
Zhaozhou Bridge
Encyclopedia
The Anji Bridge is the world's oldest open-spandrel
stone segmental arch bridge
. Credited to the design of a craftsman named Li Chun, the bridge was constructed in the years 595-605 during the Sui Dynasty
(581–618). Located in the southern part of Hebei
Province, it is the oldest standing bridge in China.
, which was formerly known as Zhaozhou (趙州). Another name for the bridge is the Great Stone Bridge . It crosses the Xiao River (洨河) in Zhao County, approximately 40 kilometres (24.9 mi) southeast of the provincial capital Shijiazhuang
.
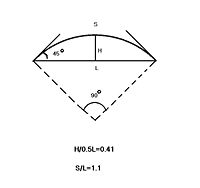 The Anji bridge is about 50 m long with a central span of 37.37 m. It stands 7.3 m tall and has a width of 9 m. The arch covers a circular segment
The Anji bridge is about 50 m long with a central span of 37.37 m. It stands 7.3 m tall and has a width of 9 m. The arch covers a circular segment
less than half of a semicircle (84°) and with a radius of 27.27 m, has a rise-to-span ratio of approximately 0.197 (7.3 to 37 m). This is considerably smaller than the rise-to-span ratio of 0.5 of a semicircular arch bridge and slightly smaller than the rise-to-span ratio of 0.207 of a quarter circle. The arch length to span ratio is 1.1, less than the arch-to-span ratio of 1.57 of
a semicircle arch bridge by 43%, thus the saving in material is about 40%, making the bridge lighter in weight. The elevation of the arch is about 45°, which subjects the abutments of the bridge to downward force and sideways force.
The central arch is made of 28 thin, curved limestone slabs which are joined with iron dovetail
s. This allows the arch to adjust to shifts in its supports, and prevents the bridge from collapsing even when a segment of the arch breaks. The bridge has two small side arches on either side of the main arch. These side arches serve two important functions: First, they reduce the total weight of the bridge by about 15.3% or approximately 700 ton
s, which is vital because of the low rise-to-span ratio and the large forces on the abutments it creates. Second, when the bridge is submerged during a flood, they allow water to pass through, thereby reducing the forces on the structure of the bridge.
Li Chun's innovative spandrel-arch construction, while economising in materials, was also of considerable aesthetic merit. An inscription left on the bridge by Tang Dynasty
officials seventy years after its construction reads:
The Anji bridge influenced the design of later Chinese bridge structures, such as the similar Yongtong Bridge near Zhaoxian in Hebei
. The Yongtong Bridge is a 26 m (85 ft) long stone segmental-arch bridge built in 1130 by the Song
structural engineer Pou Qianer.
The intriguing design of the Anji bridge has given rise to many legends. According to one legend, the bridge was built by a master architect named Lu Ban
in a single night. In another story, the bridge was put to the test by two immortals who crossed it at the same time and Lu Ban saved it by wading into the water and supporting the structure.
Although Ming Dynasty
(1368–1644) authors compared the bridge to "a new moon rising above the clouds" and "a long rainbow hanging on a mountain waterfall", it later fell into obscurity. When Professor Liang Sicheng
of Tsinghua University
rediscovered the bridge on a field exploration of ancient architecture in Hebei province, made detailed measurements, and published a report and drawing, it became world famous.
Anji bridge was dedicated as an International Historic Civil Engineering Landmark by the American Society of Civil Engineers
in 1991. In 1996, the Chinese authorities nominated it for inclusion in the World Heritage List as having "a very important place in the world bridge building history".
Spandrel
A spandrel, less often spandril or splaundrel, is the space between two arches or between an arch and a rectangular enclosure....
stone segmental arch bridge
Arch bridge
An arch bridge is a bridge with abutments at each end shaped as a curved arch. Arch bridges work by transferring the weight of the bridge and its loads partially into a horizontal thrust restrained by the abutments at either side...
. Credited to the design of a craftsman named Li Chun, the bridge was constructed in the years 595-605 during the Sui Dynasty
Sui Dynasty
The Sui Dynasty was a powerful, but short-lived Imperial Chinese dynasty. Preceded by the Southern and Northern Dynasties, it ended nearly four centuries of division between rival regimes. It was followed by the Tang Dynasty....
(581–618). Located in the southern part of Hebei
Hebei
' is a province of the People's Republic of China in the North China region. Its one-character abbreviation is "" , named after Ji Province, a Han Dynasty province that included what is now southern Hebei...
Province, it is the oldest standing bridge in China.
Name and location
The bridge is also commonly known as the Zhaozhou Bridge , after Zhao CountyZhao County
Zhao County , a historic town called Zhaozhou in the past, is located in Hebei 40 km southeast of the provincial capital Shijiazhuang, and 280 km south of Beijing. Its total land area is 675 km² and total population is around 550,000...
, which was formerly known as Zhaozhou (趙州). Another name for the bridge is the Great Stone Bridge . It crosses the Xiao River (洨河) in Zhao County, approximately 40 kilometres (24.9 mi) southeast of the provincial capital Shijiazhuang
Shijiazhuang
Shijiazhuang is the capital and largest city of North China's Hebei province. Administratively a prefecture-level city, it is about south of Beijing...
