivity is not available, using Teredo tunneling
Teredo tunneling
In computer networking, Teredo is a transition technology that gives full IPv6 connectivity for IPv6-capable hosts which are on the IPv4 Internet but which have no direct native connection to an IPv6 network...
; this can even traverse most IPv4 symmetric Network Address Translation
Network address translation
In computer networking, network address translation is the process of modifying IP address information in IP packet headers while in transit across a traffic routing device....
s (NATs) as well. Full support for multicast
Multicast
In computer networking, multicast is the delivery of a message or information to a group of destination computers simultaneously in a single transmission from the source creating copies automatically in other network elements, such as routers, only when the topology of the network requires...
is also included, via the MLDv2
Multicast Listener Discovery
Multicast Listener Discovery is a component of the Internet Protocol Version 6 suite. MLD is used by IPv6 routers for discovering multicast listeners on a directly attached link, much like IGMP is used in IPv4. The protocol is embedded in ICMPv6 instead of using a separate protocol. MLDv1 is...
and SSM
Source-specific multicast
Source-specific multicast is a method of delivering multicast packets in which the only packets that are delivered to a receiver are those originating from a specific source address requested by the receiver...
protocols. The IPv6 interface ID is randomly generated for permanent autoconfigured IPv6 addresses to prevent determining the MAC address based on known company IDs of NIC manufacturers.
Wireless networks
Support for wireless networksWireless LAN
A wireless local area network links two or more devices using some wireless distribution method , and usually providing a connection through an access point to the wider internet. This gives users the mobility to move around within a local coverage area and still be connected to the network...
is built into the network stack itself as a new set of APIs called Native Wifi, and does not emulate wired connections, as was the case with previous versions of Windows. This allows implementation of wireless-specific features such as larger frame sizes and optimized error recovery procedures. Native Wifi is exposed by Auto Configuration Module (ACM) which replaces Windows XP's Wireless Zero Configuration
Wireless Zero Configuration
Wireless Zero Configuration , also known as Wireless Auto Configuration, or WLAN AutoConfig is a wireless connection management utility included with Microsoft Windows XP and later operating systems as a service that dynamically selects a wireless network to connect to based on a user's preferences...
. The ACM is extensible, so developers can incorporate additional wireless functionality (such as automatic wireless roaming) and override the automatic configuration and connection logic without affecting the built-in framework. It is easier to find wireless networks in range and tell which networks are open and which are closed. Hidden wireless networks, which do not advertise their name (SSID
Service set identifier
A service set is all the devices associated with a local or enterprise IEEE 802.11 wireless local area network .-Service set identifier :...
) are better supported. Security for wireless networks is improved with improved support for newer wireless standards like 802.11i
IEEE 802.11i
IEEE 802.11i-2004 or 802.11i, implemented as WPA2, is an amendment to the original IEEE 802.11. The draft standard was ratified on 24 June 2004. This standard specifies security mechanisms for wireless networks. It replaced the short Authentication and privacy clause of the original standard with...
. EAP-TLS is the default authentication mode. Connections are made at the most secure connection level supported by the wireless access point. WPA2 can be used even in ad-hoc mode. Windows Vista also provides a Fast Roaming service that will allow users to move from one access point to another without loss of connectivity. Preauthentication with the new wireless access point
Wireless access point
In computer networking, a wireless access point is a device that allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or related standards...
can be used to retain the connectivity. Wireless networks are managed from either the Connect to a network dialog box within the GUI or the netsh wlan command from the shell. Settings for wireless networks can also be configured using Group policy
Group Policy
Group Policy is a feature of the Microsoft Windows NT family of operating systems. Group Policy is a set of rules that control the working environment of user accounts and computer accounts. Group Policy provides the centralized management and configuration of operating systems, applications, and...
.
Windows Vista enhances security when joining a domain over a wireless network. It can use Single Sign On
Single sign-on
Single sign-on is a property of access control of multiple related, but independent software systems. With this property a user logs in once and gains access to all systems without being prompted to log in again at each of them...
to use the same credentials to join a wireless network as well as the domain housed within the network. In this case, the same RADIUS
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial In User Service is a networking protocol that provides centralized Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting management for computers to connect and use a network service...
server is used for both PEAP
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol
The Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol, also known as Protected EAP or simply PEAP, is a protocol that encapsulates the Extensible Authentication Protocol within an encrypted and authenticated Transport Layer Security tunnel...
authentication for joining the network and MS-CHAP v2
MS-CHAP
MS-CHAP is the Microsoft version of the Challenge-handshake authentication protocol, CHAP. The protocol exists in two versions, MS-CHAPv1 and MS-CHAPv2...
authentication to log in to the domain. A bootstrap wireless profile can also be created on the wireless client, which first authenticates the computer to the wireless network and joins the network. At this stage, the machine still does not have any access to the domain resources. The machine will run a script, stored either on the system or on USB thumb drive, which authenticates it to the domain. Authentication can be done either by using username and password combination or security certificates from a Public key infrastructure
Public key infrastructure
Public Key Infrastructure is a set of hardware, software, people, policies, and procedures needed to create, manage, distribute, use, store, and revoke digital certificates. In cryptography, a PKI is an arrangement that binds public keys with respective user identities by means of a certificate...
(PKI) vendor such as VeriSign
VeriSign
Verisign, Inc. is an American company based in Dulles, Virginia that operates a diverse array of network infrastructure, including two of the Internet's thirteen root nameservers, the authoritative registry for the .com, .net, and .name generic top-level domains and the .cc and .tv country-code...
.
