
ZigBee
Encyclopedia
ZigBee is a specification
for a suite of high level communication protocols using small, low-power digital radio
s based on an IEEE 802 standard
for personal area network
s. Applications include wireless light switches, electrical meters with in-home-displays, and other consumer and industrial equipment that requires short-range wireless transfer of data at relatively low rates. The technology defined by the ZigBee specification is intended to be simpler and less expensive than other WPANs, such as Bluetooth
. ZigBee is targeted at radio-frequency
(RF) applications that require a low data rate, long battery life, and secure networking. ZigBee has a defined rate of 250 kbps best suited for periodic or intermittent data or a single signal transmission from a sensor or input device.
The name refers to the waggle dance
of honey bees after their return to the beehive.
standard. The low cost allows the technology to be widely deployed in wireless control and monitoring applications. Low power-usage allows longer life with smaller batteries. Mesh networking provides high reliability and more extensive range. ZigBee chip vendors typically sell integrated radios and microcontrollers with between 60 KB and 256 KB flash memory.
ZigBee operates in the industrial, scientific and medical (ISM
) radio bands; 868 MHz in Europe, 915 MHz in the USA and Australia, and 2.4 GHz in most jurisdictions worldwide. Data transmission rates vary from 20 to 250 kilobits/second.
The ZigBee network layer natively supports both star
and tree typical networks, and generic mesh networks. Every network must have one coordinator device, tasked with its creation, the control of its parameters and basic maintenance. Within star networks, the coordinator must be the central node. Both trees and meshes allows the use of ZigBee routers
to extend communication at the network level.
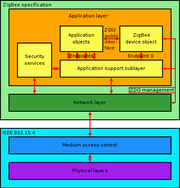 ZigBee builds upon the physical layer
ZigBee builds upon the physical layer
and medium access control defined in IEEE standard 802.15.4
(2003 version) for low-rate WPAN's. The specification goes on to complete the standard by adding four main components: network layer, application layer, ZigBee device objects (ZDOs) and manufacturer-defined application objects which allow for customization and favor total integration.
Besides adding two high-level network layers to the underlying structure, the most significant improvement is the introduction of ZDO's. These are responsible for a number of tasks, which include keeping of device roles, management of requests to join a network, device discovery and security.
ZigBee is not intended to support powerline networking
but to interface with it at least for smart meter
ing and smart appliance purposes.
Because ZigBee nodes can go from sleep to active mode in 30 ms or less, the latency can be low and devices can be responsive, particularly compared to Bluetooth wake-up delays, which are typically around three seconds.
Because ZigBee nodes can sleep most of the time, average power consumption can be low, resulting in long battery life.
of this group, not a single technical standard. The Alliance publishes application profile
s that allow multiple OEM
vendors to create interoperable products. The relationship between IEEE 802.15.4
and ZigBee is similar to that between IEEE 802.11
and the Wi-Fi Alliance
.
The requirements for membership in the Zigbee Alliance causes problems for open-source developers because the annual fee conflicts with the GNU General Public Licence. The requirement for the developer to join the ZigBee Alliance similarly conflicts with most other free software
licenses.
The ZigBee Smart Energy V2.0 specifications define an IP-based protocol
to monitor, control, inform and automate the delivery and use of energy and water. It is an enhancement of the ZigBee Smart Energy version 1 specifications, adding services for plug-in electric vehicle
(PEV) charging, installation, configuration and firmware download, prepay services, user information and messaging, load control, demand response and common information and application profile interfaces for wired and wireless networks. It is being developed by partners including:
In 2009 the RF4CE (Radio Frequency for Consumer Electronics) Consortium and ZigBee Alliance agreed to jointly deliver a standard for radio frequency remote controls. ZigBee RF4CE is designed for a wide range of consumer electronics products, such as TVs and set-top boxes. It promises many advantages over existing remote control solutions, including richer communication and increased reliability, enhanced features and flexibility, interoperability, and no line-of-sight barrier.
s and low power consumption. The resulting network will use very small amounts of power — individual devices must have a battery life of at least two years to pass ZigBee certification.
Typical application areas include:
) to automatically construct a low-speed ad-hoc network of nodes. In most large network instances, the network will be a cluster of clusters. It can also form a mesh or a single cluster. The current ZigBee protocols support beacon and non-beacon enabled networks.
In non-beacon-enabled networks, an unslotted CSMA/CA channel access mechanism is used. In this type of network, ZigBee Routers typically have their receivers continuously active, requiring a more robust power supply. However, this allows for heterogeneous networks in which some devices receive continuously, while others only transmit when an external stimulus is detected. The typical example of a heterogeneous network is a wireless light switch
: The ZigBee node at the lamp may receive constantly, since it is connected to the mains supply, while a battery-powered light switch would remain asleep until the switch is thrown. The switch then wakes up, sends a command to the lamp, receives an acknowledgment, and returns to sleep. In such a network the lamp node will be at least a ZigBee Router, if not the ZigBee Coordinator; the switch node is typically a ZigBee End Device.
In beacon-enabled networks, the special network nodes called ZigBee Routers transmit periodic beacons to confirm their presence to other network nodes. Nodes may sleep between beacons, thus lowering their duty cycle
and extending their battery life. Beacon intervals depend on data rate; they may range from 15.36 milliseconds to 251.65824 seconds at 250 kbit/s, from 24 milliseconds to 393.216 seconds at 40 kbit/s and from 48 milliseconds to 786.432 seconds at 20 kbit/s. However, low duty cycle operation with long beacon intervals requires precise timing, which can conflict with the need for low product cost.
In general, the ZigBee protocols minimize the time the radio is on, so as to reduce power use. In beaconing networks, nodes only need to be active while a beacon is being transmitted. In non-beacon-enabled networks, power consumption is decidedly asymmetrical: some devices are always active, while others spend most of their time sleeping.
Except for the Smart Energy Profile 2.0, ZigBee devices are required to conform to the IEEE 802.15.4-2003 Low-Rate Wireless Personal Area Network (LR-WPAN) standard. The standard specifies the lower protocol layers—the (physical layer
) (PHY), and the (media access control
) portion of the (data link layer
(DLL)). The basic channel access mode is "carrier sense, multiple access/collision avoidance" (CSMA/CA
). That is, the nodes talk in the same way that people converse; they briefly check to see that no one is talking before they start. There are three notable exceptions to the use of CSMA. Beacons are sent on a fixed timing schedule, and do not use CSMA. Message acknowledgments also do not use CSMA. Finally, devices in Beacon Oriented networks that have low latency real-time requirements may also use Guaranteed Time Slots (GTS), which by definition do not use CSMA.
and Bluetooth
were going to be unsuitable for many applications. In particular, many engineers saw a need for self-organizing ad-hoc digital radio networks.
