
Abraham-Minkowski controversy
Encyclopedia
The Abraham
–Minkowski
controversy is a physics
debate concerning electromagnetic
momentum
within dielectric
media. The preponderance of evidence in the debate suggests that the Abraham equation is correct, but some investigators disagree.
Two equations exist describing momentum transfer between matter
and electromagnetic field
s. Both seem to be supported by contradicting experimental data. The two existing equations were first suggested by Hermann Minkowski
(1908)
and Max Abraham
(1909),
from which the controversy name derives.
Both define the momentum of an electromagnetic field permeating matter. Abraham's equation suggests that in materials through which light travels more slowly, electromagnetic fields should have lower momentum, while Minkowski suggests it should have a greater momentum. It was suggested that Abraham only accounted for the momentum of the electromagnetic fields, and his equation was an attempt to take into account the momentum of the material as well. More recent work suggests that this characterization is incorrect.
At least one report has suggested Minkowski's formulation, if correct, would provide the physical base for a reactionless drive
. However, an independent review from the United States Air Force Academy
concluded that there would be no expected net propulsive forces, and a NASA
report determined that "The signal levels are not sufficiently above the noise as to be conclusive proof of a propulsive
effect."
The two equations for the momentum in a dielectric with refractive index
 are:
are:
where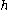 is the Planck constant
is the Planck constant
, is the frequency of the light and
is the frequency of the light and  is the speed of light
is the speed of light
in vacuum.
A 2010 study suggested that both equations are correct, with the Abraham version being the kinetic momentum
and the Minkowski version being the canonical momentum, and claims to explain the contradicting experimental results using this interpretation.
of light in a reversed Fizeau experiment
. The result was that the light speed c= 299,792,458m/s in vacuum of Lorentz transformation
should be replaced by c/n to describe electrodynamic phenomena in a dielectric medium Consequently, the momentum of a photon in vacuum is p=E/c and the value should be p=E/(c/n)=nE/c in media, although it is not measured directly. It is asserted, that this confirms Minkowski's formulation.
Max Abraham
Max Abraham was a German physicist.Abraham was born in Danzig, Imperial Germany to a family of Jewish merchants. His father was Moritz Abraham and his mother was Selma Moritzsohn. Attending the University of Berlin, he studied under Max Planck. He graduated in 1897...
–Minkowski
Hermann Minkowski
Hermann Minkowski was a German mathematician of Ashkenazi Jewish descent, who created and developed the geometry of numbers and who used geometrical methods to solve difficult problems in number theory, mathematical physics, and the theory of relativity.- Life and work :Hermann Minkowski was born...
controversy is a physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
debate concerning electromagnetic
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
momentum
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
within dielectric
Dielectric
A dielectric is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field. When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material, as in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric...
media. The preponderance of evidence in the debate suggests that the Abraham equation is correct, but some investigators disagree.
Two equations exist describing momentum transfer between matter
Matter
Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects consist. Typically, matter includes atoms and other particles which have mass. A common way of defining matter is as anything that has mass and occupies volume...
and electromagnetic field
Electromagnetic field
An electromagnetic field is a physical field produced by moving electrically charged objects. It affects the behavior of charged objects in the vicinity of the field. The electromagnetic field extends indefinitely throughout space and describes the electromagnetic interaction...
s. Both seem to be supported by contradicting experimental data. The two existing equations were first suggested by Hermann Minkowski
Hermann Minkowski
Hermann Minkowski was a German mathematician of Ashkenazi Jewish descent, who created and developed the geometry of numbers and who used geometrical methods to solve difficult problems in number theory, mathematical physics, and the theory of relativity.- Life and work :Hermann Minkowski was born...
(1908)
and Max Abraham
Max Abraham
Max Abraham was a German physicist.Abraham was born in Danzig, Imperial Germany to a family of Jewish merchants. His father was Moritz Abraham and his mother was Selma Moritzsohn. Attending the University of Berlin, he studied under Max Planck. He graduated in 1897...
(1909),
from which the controversy name derives.
Both define the momentum of an electromagnetic field permeating matter. Abraham's equation suggests that in materials through which light travels more slowly, electromagnetic fields should have lower momentum, while Minkowski suggests it should have a greater momentum. It was suggested that Abraham only accounted for the momentum of the electromagnetic fields, and his equation was an attempt to take into account the momentum of the material as well. More recent work suggests that this characterization is incorrect.
At least one report has suggested Minkowski's formulation, if correct, would provide the physical base for a reactionless drive
Reactionless drive
A reactionless drive is a fictional or theorized method of propulsion where thrust is generated without any need for any outside force or net momentum exchange to produce linear motion...
. However, an independent review from the United States Air Force Academy
United States Air Force Academy
The United States Air Force Academy is an accredited college for the undergraduate education of officer candidates for the United States Air Force. Its campus is located immediately north of Colorado Springs in El Paso County, Colorado, United States...
concluded that there would be no expected net propulsive forces, and a NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
report determined that "The signal levels are not sufficiently above the noise as to be conclusive proof of a propulsive
effect."
The two equations for the momentum in a dielectric with refractive index
Refractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
 are:
are:- The Minkowski version:
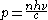
- The Abraham version:
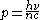
where
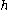 is the Planck constant
is the Planck constantPlanck constant
The Planck constant , also called Planck's constant, is a physical constant reflecting the sizes of energy quanta in quantum mechanics. It is named after Max Planck, one of the founders of quantum theory, who discovered it in 1899...
,
 is the frequency of the light and
is the frequency of the light and  is the speed of light
is the speed of lightSpeed of light
The speed of light in vacuum, usually denoted by c, is a physical constant important in many areas of physics. Its value is 299,792,458 metres per second, a figure that is exact since the length of the metre is defined from this constant and the international standard for time...
in vacuum.
A 2010 study suggested that both equations are correct, with the Abraham version being the kinetic momentum
Kinetic momentum
In physics, in particular electromagnetism, the kinetic momentum is a nonstandard term for the momentum of a charged particle due to its inertia. When a charged particle interacts with an electromagnetic field , there are two momenta: due to its inertia and due to the field...
and the Minkowski version being the canonical momentum, and claims to explain the contradicting experimental results using this interpretation.
Experimental evidence
In 2011, an optical experiment was performed to study this problem based on first principles. It tested the velocity-addition formulaVelocity-addition formula
In physics, a velocity-addition formula is an equation that relates the velocities of moving objects in different reference frames.- Galilean addition of velocities :...
of light in a reversed Fizeau experiment
Fizeau experiment
The Fizeau experiment was carried out by Hippolyte Fizeau in 1851 to measure the relative speeds of light in moving water. Albert Einstein later pointed out the importance of the experiment for special relativity...
. The result was that the light speed c= 299,792,458m/s in vacuum of Lorentz transformation
Lorentz transformation
In physics, the Lorentz transformation or Lorentz-Fitzgerald transformation describes how, according to the theory of special relativity, two observers' varying measurements of space and time can be converted into each other's frames of reference. It is named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik...
should be replaced by c/n to describe electrodynamic phenomena in a dielectric medium Consequently, the momentum of a photon in vacuum is p=E/c and the value should be p=E/(c/n)=nE/c in media, although it is not measured directly. It is asserted, that this confirms Minkowski's formulation.