Wireless setup and configuration
Windows Vista features Windows Connect Now which supports setting up a wireless network using several methods supported in the Wi-Fi Protected SetupWi-Fi Protected Setup
Wi-Fi Protected Setup is a computing standard for easy and secure establishment of a wireless home network....
standard. It implements a native code API, Web Services for Devices (WSDAPI) to support Devices Profile for Web Services
Devices Profile for Web Services
The Devices Profile for Web Services defines a minimal set of implementation constraints to enable secure Web Service messaging, discovery, description, and eventing on resource-constrained devices....
(DPWS) and also a managed code implementation in WCF
Windows Communication Foundation
The Windows Communication Foundation , previously known as "Indigo", is an application programming interface in the .NET Framework for building connected, service-oriented applications.-The architectures:...
. DPWS enables simpler device discoverability like UPnP and describes available services to those clients. Function Discovery is a new technology that serves as an abstraction layer between applications and devices, allowing applications to discover devices by referencing the device's function, rather than by its bus type or the nature of its connection. Plug and Play Extensions (PnP-X) allow network-connected devices to appear as local devices inside Windows connected physically. UPnP
Universal Plug and Play
Universal Plug and Play is a set of networking protocols for primarily residential networks without enterprise class devices that permits networked devices, such as personal computers, printers, Internet gateways, Wi-Fi access points and mobile devices to seamlessly discover each other's presence...
support has also been enhanced to include integration with PnP-X and Function Discovery.
Network performance
Windows Vista's networking stack also uses several performance optimizations, which allow higher throughput by allowing faster recovery from packet losses, when using a high packet loss environment such as wireless networks. Windows Vista uses the NewReno (RFC 2582) algorithm which allows a sender to send more data while retrying in case it receives a partial acknowledgement, which is acknowledgement from the receiver for only a part of data that has been received. It also uses Selective Acknowledgements (SACKRetransmission (data networks)
Retransmission, essentially identical with Automatic repeat request , is the resending of packets which have been either damaged or lost. It is a term that refers to one of the basic mechanisms used by protocols operating over a packet switched computer network to provide reliable communication...
) to reduce the amount of data to be retransmitted in case a portion of the data sent was not received correctly, and Forward RTO-Recovery
TCP tuning
TCP tuning techniques adjust the network congestion avoidance parameters of TCP connections over high-bandwidth, high-latency networks. Well-tuned networks can perform up to 10 times faster in some cases.- Bandwidth-delay product :...
(F-RTO) to prevent unnecessary retransmission of TCP segments when round trip time
Round-trip delay time
In telecommunications, the round-trip delay time or round-trip time is the length of time it takes for a signal to be sent plus the length of time it takes for an acknowledgment of that signal to be received...
increases. It also includes Neighbour Unreachability Detection capability in both IPv4 and IPv6, which tracks the accessibility of neighboring nodes. This allows faster error recovery, in case a neighboring node fails. NDIS
Network Driver Interface Specification
The Network Driver Interface Specification is an application programming interface for network interface cards . It was jointly developed by Microsoft and 3Com Corporation, and is mostly used in Microsoft Windows, but the open-source NDISwrapper and Project Evil driver wrapper projects allow...
6.0 introduced in Windows Vista supports offloading IPv6 traffic and checksum calculations for IPv6, improved manageability, scalability and performance with reduced complexity for NDIS miniports, and simpler models for writing Lightweight Filter Drivers (LWF). LWF drivers are a combination of NDIS intermediate drivers and a miniport driver that eliminate the need to write a separate protocol and miniport and have a bypass mode to examine only selected control and data paths. The TCP/IP stack also provides fail-back support for default gateway changes by periodically attempting to send TCP traffic through a previously detected unavailable gateway. This can provide faster throughput by sending traffic through the primary default gateway on the subnet.
Another significant change that aims to improve network throughput is the automatic resizing of TCP Receive window. The receive window (RWIN) specifies how much data a host is prepared to receive, and is limited by, among other things, the available buffer space. In other words, it is a measure of how much data the remote transmitter can send before requiring an acknowledgement for the outstanding data. When the receive window is too small, the remote transmitter will frequently find that it has hit the limit of how much outstanding data it can transmit, even though there is enough bandwidth available to transmit more data. This leads to incomplete link utilization. So using a larger RWIN size boosts throughput in such situations; an auto-adjusting RWIN tries to keep the throughput rate as high as is permissible by the bandwidth of the link. Receive window auto tuning functionality continually monitors the bandwidth and the latency of TCP connections individually and optimize the receive window for each connection. The window size is increased in high-bandwidth (~5 Mbit/s+) or high-latency
Lag
Lag is a common word meaning to fail to keep up or to fall behind. In real-time applications, the term is used when the application fails to respond in a timely fashion to inputs...
(>10ms) situations.
Traditional TCP implementations uses the TCP Slow Start
Slow-start
Slow-start is part of the congestion control strategy used by TCP, the data transmission protocol used by many Internet applications. Slow-start is used in conjunction with other algorithms to avoid sending more data than the network is capable of transmitting, that is, to avoid causing network...
algorithm to detect how fast it can transmit without choking the receiver (or intermediate nodes). In a nutshell, it specifies that transmission should start at a slow rate, by transmitting a few packets. This number is controlled by the Congestion window
Congestion window
In Transmission Control Protocol , the congestion window is one of the factors that determines the number of bytes that can be outstanding at any time. This is not to be confused with the TCP window size which is maintained by the receiver. This is a means of stopping the link between two places...
– which specifies the number of outstanding packets that has been transmitted but for which an acknowledgement of receipt from the receiver has not yet been received. As acknowledgements are received, the congestion window is expanded, one TCP segment at a time till an acknowledgement fails to arrive. Then the sender assumes that with the congestion window size of that instant, the network gets congested. However, a high bandwidth network can sustain a quite large congestion window without choking up. The slow start algorithm can take quite some time to reach that threshold – leaving the network under-utilized for a significant time.