The IEEE 802.15.4-2003 standard was completed in May 2003 and has been superseded by the publication of IEEE 802.15.4-2006. http://www.ieee802.org/15/pub/TG4.html
In the summer of 2003, Philips Semiconductors, a major mesh network supporter, ceased the investment. Philips Lighting has, however, continued Philips' participation, and Philips remains a promoter member on the ZigBee Alliance Board of Directors.
The ZigBee Alliance announced in October 2004 that the membership had more than doubled in the preceding year and had grown to more than 100 member companies, in 22 countries. By April 2005 membership had grown to more than 150 companies, and by December 2005 membership had passed 200 companies.
The ZigBee specifications were ratified on 14 December 2004. The ZigBee Alliance announced availability of Specification 1.0 on 13 June 2005, known as ZigBee 2004 Specification. In September 2006, ZigBee 2006 Specification is announced. In 2007, ZigBee PRO, the enhanced ZigBee specification was finalized.
The first stack
release is now called ZigBee 2004. The second stack release is called ZigBee 2006, and mainly replaces the MSG
/KVP
structure used in 2004 with a "cluster library". The 2004 stack is now more or less obsolete.
ZigBee 2007, now the current stack release, contains two stack profiles, stack profile 1 (simply called ZigBee), for home and light commercial use, and stack profile 2 (called ZigBee Pro). ZigBee Pro offers more features, such as multi-casting, many-to-one routing and high security with Symmetric-Key Key Exchange (SKKE), while ZigBee (stack profile 1) offers a smaller footprint in RAM and flash. Both offer full mesh networking and work with all ZigBee application profiles.
ZigBee 2007 is fully backward compatible with ZigBee 2006 devices: A ZigBee 2007 device may join and operate on a ZigBee 2006 network and vice versa. Due to differences in routing options, ZigBee Pro devices must become non-routing ZigBee End-Devices (ZEDs) on a ZigBee 2006 network, the same as for ZigBee 2006 devices on a ZigBee 2007 network must become ZEDs on a ZigBee Pro network. The applications running on those devices work the same, regardless of the stack profile beneath them.
The ZigBee 1.0 specification was ratified on 14 December 2004 and is available to members of the ZigBee Alliance. Most recently, the ZigBee 2007 specification was posted on 30 October 2007. The first ZigBee Application Profile, Home Automation, was announced 2 November 2007.
s wherever possible.
Though the radios themselves are inexpensive, the ZigBee Qualification Process involves a full validation of the requirements of the physical layer. All radios derived from the same validated semiconductor mask set would enjoy the same RF characteristics. An uncertified physical layer that malfunctions could cripple the battery lifespan of other devices on a ZigBee network. ZigBee radios have very tight constraints on power and bandwidth. Thus, radios are tested to the ISO 17025 standard with guidance given by Clause 6 of the 802.15.4-2006 Standard. Most vendors plan to integrate the radio and microcontroller onto a single chip getting smaller devices.
This standard specifies operation in the unlicensed 2.4 GHz
(worldwide), 915 MHz (Americas and Australia) and 868 MHz (Europe) ISM band
s. In the 2.4 GHz
band there are 16 ZigBee channels, with each channel requiring 5 MHz of bandwidth. The 2.4 GHz band provides up to 250 kbit/s, 915 MHz provides up to 40 kbit/s and 868 MHz provides a data rate up to 20 kbit/s. The actual data throughput will be less than the maximum specified bit rate due to the packet overhead and processing delays.
The radios use direct-sequence spread spectrum
coding, which is managed by the digital stream into the modulator. Binary phase-shift keying (BPSK) is used in the 868 and 915 MHz bands, and Offset quadrature phase-shift keying (OQPSK) that transmits four bits per symbol is used in the 2.4 GHz band. The raw, over-the-air data rate is 250 kbit
/s
per channel
in the 2.4 GHz band, 40 kbit/s per channel in the 915 MHz band, and 20 kbit/s in the 868 MHz band. Transmission range is between 10 and 75 meters (33 and 246 feet) and up to 1500 meters for zigbee pro, although it is heavily dependent on the particular environment. The output power of the radios is generally 0 dBm
(1 mW).
are to enable the correct use of the MAC sublayer and provide a suitable interface for use by the next upper layer, namely the application layer. Its capabilities and structure are those typically associated to such network layers, including routing.
On the one hand, the data entity creates and manages network layer data units from the payload of the application layer and performs routing according to the current topology. On the other hand, there is the layer control, which is used to handle configuration of new devices and establish new networks: it can determine whether a neighboring device belongs to the network and discovers new neighbors and routers. The control can also detect the presence of a receiver, which allows direct communication and MAC synchronization.
The routing protocol used by the Network layer is AODV. In order to find the destination device, it broadcasts out a route request to all of its neighbors. The neighbors then broadcast the request to their neighbors, etc. until the destination is reached. Once the destination is reached, it sends its route reply via unicast transmission following the lowest cost path back to the source. Once the source receives the reply, it will update its routing table for the destination address with the next hop in the path and the path cost.
) devices on the network and the identification of their offered services. It may then go on to establish secure links with external devices and reply to binding requests accordingly.
The application support sublayer (APS) is the other main standard component of the layer, and as such it offers a well-defined interface and control services. It works as a bridge between the network layer and the other components of the application layer: it keeps up-to-date binding tables in the form of a database, which can be used to find appropriate devices depending on the services that are needed and those the different devices offer. As the union between both specified layers, it also routes messages across the layers of the protocol stack
.
 An application may consist of communicating objects which cooperate to carry out the desired tasks. The focus of ZigBee is to distribute work among many different devices which reside within individual ZigBee nodes which in turn form a network (said work will typically be largely local to each device, for instance the control of each individual household appliance).
An application may consist of communicating objects which cooperate to carry out the desired tasks. The focus of ZigBee is to distribute work among many different devices which reside within individual ZigBee nodes which in turn form a network (said work will typically be largely local to each device, for instance the control of each individual household appliance).
The collection of objects that form the network communicate using the facilities provided by APS, supervised by ZDO interfaces. The application layer data service follows a typical request-confirm/indication-response structure. Within a single device, up to 240 application objects can exist, numbered in the range 1-240. 0 is reserved for the ZDO data interface and 255 for broadcast; the 241-254 range is not currently in use but may be in the future.
There are two services available for application objects to use (in ZigBee 1.0):
Addressing is also part of the application layer. A network node consists of an 802.15.4-conformant radio transceiver
and one or more device descriptions (basically collections of attributes which can be polled or set, or which can be monitored through events). The transceiver is the base for addressing, and devices within a node are specified by an endpoint identifier in the range 1-240.