.
Construction

Circular segment
In geometry, a circular segment is an area of a circle informally defined as an area which is "cut off" from the rest of the circle by a secant or a chord. The circle segment constitutes the part between the secant and an arc, excluding the circle's center...
less than half of a semicircle (84°) and with a radius of 27.27 m, has a rise-to-span ratio of approximately 0.197 (7.3 to 37 m). This is considerably smaller than the rise-to-span ratio of 0.5 of a semicircular arch bridge and slightly smaller than the rise-to-span ratio of 0.207 of a quarter circle. The arch length to span ratio is 1.1, less than the arch-to-span ratio of 1.57 of
a semicircle arch bridge by 43%, thus the saving in material is about 40%, making the bridge lighter in weight. The elevation of the arch is about 45°, which subjects the abutments of the bridge to downward force and sideways force.
The central arch is made of 28 thin, curved limestone slabs which are joined with iron dovetail
Dovetail joint
A dovetail joint or simply dovetail is a joint technique most commonly used in woodworking joinery. Noted for its resistance to being pulled apart , the dovetail joint is commonly used to join the sides of a drawer to the front....
s. This allows the arch to adjust to shifts in its supports, and prevents the bridge from collapsing even when a segment of the arch breaks. The bridge has two small side arches on either side of the main arch. These side arches serve two important functions: First, they reduce the total weight of the bridge by about 15.3% or approximately 700 ton
Ton
The ton is a unit of measure. It has a long history and has acquired a number of meanings and uses over the years. It is used principally as a unit of weight, and as a unit of volume. It can also be used as a measure of energy, for truck classification, or as a colloquial term.It is derived from...
s, which is vital because of the low rise-to-span ratio and the large forces on the abutments it creates. Second, when the bridge is submerged during a flood, they allow water to pass through, thereby reducing the forces on the structure of the bridge.
Li Chun's innovative spandrel-arch construction, while economising in materials, was also of considerable aesthetic merit. An inscription left on the bridge by Tang Dynasty
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
officials seventy years after its construction reads:
Later history and reputation
In the next 1400 years, the bridge survived at least eight wars, ten major floods and numerous earthquakes, the most recent being the 7.2-magnitude Xingtai Earthquake in 1966. Yet, the support structure remains intact and the bridge is still in use. Only the ornamental railings have been replaced every few hundred years.The Anji bridge influenced the design of later Chinese bridge structures, such as the similar Yongtong Bridge near Zhaoxian in Hebei
Hebei
' is a province of the People's Republic of China in the North China region. Its one-character abbreviation is "" , named after Ji Province, a Han Dynasty province that included what is now southern Hebei...
. The Yongtong Bridge is a 26 m (85 ft) long stone segmental-arch bridge built in 1130 by the Song
Song Dynasty
The Song Dynasty was a ruling dynasty in China between 960 and 1279; it succeeded the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, and was followed by the Yuan Dynasty. It was the first government in world history to issue banknotes or paper money, and the first Chinese government to establish a...
structural engineer Pou Qianer.
The intriguing design of the Anji bridge has given rise to many legends. According to one legend, the bridge was built by a master architect named Lu Ban
Lu Ban
Lu Ban was a Chinese carpenter, engineer, philosopher, inventor, military thinker, statesman and contemporary of Mozi, born in the State of Lu, and is the patron Saint of Chinese builders and contractors. He was born in a renowned family during the Spring and Autumn Period when China was...
in a single night. In another story, the bridge was put to the test by two immortals who crossed it at the same time and Lu Ban saved it by wading into the water and supporting the structure.
Although Ming Dynasty
Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
(1368–1644) authors compared the bridge to "a new moon rising above the clouds" and "a long rainbow hanging on a mountain waterfall", it later fell into obscurity. When Professor Liang Sicheng
Liang Sicheng
Liang Sicheng was the son of Liang Qichao, a well-known Chinese thinker in the late Qing Dynasty. Liang Sicheng returned to China from the United States after studying at the University of Pennsylvania...
of Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University , colloquially known in Chinese as Qinghua, is a university in Beijing, China. The school is one of the nine universities of the C9 League. It was established in 1911 under the name "Tsinghua Xuetang" or "Tsinghua College" and was renamed the "Tsinghua School" one year later...
rediscovered the bridge on a field exploration of ancient architecture in Hebei province, made detailed measurements, and published a report and drawing, it became world famous.
Anji bridge was dedicated as an International Historic Civil Engineering Landmark by the American Society of Civil Engineers
American Society of Civil Engineers
The American Society of Civil Engineers is a professional body founded in 1852 to represent members of the civil engineering profession worldwide. It is the oldest national engineering society in the United States. ASCE's vision is to have engineers positioned as global leaders who strive toward...
in 1991. In 1996, the Chinese authorities nominated it for inclusion in the World Heritage List as having "a very important place in the world bridge building history".
External links
- American Society of Civil Engineers: History and Heritage of Civil Engineering (select "Landmark Projects", then "Zhaoahou Bridge")
- Asian Research
- Chinaculture.org Site sponsored by the Ministry of Culture of the People's Republic of China

