
Sample (statistics)
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, a sample is a subset
of a population
. Typically, the population is very large, making a census
or a complete enumeration
of all the values in the population impractical or impossible. The sample represents a subset of manageable size. Samples are collected and statistics are calculated from the samples so that one can make inference
s or extrapolation
s from the sample to the population. This process of collecting information from a sample is referred to as sampling
.
A complete sample is a set of objects from a parent population that includes ALL such objects that satisfy a set of well-defined selection criteria. For example, a complete sample of Australian men taller than 2m would consist of a list of every Australian male taller than 2m. But it wouldn't include German males, or tall Australian females, or people shorter than 2m. So to compile such a complete sample requires a complete list of the parent population, including data on height, gender, and nationality for each member of that parent population. In the case of human populations, such a complete list is unlikely to exist, but such complete samples are often available in other disciplines, such as complete magnitude-limited samples of astronomical objects.
An unbiased sample is a set of objects chosen from a complete sample using a selection process that does not depend on the properties of the objects. For example, an unbiased sample of Australian men taller than 2m might consist of a randomly sampled subset of 1% of Australian males taller than 2m. But one chosen from the electoral register might not be unbiased since, for example, males aged under 18 will not be on the electoral register. In an astronomical context, an unbiased sample might consist of that fraction of a complete sample for which data are available, provided the data availability is not biased by individual source properties.
The best way to avoid a biased or unrepresentative sample is to select a random sample
, also known as a probability sample. A random sample is defined as a sample where each individual member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected as part of the sample. Several types of random samples are simple random sample
s, systematic samples
, stratified random samples
, and cluster random samples
.
A sample that is not random is called a non-random sample or a non-probability sampling. Some examples of nonrandom samples are convenience samples, judgment sample
s, purposive samples, quota samples, snowball samples
, and quadrature nodes in quasi-Monte Carlo method
s.
X with distribution
F, a random sample of length n (where n may be any of 1,2,3,...) is a set of n independent
, identically distributed (iid) random variables with distribution F.
A sample concretely represents n experiments in which the same quantity is measured. For example, if X represents the height of an individual and n individuals are measured,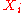 will be the height of the i-th individual. Note that a sample of random variables (i.e. a set of measurable functions) must not be confused with the realizations of these variables (which are the values that these random variables take, formally called random variate
will be the height of the i-th individual. Note that a sample of random variables (i.e. a set of measurable functions) must not be confused with the realizations of these variables (which are the values that these random variables take, formally called random variate
s). In other words,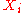 is a function representing the measurement at the i-th experiment and
is a function representing the measurement at the i-th experiment and 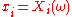 is the value actually obtained when making the measurement.
is the value actually obtained when making the measurement.
The concept of a sample thus includes the process of how the data are obtained (that is, the random variables). This is necessary so that mathematical statements can be made about the sample and statistic
s computed from it, such as the sample mean and covariance.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, a sample is a subset
Subset
In mathematics, especially in set theory, a set A is a subset of a set B if A is "contained" inside B. A and B may coincide. The relationship of one set being a subset of another is called inclusion or sometimes containment...
of a population
Statistical population
A statistical population is a set of entities concerning which statistical inferences are to be drawn, often based on a random sample taken from the population. For example, if we were interested in generalizations about crows, then we would describe the set of crows that is of interest...
. Typically, the population is very large, making a census
Census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring and recording information about the members of a given population. It is a regularly occurring and official count of a particular population. The term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common...
or a complete enumeration
Enumeration
In mathematics and theoretical computer science, the broadest and most abstract definition of an enumeration of a set is an exact listing of all of its elements . The restrictions imposed on the type of list used depend on the branch of mathematics and the context in which one is working...
of all the values in the population impractical or impossible. The sample represents a subset of manageable size. Samples are collected and statistics are calculated from the samples so that one can make inference
Inference
Inference is the act or process of deriving logical conclusions from premises known or assumed to be true. The conclusion drawn is also called an idiomatic. The laws of valid inference are studied in the field of logic.Human inference Inference is the act or process of deriving logical conclusions...
s or extrapolation
Extrapolation
In mathematics, extrapolation is the process of constructing new data points. It is similar to the process of interpolation, which constructs new points between known points, but the results of extrapolations are often less meaningful, and are subject to greater uncertainty. It may also mean...
s from the sample to the population. This process of collecting information from a sample is referred to as sampling
Sampling (statistics)
In statistics and survey methodology, sampling is concerned with the selection of a subset of individuals from within a population to estimate characteristics of the whole population....
.
A complete sample is a set of objects from a parent population that includes ALL such objects that satisfy a set of well-defined selection criteria. For example, a complete sample of Australian men taller than 2m would consist of a list of every Australian male taller than 2m. But it wouldn't include German males, or tall Australian females, or people shorter than 2m. So to compile such a complete sample requires a complete list of the parent population, including data on height, gender, and nationality for each member of that parent population. In the case of human populations, such a complete list is unlikely to exist, but such complete samples are often available in other disciplines, such as complete magnitude-limited samples of astronomical objects.