Depending on the available information, device discovery may follow different methods. When the network address is known, the IEEE address can be requested using unicast
communication. When it is not, petitions are broadcast
(the IEEE address being part of the response payload). End devices will simply respond with the requested address, while a network coordinator or a router will also send the addresses of all the devices associated with it.
This extended discovery protocol permits external devices to find out about devices in a network and the services that they offer, which endpoints can report when queried by the discovering device (which has previously obtained their addresses). Matching services can also be used.
The use of cluster identifiers enforces the binding of complementary entities by means of the binding tables, which are maintained by ZigBee coordinators, as the table must be always available within a network and coordinators are most likely to have a permanent power supply. Backups, managed by higher-level layers, may be needed by some applications. Binding requires an established communication link; after it exists, whether to add a new node to the network is decided, according to the application and security policies.
Communication can happen right after the association. Direct addressing uses both radio address and endpoint identifier, whereas indirect addressing uses every relevant field (address, endpoint, cluster and attribute) and requires that they be sent to the network coordinator, which maintains associations and translates requests for communication. Indirect addressing is particularly useful to keep some devices very simple and minimize their need for storage. Besides these two methods, broadcast to all endpoints in a device is available, and group addressing
is used to communicate with groups of endpoints belonging to a set of devices.
Keys are the cornerstone of the security architecture; as such their protection is of paramount importance, and keys are never supposed to be transported through an insecure channel. There is a momentary exception to this rule, which occurs during the initial phase of the addition to the network of a previously unconfigured device. The ZigBee network model must take particular care of security considerations, as ad hoc networks may be physically accessible to external devices and the particular working environment cannot be foretold; likewise, different applications running concurrently and using the same transceiver to communicate are supposed to be mutually trustworthy: for cost reasons the model does not assume a firewall exists between application-level entities.
Within the protocol stack, different network layers are not cryptographically separated, so access policies are needed and correct design assumed. The open trust model within a device allows for key sharing, which notably decreases potential cost. Nevertheless, the layer which creates a frame is responsible for its security. If malicious devices may exist, every network layer payload must be ciphered, so unauthorized traffic can be immediately cut off. The exception, again, is the transmission of the network key, which confers a unified security layer to the network, to a new connecting device.
Key distribution is one of the most important security functions of the network. A secure network will designate one special device which other devices trust for the distribution of security keys: the trust center. Ideally, devices will have the trust center address and initial master key preloaded; if a momentary vulnerability is allowed, it will be sent as described above. Typical applications without special security needs will use a network key provided by the trust center (through the initially insecure channel) to communicate.
Thus, the trust center maintains both the network key and provides point-to-point security. Devices will only accept communications originating from a key provided by the trust center, except for the initial master key. The security architecture is distributed among the network layers as follows:
The security levels infrastructure is based on CCM*, which adds encryption- and integrity-only features to CCM
.
Specification (technical standard)
A specification is an explicit set of requirements to be satisfied by a material, product, or service. Should a material, product or service fail to meet one or more of the applicable specifications, it may be referred to as being out of specification;the abbreviation OOS may also be used...
for a suite of high level communication protocols using small, low-power digital radio
Digital radio
Digital radio has several meanings:1. Today the most common meaning is digital radio broadcasting technologies, such as the digital audio broadcasting system, also known as Eureka 147. In these systems, the analog audio signal is digitized into zeros and ones, compressed using formats such as...
s based on an IEEE 802 standard
IEEE 802.15.4
IEEE 802.15.4 is a standard which specifies the physical layer and media access control for low-rate wireless personal area networks . It is maintained by the IEEE 802.15 working group....
for personal area network
Personal area network
A personal area network is a computer network used for communication among computer devices, including telephones and personal digital assistants, in proximity to an individual's body. The devices may or may not belong to the person in question. The reach of a PAN is typically a few meters...
s. Applications include wireless light switches, electrical meters with in-home-displays, and other consumer and industrial equipment that requires short-range wireless transfer of data at relatively low rates. The technology defined by the ZigBee specification is intended to be simpler and less expensive than other WPANs, such as Bluetooth
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a proprietary open wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances from fixed and mobile devices, creating personal area networks with high levels of security...
. ZigBee is targeted at radio-frequency
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
(RF) applications that require a low data rate, long battery life, and secure networking. ZigBee has a defined rate of 250 kbps best suited for periodic or intermittent data or a single signal transmission from a sensor or input device.
The name refers to the waggle dance
Waggle dance
Waggle dance is a term used in beekeeping and ethology for a particular figure-eight dance of the honey bee. By performing this dance, successful foragers can share with their hive mates information about the direction and distance to patches of flowers yielding nectar and pollen, to water...
of honey bees after their return to the beehive.
Technical overview
ZigBee is a low-cost, low-power, wireless mesh networkWireless mesh network
A wireless mesh network is a communications network made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology. Wireless mesh networks often consist of mesh clients, mesh routers and gateways.The mesh clients are often laptops, cell phones and other wireless devices while the mesh routers forward traffic...
standard. The low cost allows the technology to be widely deployed in wireless control and monitoring applications. Low power-usage allows longer life with smaller batteries. Mesh networking provides high reliability and more extensive range. ZigBee chip vendors typically sell integrated radios and microcontrollers with between 60 KB and 256 KB flash memory.
ZigBee operates in the industrial, scientific and medical (ISM
ISM band
The industrial, scientific and medical radio bands are radio bands reserved internationally for the use of radio frequency energy for industrial, scientific and medical purposes other than communications....
) radio bands; 868 MHz in Europe, 915 MHz in the USA and Australia, and 2.4 GHz in most jurisdictions worldwide. Data transmission rates vary from 20 to 250 kilobits/second.
The ZigBee network layer natively supports both star
Star network
Star networks are one of the most common computer network topologies. In its simplest form, a star network consists of one central switch, hub or computer, which acts as a conduit to transmit messages...
and tree typical networks, and generic mesh networks. Every network must have one coordinator device, tasked with its creation, the control of its parameters and basic maintenance. Within star networks, the coordinator must be the central node. Both trees and meshes allows the use of ZigBee routers
Routing
Routing is the process of selecting paths in a network along which to send network traffic. Routing is performed for many kinds of networks, including the telephone network , electronic data networks , and transportation networks...
to extend communication at the network level.

Physical layer
The physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer in the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. The implementation of this layer is often termed PHY....
and medium access control defined in IEEE standard 802.15.4
IEEE 802.15.4
IEEE 802.15.4 is a standard which specifies the physical layer and media access control for low-rate wireless personal area networks . It is maintained by the IEEE 802.15 working group....
