
Wire bonding
Encyclopedia

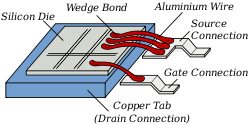
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
(IC) and a printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
(PCB) during semiconductor device fabrication. Although less common, wire bonding can be used to connect an IC to other electronics or to connect from one PCB to another. Wire bonding is generally considered the most cost-effective and flexible interconnect technology, and is used to assemble the vast majority of semiconductor packages.
Bondwires usually consist of one of the following materials:
- Aluminum
- CopperCopperCopper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
- GoldGoldGold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
Wire diameters start at 15 µm and can be up to several hundred micrometres for high-powered applications.
Copper wire has become one of the preferred materials for wire bonding interconnects in many semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
and microelectronic applications. Copper
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish...
is used for fine wire ball bonding in sizes up to 0.003 inch (75 micrometres). Copper wire has the ability of being used at smaller diameters providing the same performance as gold without the high material cost.
Copper wire up to 0.010 inch (250 micrometres) can be successfully wedge bonded with the proper set-up parameters. Large diameter copper wire can and does replace aluminum wire where high current carrying capacity is needed or where there are problems with complex geometry. Annealing and process steps used by manufacturers enhance the ability to use large diameter copper wire to wedge bond to silicon without damage occurring to the die.
Copper wire does pose some challenges in that it is harder than both gold and aluminum, so bonding parameters must be kept under tight control. The formation of oxides is inherent with this material, so storage and shelf life are issues that must be considered. Special packaging is required in order to protect copper wire and achieve a longer shelf life.
Pure gold wire doped with controlled amounts of beryllium
Beryllium
Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl...
and other elements is normally used for ball bonding
Ball bonding
Ball bonding is a type of wire bonding, and is the most common way to make the electrical interconnections between a chip and the outside world as part of semiconductor device fabrication....
. This process brings together the two materials that are to be bonded using heat, pressure and ultrasonic energy referred to as thermosonic bonding. The most common approach in thermosonic bonding
Thermosonic Bonding
Thermosonic bonding is widely used to permanently interconnect metallized silicon integrated circuits and other components into computers as well as into a myriad of other electronic equipment....
is to ball-bond to the chip, then stitch-bond to the substrate
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
. Very tight controls during processing enhance looping characteristics and eliminate sagging.
Junction size, bond strength and conductivity requirements typically determine the most suitable wire size for a specific wire bonding application. Typical manufacturers make gold wire in diameters from 0.0005 inch (12.5 micrometres) and larger. Production tolerance on gold wire diameter is +/-3%.
Alloyed aluminum wires are generally preferred to pure aluminum wire except in high-current devices because of greater drawing ease to fine sizes and higher pull-test strengths in finished devices. Pure aluminum and 0.5% magnesium-aluminum are most commonly used in sizes larger than 0.004 inch.
All aluminum systems in semiconductor fabrication
Semiconductor fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to create the integrated circuits that are present in everyday electrical and electronic devices. It is a multiple-step sequence of photolithographic and chemical processing steps during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer...
eliminate the "purple plague" (brittle gold-aluminum intermetallic compound) sometimes associated with pure gold bonding wire. Aluminum is particularly suitable for ultrasonic bonding.
In order to assure that high quality bonds can be obtained at high production speeds, special controls are used in the manufacture of 1% silicon-aluminum wire. One of the most important characteristics of high grade bonding wire of this type is homogeneity
Homogeneous (chemistry)
A substance that is uniform in composition is a definition of homogeneous. This is in contrast to a substance that is heterogeneous.The definition of homogeneous strongly depends on the context used. In Chemistry, a homogeneous suspension of material means that when dividing the volume in half, the...
of the alloy system. Homogeneity is given special attention during the manufacturing process. Microscopic checks of the alloy structure of finished lots of 1% silicon-aluminum wire are performed routinely. Processing also is carried out under conditions which yield the ultimate in surface cleanliness and smooth finish and permits entirely snag-free de-reeling.
There are two main classes of wire bonding:
- Ball bondingBall bondingBall bonding is a type of wire bonding, and is the most common way to make the electrical interconnections between a chip and the outside world as part of semiconductor device fabrication....
- Wedge bonding
Ball bonding usually is restricted to gold and copper wire and usually requires heat. Wedge bonding can use either gold or aluminum wire, with only the gold wire requiring heat.
In either type of wire bonding, the wire is attached at both ends using some combination of heat, pressure, and ultrasonic energy to make a weld
Welding
Welding is a fabrication or sculptural process that joins materials, usually metals or thermoplastics, by causing coalescence. This is often done by melting the workpieces and adding a filler material to form a pool of molten material that cools to become a strong joint, with pressure sometimes...
.
See also
- Purple plague (intermetallic)
- Ball bondingBall bondingBall bonding is a type of wire bonding, and is the most common way to make the electrical interconnections between a chip and the outside world as part of semiconductor device fabrication....
- Chip bonding
- Silver epoxy
- Eutectic bondingEutectic bondingEutectic bonding, also referred to as eutectic soldering, describes a wafer bonding technique with an intermediate metal layer. Those eutectic metals are alloys that transform directly from solid to liquid state at a specific composition and temperature without passing a two phase equilibrium, i.e...
- Thermosonic BondingThermosonic BondingThermosonic bonding is widely used to permanently interconnect metallized silicon integrated circuits and other components into computers as well as into a myriad of other electronic equipment....
- Gold ribbon bonding
- Parallel gap welding
- Tape-automated bondingTape-Automated BondingTape-automated bonding is a process that places bare integrated circuits onto a printed circuit board by attaching them to a polyamide or polyimide film....
(TAB)

