
Zeroth
Encyclopedia
Zero-based numbering is numbering in which the initial element of a sequence is assigned the index 0, rather than the index 1 as is typical in everyday circumstances. Under zero-based numbering, the initial element is sometimes termed the zeroth element, rather than the first element; zeroth is a coined ordinal number
corresponding to the number zero
. In some cases, an object or value that does not (originally) belong to a given sequence, but which could be naturally placed before its initial element, may be termed the zeroth element. There is not wide agreement regarding the correctness of using zero as an ordinal (nor regarding use of the term zeroth) as it creates ambiguity for all subsequent elements of the sequence when lacking context.
Numbering sequences starting at 0 is quite common in mathematics, in particular in combinatorics
. In computer science
, array indices also often start at 0, so computer programmers might use zeroth in situations where others might use first, and so forth. In some mathematical contexts, zero-based numbering can be used without confusion, when ordinal forms have well established meaning with an obvious candidate to come before first; for instance a zeroth derivative of a function is the function itself, obtained by differentiating zero times. Such usage corresponds to naming an element not properly belonging to the sequence but preceding it: the zeroth derivative is not really a derivative at all.
s, including C
, Java
, and Lisp
. In these three, sequence types (C arrays, Java arrays and lists, and Lisp lists and vectors) are indexed beginning with the zero subscript. Particularly in C, where arrays are closely tied to pointer arithmetic, this makes for a simpler implementation: the subscript refers to an offset from the starting position of an array, so the first element has an offset of zero.
Referencing memory by an address and an offset is represented directly in hardware on virtually all computer architectures, so this design detail in C makes compilation easier, at the cost of some human factors. In this context using "zeroth" as an ordinal is not strictly correct, but professional shorthand. Older programming languages, such as Fortran
or Cobol
have array subscripts starting with one, because they were meant as high-level programming language
s, and as such they had to have a correspondence to the usual ordinal number
s. Some recent languages, such as Lua, have adopted the same convention for the same reason.
Zero is the lowest unsigned integer value, one of the most fundamental types in programming and hardware
design. In computer science, zero
is thus often used as the base case for many kinds of numerical recursion
. Proofs and other sorts of mathematical reasoning in computer science often begin with zero. For these reasons, in computer science it is not unusual to number from zero rather than one.
Hackers and computer scientists often like to call the first chapter of a publication "Chapter 0", especially if it is of an introductory nature. One of the classic instances was in the First Edition of K&R
. In recent years this trait has also been observed among many pure mathematicians
, where many constructions are defined to be numbered from 0.
If an array is used to represent a cycle, it is convenient to obtain the index with a modulo operator, which can result in zero.
as implemented in modern computers. Usually, the modulo function
maps any integer modulo N to one of the numbers 0, 1, 2, ..., , where . Because of this, many formulas in algorithms (such as that for calculating hash table indices) can be elegantly expressed in code using the modulo operation when array indices at zero.
A second advantage of zero-based array indexes is that this can improve efficiency under certain circumstances. To illustrate, suppose a is the memory address
of the first element of an array, and i is the index of the desired element. In this fairly typical scenario, it is quite common to want the address of the desired element. If the index numbers count from 1, the desired address is computed by this expression:

where s is the size of each element. In contrast, if the index numbers count from 0, the expression becomes this:
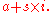
This simpler expression can be more efficient to compute in certain situations.
Note, however, that a language wishing to index arrays from 1 could simply adopt the convention that every "array address" is represented by a′ = a – s; that is, rather than using the address of the first array element, such a language would use the address of an imaginary element located immediately before the first actual element. The indexing expression for a 1-based index would be the following:
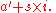
Hence, the efficiency benefit of zero-based indexing is not inherent, but is an artifact of the decision to represent an array by the address of its first element.