(2003 version) for low-rate WPAN's. The specification goes on to complete the standard by adding four main components: network layer, application layer, ZigBee device objects (ZDOs) and manufacturer-defined application objects which allow for customization and favor total integration.
Besides adding two high-level network layers to the underlying structure, the most significant improvement is the introduction of ZDO's. These are responsible for a number of tasks, which include keeping of device roles, management of requests to join a network, device discovery and security.
ZigBee is not intended to support powerline networking
Power line communication
Power line communication or power line carrier , also known as power line digital subscriber line , mains communication, power line telecom , power line networking , or broadband over power lines are systems for carrying data on a conductor also used for electric power transmission.A wide range...
but to interface with it at least for smart meter
Smart meter
A smart meter is usually an electrical meter that records consumption of electric energy in intervals of an hour or less and communicates that information at least daily back to the utility for monitoring and billing purposes. Smart meters enable two-way communication between the meter and the...
ing and smart appliance purposes.
Because ZigBee nodes can go from sleep to active mode in 30 ms or less, the latency can be low and devices can be responsive, particularly compared to Bluetooth wake-up delays, which are typically around three seconds.
Because ZigBee nodes can sleep most of the time, average power consumption can be low, resulting in long battery life.
Trademark and alliance
The ZigBee Alliance is a group of companies that maintain and publish the ZigBee standard. The term ZigBee is a registered trademarkTrademark
A trademark, trade mark, or trade-mark is a distinctive sign or indicator used by an individual, business organization, or other legal entity to identify that the products or services to consumers with which the trademark appears originate from a unique source, and to distinguish its products or...
of this group, not a single technical standard. The Alliance publishes application profile
Application profile
In computer science, an application profile is a set of metadata elements, policies, and guidelines defined for a particular application.The elements may be from one or more element sets, thus allowing a given application to meet its functional requirements by using metadata from several element...
s that allow multiple OEM
Original Equipment Manufacturer
An original equipment manufacturer, or OEM, manufactures products or components that are purchased by a company and retailed under that purchasing company's brand name. OEM refers to the company that originally manufactured the product. When referring to automotive parts, OEM designates a...
vendors to create interoperable products. The relationship between IEEE 802.15.4
IEEE 802.15.4
IEEE 802.15.4 is a standard which specifies the physical layer and media access control for low-rate wireless personal area networks . It is maintained by the IEEE 802.15 working group....
and ZigBee is similar to that between IEEE 802.11
IEEE 802.11
IEEE 802.11 is a set of standards for implementing wireless local area network computer communication in the 2.4, 3.6 and 5 GHz frequency bands. They are created and maintained by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee . The base version of the standard IEEE 802.11-2007 has had subsequent...
and the Wi-Fi Alliance
Wi-Fi Alliance
The Wi-Fi Alliance is a trade association that promotes Wireless LAN technology and certifies products if they conform to certain standards of interoperability. Not every IEEE 802.11-compliant device is submitted for certification to the Wi-Fi Alliance, sometimes because of costs associated with...
.
License
For non-commercial purposes, the ZigBee specification is available free to the general public. An entry level membership in the ZigBee Alliance, called Adopter, provides access to the as-yet unpublished specifications and permission to create products for market using the specifications.The requirements for membership in the Zigbee Alliance causes problems for open-source developers because the annual fee conflicts with the GNU General Public Licence. The requirement for the developer to join the ZigBee Alliance similarly conflicts with most other free software
Free software
Free software, software libre or libre software is software that can be used, studied, and modified without restriction, and which can be copied and redistributed in modified or unmodified form either without restriction, or with restrictions that only ensure that further recipients can also do...
licenses.
Application profiles
The current list of application profiles either published, or in the works are:- Released specifications
- ZigBee Home Automation
- ZigBee Smart Energy 1.0
- ZigBee Telecommunication Services
- ZigBee Health Care
- ZigBee RF4CE - Remote Control
- Specifications under development
- ZigBee Smart Energy 2.0
- ZigBee Building Automation
- ZigBee Retail Services
The ZigBee Smart Energy V2.0 specifications define an IP-based protocol
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol is the principal communications protocol used for relaying datagrams across an internetwork using the Internet Protocol Suite...
to monitor, control, inform and automate the delivery and use of energy and water. It is an enhancement of the ZigBee Smart Energy version 1 specifications, adding services for plug-in electric vehicle
Plug-in electric vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle is any motor vehicle that can be recharged from any external source of electricity, such as wall sockets, and the electricity stored in the rechargeable battery packs drives or contributes to drive the wheels...
(PEV) charging, installation, configuration and firmware download, prepay services, user information and messaging, load control, demand response and common information and application profile interfaces for wired and wireless networks. It is being developed by partners including:
- HomeGrid Forum responsible for marketing and certifying ITU-T G.hnG.hnG.hn is the common name for a home network technology family of standards developed under the International Telecommunication Union's Standardization arm and promoted by the HomeGrid Forum...
technology and products - HomePlugHomePlugHomePlug is the family name for various power line communications specifications that support networking over existing home electrical wiring. Several specifications exist under the HomePlug moniker, with each offering unique performance capabilities and coexistence or compatibility with other...
Powerline Alliance - International Society of Automative Engineers SAE InternationalSAE InternationalSAE International is an organization for engineering professionals in the aerospace, automotive, and commercial vehicle industries. The Society is a standards development organization for the engineering of powered vehicles of all kinds, including cars, trucks, boats, aircraft, and others.SAE...
- IPSO Alliance
- SunSpec Alliance
- Wi-Fi AllianceWi-Fi AllianceThe Wi-Fi Alliance is a trade association that promotes Wireless LAN technology and certifies products if they conform to certain standards of interoperability. Not every IEEE 802.11-compliant device is submitted for certification to the Wi-Fi Alliance, sometimes because of costs associated with...
.
In 2009 the RF4CE (Radio Frequency for Consumer Electronics) Consortium and ZigBee Alliance agreed to jointly deliver a standard for radio frequency remote controls. ZigBee RF4CE is designed for a wide range of consumer electronics products, such as TVs and set-top boxes. It promises many advantages over existing remote control solutions, including richer communication and increased reliability, enhanced features and flexibility, interoperability, and no line-of-sight barrier.
Uses
ZigBee protocols are intended for embedded applications requiring low data rateData rate
Data rate can refer to:* Bit rate, or data transfer rate* Data signaling rate* Data rate units-See also:* Baud rate* Channel capacity* Throughput* Bandwidth everything in this page is falsified...
s and low power consumption. The resulting network will use very small amounts of power — individual devices must have a battery life of at least two years to pass ZigBee certification.
