
Yellowstone Lake
Encyclopedia
Yellowstone Lake is the largest body of water in Yellowstone National Park
, The lake is 7,732 feet (2,376 m) above sea level and covers 136 square miles (352.2 km²) with 110 miles (177 km) of shoreline. While the average depth of the lake is 139 feet (42 m) its deepest spot is at least 390 feet (118 m). Yellowstone Lake is the largest freshwater lake above 7,000 feet (2,133 m) in North America
.
In winter, ice nearly 3 feet (1 m) thick covers much of the lake, except where shallow water covers hot springs. The lake freezes over by early December and can remain frozen until late May or early June.
in the early 19th century. During the fur trading era of 1820 - 1840, the lake was probably visited by many trapping parties moving through the park region. In trapper Osborne Russell
's diary he describes a visit to the lake in 1836:
and explorer William Clark referred to the lake as Yellow Stone. Osborne Russell referred to the lake as Yellow Stone Lake in his 1834 journal. On some William Clark maps, the lake has the name Eustis Lake and the name Sublette
's Lake was also used to name the lake in the early 19th century. The name Yellowstone Lake appears formally first in the 1839 maps of the Oregon Territory
by U.S. Army topographical engineer, Captain Washington Hood and has remained so since that time.
and the Hayden Geological Survey of 1871
.
Cook, Folsom and Peterson first encountered the lake near Pelican Creek 44°33′12"N 110°21′37"W as they moved south along the Yellowstone River on September 24, 1869. They eventually followed the western shoreline to West Thumb before moving west to the geyser basins. Cook described the lake at Pelican Creek thus:
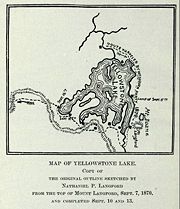 The Washburn party was the first to describe the remote eastern and southern shorelines of the lake. From September 3 to September 17, 1870 the Washburn party traveled from the outlet of the lake around the northern, eastern and southern shorelines to West Thumb 44°25′40"N 110°31′57"W. The September 4, 1870 journal entry of Lieutenant Gustavus C. Doane
The Washburn party was the first to describe the remote eastern and southern shorelines of the lake. From September 3 to September 17, 1870 the Washburn party traveled from the outlet of the lake around the northern, eastern and southern shorelines to West Thumb 44°25′40"N 110°31′57"W. The September 4, 1870 journal entry of Lieutenant Gustavus C. Doane
, the leader of the U.S. Army escort during the expedition, describes the lake:
 The Hayden Geological Survey of 1871 provided the most detailed and scientific descriptions of the lake in the pre-park era. The Hayden party, 34 men in all, encountered the lake at the outlet on July 28, 1871 spending two days there and returned to the lake at West Thumb on August 7, 1871. From West Thumb the survey party took 15 days to explore the southern and eastern flanks of the lake. On July 28, 1871, they launched Annie, the first boat ever to sail on the lake and began exploring the islands and shoreline. Additionally, the first ever photographs of the lake were taken during this expedition by William Henry Jackson
The Hayden Geological Survey of 1871 provided the most detailed and scientific descriptions of the lake in the pre-park era. The Hayden party, 34 men in all, encountered the lake at the outlet on July 28, 1871 spending two days there and returned to the lake at West Thumb on August 7, 1871. From West Thumb the survey party took 15 days to explore the southern and eastern flanks of the lake. On July 28, 1871, they launched Annie, the first boat ever to sail on the lake and began exploring the islands and shoreline. Additionally, the first ever photographs of the lake were taken during this expedition by William Henry Jackson
.
In correspondence that was Hayden's Report No. 7 to Assistant Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution
, Dr. Spencer Baird
, a bit of which is excerpted below, Dr. Ferdinand V. Hayden
described some of the explorations being conducted on the lake:
 In the southwest area of the lake the West Thumb geothermal area is easily accessible to visitors. Geyser
In the southwest area of the lake the West Thumb geothermal area is easily accessible to visitors. Geyser
s, fumarole
s and hot spring
s are found alongside and even in the lake. See Geothermal areas of Yellowstone
.