A third advantage is that ranges are more elegantly expressed as the half-open interval
, [0,n), as opposed to the closed interval, [1,n], because empty ranges often occur as input to algorithms (which would be tricky to express with the closed interval without resorting to obtuse conventions like [1,0]). On the other hand, closed intervals occur in mathematics because it is often necessary to calculate the terminating condition (which would be impossible in some cases because the half-open interval isn't always a closed set
) which would have a subtraction by 1 everywhere.
This situation can lead to some confusion in terminology. In a zero-based indexing scheme, the first element is "element number zero"; likewise, the twelfth element is "element number eleven". Therefore, an analogy from the ordinal numbers to the quantity of objects numbered appears; the highest index of n objects will be and referred to the nth element. For this reason, the first element is often referred to as the zeroth
element to avoid confusion.
, many sequences of numbers or of polynomials are indexed by nonnegative integers, for example the Bernoulli numbers and the Bell numbers.
The zeroth law of thermodynamics
was formulated after the first, second, and third laws, but considered more fundamental, hence its name.
In biology, an organism is said to have zero order intentionality if it shows "no intention of anything at all". This would include a situation where the organism's genetically predetermined phenotype results in a fitness benefit to itself, because it did not "intend" to express its genes. In the similar sense, a computer may be considered from this perspective a zero order intentional entity as it does not "intend" to express the code of the programs it runs.
In biological or medical experiments, initial measurements made before any experimental time has passed are said to be on the 0 day of the experiment.
Patient zero (or index case) is the initial patient
in the population sample
of an epidemiological
investigation.
eventually added a Zeroth Law to his Three Laws of Robotics
, essentially making them four laws.
The year zero
does not exist in the widely used Gregorian calendar
or in its predecessor, the Julian calendar
. Under those systems, the year 1 BC
is followed by AD 1
. However, there is a year zero in astronomical year numbering
(where it coincides with the Julian year 1 BC) and in ISO 8601:2004
(where it coincides with the Gregorian year 1 BC) as well as in all Buddhist
and Hindu calendar
s.
Some buildings in the British English
speaking world refer to the ground floor as floor 0. This makes a consistent set with underground floors marked with negative numbers. Notice that, for buildings with subterranean stories, this labeling scheme is asymmetric. The asymmetry is apparent when the building has the same number of stories both above and below the street surface.
While the ordinal of 0 is rarely used outside of communities closely connected to mathematics, physics, and computer science, there are a few instances in classical music. The composer Anton Bruckner
regarded his early Symphony in D minor to be unworthy of including in the canon of his works, and he wrote 'gilt nicht' on the score and a circle with a crossbar, intending it to mean "invalid". But posthumously, this work came to be known as Symphony No. 0 in D minor
, even though it was actually written after Symphony No. 1 in C minor
. There is an even earlier Symphony in F minor of Bruckner's that is sometimes called No. 00. The Russian composer Alfred Schnittke
also wrote a Symphony No. 0.
In some universities, including Oxford and Cambridge, "week 0" or occasionally "noughth week" refers to the week before the first week of lectures in a term. In Australia, some universities refer to this as "O Week", which serves as a pun on "orientation week
". As a parallel, the introductory weeks at university educations in Sweden
are generally called "nollning" (zeroing).
The United States Air Force
starts basic training each Wednesday, and the first week (of eight) is considered to begin with the following Sunday. The four days before that Sunday are often referred to as "Zero Week."
Note also the use of 00 hours in the 24-hour clock as beginning of the day.
In London King's Cross
, Uppsala
, Yonago, Edinburgh Haymarket
and Cardiff
the train stations have a platform
0.
Robert Crumb
's drawings for the first issue of Zap Comix
were stolen, so he drew a whole new issue which was published as issue 1. Later he re-inked his photocopies of the stolen artwork and published it as issue 0.
The ring road
around Brussels
is called R0. It was built after the ring road around Antwerp, but Brussels (being the capital city) was deemed deserving of a more basic number.