Typical application areas include:
- Home Entertainment and Control — Home automationHome automationHome automation is the residential extension of "building automation". It is automation of the home, housework or household activity. Home automation may include centralized control of lighting, HVAC , appliances, and other systems, to provide improved convenience, comfort, energy efficiency and...
, smart lighting, advanced temperature control, safety and security, movies and music - Wireless Sensor Networks' — Starting with individual sensors like Telosb/Tmote and Iris from Memsic.
- Industrial control,
- Embedded sensing,
- Medical data collection,
- Smoke and intruder warning,
- Building automation.
Device types
There are three different types of ZigBee devices:- ZigBee coordinator (ZC): The most capable device, the coordinator forms the root of the network tree and might bridge to other networks. There is exactly one ZigBee coordinator in each network since it is the device that started the network originally. It is able to store information about the network, including acting as the Trust Center & repository for security keys.
- ZigBee Router (ZR): As well as running an application function, a router can act as an intermediate router, passing on data from other devices.
- ZigBee End Device (ZED): Contains just enough functionality to talk to the parent node (either the coordinator or a router); it cannot relay data from other devices. This relationship allows the node to be asleep a significant amount of the time thereby giving long battery life. A ZED requires the least amount of memory, and therefore can be less expensive to manufacture than a ZR or ZC.
Protocols
The protocols build on recent algorithmic research (Ad-hoc On-demand Distance Vector, neuRFonNeuRFon
The neuRFon project was a research program begun in 1999 at Motorola Labs to develop ad hoc wireless networking for wireless sensor network applications...
) to automatically construct a low-speed ad-hoc network of nodes. In most large network instances, the network will be a cluster of clusters. It can also form a mesh or a single cluster. The current ZigBee protocols support beacon and non-beacon enabled networks.
In non-beacon-enabled networks, an unslotted CSMA/CA channel access mechanism is used. In this type of network, ZigBee Routers typically have their receivers continuously active, requiring a more robust power supply. However, this allows for heterogeneous networks in which some devices receive continuously, while others only transmit when an external stimulus is detected. The typical example of a heterogeneous network is a wireless light switch
Wireless light switch
A wireless light switch is a light switch that commands a light or home appliance to turn itself off or on, instead of interrupting the power line going to the light fixture...
: The ZigBee node at the lamp may receive constantly, since it is connected to the mains supply, while a battery-powered light switch would remain asleep until the switch is thrown. The switch then wakes up, sends a command to the lamp, receives an acknowledgment, and returns to sleep. In such a network the lamp node will be at least a ZigBee Router, if not the ZigBee Coordinator; the switch node is typically a ZigBee End Device.
In beacon-enabled networks, the special network nodes called ZigBee Routers transmit periodic beacons to confirm their presence to other network nodes. Nodes may sleep between beacons, thus lowering their duty cycle
Duty cycle
In engineering, the duty cycle of a machine or system is the time that it spends in an active state as a fraction of the total time under consideration....
and extending their battery life. Beacon intervals depend on data rate; they may range from 15.36 milliseconds to 251.65824 seconds at 250 kbit/s, from 24 milliseconds to 393.216 seconds at 40 kbit/s and from 48 milliseconds to 786.432 seconds at 20 kbit/s. However, low duty cycle operation with long beacon intervals requires precise timing, which can conflict with the need for low product cost.
In general, the ZigBee protocols minimize the time the radio is on, so as to reduce power use. In beaconing networks, nodes only need to be active while a beacon is being transmitted. In non-beacon-enabled networks, power consumption is decidedly asymmetrical: some devices are always active, while others spend most of their time sleeping.
Except for the Smart Energy Profile 2.0, ZigBee devices are required to conform to the IEEE 802.15.4-2003 Low-Rate Wireless Personal Area Network (LR-WPAN) standard. The standard specifies the lower protocol layers—the (physical layer
Physical layer
The physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer in the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. The implementation of this layer is often termed PHY....
) (PHY), and the (media access control
Media Access Control
The media access control data communication protocol sub-layer, also known as the medium access control, is a sublayer of the data link layer specified in the seven-layer OSI model , and in the four-layer TCP/IP model...
) portion of the (data link layer
Data link layer
The data link layer is layer 2 of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. It corresponds to, or is part of the link layer of the TCP/IP reference model....
(DLL)). The basic channel access mode is "carrier sense, multiple access/collision avoidance" (CSMA/CA
Carrier Sense Multiple Access
Carrier Sense Multiple Access is a probabilistic Media Access Control protocol in which a node verifies the absence of other traffic before transmitting on a shared transmission medium, such as an electrical bus, or a band of the electromagnetic spectrum."Carrier Sense" describes the fact that a...
). That is, the nodes talk in the same way that people converse; they briefly check to see that no one is talking before they start. There are three notable exceptions to the use of CSMA. Beacons are sent on a fixed timing schedule, and do not use CSMA. Message acknowledgments also do not use CSMA. Finally, devices in Beacon Oriented networks that have low latency real-time requirements may also use Guaranteed Time Slots (GTS), which by definition do not use CSMA.
History
ZigBee-style networks began to be conceived around 1998, when many installers realized that both Wi-FiWi-Fi
Wi-Fi or Wifi, is a mechanism for wirelessly connecting electronic devices. A device enabled with Wi-Fi, such as a personal computer, video game console, smartphone, or digital audio player, can connect to the Internet via a wireless network access point. An access point has a range of about 20...
and Bluetooth
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a proprietary open wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances from fixed and mobile devices, creating personal area networks with high levels of security...
were going to be unsuitable for many applications. In particular, many engineers saw a need for self-organizing ad-hoc digital radio networks.
The IEEE 802.15.4-2003 standard was completed in May 2003 and has been superseded by the publication of IEEE 802.15.4-2006. http://www.ieee802.org/15/pub/TG4.html
In the summer of 2003, Philips Semiconductors, a major mesh network supporter, ceased the investment. Philips Lighting has, however, continued Philips' participation, and Philips remains a promoter member on the ZigBee Alliance Board of Directors.
The ZigBee Alliance announced in October 2004 that the membership had more than doubled in the preceding year and had grown to more than 100 member companies, in 22 countries. By April 2005 membership had grown to more than 150 companies, and by December 2005 membership had passed 200 companies.
The ZigBee specifications were ratified on 14 December 2004. The ZigBee Alliance announced availability of Specification 1.0 on 13 June 2005, known as ZigBee 2004 Specification. In September 2006, ZigBee 2006 Specification is announced. In 2007, ZigBee PRO, the enhanced ZigBee specification was finalized.