In recent years (as of 2004), the ground under the lake has started to rise significantly, indicating increased geological activity, and limited areas of the national park have been closed to the public. As of 2005, no areas are currently off limits aside from those normally allowing limited access such as around the West Thumb Geyser Basin. There is a 'bulge' about 2,000 feet (600 m) long and 100 feet (30 m) high under a section of Yellowstone Lake, where there are a variety of faults, hot springs and small craters. Seismic imaging has recently shown that sediment layers are tilted, but how old this feature is has not yet been established.
After the magma chamber
under the Yellowstone area collapsed 600,000 years ago in its previous great eruption, it formed a large caldera
that was later partially filled by subsequent lava
flows (see Yellowstone Caldera
). Part of this caldera is the 136 square miles (352.2 km²) basin of Yellowstone Lake. The original lake was 200 feet (60 m) higher than the present-day lake, extending northward across Hayden Valley
to the base of Mount Washburn
.
It is thought that Yellowstone Lake originally drained south into the Pacific Ocean
via the Snake River
. The lake currently drains north from its only outlet, the Yellowstone River
, at Fishing Bridge. The elevation of the lake's north end does not drop substantially until LeHardy Rapids. Therefore, this spot is considered the actual northern boundary of Yellowstone Lake. Within a short distance downstream the Yellowstone River plunges first over the upper and then the lower falls
and races north through the Grand Canyon of the Yellowstone
.
In the 1990s, geological research has determined that the two volcanic vents, now known as "resurgent dome
s", are rising again. From year to year, they either rise or fall, with an average net uplift of about one inch per year. During the period between 1923 and 1985, the Sour Creek Dome was rising. In the years since 1986, it has either declined or remained the same. The resurgence of the Sour Creek dome, just north of Fishing Bridge is causing Yellowstone Lake to "tilt" southward. Larger sandy beaches can now be found on the north shore of the lake, and flooded areas can be found in the southern arms.
The Hayden Valley
was once filled by an arm of Yellowstone Lake. As a result, it contains fine-grained lake sediments that are now covered with glacial till left from the most recent glacial
retreat 13,000 years ago. Because the glacial till contains many different grain sizes, including clay and a thin layer of lake sediments, water cannot percolate readily into the ground. This is why the Hayden Valley is marsh
y and has little encroachment of tree
s.
 Angling
Angling
for Yellowstone cutthroat trout
in Yellowstone Lake has been a popular pastime for both subsistence and recreation since the first explorers, surveyors and tourists visited the park. During the early days of fish stocking in Yellowstone (1890–1910), Atlantic Salmon
, Mountain whitefish
and Rainbow trout
were stocked in the lake. None of these introduced species survived. Today only native cutthroat and non-native Lake trout
exist in the lake. Today, Yellowstone Lake is open for angling from June 15 to the first Sunday in November. All Cutthroat trout caught must be released. In 1994, non-native Lake trout were discovered in Yellowstone Lake and were believed to have been either accidentally or intentionally introduced as early as 1989 with fish taken from Lewis Lake
. The introduction of Lake trout has caused a serious decline in the Cutthroat trout population and the National Park Service has an aggressive Lake trout eradication program on the lake. All Lake trout caught by anglers must be killed.
Recreational boating has been permitted on the lake in various forms since 1890 when the first permits for the Yellowstone Boat Company were issued to operate a ferry across the lake between road junctions. Today, powerboats, sailboats, canoes and kayaks are allowed on the lake with a Yellowstone Boating Permit. Marinas are operated at Bridge Bay and West Thumb. Areas in the southern arms of the lake are speed-restricted and/or no-motor zones to protect sensitive wildlife areas. Access to some of the lake's islands is also restricted. Xanterra Parks and Resorts
at Bridge Bay Marina on Yellowstone Lake provides boat rentals and other boating services. Numerous outfitters operating outside the park are licensed to provide boating services in the park. Several dozen backcountry campsites line the southern shoreline that are accessible only by boat. Two major hiking trails provide access to the lake shore away from the major road. The Nine Mile Post trail hugs the eastern shoreline into the Thorofare region and intersects with the Trail Creek and Heart Lake trails that touch the ends of both the south and southeast arms of the lake.
Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park, established by the U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Ulysses S. Grant on March 1, 1872, is a national park located primarily in the U.S. state of Wyoming, although it also extends into Montana and Idaho...
, The lake is 7,732 feet (2,376 m) above sea level and covers 136 square miles (352.2 km²) with 110 miles (177 km) of shoreline. While the average depth of the lake is 139 feet (42 m) its deepest spot is at least 390 feet (118 m). Yellowstone Lake is the largest freshwater lake above 7,000 feet (2,133 m) in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
.
In winter, ice nearly 3 feet (1 m) thick covers much of the lake, except where shallow water covers hot springs. The lake freezes over by early December and can remain frozen until late May or early June.
History
The forest and valleys surrounding Yellowstone Lake had been populated with Native Americans since pre-historic times. The first human of European descent to see the lake was trapper John ColterJohn Colter
John Colter was a member of the Lewis and Clark Expedition . Though party to one of the more famous expeditions in history, Colter is best remembered for explorations he made during the winter of 1807–1808, when Colter became the first known person of European descent to enter the region now known...
in the early 19th century. During the fur trading era of 1820 - 1840, the lake was probably visited by many trapping parties moving through the park region. In trapper Osborne Russell
Osborne Russell
Osborne Russell was a mountain man and politician who helped form the government of the U.S. state of Oregon. He was born in Maine....
's diary he describes a visit to the lake in 1836:
Interesting Description of What Is Known as Yellowstone National Park: 16th [August] -Mr. Bridger came up with the remainder of the party. 18th-The whole camp moved down the east shore of the lake through thick pines and fallen timber about eighteen miles and encamped in a small prairie. 19th-continued down the shore to the outlet about twenty miles, and encamped in a beautiful plain { Hayden ValleyHayden ValleyHayden Valley is a large, sub-alpine valley in Yellowstone National Park straddling the Yellowstone River between Yellowstone Falls and Yellowstone Lake. The valley floor along the river is an ancient lake bed from a time when Yellowstone Lake was much larger...
} which extended along the northern extremity of the lake. This valley was interspersed with scattering groves of tall pines, forming
shady retreats for the numerous elk and deer during the heat of the day. The lake is about 100 miles in circumference, bordered on the east by high ranges of mountains whose spurs terminate at the shore and on the west by a low bed of piney mountains. Its greatest width is about fifteen miles, lying in an oblong form south to north, or rather in the shape of a crescent. Near where we encamped were several hot springs which boiled perpetually. Near these was an
opening in the ground about eight inches in diameter from which hot steam issued continually with a noise similar to that made by the steam issuing from the safety valve of an engine, and could be heard five or six miles distant.
Name
The lake has been known by various names as depicted on early maps and in journals. Both fur trader David ThompsonDavid Thompson (explorer)
David Thompson was an English-Canadian fur trader, surveyor, and map-maker, known to some native peoples as "Koo-Koo-Sint" or "the Stargazer"...
and explorer William Clark referred to the lake as Yellow Stone. Osborne Russell referred to the lake as Yellow Stone Lake in his 1834 journal. On some William Clark maps, the lake has the name Eustis Lake and the name Sublette
William Sublette
William Lewis Sublette Born near Stamford, Lincoln County, Kentucky on September 21, 1798. Died on July 23, 1845 in Pittsburg. W.L. Sublette was a fur trapper, pioneer and mountain man, who with his brothers after 1823 became an agent of the Rocky Mountain Fur Company exploiting the riches of the...
's Lake was also used to name the lake in the early 19th century. The name Yellowstone Lake appears formally first in the 1839 maps of the Oregon Territory
Oregon Territory
The Territory of Oregon was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from August 14, 1848, until February 14, 1859, when the southwestern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Oregon. Originally claimed by several countries , the region was...
by U.S. Army topographical engineer, Captain Washington Hood and has remained so since that time.