In Formula One, when a defending world champion does not compete in the following season, the number 1 is not assigned to any driver, but one driver of the world champion team will carry the number 0, and the other, number 2. This did happen both in 1993 and 1994 with Damon Hill carrying the number 0 in both seasons, as defending champion Nigel Mansell quit after 1992, and defending champion Alain Prost quit after 1993.
A chronological prequel of a series may be numbered as 0, such as Ring 0: Birthday
or Zork Zero
.
Ordinal number (linguistics)
In linguistics, ordinal numbers are the words representing the rank of a number with respect to some order, in particular order or position . Its use may refer to size, importance, chronology, etc...
corresponding to the number zero
0 (number)
0 is both a numberand the numerical digit used to represent that number in numerals.It fulfills a central role in mathematics as the additive identity of the integers, real numbers, and many other algebraic structures. As a digit, 0 is used as a placeholder in place value systems...
. In some cases, an object or value that does not (originally) belong to a given sequence, but which could be naturally placed before its initial element, may be termed the zeroth element. There is not wide agreement regarding the correctness of using zero as an ordinal (nor regarding use of the term zeroth) as it creates ambiguity for all subsequent elements of the sequence when lacking context.
Numbering sequences starting at 0 is quite common in mathematics, in particular in combinatorics
Combinatorics
Combinatorics is a branch of mathematics concerning the study of finite or countable discrete structures. Aspects of combinatorics include counting the structures of a given kind and size , deciding when certain criteria can be met, and constructing and analyzing objects meeting the criteria ,...
. In computer science
Computer science
Computer science or computing science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and of practical techniques for their implementation and application in computer systems...
, array indices also often start at 0, so computer programmers might use zeroth in situations where others might use first, and so forth. In some mathematical contexts, zero-based numbering can be used without confusion, when ordinal forms have well established meaning with an obvious candidate to come before first; for instance a zeroth derivative of a function is the function itself, obtained by differentiating zero times. Such usage corresponds to naming an element not properly belonging to the sequence but preceding it: the zeroth derivative is not really a derivative at all.
In computer programming
This usage follows from design choices embedded in many influential programming languageProgramming language
A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs that control the behavior of a machine and/or to express algorithms precisely....
s, including C
C (programming language)
C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating system....
, Java
Java (programming language)
Java is a programming language originally developed by James Gosling at Sun Microsystems and released in 1995 as a core component of Sun Microsystems' Java platform. The language derives much of its syntax from C and C++ but has a simpler object model and fewer low-level facilities...
, and Lisp
Lisp programming language
Lisp is a family of computer programming languages with a long history and a distinctive, fully parenthesized syntax. Originally specified in 1958, Lisp is the second-oldest high-level programming language in widespread use today; only Fortran is older...
. In these three, sequence types (C arrays, Java arrays and lists, and Lisp lists and vectors) are indexed beginning with the zero subscript. Particularly in C, where arrays are closely tied to pointer arithmetic, this makes for a simpler implementation: the subscript refers to an offset from the starting position of an array, so the first element has an offset of zero.
Referencing memory by an address and an offset is represented directly in hardware on virtually all computer architectures, so this design detail in C makes compilation easier, at the cost of some human factors. In this context using "zeroth" as an ordinal is not strictly correct, but professional shorthand. Older programming languages, such as Fortran
Fortran
Fortran is a general-purpose, procedural, imperative programming language that is especially suited to numeric computation and scientific computing...
or Cobol
COBOL
COBOL is one of the oldest programming languages. Its name is an acronym for COmmon Business-Oriented Language, defining its primary domain in business, finance, and administrative systems for companies and governments....
have array subscripts starting with one, because they were meant as high-level programming language
High-level programming language
A high-level programming language is a programming language with strong abstraction from the details of the computer. In comparison to low-level programming languages, it may use natural language elements, be easier to use, or be from the specification of the program, making the process of...
s, and as such they had to have a correspondence to the usual ordinal number
Ordinal number
In set theory, an ordinal number, or just ordinal, is the order type of a well-ordered set. They are usually identified with hereditarily transitive sets. Ordinals are an extension of the natural numbers different from integers and from cardinals...
s. Some recent languages, such as Lua, have adopted the same convention for the same reason.