The new TCP/IP stack also supports Explicit Congestion Notification
Explicit Congestion Notification
Explicit Congestion Notification is an extension to the Internet Protocol and to the Transmission Control Protocol and is defined in RFC 3168 . ECN allows end-to-end notification of network congestion without dropping packets. ECN is an optional feature that is only used when both endpoints...
(ECN) to keep throughput hit due to network congestion as low as possible. Without ECN, a TCP message segment is dropped by some router when its buffer is full. Hosts get no notice of building congestion until packets start being dropped. The sender detects the segment did not reach the destination; but due to lack of feedback from the congested router, it has no information on the extent of reduction in transmission rate it needs to make. Standard TCP implementations detect this drop when they time out waiting for acknowledgement from the receiver. The sender then reduces the size of its congestion window
Congestion window
In Transmission Control Protocol , the congestion window is one of the factors that determines the number of bytes that can be outstanding at any time. This is not to be confused with the TCP window size which is maintained by the receiver. This is a means of stopping the link between two places...
, which is the limit on the amount of data in flight at any time. Multiple packet drops can even result in a reset of the congestion window, to TCP's Maximum Segment Size
Maximum segment size
The maximum segment size is a parameter of the TCP protocol that specifies the largest amount of data, specified in octets, that a computer or communications device can receive in a single TCP segment, and therefore in a single IP datagram. It does not count the TCP header or the IP header...
, and a TCP Slow Start
Slow-start
Slow-start is part of the congestion control strategy used by TCP, the data transmission protocol used by many Internet applications. Slow-start is used in conjunction with other algorithms to avoid sending more data than the network is capable of transmitting, that is, to avoid causing network...
. Exponential back-off and only additive increase produce stable network behaviour, letting routers recover from congestion. However, the dropping of packets has noticeable impacts on time-sensitive streams like streaming media, because it takes time for the drop to be noticed and retransmitted. With ECN support enabled, the router sets two bits in the data packets that indicate to the receiver it is experiencing congestion (but not yet fully choked). The receiver in turn lets the sender know that a router is facing congestion and then the sender lowers its transmission rate by some amount. If the router is still congested, it will set the bits again, and eventually the sender will slow down even more. The advantage of this approach is that the router does not get full enough to drop packets, and thus the sender does not have to lower the transmission rate significantly to cause serious delays in time-sensitive streams; nor does it risk severe under-utilization of bandwidth. Without ECN, the only way routers can tell hosts anything is by dropping packets. ECN is like Random Early Drop
Random early detection
Random early detection , also known as random early discard or random early drop is an active queue management algorithm. It is also a congestion avoidance algorithm....
, except that the packets are marked instead of dropped. The only caveat is that both sender and receiver, as well as all intermediate routers, have to be ECN-friendly. Any router along the way can prevent the use of ECN if it considers ECN-marked packets invalid and drops them (or more typically the whole connection setup fails because of a piece of network equipment that drops connection setup packets with ECN flags set). Routers that don't know about ECN can still drop packets normally, but there is some ECN-hostile network equipment on the Internet. For this reason, ECN is disabled by default. It can be enabled via the
netsh interface tcp set global ecncapability=enabled command.In previous versions of Windows, all processing needed to receive or transfer data over one network interface was done by a single processor, even in a multi processor system. With supported network interface adapters, Windows Vista can distribute the job of traffic processing in network communication among multiple processors. This feature is called Receive Side Scaling. Windows Vista also supports network cards with TCP Offload Engine
TCP Offload Engine
TCP offload engine or TOE is a technology used in network interface cards to offload processing of the entire TCP/IP stack to the network controller...
, that have certain hardware-accelerated TCP/IP-related functionality. Windows Vista uses its TCP Chimney Offload system to offload to such cards framing, routing, error-correction and acknowledgement and retransmission jobs required in TCP. However, for application compatibility, only TCP data transfer functionality is offloaded to the NIC, not TCP connection setup. This will remove some load from the CPU. Traffic processing in both IPv4 and IPv6 can be offloaded. Windows Vista also supports NetDMA, which uses the DMA engine to allow processors to be freed from the hassles of moving data between network card data buffers and application buffers. It requires specific hardware DMA architectures, such as Intel I/O Acceleration to be enabled.
Compound TCP
Compound TCP is a modified TCP congestion avoidance algorithmTCP congestion avoidance algorithm
Transmission Control Protocol uses a network congestion avoidance algorithm that includes various aspects of an additive increase/multiplicative decrease scheme, with other schemes such as slow-start in order to achieve congestion avoidance....
, meant to improve networking performance in all applications. It is not enabled by default in the pre-Service Pack 1 version of Windows Vista, but enabled in SP1 and Windows Server 2008. It uses a different algorithm to modify the congestion window – borrowing from TCP Vegas
TCP Vegas
TCP Vegas is a TCP congestion avoidance algorithm that emphasizes packet delay, rather than packet loss, as a signal to help determine the rate at which to send packets. It was developed at the University of Arizona by Lawrence Brakmo and Larry L...
and TCP New Reno. For every acknowledgement received, it increases the congestion window more aggressively, thus reaching the peak throughput much faster, increasing overall throughput.
Quality of Service
Windows Vista's networking stack includes integrated policy-based Quality of ServiceQuality of service
The quality of service refers to several related aspects of telephony and computer networks that allow the transport of traffic with special requirements...
