
499 BC
Encyclopedia
Roman calendar
The Roman calendar changed its form several times in the time between the founding of Rome and the fall of the Roman Empire. This article generally discusses the early Roman or pre-Julian calendars...
. In the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aebutius and Cicurinus (or, less frequently, year 255 Ab urbe condita
Ab urbe condita
Ab urbe condita is Latin for "from the founding of the City ", traditionally set in 753 BC. AUC is a year-numbering system used by some ancient Roman historians to identify particular Roman years...
). The denomination 499 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini
Anno Domini
and Before Christ are designations used to label or number years used with the Julian and Gregorian calendars....
calendar era
Calendar era
A calendar era is the year numbering system used by a calendar. For example, the Gregorian calendar numbers its years in the Western Christian era . The instant, date, or year from which time is marked is called the epoch of the era...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
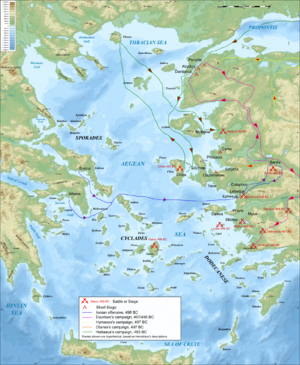
Greece
- After a failed attack on the rebellious island of Naxos in 502 BC (on behalf of the PersiansAchaemenid EmpireThe Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
), AristagorasAristagorasAristagoras was the leader of Miletus in the late 6th century BC and early 5th century BC.- Background :Aristagoras served as deputy governor of Miletus, a polis on the western coast of Anatolia around 500 BC. He was the son of Molpagoras, and son-in-law of Histiaeus, whom the Persians had set up...
, to save himself from the wrathAngerAnger is an automatic response to ill treatment. It is the way a person indicates he or she will not tolerate certain types of behaviour. It is a feedback mechanism in which an unpleasant stimulus is met with an unpleasant response....
of Persia, plans a revolt with the MilesiansMiletusMiletus was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia , near the mouth of the Maeander River in ancient Caria...
and the other Ionians. With the encouragement of HistiaeusHistiaeusHistiaeus , the son of Lysagoras, was the tyrant of Miletus in the late 6th century BC.Histiaeus owed his status as tyrant of Miletus to Darius I, king of Persia, who had subjugated Miletus and the other Ionian states in Asia Minor....
(his father-in-law and former tyrant of MiletusMiletusMiletus was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia , near the mouth of the Maeander River in ancient Caria...
), AristagorasAristagorasAristagoras was the leader of Miletus in the late 6th century BC and early 5th century BC.- Background :Aristagoras served as deputy governor of Miletus, a polis on the western coast of Anatolia around 500 BC. He was the son of Molpagoras, and son-in-law of Histiaeus, whom the Persians had set up...
, governor of MiletusMiletusMiletus was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia , near the mouth of the Maeander River in ancient Caria...
, induces the Ionian cities of Asia Minor to revolt against PersiaAchaemenid EmpireThe Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
, thus instigating the Ionian RevoltIonian RevoltThe Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC...
and beginning the Greco-Persian WarsGreco-Persian WarsThe Greco-Persian Wars were a series of conflicts between the Achaemenid Empire of Persia and city-states of the Hellenic world that started in 499 BC and lasted until 449 BC. The collision between the fractious political world of the Greeks and the enormous empire of the Persians began when Cyrus...
between GreeceAncient GreeceAncient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
and Persia. The pro-Persian tyrant of MytileneMytileneMytilene is a town and a former municipality on the island of Lesbos, North Aegean, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Lesbos, of which it is a municipal unit. It is the capital of the island of Lesbos. Mytilene, whose name is pre-Greek, is built on the...
is stoned to death. - AristagorasAristagorasAristagoras was the leader of Miletus in the late 6th century BC and early 5th century BC.- Background :Aristagoras served as deputy governor of Miletus, a polis on the western coast of Anatolia around 500 BC. He was the son of Molpagoras, and son-in-law of Histiaeus, whom the Persians had set up...
seeks help with the revolt against the Persians from Cleomenes ICleomenes ICleomenes or Kleomenes was an Agiad King of Sparta in the late 6th and early 5th centuries BC. During his reign, which started around 520 BC, he pursued an adventurous and at times unscrupulous foreign policy aimed at crushing Argos and extending Sparta's influence both inside and outside the...
, the King of SpartaSpartaSparta or Lacedaemon, was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the River Eurotas in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. From c...
, but the Spartans are unwilling to respond. - Miltiades the YoungerMiltiades the YoungerMiltiades the Younger or Miltiades IV was the son of one Cimon, a renowned Olympic chariot-racer. Miltiades considered himself a member of the Aeacidae, and is known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon; as well as his rather tragic downfall afterwards. His son Cimon was a major Athenian...
, the ruler of the Thracian ChersoneseThracian ChersoneseThe Thracian Chersonese was the ancient name of the Gallipoli peninsula, in the part of historic Thrace that is now part of modern Turkey.The peninsula runs in a south-westerly direction into the Aegean Sea, between the Hellespont and the bay of Melas . Near Agora it was protected by a wall...
, which has been under Persian suzeraintySuzeraintySuzerainty occurs where a region or people is a tributary to a more powerful entity which controls its foreign affairs while allowing the tributary vassal state some limited domestic autonomy. The dominant entity in the suzerainty relationship, or the more powerful entity itself, is called a...
since approximately 514 BC, joins the Ionian revolt. He seizes the islands of LemnosLemnosLemnos is an island of Greece in the northern part of the Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos peripheral unit, which is part of the North Aegean Periphery. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Myrina...
and ImbrosImbrosImbros or Imroz, officially referred to as Gökçeada since July 29, 1970 , is an island in the Aegean Sea and the largest island of Turkey, part of Çanakkale Province. It is located at the entrance of Saros Bay and is also the westernmost point of Turkey...
from the Persians.