Pre-park era exploration
Although many prospecting parties traversed the Yellowstone region throughout the 1850-60s, the first detailed descriptions of the lake came in 1869, 1870 and 1871 as a result of the Cook–Folsom–Peterson Expedition, the Washburn-Langford-Doane ExpeditionWashburn-Langford-Doane Expedition
The Washburn Expedition of 1870, explored the region of northwestern Wyoming that a couple years later became Yellowstone National Park. Led by Henry Washburn, Nathaniel P. Langford and under U.S. Army escort led by Lt. Gustavus C...
and the Hayden Geological Survey of 1871
Hayden Geological Survey of 1871
The Hayden Geological Survey of 1871 explored the region of northwestern Wyoming that later became Yellowstone National Park in 1872. It was led by geologist Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden...
.
Cook, Folsom and Peterson first encountered the lake near Pelican Creek 44°33′12"N 110°21′37"W as they moved south along the Yellowstone River on September 24, 1869. They eventually followed the western shoreline to West Thumb before moving west to the geyser basins. Cook described the lake at Pelican Creek thus:
The main body is ten miles long from east to west and sixteen miles long from north to south, but at the south end it puts out two arms, one to the southeast and the other to the southwest, making the entire length about 30 miles. ...There are three small islands which are also heavily timbered. ...The shallow water in some of the coves affords feeding ground for thousands of water fowl and we can take our choice of ducks, geese, trout, pelican or swan.

Gustavus Cheyney Doane
Gustavus Cheyney Doane was a U.S. Army Cavalry Captain, explorer, inventor and Civil War soldier who played a prominent role in the exploration of Yellowstone as a member of the Washburn-Langford-Doane Expedition.-Early life:...
, the leader of the U.S. Army escort during the expedition, describes the lake:
On the south side these promontories project far into the lake in great numbers, dividing it into bays and channels. On the west side is a low bluff of the timbered ridges, with a sand beach in front along the margins of the waters. The greatest width of open water in any direction is about eighteen miles. Several islands are seen, one of which is opposite the channel of the river and five miles from the east shore; another is ten miles farther south, and two miles from the shore a mountain isle with a bold bluff all around to the water's edge. These islands doubtless have never been trodden by human footsteps, and still belong to the regions of the unexplored. We built a raft for the purpose of attempting to visit them, but the strong waves of the lake dashed it to pieces in an hour. Numerous steam jets pour out from the bluffs on the shore at different points. The waters of the lake reflect a deep blue color, are clear as crystal, and doubtless of great depth near the center. The extreme elevation of this great body of water, 7,714 3/5 feet, is difficult to realize. Place Mount Washington, the pride of New England, with its base at the sea level, at the bottom of the lake, and the clear waters of the latter would roll 2,214 feet above its summit. With the single exception of Lake Titticaeca, Peru, it is the highest great body of water on the globe. No shells of any description are found on the lake shore, nor is there any evidence of the waters ever having stood at a much higher level than the present. Twenty-five feet will cover the whole range of the water-marks. Its annual rise and fall is about two feet. Its waters abound with trout to such an extent that the fish at this season are in poor condition, for want of food. No other fish are seen; no minnows, and no small trout. There are also no clams, crabs, nor turtles -- nothing but full-grown trout. These could be caught in mule loads by wading out a few feet in the open waters at any point with a grasshopper bait. Two men could catch them faster than half a dozen could clean and get them ready for the frying pan. Caught in the open lake, their flesh was yellow; but in bays, where the water was strongly impregnated with chemicals, it was blood-red. Many of them were full of long white worms, woven across the interior of the body, and through to the skin on either side. These did not appear to materially affect the condition of the fish, which were apparently as active as the others.

William Henry Jackson
William Henry Jackson was an American painter, Civil War, geological survey photographer and an explorer famous for his images of the American West...
.
In correspondence that was Hayden's Report No. 7 to Assistant Secretary of the Smithsonian Institution
Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution is an educational and research institute and associated museum complex, administered and funded by the government of the United States and by funds from its endowment, contributions, and profits from its retail operations, concessions, licensing activities, and magazines...