The first stack
Stack
-Mathematics:* Stack , general category-theoretical concept to formalise "pull-back" operations in geometry and algebra* Algebraic stack, a generalisation of scheme and algebraic space in algebraic geometry; a specific type of the above-Computers:...
release is now called ZigBee 2004. The second stack release is called ZigBee 2006, and mainly replaces the MSG
MSG
MSG or msg may refer to:* Monosodium glutamate, a common food additive** See also glutamic acid for MSG's use in food flavoring and health concerns* A common abbreviation for message* Madison Square Garden, a sports arena in New York City...
/KVP
KVP
KVP could refer to:*Katholieke Volkspartij, a Dutch political party*Kalamazoo Vegetable Parchment, a defunct papermill once headquartered in Parchment, Michigan, USA*Karur Vysya Bank...
structure used in 2004 with a "cluster library". The 2004 stack is now more or less obsolete.
ZigBee 2007, now the current stack release, contains two stack profiles, stack profile 1 (simply called ZigBee), for home and light commercial use, and stack profile 2 (called ZigBee Pro). ZigBee Pro offers more features, such as multi-casting, many-to-one routing and high security with Symmetric-Key Key Exchange (SKKE), while ZigBee (stack profile 1) offers a smaller footprint in RAM and flash. Both offer full mesh networking and work with all ZigBee application profiles.
ZigBee 2007 is fully backward compatible with ZigBee 2006 devices: A ZigBee 2007 device may join and operate on a ZigBee 2006 network and vice versa. Due to differences in routing options, ZigBee Pro devices must become non-routing ZigBee End-Devices (ZEDs) on a ZigBee 2006 network, the same as for ZigBee 2006 devices on a ZigBee 2007 network must become ZEDs on a ZigBee Pro network. The applications running on those devices work the same, regardless of the stack profile beneath them.
The ZigBee 1.0 specification was ratified on 14 December 2004 and is available to members of the ZigBee Alliance. Most recently, the ZigBee 2007 specification was posted on 30 October 2007. The first ZigBee Application Profile, Home Automation, was announced 2 November 2007.
Radio hardware
The radio design used by ZigBee has been carefully optimized for low cost in large scale production. It has few analog stages and uses digital circuitDigital circuit
Digital electronics represent signals by discrete bands of analog levels, rather than by a continuous range. All levels within a band represent the same signal state...
s wherever possible.
Though the radios themselves are inexpensive, the ZigBee Qualification Process involves a full validation of the requirements of the physical layer. All radios derived from the same validated semiconductor mask set would enjoy the same RF characteristics. An uncertified physical layer that malfunctions could cripple the battery lifespan of other devices on a ZigBee network. ZigBee radios have very tight constraints on power and bandwidth. Thus, radios are tested to the ISO 17025 standard with guidance given by Clause 6 of the 802.15.4-2006 Standard. Most vendors plan to integrate the radio and microcontroller onto a single chip getting smaller devices.
This standard specifies operation in the unlicensed 2.4 GHz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
(worldwide), 915 MHz (Americas and Australia) and 868 MHz (Europe) ISM band
ISM band
The industrial, scientific and medical radio bands are radio bands reserved internationally for the use of radio frequency energy for industrial, scientific and medical purposes other than communications....
s. In the 2.4 GHz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
band there are 16 ZigBee channels, with each channel requiring 5 MHz of bandwidth. The 2.4 GHz band provides up to 250 kbit/s, 915 MHz provides up to 40 kbit/s and 868 MHz provides a data rate up to 20 kbit/s. The actual data throughput will be less than the maximum specified bit rate due to the packet overhead and processing delays.
The radios use direct-sequence spread spectrum
Direct-sequence spread spectrum
In telecommunications, direct-sequence spread spectrum is a modulation technique. As with other spread spectrum technologies, the transmitted signal takes up more bandwidth than the information signal that is being modulated. The name 'spread spectrum' comes from the fact that the carrier signals...
coding, which is managed by the digital stream into the modulator. Binary phase-shift keying (BPSK) is used in the 868 and 915 MHz bands, and Offset quadrature phase-shift keying (OQPSK) that transmits four bits per symbol is used in the 2.4 GHz band. The raw, over-the-air data rate is 250 kbit
Kilobit
The kilobit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information or computer storage. The prefix kilo is defined in the International System of Units as a multiplier of 103 , and therefore,...
/s
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
per channel
Channel (communications)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
in the 2.4 GHz band, 40 kbit/s per channel in the 915 MHz band, and 20 kbit/s in the 868 MHz band. Transmission range is between 10 and 75 meters (33 and 246 feet) and up to 1500 meters for zigbee pro, although it is heavily dependent on the particular environment. The output power of the radios is generally 0 dBm
DBm
dBm is an abbreviation for the power ratio in decibels of the measured power referenced to one milliwatt . It is used in radio, microwave and fiber optic networks as a convenient measure of absolute power because of its capability to express both very large and very small values in a short form...
(1 mW).
Network layer
The main functions of the network layerNetwork layer
The network layer is layer 3 of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking.The network layer is responsible for packet forwarding including routing through intermediate routers, whereas the data link layer is responsible for media access control, flow control and error checking.The network...
are to enable the correct use of the MAC sublayer and provide a suitable interface for use by the next upper layer, namely the application layer. Its capabilities and structure are those typically associated to such network layers, including routing.
On the one hand, the data entity creates and manages network layer data units from the payload of the application layer and performs routing according to the current topology. On the other hand, there is the layer control, which is used to handle configuration of new devices and establish new networks: it can determine whether a neighboring device belongs to the network and discovers new neighbors and routers. The control can also detect the presence of a receiver, which allows direct communication and MAC synchronization.
The routing protocol used by the Network layer is AODV. In order to find the destination device, it broadcasts out a route request to all of its neighbors. The neighbors then broadcast the request to their neighbors, etc. until the destination is reached. Once the destination is reached, it sends its route reply via unicast transmission following the lowest cost path back to the source. Once the source receives the reply, it will update its routing table for the destination address with the next hop in the path and the path cost.
Application layer
The application layer is the highest-level layer defined by the specification, and is the effective interface of the ZigBee system to its end users. It comprises the majority of components added by the ZigBee specification: both ZDO and its management procedures, together with application objects defined by the manufacturer, are considered part of this layer.Main components
The ZDO is responsible for defining the role of a device as either coordinator or end device, as mentioned above, but also for the discovery of new (one-hopHop (telecommunications)
In telecommunication, the term hop has the following meanings:#The excursion of a radio wave from the Earth to the ionosphere and back to the Earth...
) devices on the network and the identification of their offered services. It may then go on to establish secure links with external devices and reply to binding requests accordingly.