Zero is the lowest unsigned integer value, one of the most fundamental types in programming and hardware
Hardware
Hardware is a general term for equipment such as keys, locks, hinges, latches, handles, wire, chains, plumbing supplies, tools, utensils, cutlery and machine parts. Household hardware is typically sold in hardware stores....
design. In computer science, zero
0 (number)
0 is both a numberand the numerical digit used to represent that number in numerals.It fulfills a central role in mathematics as the additive identity of the integers, real numbers, and many other algebraic structures. As a digit, 0 is used as a placeholder in place value systems...
is thus often used as the base case for many kinds of numerical recursion
Recursion
Recursion is the process of repeating items in a self-similar way. For instance, when the surfaces of two mirrors are exactly parallel with each other the nested images that occur are a form of infinite recursion. The term has a variety of meanings specific to a variety of disciplines ranging from...
. Proofs and other sorts of mathematical reasoning in computer science often begin with zero. For these reasons, in computer science it is not unusual to number from zero rather than one.
Hackers and computer scientists often like to call the first chapter of a publication "Chapter 0", especially if it is of an introductory nature. One of the classic instances was in the First Edition of K&R
The C Programming Language (book)
The C Programming Language is a well-known programming book written by Brian Kernighan and Dennis Ritchie, the latter of whom originally designed and implemented the language, as well as co-designed the Unix operating system with which development of the language was closely intertwined...
. In recent years this trait has also been observed among many pure mathematicians
Pure mathematics
Broadly speaking, pure mathematics is mathematics which studies entirely abstract concepts. From the eighteenth century onwards, this was a recognized category of mathematical activity, sometimes characterized as speculative mathematics, and at variance with the trend towards meeting the needs of...
, where many constructions are defined to be numbered from 0.
If an array is used to represent a cycle, it is convenient to obtain the index with a modulo operator, which can result in zero.
Advantages
One advantage of this convention is in the use of modular arithmeticModular arithmetic
In mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" after they reach a certain value—the modulus....
as implemented in modern computers. Usually, the modulo function
Modulo operation
In computing, the modulo operation finds the remainder of division of one number by another.Given two positive numbers, and , a modulo n can be thought of as the remainder, on division of a by n...
maps any integer modulo N to one of the numbers 0, 1, 2, ..., , where . Because of this, many formulas in algorithms (such as that for calculating hash table indices) can be elegantly expressed in code using the modulo operation when array indices at zero.
A second advantage of zero-based array indexes is that this can improve efficiency under certain circumstances. To illustrate, suppose a is the memory address
Memory address
A digital computer's memory, more specifically main memory, consists of many memory locations, each having a memory address, a number, analogous to a street address, at which computer programs store and retrieve, machine code or data. Most application programs do not directly read and write to...
of the first element of an array, and i is the index of the desired element. In this fairly typical scenario, it is quite common to want the address of the desired element. If the index numbers count from 1, the desired address is computed by this expression:

where s is the size of each element. In contrast, if the index numbers count from 0, the expression becomes this:
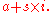
This simpler expression can be more efficient to compute in certain situations.
Note, however, that a language wishing to index arrays from 1 could simply adopt the convention that every "array address" is represented by a′ = a – s; that is, rather than using the address of the first array element, such a language would use the address of an imaginary element located immediately before the first actual element. The indexing expression for a 1-based index would be the following:
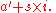
Hence, the efficiency benefit of zero-based indexing is not inherent, but is an artifact of the decision to represent an array by the address of its first element.
A third advantage is that ranges are more elegantly expressed as the half-open interval
Interval (mathematics)
In mathematics, a interval is a set of real numbers with the property that any number that lies between two numbers in the set is also included in the set. For example, the set of all numbers satisfying is an interval which contains and , as well as all numbers between them...
