
Witsenhausen's counterexample
Encyclopedia
A deceptively simple problem
Witsenhausen's counterexampleCounterexample
In logic, and especially in its applications to mathematics and philosophy, a counterexample is an exception to a proposed general rule. For example, consider the proposition "all students are lazy"....
, shown in the figure above, is a deceptively simple toy problem
Toy problem
In scientific disciplines, a toy problem is a problem that is not of immediate scientific interest, yet is used as an expository device to illustrate a trait that may be shared by other, more complicated, instances of the problem, or as a way to explain a particular, more general, problem solving...
in decentralized stochastic control
Stochastic control
Stochastic control is a subfield of control theory which deals with the existence of uncertainty in the data. The designer assumes, in a Bayesian probability-driven fashion, that a random noise with known probability distribution affects the state evolution and the observation of the controllers...
. It was formulated by Hans Witsenhausen
Hans Witsenhausen
Hans S. Witsenhausen is notable for his work in the fields of control and information theory, and their intersection. He has many foundational results including the intrinsic model in stochastic decentralized control, the Witsenhausen counterexample, his work on Turán graph, and the various...
in 1968, and remains unsolved. The importance of the problem was recently reflected upon in the 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control (CDC) 2008, Cancun, Mexico, where an entire session was dedicated to understanding the counterexample 40 years after it was first formulated.
The statement of the counterexample is simple: two controllers attempt to control the system by attempting to bring the state close to zero in exactly two time steps. There is a cost on the input
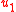 of the first controller, and the state
of the first controller, and the state 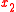 after the input of the second controller. The input
after the input of the second controller. The input 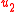 of the second controller is free, but its observations
of the second controller is free, but its observations 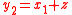 are noisy. The objective is to minimize an average cost function,
are noisy. The objective is to minimize an average cost function, 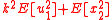 , where the average is over the randomness in the initial state
, where the average is over the randomness in the initial state 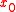 and the observation noise
and the observation noise  , both of which are distributed independently and in a Gaussian manner.
, both of which are distributed independently and in a Gaussian manner.The significance of the problem
The counterexample lies at the intersection of control theoryControl theory
Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
and information theory
Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
. Due to its hardness, the problem has also received attention from the theoretical computer science
Theoretical computer science
Theoretical computer science is a division or subset of general computer science and mathematics which focuses on more abstract or mathematical aspects of computing....
community.
The problem is of conceptual significance in decentralized control because it shows that it is important for the controllers to communicate with each other implicitly in order to minimize the cost. This suggests that control actions in decentralized control may have a dual role: those of control and communication.
What conjecture is the problem a counterexample to?
The problem is a counterexample to the natural conjecture from centralized linear-quadratic-Gaussian controlLinear-quadratic-Gaussian control
In control theory, the linear-quadratic-Gaussian control problem is one of the most fundamental optimal control problems. It concerns uncertain linear systems disturbed by additive white Gaussian noise, having incomplete state information and undergoing control subject to quadratic costs...
systems: that affine control laws are optimal. Witsenhausen showed that there exists a nonlinear control law that outperforms all linear laws.
The hardness of the problem
The hardness of the problem is attributed to the fact that information of the second controller depends on the decisions of the first controller. Variations considered by Tamer BasarTamer Basar
Tamer Başar is a Turkish control theorist who holds the Swanlund Endowed Chair at the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, USA....
show that the hardness is also because of the structure of the performance index and the coupling of different decision variables. It has also been shown that problems of the spirit of Witsenhausen's counterexample become simpler if the transmission delay
Transmission delay
In a network based on packet switching, transmission delay is the amount of time required to push all of the packet's bits into the wire. In other words, this is the delay caused by the data-rate of the link....
along an external channel that connects the controllers is smaller than the propagation delay
Propagation delay
Propagation delay is a technical term that can have a different meaning depending on the context. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics...
in the problem. However, this result requires the channels to be perfect and instantaneous, and hence is of limited applicability. In practical situations, the channel is always imperfect, and thus one can not assume that decentralized control problems are simple in presence of external channels.
A justification of the failure of attempts that discretize the problem came from the computer science literature: Christos Papadimitriou
Christos Papadimitriou
Christos Harilaos Papadimitriou is a Professor in the Computer Science Division at the University of California, Berkeley, United States...
and John Tsitsiklis showed that the discrete version of the counterexample is NP-complete
NP-complete
In computational complexity theory, the complexity class NP-complete is a class of decision problems. A decision problem L is NP-complete if it is in the set of NP problems so that any given solution to the decision problem can be verified in polynomial time, and also in the set of NP-hard...
.
Attempts on obtaining a solution
A number of numerical attempts have been made to solve the counterexample. Focusing on a particular choice of problem parameters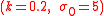 , researchers have obtained strategies by discretization
, researchers have obtained strategies by discretizationDiscretization
In mathematics, discretization concerns the process of transferring continuous models and equations into discrete counterparts. This process is usually carried out as a first step toward making them suitable for numerical evaluation and implementation on digital computers...
and using neural networks
Neural Networks
Neural Networks is the official journal of the three oldest societies dedicated to research in neural networks: International Neural Network Society, European Neural Network Society and Japanese Neural Network Society, published by Elsevier...
. Further research (notably, the work of Yu-Chi Ho
Yu-Chi Ho
This article is about the Chinese-American mathematician.Yu-Chi "Larry" Ho is a renowned Chinese-American mathematician, control theorist, and a professor at the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University.He is the co-author of Applied Optimal Control, and an influential...
, and the work of Li, Marden and Shamma
Jeff S. Shamma
Jeff S. Shamma is an American control theorist and the Professor and Julian T. Hightower Chair in Systems & Control Systems and Controls at the Georgia Institute of Technology...
) has obtained slightly improved costs for the same parameter choice. The first provably approximately optimal strategies appeared recently (Grover, Park, Sahai) where information theory
Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
is used to understand the communication in the counterexample. In the absence of an optimal solution, the problem still remains a puzzle.