, Dr. Spencer Baird
Spencer Fullerton Baird
Spencer Fullerton Baird was an American ornithologist, ichthyologist and herpetologist. Starting in 1850 he was assistant-secretary and later secretary of the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, D.C...
, a bit of which is excerpted below, Dr. Ferdinand V. Hayden
Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden
Dr. Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden was an American geologist noted for his pioneering surveying expeditions of the Rocky Mountains in the late 19th century. He was also a physician who served with the Union Army during the Civil War.-Early life:Ferdinand Hayden was born in Westfield, Massachusetts...
described some of the explorations being conducted on the lake:
Yellowstone Lake, WY August 8th, 1871 - Dear Professor Baird, Your letters of June 6th and July 3rd were brought us from Fort Ellis by Lt. Doane who has just arrived to take command of our escort and accompany my party the remainder of the season. ...We arrived at the banks of the Yellow Stone Lake [sic] July 26th [actually July 28] and pitched our camp near the point where the river leaves the Lake. Hence we brought the first pair of wheels that ever came to the Lake with our Odometer. We launched the first Boat on the Lake, 4.5 feet wide and 11 feet long, with sails and oars. ...A chart of this soundings will be made. Points have been located with a prismatic compass all around the Lake. A man stands on the shore with a compass and takes a bearing to the man in the Boat as he drops the lead, giving a signal at the time. Then a man in the Boat takes a bearing to the fixed point on the shore where the first man is located and thus the soundings will be located on the chart. Henry Elliot and Mr. Carrington have just left in our little boat, the Annie. [They] will make a systematic sketch of the shore with all its indentations, with the banks down, indeed, making a complete topographical as well as pictorial sketch of the shores as seen from the water, for a circuit--of at least 130 miles. ...One of the islands has been explored. We have called it Stevenson's Island as he was undoubtedly the first human that ever set foot upon it. ...Write at once. Yours Truly, F. V. Hayden, I will send you some Photographs soon.
Proposals to dam the lake
Between 1920 and 1937, multiple proposals were made to Congress and the Department of the Interior to construct dams of various sizes at the Yellowstone Lake outlet or a few miles downstream. Montana and Wyoming politicians, the Army Corps of Engineers and lobbying groups in both states all had a variety of reasons to support the dams—flood control in the Yellowstone Valley, reclamation, or diversion of water over the continental divide to the Snake river. All the proposals and legislation were eventually defeated.Geology

Geyser
A geyser is a spring characterized by intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by a vapour phase . The word geyser comes from Geysir, the name of an erupting spring at Haukadalur, Iceland; that name, in turn, comes from the Icelandic verb geysa, "to gush", the verb...
s, fumarole
Fumarole
A fumarole is an opening in a planet's crust, often in the neighborhood of volcanoes, which emits steam and gases such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, hydrochloric acid, and hydrogen sulfide. The steam is created when superheated water turns to steam as its pressure drops when it emerges from...
s and hot spring
Hot spring
A hot spring is a spring that is produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater from the Earth's crust. There are geothermal hot springs in many locations all over the crust of the earth.-Definitions:...
s are found alongside and even in the lake. See Geothermal areas of Yellowstone
Geothermal areas of Yellowstone
The geothermal areas of Yellowstone include several geyser basins in Yellowstone National Park as well as other geothermal features such as hot springs, mud pots, and fumaroles...
.
In recent years (as of 2004), the ground under the lake has started to rise significantly, indicating increased geological activity, and limited areas of the national park have been closed to the public. As of 2005, no areas are currently off limits aside from those normally allowing limited access such as around the West Thumb Geyser Basin. There is a 'bulge' about 2,000 feet (600 m) long and 100 feet (30 m) high under a section of Yellowstone Lake, where there are a variety of faults, hot springs and small craters. Seismic imaging has recently shown that sediment layers are tilted, but how old this feature is has not yet been established.
