Zeta potential titration
Encyclopedia
Zeta potential titration is a titration
of heterogeneous systems, such as colloid
s, emulsion
s, etc. Solids in such systems have very high surface area
. This type of titration is used to study the zeta potential
of these surface
s under different conditions.
is approximately zero. At a pH near the iso-electric point (± 2 pH units), colloids are usually unstable; the particles tend to coagulate
or flocculate
. Such titrations use acids or bases as titration reagent
s. Tables of iso-electric points for different materials are available. The attached figure illustrates results of such titrations for concentrated dispersions of alumina (4% v/v) and rutile
(7% v/v). It is seen that iso-electric point of alumina is around pH 9.3, whereas for rutile it is around pH 4. Alumina is unstable in the pH range from 7 to 11. Rutile is unstable in the pH range from 2 to 6.
for achieving stabilization or flocculation
of a heterogeneous system. Examples can be found in the book by Dukhin and Goetz.
is the indicator. Measurement of the zeta potential can be performed using microelectrophoresis
, or electrophoretic light scattering
, or electroacoustic phenomena
. The last method makes possible to perform titrations in concentrated systems, with no dilution. The book by Dukhin and Goetz provides a detailed description of such titrations.
Titration
Titration, also known as titrimetry, is a common laboratory method of quantitative chemical analysis that is used to determine the unknown concentration of an identified analyte. Because volume measurements play a key role in titration, it is also known as volumetric analysis. A reagent, called the...
of heterogeneous systems, such as colloid
Colloid
A colloid is a substance microscopically dispersed evenly throughout another substance.A colloidal system consists of two separate phases: a dispersed phase and a continuous phase . A colloidal system may be solid, liquid, or gaseous.Many familiar substances are colloids, as shown in the chart below...
s, emulsion
Emulsion
An emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible . Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms colloid and emulsion are sometimes used interchangeably, emulsion is used when both the dispersed and the...
s, etc. Solids in such systems have very high surface area
Surface area
Surface area is the measure of how much exposed area a solid object has, expressed in square units. Mathematical description of the surface area is considerably more involved than the definition of arc length of a curve. For polyhedra the surface area is the sum of the areas of its faces...
. This type of titration is used to study the zeta potential
Zeta potential
Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in colloidal systems. In the colloidal chemistry literature, it is usually denoted using the Greek letter zeta, hence ζ-potential...
of these surface
Surface
In mathematics, specifically in topology, a surface is a two-dimensional topological manifold. The most familiar examples are those that arise as the boundaries of solid objects in ordinary three-dimensional Euclidean space R3 — for example, the surface of a ball...
s under different conditions.

Iso-electric Point
The Iso-electric point is one such property. The iso-electric point is the pH value at which the zeta potentialZeta potential
Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in colloidal systems. In the colloidal chemistry literature, it is usually denoted using the Greek letter zeta, hence ζ-potential...
is approximately zero. At a pH near the iso-electric point (± 2 pH units), colloids are usually unstable; the particles tend to coagulate
Coagulation
Coagulation is a complex process by which blood forms clots. It is an important part of hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, wherein a damaged blood vessel wall is covered by a platelet and fibrin-containing clot to stop bleeding and begin repair of the damaged vessel...
or flocculate
Flocculation
Flocculation, in the field of chemistry, is a process wherein colloids come out of suspension in the form of floc or flakes by the addition of a clarifying agent. The action differs from precipitation in that, prior to flocculation, colloids are merely suspended in a liquid and not actually...
. Such titrations use acids or bases as titration reagent
Reagent
A reagent is a "substance or compound that is added to a system in order to bring about a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs." Although the terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably, a reactant is less specifically a "substance that is consumed in the course of...
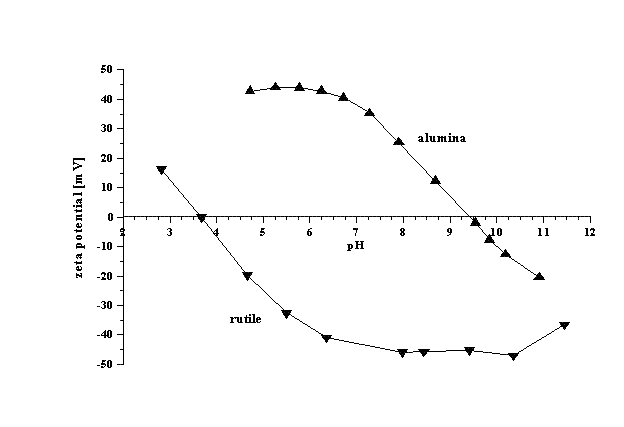
s. Tables of iso-electric points for different materials are available. The attached figure illustrates results of such titrations for concentrated dispersions of alumina (4% v/v) and rutile
Rutile
Rutile is a mineral composed primarily of titanium dioxide, TiO2.Rutile is the most common natural form of TiO2. Two rarer polymorphs of TiO2 are known:...
(7% v/v). It is seen that iso-electric point of alumina is around pH 9.3, whereas for rutile it is around pH 4. Alumina is unstable in the pH range from 7 to 11. Rutile is unstable in the pH range from 2 to 6.
Surfactants and Stabilization
Another purpose of this titration is determination of the optimum dose of surfactantSurfactant
Surfactants are compounds that lower the surface tension of a liquid, the interfacial tension between two liquids, or that between a liquid and a solid...
for achieving stabilization or flocculation
Flocculation
Flocculation, in the field of chemistry, is a process wherein colloids come out of suspension in the form of floc or flakes by the addition of a clarifying agent. The action differs from precipitation in that, prior to flocculation, colloids are merely suspended in a liquid and not actually...
of a heterogeneous system. Examples can be found in the book by Dukhin and Goetz.
Measurement
In a zeta-potential titration, the Zeta potentialZeta potential
Zeta potential is a scientific term for electrokinetic potential in colloidal systems. In the colloidal chemistry literature, it is usually denoted using the Greek letter zeta, hence ζ-potential...
is the indicator. Measurement of the zeta potential can be performed using microelectrophoresis
Microelectrophoresis
Microelectrophoresis is a method of studying electrophoresis of various dispersed particles using optical microscopy. This method provides image of moving particles, which is its unique advantage....
, or electrophoretic light scattering
Electrophoretic light scattering
Electrophoretic light scattering is based on dynamic light scattering. The frequency shift or phase shift of an incident laser beam depends on the dispersed particles mobility. In the case of dynamic light scattering, Brownian motion causes particle motion...
, or electroacoustic phenomena
Electroacoustic phenomena
Electroacoustic phenomena arise when ultrasound propagates through a fluid containing ions. The associated particle motion generates electric signals because ions have electric charge. This coupling between ultrasound and electric field is called electroacoustic phenomena. Fluid might be a simple...
. The last method makes possible to perform titrations in concentrated systems, with no dilution. The book by Dukhin and Goetz provides a detailed description of such titrations.