(QoS) functionality to prioritize network traffic. Quality of Service can be used to manage network usage by specific applications or users, by throttling the bandwidth available to them, or it can be used to limit bandwidth usage by other applications when high priority applications, such as real time conferencing applications, are being run, to ensure they get the bandwidth they need. Traffic throttling can also be used to prevent large data transfer operations from using up all the available bandwidth. QoS policies can be confined by application executable name, folder path, source and destination IPv4 or IPv6 addresses, source and destination TCP or UDP ports or a range of ports. In Windows Vista, QoS policies can be applied to any application at the Network Layer
Network Layer
The network layer is layer 3 of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking.The network layer is responsible for packet forwarding including routing through intermediate routers, whereas the data link layer is responsible for media access control, flow control and error checking.The network...
, thus eliminating the need to rewrite applications using QoS APIs to be QoS-aware. QoS policies can either be set on a per-machine basis or set by Active Directory
Active Directory
Active Directory is a directory service created by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It is included in most Windows Server operating systems. Server computers on which Active Directory is running are called domain controllers....
Group policy
Group Policy
Group Policy is a feature of the Microsoft Windows NT family of operating systems. Group Policy is a set of rules that control the working environment of user accounts and computer accounts. Group Policy provides the centralized management and configuration of operating systems, applications, and...
objects which ensures that all Windows Vista clients connected to the Active Directory
Active Directory
Active Directory is a directory service created by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It is included in most Windows Server operating systems. Server computers on which Active Directory is running are called domain controllers....
container (a domain, a site or an organizational unit) will enforce the policy settings.
Windows Vista supports the Wireless Multimedia
Wireless Multimedia Extensions
Wireless Multimedia Extensions , also known as Wi-Fi Multimedia , is a Wi-Fi Alliance interoperability certification, based on the IEEE 802.11e standard. It provides basic Quality of service features to IEEE 802.11 networks. WMM prioritizes traffic according to four Access Categories - voice,...
(WMM) profile classes for QoS in wireless networks as certified by the Wi-Fi Alliance
Wi-Fi Alliance
The Wi-Fi Alliance is a trade association that promotes Wireless LAN technology and certifies products if they conform to certain standards of interoperability. Not every IEEE 802.11-compliant device is submitted for certification to the Wi-Fi Alliance, sometimes because of costs associated with...
: BG (for background data), BE (for Best Effort
Best effort delivery
Best effort delivery describes a network service in which the network does not provide any guarantees that data is delivered or that a user is given a guaranteed quality of service level or a certain priority...
non real time data), VI (for real time videos) and VO (for real time voice data). When both the wireless access point as well as the wireless NIC supports the WMM profiles, Windows Vista can provide preferential treatment to the data sent.
qWave

qWave is intended to ensure real-time transport of multimedia networks within a wireless network. qWave supports multiple simultaneous multimedia as well as data streams. qWave does not depend solely on bandwidth reservation schemes, as provided by RSVP
Resource Reservation Protocol
The Resource Reservation Protocol is a Transport Layer protocol designed to reserve resources across a network for an integrated services Internet. RSVP operates over an IPv4 or IPv6 Internet Layer and provides receiver-initiated setup of resource reservations for multicast or unicast data flows...
for providing QoS
Quality of service
The quality of service refers to several related aspects of telephony and computer networks that allow the transport of traffic with special requirements...
guarantees, as the bandwidth in a wireless network fluctuates constantly. As a result, it also uses continuous bandwidth monitoring to implement service guarantees.
Applications have to explicitly use the qWave API
Application programming interface
An application programming interface is a source code based specification intended to be used as an interface by software components to communicate with each other...
s to use the service. When the multimedia application requests qWave to initiate a new media stream, qWave tries to reserve bandwidth using RSVP
Resource Reservation Protocol
The Resource Reservation Protocol is a Transport Layer protocol designed to reserve resources across a network for an integrated services Internet. RSVP operates over an IPv4 or IPv6 Internet Layer and provides receiver-initiated setup of resource reservations for multicast or unicast data flows...
. At the same time, it uses QoS probes to make sure the network has enough bandwidth to support the stream. If the conditions are met, the stream is allowed, and prioritized so that other applications do not eat into its share of bandwidth. However, environmental factors can affect the reception of the wireless signals, which can reduce the bandwidth, even if no other stream is allowed to access the reserved bandwidth. Due to this, qWave continuously monitors the available bandwidth, and if it decreases, the application is informed, creating a feedback loop, so that it can adapt the stream to fit into the lower bandwidth range. If more bandwidth is available, qWave automatically reserves it and informs the application of the improvement.
For probing the quality of the network, probe packets are sent to the source and statistics (such as round trip time, loss, latency jitter etc.) of their path analyzed and the results are cached. The probe is repeated after specific time intervals to update the cache. Whenever the stream is requested, the cache is looked up. qWave also serializes creation of multiple simultaneous streams, even across devices, so that probes sent for one stream are not interfered by others. qWave uses client side buffers to keep transmission rate within range of the slowest part in the network, so that the access point buffers are not overwhelmed, thus reducing packet loss.
qWave works best if both the source and sink (client) of the multimedia stream are qWave aware. Also, the wireless access point
Wireless access point
In computer networking, a wireless access point is a device that allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi, Bluetooth or related standards...
(AP) needs to be QoS
Quality of service
The quality of service refers to several related aspects of telephony and computer networks that allow the transport of traffic with special requirements...
-enabled, supporting bandwidth reservation. It can also work without QoS-aware APs; however, since qWave cannot reserve bandwidth in this case, its has to depend on the application to adapt the stream based on the available bandwidth, which not only will be affected by network conditions, but other data in the network as well. qWave is also available for other devices as a part of the Windows Rally
Windows Rally
Windows Rally is a set of technologies from Microsoft intended to simplify the setup and maintenance of wired and wireless network-connected devices. They aim to increase reliability and security of connectivity for users who connect the devices to the Internet or to computers running Microsoft...
technologies.