, [0,n), as opposed to the closed interval, [1,n], because empty ranges often occur as input to algorithms (which would be tricky to express with the closed interval without resorting to obtuse conventions like [1,0]). On the other hand, closed intervals occur in mathematics because it is often necessary to calculate the terminating condition (which would be impossible in some cases because the half-open interval isn't always a closed set
Closed set
In geometry, topology, and related branches of mathematics, a closed set is a set whose complement is an open set. In a topological space, a closed set can be defined as a set which contains all its limit points...
) which would have a subtraction by 1 everywhere.
This situation can lead to some confusion in terminology. In a zero-based indexing scheme, the first element is "element number zero"; likewise, the twelfth element is "element number eleven". Therefore, an analogy from the ordinal numbers to the quantity of objects numbered appears; the highest index of n objects will be and referred to the nth element. For this reason, the first element is often referred to as the zeroth
Zeroth
Zero-based numbering is numbering in which the initial element of a sequence is assigned the index 0, rather than the index 1 as is typical in everyday circumstances. Under zero-based numbering, the initial element is sometimes termed the zeroth element, rather than the first element; zeroth is a...
element to avoid confusion.
In science
In mathematicsMathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, many sequences of numbers or of polynomials are indexed by nonnegative integers, for example the Bernoulli numbers and the Bell numbers.
The zeroth law of thermodynamics
Zeroth law of thermodynamics
The zeroth law of thermodynamics is a generalization principle of thermal equilibrium among bodies, or thermodynamic systems, in contact.The zeroth law states that if two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, they are also in thermal equilibrium with each other.Systems are said to...
was formulated after the first, second, and third laws, but considered more fundamental, hence its name.
In biology, an organism is said to have zero order intentionality if it shows "no intention of anything at all". This would include a situation where the organism's genetically predetermined phenotype results in a fitness benefit to itself, because it did not "intend" to express its genes. In the similar sense, a computer may be considered from this perspective a zero order intentional entity as it does not "intend" to express the code of the programs it runs.
In biological or medical experiments, initial measurements made before any experimental time has passed are said to be on the 0 day of the experiment.
Patient zero (or index case) is the initial patient
Patient
A patient is any recipient of healthcare services. The patient is most often ill or injured and in need of treatment by a physician, advanced practice registered nurse, veterinarian, or other health care provider....
in the population sample
Sample (statistics)
In statistics, a sample is a subset of a population. Typically, the population is very large, making a census or a complete enumeration of all the values in the population impractical or impossible. The sample represents a subset of manageable size...
of an epidemiological
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study of health-event, health-characteristic, or health-determinant patterns in a population. It is the cornerstone method of public health research, and helps inform policy decisions and evidence-based medicine by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive...
investigation.
In other fields
In the realm of fiction, Isaac AsimovIsaac Asimov
Isaac Asimov was an American author and professor of biochemistry at Boston University, best known for his works of science fiction and for his popular science books. Asimov was one of the most prolific writers of all time, having written or edited more than 500 books and an estimated 90,000...
eventually added a Zeroth Law to his Three Laws of Robotics
Three Laws of Robotics
The Three Laws of Robotics are a set of rules devised by the science fiction author Isaac Asimov and later added to. The rules are introduced in his 1942 short story "Runaround", although they were foreshadowed in a few earlier stories...
, essentially making them four laws.
The year zero
Year zero
"Year zero" does not exist in the widely used Gregorian calendar or in its predecessor, the Julian calendar. Under those systems, the year 1 BC is followed by AD 1...
does not exist in the widely used Gregorian calendar
Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar, also known as the Western calendar, or Christian calendar, is the internationally accepted civil calendar. It was introduced by Pope Gregory XIII, after whom the calendar was named, by a decree signed on 24 February 1582, a papal bull known by its opening words Inter...
or in its predecessor, the Julian calendar
Julian calendar
The Julian calendar began in 45 BC as a reform of the Roman calendar by Julius Caesar. It was chosen after consultation with the astronomer Sosigenes of Alexandria and was probably designed to approximate the tropical year .The Julian calendar has a regular year of 365 days divided into 12 months...