After the magma chamber
Magma chamber
A magma chamber is a large underground pool of molten rock found beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock in such a chamber is under great pressure, and given enough time, that pressure can gradually fracture the rock around it creating outlets for the magma...
under the Yellowstone area collapsed 600,000 years ago in its previous great eruption, it formed a large caldera
Caldera
A caldera is a cauldron-like volcanic feature usually formed by the collapse of land following a volcanic eruption, such as the one at Yellowstone National Park in the US. They are sometimes confused with volcanic craters...
that was later partially filled by subsequent lava
Lava
Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at...
flows (see Yellowstone Caldera
Yellowstone Caldera
The Yellowstone Caldera is the volcanic caldera located in Yellowstone National Park in the United States, sometimes referred to as the Yellowstone Supervolcano. The caldera is located in the northwest corner of Wyoming, in which the vast majority of the park is contained. The major features of...
). Part of this caldera is the 136 square miles (352.2 km²) basin of Yellowstone Lake. The original lake was 200 feet (60 m) higher than the present-day lake, extending northward across Hayden Valley
Hayden Valley
Hayden Valley is a large, sub-alpine valley in Yellowstone National Park straddling the Yellowstone River between Yellowstone Falls and Yellowstone Lake. The valley floor along the river is an ancient lake bed from a time when Yellowstone Lake was much larger...
to the base of Mount Washburn
Mount Washburn
Mount Washburn el. is a prominent mountain peak in the Washburn Range in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. The peak was named in 1870 to honor Henry D. Washburn, leader of the Washburn–Langford–Doane Expedition...
.
It is thought that Yellowstone Lake originally drained south into the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
via the Snake River
Snake River
The Snake is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean...
. The lake currently drains north from its only outlet, the Yellowstone River
Yellowstone River
The Yellowstone River is a tributary of the Missouri River, approximately long, in the western United States. Considered the principal tributary of the upper Missouri, the river and its tributaries drain a wide area stretching from the Rocky Mountains in the vicinity of the Yellowstone National...
, at Fishing Bridge. The elevation of the lake's north end does not drop substantially until LeHardy Rapids. Therefore, this spot is considered the actual northern boundary of Yellowstone Lake. Within a short distance downstream the Yellowstone River plunges first over the upper and then the lower falls
Yellowstone Falls
Yellowstone Falls consist of two major waterfalls on the Yellowstone River, within Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming, United States. As the Yellowstone river flows north from Yellowstone Lake, it leaves the Hayden Valley and plunges first over Upper Yellowstone Falls and then a quarter mile ...
and races north through the Grand Canyon of the Yellowstone
Grand Canyon of the Yellowstone
The Grand Canyon of the Yellowstone is the first large canyon on the Yellowstone River downstream from Yellowstone Falls in Yellowstone National Park...
.
In the 1990s, geological research has determined that the two volcanic vents, now known as "resurgent dome
Resurgent dome
In geology, a resurgent dome is a dome formed by swelling or rising of a caldera floor due to movement in the magma chamber beneath it. Unlike a lava dome, a resurgent dome is not formed by the extrusion of highly viscous lava onto the surface, but rather by the uplift and deformation of the...
s", are rising again. From year to year, they either rise or fall, with an average net uplift of about one inch per year. During the period between 1923 and 1985, the Sour Creek Dome was rising. In the years since 1986, it has either declined or remained the same. The resurgence of the Sour Creek dome, just north of Fishing Bridge is causing Yellowstone Lake to "tilt" southward. Larger sandy beaches can now be found on the north shore of the lake, and flooded areas can be found in the southern arms.
The Hayden Valley
Hayden Valley
Hayden Valley is a large, sub-alpine valley in Yellowstone National Park straddling the Yellowstone River between Yellowstone Falls and Yellowstone Lake. The valley floor along the river is an ancient lake bed from a time when Yellowstone Lake was much larger...
was once filled by an arm of Yellowstone Lake. As a result, it contains fine-grained lake sediments that are now covered with glacial till left from the most recent glacial
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
retreat 13,000 years ago. Because the glacial till contains many different grain sizes, including clay and a thin layer of lake sediments, water cannot percolate readily into the ground. This is why the Hayden Valley is marsh
Marsh
In geography, a marsh, or morass, is a type of wetland that is subject to frequent or continuous flood. Typically the water is shallow and features grasses, rushes, reeds, typhas, sedges, other herbaceous plants, and moss....
y and has little encroachment of tree
Tree
A tree is a perennial woody plant. It is most often defined as a woody plant that has many secondary branches supported clear of the ground on a single main stem or trunk with clear apical dominance. A minimum height specification at maturity is cited by some authors, varying from 3 m to...
s.