An unbiased sample is a set of objects chosen from a complete sample using a selection process that does not depend on the properties of the objects. For example, an unbiased sample of Australian men taller than 2m might consist of a randomly sampled subset of 1% of Australian males taller than 2m. But one chosen from the electoral register might not be unbiased since, for example, males aged under 18 will not be on the electoral register. In an astronomical context, an unbiased sample might consist of that fraction of a complete sample for which data are available, provided the data availability is not biased by individual source properties.
The best way to avoid a biased or unrepresentative sample is to select a random sample
Random sample
In statistics, a sample is a subject chosen from a population for investigation; a random sample is one chosen by a method involving an unpredictable component...
, also known as a probability sample. A random sample is defined as a sample where each individual member of the population has a known, non-zero chance of being selected as part of the sample. Several types of random samples are simple random sample
Simple random sample
In statistics, a simple random sample is a subset of individuals chosen from a larger set . Each individual is chosen randomly and entirely by chance, such that each individual has the same probability of being chosen at any stage during the sampling process, and each subset of k individuals has...
s, systematic samples
Systematic sampling
Systematic sampling is a statistical method involving the selection of elements from an ordered sampling frame. The most common form of systematic sampling is an equal-probability method, in which every kth element in the frame is selected, where k, the sampling interval , is calculated as:k =...
, stratified random samples
Stratified sampling
In statistics, stratified sampling is a method of sampling from a population.In statistical surveys, when subpopulations within an overall population vary, it is advantageous to sample each subpopulation independently. Stratification is the process of dividing members of the population into...
, and cluster random samples
Cluster sampling
Cluster Sampling is a sampling technique used when "natural" groupings are evident in a statistical population. It is often used in marketing research. In this technique, the total population is divided into these groups and a sample of the groups is selected. Then the required information is...
.
A sample that is not random is called a non-random sample or a non-probability sampling. Some examples of nonrandom samples are convenience samples, judgment sample
Judgment sample
Judgment sample is a type of nonrandom sample, which is selected based on the opinion of an expert. Results obtained from a judgment sample are subject to some degree of bias, due to the frame and population not being identical. The frame is a list of all the units, items, people, etc that define...
s, purposive samples, quota samples, snowball samples
Snowball sampling
In sociology and statistics research, snowball sampling is a non-probability sampling technique where existing study subjects recruit future subjects from among their acquaintances. Thus the sample group appears to grow like a rolling snowball...
, and quadrature nodes in quasi-Monte Carlo method
Quasi-Monte Carlo method
In numerical analysis, a quasi-Monte Carlo method is a method for the computation of an integral that is based on low-discrepancy sequences...
s.
Mathematical description of random sample
In mathematical terms, given a random variableRandom variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
X with distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
F, a random sample of length n (where n may be any of 1,2,3,...) is a set of n independent
Statistical independence
In probability theory, to say that two events are independent intuitively means that the occurrence of one event makes it neither more nor less probable that the other occurs...
, identically distributed (iid) random variables with distribution F.
A sample concretely represents n experiments in which the same quantity is measured. For example, if X represents the height of an individual and n individuals are measured,
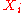 will be the height of the i-th individual. Note that a sample of random variables (i.e. a set of measurable functions) must not be confused with the realizations of these variables (which are the values that these random variables take, formally called random variate
will be the height of the i-th individual. Note that a sample of random variables (i.e. a set of measurable functions) must not be confused with the realizations of these variables (which are the values that these random variables take, formally called random variateRandom variate
A random variate is a particular outcome of a random variable: the random variates which are other outcomes of the same random variable would have different values. Random variates are used when simulating processes driven by random influences...
s). In other words,
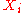 is a function representing the measurement at the i-th experiment and
is a function representing the measurement at the i-th experiment and 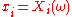 is the value actually obtained when making the measurement.
is the value actually obtained when making the measurement.The concept of a sample thus includes the process of how the data are obtained (that is, the random variables). This is necessary so that mathematical statements can be made about the sample and statistic
Statistic
A statistic is a single measure of some attribute of a sample . It is calculated by applying a function to the values of the items comprising the sample which are known together as a set of data.More formally, statistical theory defines a statistic as a function of a sample where the function...
s computed from it, such as the sample mean and covariance.
See also
- Estimation theoryEstimation theoryEstimation theory is a branch of statistics and signal processing that deals with estimating the values of parameters based on measured/empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such a way that their value affects the distribution of the...
- Replication (statistics)Replication (statistics)In engineering, science, and statistics, replication is the repetition of an experimental condition so that the variability associated with the phenomenon can be estimated. ASTM, in standard E1847, defines replication as "the repetition of the set of all the treatment combinations to be compared in...
- Sample sizeSample sizeSample size determination is the act of choosing the number of observations to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences about a population from a sample...
- Sampling (statistics)Sampling (statistics)In statistics and survey methodology, sampling is concerned with the selection of a subset of individuals from within a population to estimate characteristics of the whole population....
- Survey samplingSurvey samplingIn statistics, survey sampling describes the process of selecting a sample of elements from a target population in order to conduct a survey.A survey may refer to many different types or techniques of observation, but in the context of survey sampling it most often involves a questionnaire used to...