Network security
In order to provide better security when transferring data over a network, Windows Vista provides enhancements to the cryptographic algorithms used to obfuscate data. Support for 256-bit, 384-bit and 512-bit Elliptic curve Diffie–Hellman (ECDH) algorithms, as well as for 128-bit, 192-bit and 256-bit Advanced Encryption StandardAdvanced Encryption Standard
Advanced Encryption Standard is a specification for the encryption of electronic data. It has been adopted by the U.S. government and is now used worldwide. It supersedes DES...
(AES) is included in the network stack itself. Direct support for SSL
Transport Layer Security
Transport Layer Security and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer , are cryptographic protocols that provide communication security over the Internet...
connections in new Winsock
Winsock
In computing, the Windows Sockets API , which was later shortened to Winsock, is a technical specification that defines how Windows network software should access network services, especially TCP/IP. It defines a standard interface between a Windows TCP/IP client application and the underlying...
API allows socket applications to directly control security of their traffic over a network (such as providing security policy and requirements for traffic, querying security settings) rather than having to add extra code to support a secure connection. Computers running Windows Vista can be a part of logically isolated networks within an Active Directory
Active Directory
Active Directory is a directory service created by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It is included in most Windows Server operating systems. Server computers on which Active Directory is running are called domain controllers....
domain. Only the computers which are in the same logical network partition will be able to access the resources in the domain. Even though other systems may be physically on the same network, unless they are in the same logical partition, they won't be able to access partitioned resources. A system may be part of multiple network partitions.
Windows Vista also includes an Extensible Authentication Protocol
Extensible Authentication Protocol
Extensible Authentication Protocol, or EAP, is an authentication framework frequently used in wireless networks and Point-to-Point connections. It is defined in RFC 3748, which made RFC 2284 obsolete, and was updated by RFC 5247....
Host (EAPHost) framework that provides extensibility for authentication methods for commonly used protected network access technologies such as 802.1X
IEEE 802.1X
IEEE 802.1X is an IEEE Standard for port-based Network Access Control . It is part of the IEEE 802.1 group of networking protocols. It provides an authentication mechanism to devices wishing to attach to a LAN or WLAN....
and PPP. It allows networking vendors to develop and easily install new authentication methods known as EAP methods.
A planned feature in the new TCP/IP suite known as "Routing Compartments", utilized a per-user routing table
Routing table
In computer networking a routing table, or Routing Information Base , is a data table stored in a router or a networked computer that lists the routes to particular network destinations, and in some cases, metrics associated with those routes. The routing table contains information about the...
, thus compartmentalizing the network according to the user's needs, so that data from one segment would not go into another. This feature however was removed before the release of Windows Vista, and is slated to be included possibly in a future release of Windows.
Network Access Protection
Windows Vista also introduces Network Access ProtectionNetwork Access Protection
Network Access Protection is a Microsoft technology for controlling network access of a computer host based on the system health of the host, first introduced in Windows Server 2008....
(NAP), which makes sure that computers connecting to a network conform to a required level of system health as has been set by the administrator of the network. With NAP enabled on a network, when a Windows Vista computer attempts to join a network, it is verified that the computer is up-to-date with security updates, virus signatures and other factors, including configuration of IPsec
IPsec
Internet Protocol Security is a protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session...
and 802.1x authentication settings, specified by the network administrator. It will be granted full access to the network only when the criteria is met, failing which it may be either denied access to the network or granted limited access only to certain resources. It may optionally be granted access to servers which will provide it with the latest updates. Once the updates are installed, the computer is granted access to the network. However, Windows Vista can only be a NAP client, i.e., a client computer which connects to a NAP enabled network. Health policy and verification servers have to be running Windows Server 2008.
IPsec and Windows Firewall
IPsec configuration is now fully integrated into the Windows Firewall with Advanced Security snap-in and netsh advfirewall command-line tool to prevent contradictory rules and offer simplified configuration along with an authenticating firewall. Advanced firewall filtering rules (exceptions) and IPsec policies can be set up such as by domain, public, and private profiles, source and destination IP addresses, IP address range, source and destination TCP and UDP ports, all or multiple ports, specific types of interfaces, ICMP and ICMPv6 traffic by Type and Code, services, edge traversal, IPsec protection state and specified users and computers based on Active DirectoryActive Directory
Active Directory is a directory service created by Microsoft for Windows domain networks. It is included in most Windows Server operating systems. Server computers on which Active Directory is running are called domain controllers....
accounts.
Prior to Windows Vista, setting up and maintaining IPsec policy configuration in many scenarios required setting up a set of rules for protection and another set of rules for traffic exemptions. IPsec nodes in Windows Vista communicate while simultaneously negotiating protected communications and if a response is received and negotiation completes, subsequent communications are protected. This eliminates the need to set up IPsec filters for exemptions for the set of hosts that do not or cannot support IPsec, allows setting up required incoming protected initiated communication and optional outgoing communication. IPsec also allows securing traffic between domain controllers and member computers, while still allowing clear text for domain joins and other communication types. IPsec protected domain joins are allowed if using NTLM
NTLM
In a Windows network, NTLM is a suite of Microsoft security protocols that provides authentication, integrity, and confidentiality to users....
v2 and if both, the domain controllers and member computers are running Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista respectively.
IPsec fully supports IPv6, AuthIP
AuthIP
AuthIP is a Microsoft proprietary extension of the IKE cryptographic protocol. AuthIP is supported in Windows Vista and later on the client and Windows Server 2008 and later on the server. AuthIP adds a second authentication to the standard IKE authentication which, according to Microsoft,...