Angling and boating

Angling
Angling is a method of fishing by means of an "angle" . The hook is usually attached to a fishing line and the line is often attached to a fishing rod. Fishing rods are usually fitted with a fishing reel that functions as a mechanism for storing, retrieving and paying out the line. The hook itself...
for Yellowstone cutthroat trout
Yellowstone cutthroat trout
The Yellowstone cutthroat trout is a subspecies of the cutthroat trout and is a freshwater fish in the salmon family of the order Salmoniformes. Native only to a few U.S...
in Yellowstone Lake has been a popular pastime for both subsistence and recreation since the first explorers, surveyors and tourists visited the park. During the early days of fish stocking in Yellowstone (1890–1910), Atlantic Salmon
Atlantic salmon
The Atlantic salmon is a species of fish in the family Salmonidae, which is found in the northern Atlantic Ocean and in rivers that flow into the north Atlantic and the north Pacific....
, Mountain whitefish
Mountain whitefish
The mountain whitefish is one of the most widely distributed salmonid fish of western North America. It is found from the Mackenzie River drainage in Northwest Territory, Canada south through western Canada and the northwestern USA in the Pacific, Hudson Bay and upper Missouri River basins to the...
and Rainbow trout
Rainbow trout
The rainbow trout is a species of salmonid native to tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead is a sea run rainbow trout usually returning to freshwater to spawn after 2 to 3 years at sea. In other words, rainbow trout and steelhead trout are the same species....
were stocked in the lake. None of these introduced species survived. Today only native cutthroat and non-native Lake trout
Lake trout
Lake trout is a freshwater char living mainly in lakes in northern North America. Other names for it include mackinaw, lake char , touladi, togue, and grey trout. In Lake Superior, they can also be variously known as siscowet, paperbellies and leans...
exist in the lake. Today, Yellowstone Lake is open for angling from June 15 to the first Sunday in November. All Cutthroat trout caught must be released. In 1994, non-native Lake trout were discovered in Yellowstone Lake and were believed to have been either accidentally or intentionally introduced as early as 1989 with fish taken from Lewis Lake
Lewis Lake (Wyoming)
Lewis Lake is located in the U. S. state of Wyoming in the southern part of Yellowstone National Park, about southeast of Shoshone Lake, and approximately southwest of Yellowstone Lake. Lewis Lake and Shoshone Lake are both located a few miles northeast of the Pitchstone Plateau.The Lewis River...
. The introduction of Lake trout has caused a serious decline in the Cutthroat trout population and the National Park Service has an aggressive Lake trout eradication program on the lake. All Lake trout caught by anglers must be killed.
Recreational boating has been permitted on the lake in various forms since 1890 when the first permits for the Yellowstone Boat Company were issued to operate a ferry across the lake between road junctions. Today, powerboats, sailboats, canoes and kayaks are allowed on the lake with a Yellowstone Boating Permit. Marinas are operated at Bridge Bay and West Thumb. Areas in the southern arms of the lake are speed-restricted and/or no-motor zones to protect sensitive wildlife areas. Access to some of the lake's islands is also restricted. Xanterra Parks and Resorts
Xanterra Parks and Resorts
Xanterra Parks & Resorts is a privately-owned United States park and resort management company based in Greenwood Village, Colorado, controlled by entertainment magnate Phillip Anschutz...
at Bridge Bay Marina on Yellowstone Lake provides boat rentals and other boating services. Numerous outfitters operating outside the park are licensed to provide boating services in the park. Several dozen backcountry campsites line the southern shoreline that are accessible only by boat. Two major hiking trails provide access to the lake shore away from the major road. The Nine Mile Post trail hugs the eastern shoreline into the Thorofare region and intersects with the Trail Creek and Heart Lake trails that touch the ends of both the south and southeast arms of the lake.