The application support sublayer (APS) is the other main standard component of the layer, and as such it offers a well-defined interface and control services. It works as a bridge between the network layer and the other components of the application layer: it keeps up-to-date binding tables in the form of a database, which can be used to find appropriate devices depending on the services that are needed and those the different devices offer. As the union between both specified layers, it also routes messages across the layers of the protocol stack
Protocol stack
The protocol stack is an implementation of a computer networking protocol suite. The terms are often used interchangeably. Strictly speaking, the suite is the definition of the protocols, and the stack is the software implementation of them....
.
Communication models

The collection of objects that form the network communicate using the facilities provided by APS, supervised by ZDO interfaces. The application layer data service follows a typical request-confirm/indication-response structure. Within a single device, up to 240 application objects can exist, numbered in the range 1-240. 0 is reserved for the ZDO data interface and 255 for broadcast; the 241-254 range is not currently in use but may be in the future.
There are two services available for application objects to use (in ZigBee 1.0):
- The key-value pairAssociative arrayIn computer science, an associative array is an abstract data type composed of a collection of pairs, such that each possible key appears at most once in the collection....
service (KVP) is meant for configuration purposes. It enables description, request and modification of object attributes through a simple interface based on get/set and event primitives, some allowing a request for response. Configuration uses compressed XMLXMLExtensible Markup Language is a set of rules for encoding documents in machine-readable form. It is defined in the XML 1.0 Specification produced by the W3C, and several other related specifications, all gratis open standards....
(full XML can be used) to provide an adaptable and elegant solution. - The message service is designed to offer a general approach to information treatment, avoiding the necessity to adapt application protocols and potential overhead incurred on by KPV. It allows arbitrary payloads to be transmitted over APS frames.
Addressing is also part of the application layer. A network node consists of an 802.15.4-conformant radio transceiver
Transceiver
A transceiver is a device comprising both a transmitter and a receiver which are combined and share common circuitry or a single housing. When no circuitry is common between transmit and receive functions, the device is a transmitter-receiver. The term originated in the early 1920s...
and one or more device descriptions (basically collections of attributes which can be polled or set, or which can be monitored through events). The transceiver is the base for addressing, and devices within a node are specified by an endpoint identifier in the range 1-240.
Communication and device discovery
In order for applications to communicate, their comprising devices must use a common application protocol (types of messages, formats and so on); these sets of conventions are grouped in profiles. Furthermore, binding is decided upon by matching input and output cluster identifiers, unique within the context of a given profile and associated to an incoming or outgoing data flow in a device. Binding tables contain source and destination pairs.Depending on the available information, device discovery may follow different methods. When the network address is known, the IEEE address can be requested using unicast
Unicast
right|200pxIn computer networking, unicast transmission is the sending of messages to a single network destination identified by a unique address.-Addressing methodologies:...
communication. When it is not, petitions are broadcast
Broadcast
Broadcast or Broadcasting may refer to:* Broadcasting, the transmission of audio and video signals* Broadcast, an individual television program or radio program* Broadcast , an English electronic music band...
(the IEEE address being part of the response payload). End devices will simply respond with the requested address, while a network coordinator or a router will also send the addresses of all the devices associated with it.
This extended discovery protocol permits external devices to find out about devices in a network and the services that they offer, which endpoints can report when queried by the discovering device (which has previously obtained their addresses). Matching services can also be used.
The use of cluster identifiers enforces the binding of complementary entities by means of the binding tables, which are maintained by ZigBee coordinators, as the table must be always available within a network and coordinators are most likely to have a permanent power supply. Backups, managed by higher-level layers, may be needed by some applications. Binding requires an established communication link; after it exists, whether to add a new node to the network is decided, according to the application and security policies.
Communication can happen right after the association. Direct addressing uses both radio address and endpoint identifier, whereas indirect addressing uses every relevant field (address, endpoint, cluster and attribute) and requires that they be sent to the network coordinator, which maintains associations and translates requests for communication. Indirect addressing is particularly useful to keep some devices very simple and minimize their need for storage. Besides these two methods, broadcast to all endpoints in a device is available, and group addressing
Multicast
In computer networking, multicast is the delivery of a message or information to a group of destination computers simultaneously in a single transmission from the source creating copies automatically in other network elements, such as routers, only when the topology of the network requires...
is used to communicate with groups of endpoints belonging to a set of devices.
Security services
As one of its defining features, ZigBee provides facilities for carrying out secure communications, protecting establishment and transport of cryptographic keys, cyphering frames and controlling devices. It builds on the basic security framework defined in IEEE 802.15.4. This part of the architecture relies on the correct management of symmetric keys and the correct implementation of methods and security policies.Basic security model
The basic mechanism to ensure confidentiality is the adequate protection of all keying material. Trust must be assumed in the initial installation of the keys, as well as in the processing of security information. In order for an implementation to globally work, its general correctness (e.g., conformance to specified behaviors) is assumed.Keys are the cornerstone of the security architecture; as such their protection is of paramount importance, and keys are never supposed to be transported through an insecure channel. There is a momentary exception to this rule, which occurs during the initial phase of the addition to the network of a previously unconfigured device. The ZigBee network model must take particular care of security considerations, as ad hoc networks may be physically accessible to external devices and the particular working environment cannot be foretold; likewise, different applications running concurrently and using the same transceiver to communicate are supposed to be mutually trustworthy: for cost reasons the model does not assume a firewall exists between application-level entities.
Within the protocol stack, different network layers are not cryptographically separated, so access policies are needed and correct design assumed. The open trust model within a device allows for key sharing, which notably decreases potential cost. Nevertheless, the layer which creates a frame is responsible for its security. If malicious devices may exist, every network layer payload must be ciphered, so unauthorized traffic can be immediately cut off. The exception, again, is the transmission of the network key, which confers a unified security layer to the network, to a new connecting device.
Security architecture
ZigBee uses 128-bit keys to implement its security mechanisms. A key can be associated either to a network, being usable by both ZigBee layers and the MAC sublayer, or to a link, acquired through pre-installation, agreement or transport. Establishment of link keys is based on a master key which controls link key correspondence. Ultimately, at least the initial master key must be obtained through a secure medium (transport or pre-installation), as the security of the whole network depends on it. Link and master keys are only visible to the application layer. Different services use different one-way variations of the link key in order to avoid leaks and security risks.Key distribution is one of the most important security functions of the network. A secure network will designate one special device which other devices trust for the distribution of security keys: the trust center. Ideally, devices will have the trust center address and initial master key preloaded; if a momentary vulnerability is allowed, it will be sent as described above. Typical applications without special security needs will use a network key provided by the trust center (through the initially insecure channel) to communicate.