(which allows for a second authentication), integration with NAP
Network Access Protection
Network Access Protection is a Microsoft technology for controlling network access of a computer host based on the system health of the host, first introduced in Windows Server 2008....
for authenticating with a health certificate, Network Diagnostics Framework support for failed IPsec negotiation, new IPsec performance counters, and improved detection of cluster node failure and faster renegotiation of security associations. There is support for stronger algorithms for main mode negotiation (stronger DH algorithms and Suite B) and data integrity and encryption (AES with CBC, AES-GMAC, SHA-256, AES-GCM).
Network Diagnostics Framework (NDF)
The ability to assist the user in diagnosing a network problem is expected to be a major new networking feature. There is extensive support for runtime diagnostics for both wired and wireless networks, including support for TCP Management information baseManagement information base
A management information base is a virtual database used for managing the entities in a communications network. Most often associated with the Simple Network Management Protocol , the term is also used more generically in contexts such as in OSI/ISO Network management model...
(MIB)-II and better system event logging and tracing. The Vista TCP/IP stack also supports ESTATS which defines extended performance statistics for TCP and can help in determining the cause of network performance bottlenecks. Windows Vista can inform the user of most causes of network transmission failure, such as incorrect IP address
IP address
An Internet Protocol address is a numerical label assigned to each device participating in a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. An IP address serves two principal functions: host or network interface identification and location addressing...
, incorrect DNS and default gateway settings, gateway failure, port in use or blocked, receiver not ready, DHCP service not running, NetBIOS over TCP/IP name resolution failure etc. Transmission errors are also exhaustively logged, which can be analyzed to better find the cause of error. Windows Vista has a greater awareness of the network topology the host computer is in, using technologies such as Universal Plug and Play
Universal Plug and Play
Universal Plug and Play is a set of networking protocols for primarily residential networks without enterprise class devices that permits networked devices, such as personal computers, printers, Internet gateways, Wi-Fi access points and mobile devices to seamlessly discover each other's presence...
. With this new network awareness technology, Windows Vista can provide help to the user in fixing network issues or simply provide a graphical view of the perceived network configuration.
Windows Filtering Platform
The Windows Vista network stack includes Windows Filtering PlatformWindows Filtering Platform
Windows Filtering Platform is a set of system services and an application programming interface introduced with Windows Vista that allows applications to tie into the packet processing and filtering pipeline of the new network stack. It provides features such as integrated communication and it can...
, which allows external applications to access and hook into the packet processing pipeline of the networking subsystem. WFP allows incoming and outgoing packets to be filtered, analyzed or modified at several layers of the TCP/IP protocol stack. Because WFP has an inbuilt filtering engine, applications need not write any custom engine, they just need to provide the custom logic for the engine to use. WFP includes a Base Filtering Engine which implements the filter requests. The packets are then processed using the Generic Filtering Engine, which also includes a Callout Module, where applications providing the custom processing logic can be hooked up. WFP can be put to uses such as inspecting packets for malware, selective packet restriction, such as in firewalls, or providing custom encryption systems, among others. Upon its initial release WFP was plagued with bugs including memory leaks and race conditions.
Peer-to-peer communication
Windows Vista includes support for peer-to-peerPeer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads among peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application...
communication and includes implementation of peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads among peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application...
protocols out-of-the-box. It also includes a new version of the Peer Name Resolution Protocol
Peer Name Resolution Protocol
Peer Name Resolution Protocol is a peer-to-peer protocol designed by Microsoft. PNRP enables dynamic name publication and resolution, and requires IPv6.PNRP was first mentioned during a presentation at a P2P conference in November 2001...
(PNRPv2), which is faster and more scalable. Windows Vista also includes a peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads among peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application...
API for name resolution and secure Group creation. Peer-to-peer networking functionality can be accessed from the Winsock
Winsock
In computing, the Windows Sockets API , which was later shortened to Winsock, is a technical specification that defines how Windows network software should access network services, especially TCP/IP. It defines a standard interface between a Windows TCP/IP client application and the underlying...
API as well. The peer-to-peer networking subsystem can also discover other people running the same service in the local subnet, using a feature dubbed People Near Me and integrate with Windows Contacts to store their information. This facility can be used to develop ad-hoc collaborative applications, such as Windows Meeting Space
Windows Meeting Space
Windows Meeting Space is the name of a peer-to-peer collaboration program in Windows Vista that supports 2–10 users. Meeting Space does not exist in any version of Windows 7...
. Peer-to-peer networking settings are configurable through netsh p2p and Group Policy
Group Policy
Group Policy is a feature of the Microsoft Windows NT family of operating systems. Group Policy is a set of rules that control the working environment of user accounts and computer accounts. Group Policy provides the centralized management and configuration of operating systems, applications, and...
.
A feature called Windows Internet Computer Names (WICN) based on PNRP allows any computer connected to an IPv6 network to get a unique domain name. If the computer is connected to the Internet, users can easily specify a secured or unsecured host name for their computer from a console command and their computer can be easily accessible from any remote computer, without requiring to register a domain name and configuring a dynamic DNS. Windows Internet Computer Names can be used in any application that accepts an IP address or DNS name. PNRP performs all the domain name resolution at the peer-to-peer level.
PNRP also allows creating an overlay network
Overlay network
An overlay network is a computer network which is built on the top of another network. Nodes in the overlay can be thought of as being connected by virtual or logical links, each of which corresponds to a path, perhaps through many physical links, in the underlying network...
called a Graph. Each peer in the overlay network corresponds to a node in the graph. Nodes are resolved to addresses using PNRP
Peer Name Resolution Protocol
Peer Name Resolution Protocol is a peer-to-peer protocol designed by Microsoft. PNRP enables dynamic name publication and resolution, and requires IPv6.PNRP was first mentioned during a presentation at a P2P conference in November 2001...