. Under those systems, the year 1 BC
1 BC
Year 1 BC was a common year starting on Friday or Saturday of the Julian calendar and a leap year starting on Thursday of the Proleptic Julian calendar...
is followed by AD 1
1
Year 1 was a common year starting on Saturday or Sunday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Saturday of the Proleptic Julian calendar...
. However, there is a year zero in astronomical year numbering
Astronomical year numbering
Astronomical year numbering is based on AD/CE year numbering, but follows normal decimal integer numbering more strictly. Thus, it has a year 0, the years before that are designated with negative numbers and the years after that are designated with positive numbers...
(where it coincides with the Julian year 1 BC) and in ISO 8601:2004
ISO 8601
ISO 8601 Data elements and interchange formats – Information interchange – Representation of dates and times is an international standard covering the exchange of date and time-related data. It was issued by the International Organization for Standardization and was first published in 1988...
(where it coincides with the Gregorian year 1 BC) as well as in all Buddhist
Buddhist calendar
The Buddhist calendar is used on mainland Southeast Asia in the countries of Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Burma and Sri Lanka in several related forms. It is a lunisolar calendar having months that are alternately 29 and 30 days, with an intercalated day and a 30-day month added at regular intervals...
and Hindu calendar
Hindu calendar
The hindu calendar used in ancient times has undergone many changes in the process of regionalization, and today there are several regional Indian calendars, as well as an Indian national calendar. Nepali calendar, Bengali calendar, Malayalam calendar, Tamil calendar, Telugu calendar, Kannada...
s.
Some buildings in the British English
British English
British English, or English , is the broad term used to distinguish the forms of the English language used in the United Kingdom from forms used elsewhere...
speaking world refer to the ground floor as floor 0. This makes a consistent set with underground floors marked with negative numbers. Notice that, for buildings with subterranean stories, this labeling scheme is asymmetric. The asymmetry is apparent when the building has the same number of stories both above and below the street surface.
While the ordinal of 0 is rarely used outside of communities closely connected to mathematics, physics, and computer science, there are a few instances in classical music. The composer Anton Bruckner
Anton Bruckner
Anton Bruckner was an Austrian composer known for his symphonies, masses, and motets. The first are considered emblematic of the final stage of Austro-German Romanticism because of their rich harmonic language, complex polyphony, and considerable length...
regarded his early Symphony in D minor to be unworthy of including in the canon of his works, and he wrote 'gilt nicht' on the score and a circle with a crossbar, intending it to mean "invalid". But posthumously, this work came to be known as Symphony No. 0 in D minor
Symphony No. 0 (Bruckner)
This Symphony in D minor composed by Anton Bruckner was not assigned a number by its composer, and has subsequently become known by the German designation Die Nullte .-Composition:...
, even though it was actually written after Symphony No. 1 in C minor
Symphony No. 1 (Bruckner)
Anton Bruckner's Symphony No. 1 in C minor was the first symphony the composer thought worthy of performing, and bequeathing to the Vienna national library. Chronologically, it comes after the Study Symphony in F minor and before Symphony No. 0 in D minor. The first version of the Symphony No. 2...
. There is an even earlier Symphony in F minor of Bruckner's that is sometimes called No. 00. The Russian composer Alfred Schnittke
Alfred Schnittke
Alfred Schnittke ; November 24, 1934 – August 3, 1998) was a Russian and Soviet composer. Schnittke's early music shows the strong influence of Dmitri Shostakovich. He developed a polystylistic technique in works such as the epic First Symphony and First Concerto Grosso...
also wrote a Symphony No. 0.
In some universities, including Oxford and Cambridge, "week 0" or occasionally "noughth week" refers to the week before the first week of lectures in a term. In Australia, some universities refer to this as "O Week", which serves as a pun on "orientation week
Orientation week
Student orientation or new student orientation, is a period of time at the beginning of the academic year at a university or other tertiary institution during which a variety of events are held to orient and welcome new students. The name of the period varies by country...