Thus, the trust center maintains both the network key and provides point-to-point security. Devices will only accept communications originating from a key provided by the trust center, except for the initial master key. The security architecture is distributed among the network layers as follows:
- The MAC sublayer is capable of single-hop reliable communications. As a rule, the security level it is to use is specified by the upper layers.
- The network layer manages routing, processing received messages and being capable of broadcasting requests. Outgoing frames will use the adequate link key according to the routing, if it is available; otherwise, the network key will be used to protect the payload from external devices.
- The application layer offers key establishment and transport services to both ZDO and applications. It is also responsible for the propagation across the network of changes in devices within it, which may originate in the devices themselves (for instance, a simple status change) or in the trust manager (which may inform the network that a certain device is to be eliminated from it). It also routes requests from devices to the trust center and network key renewals from the trust center to all devices. Besides this, the ZDO maintains the security policies of the device.
The security levels infrastructure is based on CCM*, which adds encryption- and integrity-only features to CCM
CCM mode
CCM mode is a mode of operation for cryptographic block ciphers. It is an authenticated encryption algorithm designed to provide both authentication and confidentiality. CCM mode is only defined for block ciphers with a block length of 128 bits...
.
Chip vendors/devices include
To become ZigBee certified as a semiconductor company, vendors must ensure their applications are interoperable. Periodic interoperability events verify that devices work with other certified devices.- AtmelAtmelAtmel Corporation is a manufacturer of semiconductors, founded in 1984. Its focus is on system-level solutions built around flash microcontrollers...
ATmega128RFA1, AT86RF230/231 - Digi InternationalDigi InternationalDigi International was founded in 1985 as DigiBoard and is headquartered in Minnetonka, Minnesota, USA. The company went public as Digi International in 1989 and is traded on the NASDAQ National Market under the symbol DGII. The company initially offered intelligent ISA/PCI boards with multiple...
XBee XB24CZ7PIS-004 - Ember EM250, EM351, EM357
- Freescale MC13224
- GreenPeak GP520-GP530-GP540
- Jennic JN5148
- RadioPulse MG2410, MG2450/55, and MG2470
- RenesasRenesas Electronicsis a Japanese semiconductor manufacturer. It is based in Tokyo and has manufacturing, design and sales operations in around 20 countries. Renesas is one of the world's largest manufacturers of semiconductor systems for mobile phones and automotive applications. It is the world's largest...
uPD78F8056/57/58, M16C/6B3 and R8C/3MQ - Sena Technologies Inc., ProBee, ProBee-ZU/ProBee-ZS/ProBee-ZE
- STMicroelectronicsSTMicroelectronicsSTMicroelectronics is an Italian-French electronics and semiconductor manufacturer headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.While STMicroelectronics corporate headquarters and the headquarters for EMEA region are based in Geneva, the holding company, STMicroelectronics N.V. is registered in Amsterdam,...
STM32W - Samsung Electro-Mechanics ZBS240
- Telegesis ETRX357(HR)
- Texas InstrumentsTexas InstrumentsTexas Instruments Inc. , widely known as TI, is an American company based in Dallas, Texas, United States, which develops and commercializes semiconductor and computer technology...
CC2530 and CC2520 - Microchip Zigbee MRF24J40MB
- muRataMurataIn Japanese, Murata means ‘village rice paddy’. It is a surname and also a company name that is found throughout Japan, but not in large numbers...
Zigbee Module
See also
- BluetoothBluetoothBluetooth is a proprietary open wireless technology standard for exchanging data over short distances from fixed and mobile devices, creating personal area networks with high levels of security...
- 6loWPAN6loWPAN6LoWPAN is an acronym of IPv6 over Low power Wireless Personal Area Networks. 6lowpan is the name of a working group in the internet area of the IETF....
- Comparison of 802.15.4 radio modulesComparison of 802.15.4 radio modulesThis table lists production ready-to-use modules only, not radio chips. A ready-to-use module is a complete MCU+Transceiver+Antenna on a printed circuit board...
- Comparison of wireless data standardsComparison of wireless data standards- Introduction :A wide variety of different wireless data technologies exist, some in direct competition with one another, others designed for specific applications...
- Continua Health Alliance
- DASH7DASH7DASH7 is an open source wireless sensor networking standard for wireless sensor networking, which operates in the 433 MHz unlicensed ISM band. DASH7 provides multi-year battery life, range of up to 2 km, low latency for connecting with moving things, a very small open source protocol...
- EnOceanEnOceanEnOcean is a German wireless, energy harvesting technology used primarily in building automation systems, based in Oberhaching. It is not set out for international, European or national standardization; however, EnOcean GmbH is offering its technology and licenses for the patented features under...
- Home automationHome automationHome automation is the residential extension of "building automation". It is automation of the home, housework or household activity. Home automation may include centralized control of lighting, HVAC , appliances, and other systems, to provide improved convenience, comfort, energy efficiency and...
- The Intelligent StreetThe Intelligent StreetThe Intelligent Street is the name given to a type of intelligent environment which can be found on public transit street*. It has arisen from the convergence of communications and Ubiquitous Computing, intelligent and adaptable user interfaces, and the common infrastructure of the intelligent or...
- Internet 0Internet 0Internet 0 is a low-speed physical layer designed to route 'IP over anything.' It was developed at MIT's Center for Bits and Atoms by Neil Gershenfeld, Raffi Krikorian, and Danny Cohen...
- InsteonINSTEONInsteon is a system for connecting lighting switches and loads without extra wiring. INSTEON is a dual-band mesh home area networking topology employing AC-power lines and a radio-frequency protocol to communicate with devices...
- NeuRFonNeuRFonThe neuRFon project was a research program begun in 1999 at Motorola Labs to develop ad hoc wireless networking for wireless sensor network applications...
- ONE-NETONE-NETONE-NET is an open-source standard for wireless networking. ONE-NET was designed for low-cost, low-power control networks for applications such as home automation, security & monitoring, device control, and sensor networks...
- RuBeeRuBeeRuBee is a two way, active wireless protocol designed for harsh environment, high security asset visibility applications. RuBee utilizes Long Wave magnetic signals to send and receive short data packets in a local regional network...
- Wibree
- XBeeXBeeXBee is the brand name from Digi International for a family of form factor compatible radio modules. The first XBee radios were introduced under the MaxStream brand in 2005 and were based on the 802.15.4-2003 standard designed for point-to-point and point-to-multipoint communications at...
- Z-WaveZ-WaveZ-Wave is a proprietary wireless communications protocol designed for home automation, specifically to remote control applications in residential and light commercial environments...