. All the nodes in a graph share book-keeping information responsible for the functioning of the network as a whole. For example, in a distributed resource management network, which node has what resource needs to be shared. Such information is shared as Records, which are flooded to all the peers in a graph. Each peer stores the Record to a local database. A Record consists of a header and a body. The body contains data specific to the application that is using the API; the header contains metadata to describe the data in the body as name-value pairs serialized using XML
XML
Extensible Markup Language is a set of rules for encoding documents in machine-readable form. It is defined in the XML 1.0 Specification produced by the W3C, and several other related specifications, all gratis open standards....
, in addition to author and version information. It can also contain an index of the body data, for fast searching. A node can connect to other nodes directly as well, for communication that need not be shared with the entire Graph. The API also allows creation of a secure overlay network
Overlay network
An overlay network is a computer network which is built on the top of another network. Nodes in the overlay can be thought of as being connected by virtual or logical links, each of which corresponds to a path, perhaps through many physical links, in the underlying network...
called a Group, consisting of all or a subset of nodes in a Graph. A Group can be shared by multiple applications, unlike a Graph. All peers in a Group must be identifiable by a unique named, registered using PNRP
Peer Name Resolution Protocol
Peer Name Resolution Protocol is a peer-to-peer protocol designed by Microsoft. PNRP enables dynamic name publication and resolution, and requires IPv6.PNRP was first mentioned during a presentation at a P2P conference in November 2001...
, and have a digital signature
Digital signature
A digital signature or digital signature scheme is a mathematical scheme for demonstrating the authenticity of a digital message or document. A valid digital signature gives a recipient reason to believe that the message was created by a known sender, and that it was not altered in transit...
certificate termed as Group Member Certificate (GMC). All Records exchanged are digitally signed. Peers must be invited into a Group. The invitation contains the GMC that enables it to join the group.
Another planned feature in Windows Vista would have taken advantage of peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads among peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the application...
technology to provide a new type of domain-like networking setup known as a Castle, but this did not make it into the release version. Castle would have made it possible to have an identification service, which provides user authentication, for all members on the network, without a centralized server. It would have allowed user credentials to propagate across the peer-to-peer network, making them more suitable for a home network. This feature eventually materialized in Windows 7 as HomeGroup.
Background Intelligent Transfer Service
The new Background Intelligent Transfer ServiceBackground Intelligent Transfer Service
Background Intelligent Transfer Service is a component of Microsoft Windows XP and later operating systems that facilitates prioritized, throttled, and asynchronous transfer of files between machines using idle network bandwidth...
(BITS) 3.0 has a new feature called Neighbor Casting which supports peer-to-peer file transfers within a domain
Windows Server domain
A Windows domain is a collection of security principals that share a central directory database. This central database contains the user accounts and security information for...
. This facilitates peer caching, allows users to download and serve content (such as WSUS
Windows Server Update Services
- External links :* * * – contains many detailed documents on WSUS operation, known issues, and troubleshooting* - German WSUS-Community * - Control installation of WSUS updates from command line...
updates) from peers on the same subnet, receive notification when a file is downloaded, access the temporary file while the download is in progress, and control HTTP redirects. This saves bandwidth on the network and reduces performance load on the server. BITS 3.0 also uses Internet Gateway Device Protocol counters to more accurately calculate available bandwidth.
Core networking driver and API improvements
The HTTP kernel mode driver in Windows Vista, Http.sys has been enhanced to support server-side authentication, logging, IDN hostnames, Event Tracing and better manageability through netsh http and new performance counters. WinINet, the protocol handler for HTTP and FTP handles IPv6 literal addresses, includes support for Gzip and deflate decompression to improve content encoding performance, Internationalized domain nameInternationalized domain name
An internationalized domain name is an Internet domain name that contains at least one label that is displayed in software applications, in whole or in part, in a language-specific script or alphabet, such as Arabic, Chinese, Russian, Hindi or the Latin alphabet-based characters with diacritics,...
s support and Event Tracing. WinHTTP, the client API for server-based applications and services
Windows Service
On Microsoft Windows operating systems, a Windows service is a long-running executable that performs specific functions and which is designed not to require user intervention. Windows services can be configured to start when the operating system is booted and run in the background as long as...
supports IPv6, AutoProxy
Web Proxy Autodiscovery Protocol
The Web Proxy Auto-Discovery Protocol is a method used by clients to locate a URL of a configuration file using DHCP and/or DNS discovery methods. Once detection and download of the configuration file is complete it can be executed to determine the proxy for a specified URL...
, HTTP/1.1 chunked transfer encoding
Chunked transfer encoding
Chunked transfer encoding is a data transfer mechanism in version 1.1 of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol in which a web server serves content in a series of chunks. It uses the Transfer-Encoding HTTP response header in place of the Content-Length header, which the protocol would otherwise require...
, larger data uploads, SSL and client certificates, server and proxy authentication, automatic handling of redirects and keep-alive connections and HTTP/1.0 protocol, including support for keep-alive (persistent) connections and session cookies. Winsock
Winsock
In computing, the Windows Sockets API , which was later shortened to Winsock, is a technical specification that defines how Windows network software should access network services, especially TCP/IP. It defines a standard interface between a Windows TCP/IP client application and the underlying...
has been updated with new APIs and support for Event Tracing. Winsock Layered Service Provider
Layered Service Provider
Layered Service Provider is a feature of the Microsoft Windows Winsock 2 Service Provider Interface . A Layered Service Provider is a DLL that uses Winsock APIs to insert itself into the TCP/IP protocol stack. Once in the stack, a Layered Service Provider can intercept and modify inbound and...
support has been enhanced with logged installations and removals, a new API for reliably installing LSPs, a command to reliably remove LSPs, facilities to categorize LSPs and to remove most LSPs from the processing path for system critical services and support for Network Diagnostics Framework.