". As a parallel, the introductory weeks at university educations in Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
are generally called "nollning" (zeroing).
The United States Air Force
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force is the aerial warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the American uniformed services. Initially part of the United States Army, the USAF was formed as a separate branch of the military on September 18, 1947 under the National Security Act of...
starts basic training each Wednesday, and the first week (of eight) is considered to begin with the following Sunday. The four days before that Sunday are often referred to as "Zero Week."
Note also the use of 00 hours in the 24-hour clock as beginning of the day.
In London King's Cross
King's Cross station
King's Cross station may refer to::* London King's Cross railway station in London, England** King's Cross St. Pancras tube station for London Underground lines.** King's Cross Thameslink, a disused railway station in London, England...
, Uppsala
Uppsala
- Economy :Today Uppsala is well established in medical research and recognized for its leading position in biotechnology.*Abbott Medical Optics *GE Healthcare*Pfizer *Phadia, an offshoot of Pharmacia*Fresenius*Q-Med...
, Yonago, Edinburgh Haymarket
Haymarket railway station
For the Tyne and Wear Metro see Haymarket Metro station.Haymarket railway station is in Haymarket, Edinburgh, Scotland. It is Edinburgh's second largest station after Waverley, a major commuter and long-distance destination, located quite centrally near the West End...
and Cardiff
Cardiff central station
Cardiff Central Station can refer to:*Cardiff Central railway station*Cardiff central bus station...
the train stations have a platform
Railway platform
A railway platform is a section of pathway, alongside rail tracks at a train station, metro station or tram stop, at which passengers may board or alight from trains or trams. Almost all stations for rail transport have some form of platforms, with larger stations having multiple platforms...
0.
Robert Crumb
Robert Crumb
Robert Dennis Crumb —known as Robert Crumb and R. Crumb—is an American artist, illustrator, and musician recognized for the distinctive style of his drawings and his critical, satirical, subversive view of the American mainstream.Crumb was a founder of the underground comix movement and is regarded...
's drawings for the first issue of Zap Comix
Zap Comix
Zap Comix is the best-known and one of the most popular of the underground comics that emerged as part of the youth counterculture of the late 1960s. While not believed to be the first underground comic to have been published, Zap is considered to mark the beginning of the "underground comix"...
were stolen, so he drew a whole new issue which was published as issue 1. Later he re-inked his photocopies of the stolen artwork and published it as issue 0.
The ring road
Ring road
A ring road, orbital motorway, beltway, circumferential highway, or loop highway is a road that encircles a town or city...
around Brussels
Brussels
Brussels , officially the Brussels Region or Brussels-Capital Region , is the capital of Belgium and the de facto capital of the European Union...
is called R0. It was built after the ring road around Antwerp, but Brussels (being the capital city) was deemed deserving of a more basic number.
In Formula One, when a defending world champion does not compete in the following season, the number 1 is not assigned to any driver, but one driver of the world champion team will carry the number 0, and the other, number 2. This did happen both in 1993 and 1994 with Damon Hill carrying the number 0 in both seasons, as defending champion Nigel Mansell quit after 1992, and defending champion Alain Prost quit after 1993.
A chronological prequel of a series may be numbered as 0, such as Ring 0: Birthday
Ring 0: Birthday
Ring 0: Birthday is a 2000 Japanese film. It's the prequel to the film Ring. It was directed by Norio Tsuruta, based on a screenplay by Hiroshi Takahashi. The film's screenplay is based on the short story Lemonheart from the Birthday anthology by Koji Suzuki. There is also a manga adaptation...
or Zork Zero
Zork Zero
Zork Zero: The Revenge of Megaboz is an interactive fiction computer game, written by Steve Meretzky over nearly 18 months and published by Infocom in 1988, with an original retail price of $59.95...
.

