
5 Astraea
Encyclopedia
5 Astraea is a large main-belt asteroid
. Its surface is highly reflective (bright) and its composition is probably a mixture of nickel
-iron
with magnesium
- and iron
-silicate
s.
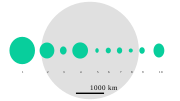 Astraea was the fifth asteroid
Astraea was the fifth asteroid
discovered, on December 8, 1845, by K. L. Hencke
and named for Astraea, a goddess of justice named after the stars. It was his first of two asteroid discoveries. The second was 6 Hebe
. An amateur astronomer and post office employee, Hencke was looking for 4 Vesta
when he stumbled on Astraea. The King of Prussia
awarded him an annual pension of 1,200 marks
for the discovery.
Photometry indicates prograde
rotation, that the north pole points in the direction of right ascension
9 h 52 min, declination
73° with a 5° uncertainty. This gives an axial tilt
of about 33°.
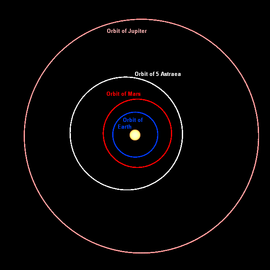 Astraea is physically unremarkable but notable mainly because for 38 years (after the discovery of Vesta
Astraea is physically unremarkable but notable mainly because for 38 years (after the discovery of Vesta
in 1807) it had been thought that there were only four asteroids. In terms of maximum brightness
, it is indeed only the seventeenth brightest main-belt asteroid, being fainter than 192 Nausikaa
and even, at rare near-perihelion oppositions, the highly eccentric carbonaceous 324 Bamberga
.http://www.spacebanter.com/archive/index.php/t-18464.html It will be at magnitude +8.7 on a favorable opposition on February 15, 2016.
After the discovery of Astraea, thousands of other asteroids would follow. Indeed, the discovery of Astraea proved to be the starting point for the eventual demotion of the four original asteroids (which were regarded as planets at the time) to their current status, as it became apparent that these four were only the largest of a whole new type of celestial body.
There has been only one observed stellar
occultation
by Astraea (February 2, 1991).
Asteroid
Asteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones...
. Its surface is highly reflective (bright) and its composition is probably a mixture of nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
-iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
with magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
- and iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
-silicate
Silicate
A silicate is a compound containing a silicon bearing anion. The great majority of silicates are oxides, but hexafluorosilicate and other anions are also included. This article focuses mainly on the Si-O anions. Silicates comprise the majority of the earth's crust, as well as the other...
s.

Asteroid
Asteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones...
discovered, on December 8, 1845, by K. L. Hencke
Karl Ludwig Hencke
Karl Ludwig Hencke was a German amateur astronomer. He is sometimes confused with Johann Franz Encke, another German astronomer....
and named for Astraea, a goddess of justice named after the stars. It was his first of two asteroid discoveries. The second was 6 Hebe
6 Hebe
6 Hebe is a large main-belt asteroid, containing around half a percent of the mass of the belt. Its apparently high bulk density , however, means that by volume it does not rank among the top twenty asteroids...
. An amateur astronomer and post office employee, Hencke was looking for 4 Vesta
4 Vesta
Vesta, formally designated 4 Vesta, is one of the largest asteroids, with a mean diameter of about . It was discovered by Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers on March 29, 1807, and is named after the Roman virgin goddess of home and hearth, Vesta....
when he stumbled on Astraea. The King of Prussia
Prussia
Prussia was a German kingdom and historic state originating out of the Duchy of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia shaped the history...
awarded him an annual pension of 1,200 marks
Mark (money)
Mark was a measure of weight mainly for gold and silver, commonly used throughout western Europe and often equivalent to 8 ounces. Considerable variations, however, occurred throughout the Middle Ages Mark (from a merging of three Teutonic/Germanic languages words, Latinized in 9th century...
for the discovery.
Photometry indicates prograde
Prograde
Prograde can refer to:*Prograde or direct motion, in astronomy, a type of motion of astronomical bodies* Prograde metamorphism, in geology, describes mineral changes in rocks under increasing pressure and/or temperature conditions...
rotation, that the north pole points in the direction of right ascension
Right ascension
Right ascension is the astronomical term for one of the two coordinates of a point on the celestial sphere when using the equatorial coordinate system. The other coordinate is the declination.-Explanation:...
9 h 52 min, declination
Declination
In astronomy, declination is one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and...
73° with a 5° uncertainty. This gives an axial tilt
Axial tilt
In astronomy, axial tilt is the angle between an object's rotational axis, and a line perpendicular to its orbital plane...
of about 33°.

4 Vesta
Vesta, formally designated 4 Vesta, is one of the largest asteroids, with a mean diameter of about . It was discovered by Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers on March 29, 1807, and is named after the Roman virgin goddess of home and hearth, Vesta....
in 1807) it had been thought that there were only four asteroids. In terms of maximum brightness
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
, it is indeed only the seventeenth brightest main-belt asteroid, being fainter than 192 Nausikaa
192 Nausikaa
192 Nausikaa is a large main-belt asteroid. It is an S-type asteroid.It was discovered by Johann Palisa on February 17, 1879 at Pula, then in Austria, now in Croatia. The name derives from Nausicaä, a princess in Homer's Odyssey....
and even, at rare near-perihelion oppositions, the highly eccentric carbonaceous 324 Bamberga
324 Bamberga
324 Bamberga is one of the largest asteroids in the asteroid belt. It was discovered by Johann Palisa on February 25, 1892 in Vienna, making it one of the last large asteroids discovered...
.http://www.spacebanter.com/archive/index.php/t-18464.html It will be at magnitude +8.7 on a favorable opposition on February 15, 2016.
After the discovery of Astraea, thousands of other asteroids would follow. Indeed, the discovery of Astraea proved to be the starting point for the eventual demotion of the four original asteroids (which were regarded as planets at the time) to their current status, as it became apparent that these four were only the largest of a whole new type of celestial body.
There has been only one observed stellar
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
occultation
Occultation
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden by another object that passes between it and the observer. The word is used in astronomy . It can also refer to any situation wherein an object in the foreground blocks from view an object in the background...
by Astraea (February 2, 1991).