Winsock Kernel
WinsockWinsock
In computing, the Windows Sockets API , which was later shortened to Winsock, is a technical specification that defines how Windows network software should access network services, especially TCP/IP. It defines a standard interface between a Windows TCP/IP client application and the underlying...
Kernel (WSK) is a new transport-independent kernel-mode Network Programming Interface (NPI) for that provides TDI client developers with a sockets-like programming model similar to those supported in user-mode Winsock
Winsock
In computing, the Windows Sockets API , which was later shortened to Winsock, is a technical specification that defines how Windows network software should access network services, especially TCP/IP. It defines a standard interface between a Windows TCP/IP client application and the underlying...
. While most of the same sockets
Internet socket
In computer networking, an Internet socket or network socket is an endpoint of a bidirectional inter-process communication flow across an Internet Protocol-based computer network, such as the Internet....
programming concepts exist as in user-mode Winsock such as socket, creation, bind, connect, accept, send and receive, Winsock Kernel is a completely new programming interface with unique characteristics such as asynchronous I/O
Asynchronous I/O
Asynchronous I/O, or non-blocking I/O, is a form of input/output processing that permits other processing to continue before the transmission has finished....
that uses IRPs and event callbacks to enhance performance. TDI is supported in Windows Vista for backward compatibility.
Server Message Block 2.0
A new version of the Server Message BlockServer Message Block
In computer networking, Server Message Block , also known as Common Internet File System operates as an application-layer network protocol mainly used to provide shared access to files, printers, serial ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. It also provides an...
(SMB) protocol has been introduced with Windows Vista. A significant improvement over SMB support in prior versions of Windows is the ability to compound multiple actions into a single request, which significantly reduces the number of round-trips
Round-trip delay time
In telecommunications, the round-trip delay time or round-trip time is the length of time it takes for a signal to be sent plus the length of time it takes for an acknowledgment of that signal to be received...
the client needs to make to the server, improving performance as a result. SMB1 also has a compounding mechanism (known as AndX) to compound multiple actions, but is rarely used by Microsoft clients. Larger buffer sizes are supported, also increasing performance with large file transfers. The notion of "durable file handles" is introduced, which allow a connection to an SMB server to survive brief network outages, such as with a wireless network, without having to construct a new session. Support for symbolic links is included as well. In SMB 1, various sizes in the protocol are 16 bits. Many have been changed to 32 or 64 bit, and in the case of file handles to 16 bytes.
SMB2 reduces the 'chattiness' of the protocol by reducing the number of commands and subcommands to 19 from over 100. It has mechanisms for pipelining, that is, sending additional requests before the response to a previous request arrives. Other improvements include caching of file properties, improved message signing with HMAC SHA-256 hashing algorithm and better scalability by increasing number of users, shares and open files per server among others.
Windows Vista and later operating systems use SMB 2.0 when communicating with other machines running Windows Vista or later. SMB 1.0 continues in use for connections to any previous version of Windows, or to Samba. Samba 3.6 also includes support for SMB 2.0.
SMB 2 has two big benefits to Microsoft. The first is clear intellectual property ownership. SMB 1 was originally designed by IBM and was shipped on a wide variety of non-Windows operating systems such as SCO Xenix, OS/2 and DEC VMS (Pathworks). It was partially standardised by X/Open
X/Open
X/Open Company, Ltd. was a consortium founded by several European UNIX systems manufacturers in 1984 to identify and promote open standards in the field of information technology. More specifically, the original aim was to define a single specification for operating systems derived from UNIX, to...
and also had draft standards for IETF which lapsed. (See http://ubiqx.org/cifs/Intro.html for historical detail).
The second benefit is a clean break. Microsoft's SMB1 code has to work with a huge variety of SMB clients and servers. A large number of items in the protocol are optional (such as short and long filenames), there are many infolevels for commands (selecting what structure is returned to a particular request), Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
was a later addition etc. With SMB2 there is significantly reduced compatibility testing (currently only other Windows Vista clients and servers). Additionally the code is a lot less complex since there is far less variability (e.g. there is no need to worry about having Unicode and non-Unicode code paths as SMB2 requires Unicode support).
Remote Differential Compression
Remote Differential Compression (RDC) is a client-server synchronization protocol allows data to be synchronized with a remote source using compression techniques to minimize the amount of data sent across the network. It synchronizes files by calculating and transferring only the differences between them on-the-fly. Therefore, RDC is suitable for efficient synchronization of files that have been updated independently, or when network bandwidth is small or in scenarios where the files are large but the differences between them are small.Bluetooth support
The Windows VistaWindows Vista
Windows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
Bluetooth
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a proprietary open wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances from fixed and mobile devices, creating personal area networks with high levels of security...
stack is improved with support for more hardware IDs, EDR performance improvements, Adaptive frequency hopping for Wi-Fi co-existence, and Synchronous Connection Oriented (SCO) protocol support which is needed for audio profiles. The Windows Vista Bluetooth stack supports a kernel mode device driver interface
Device driver
In computing, a device driver or software driver is a computer program allowing higher-level computer programs to interact with a hardware device....
besides the user-mode programming interface, which enables third-parties to add support for additional Bluetooth Profiles such as SCO, SDP, and L2CAP. This was lacking in the Windows XP Service Pack 2 built-in Bluetooth stack, which had to be entirely replaced by a third-party stack for additional profile support. It also provides RFCOMM support using sockets besides virtual COM ports. KB942567 called Windows Vista Feature Pack for Wireless adds Bluetooth 2.1+EDR support and remote wake from S3 or S4 support for self-powered Bluetooth modules. This feature pack while initially only available to OEMs, was eventually included in Windows Vista Service Pack 2.

