
Acene
Encyclopedia
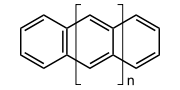
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
s and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons , also known as poly-aromatic hydrocarbons or polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons, are potent atmospheric pollutants that consist of fused aromatic rings and do not contain heteroatoms or carry substituents. Naphthalene is the simplest example of a PAH...
s made up of linearly fused benzene rings. The larger representatives have potential interest in optoelectronic applications and are actively researched in chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
and electrical engineering
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
. Pentacene has been incorporated into organic field-effect transistors, reaching charge carrier mobilities as high as 5 cm2/Vs.
The first 6 unsubstituted members are listed in table 1.
| Name | Molecular formula | Number of rings | Molar mass Molar mass Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol... |
CAS number | Structural formula Structural formula The structural formula of a chemical compound is a graphical representation of the molecular structure, showing how the atoms are arranged. The chemical bonding within the molecule is also shown, either explicitly or implicitly... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naphthalene Naphthalene Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings... |
C10H8 | 2 | 128.17 g/mol Mole (unit) The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value... |
91-20-3 | 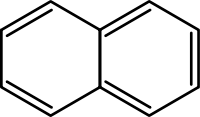 |
| Anthracene Anthracene Anthracene is a solid polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of three fused benzene rings. It is a component of coal-tar. Anthracene is used in the production of the red dye alizarin and other dyes... |
C14H10 | 3 | 178.23 g/mol Mole (unit) The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value... |
120-12-7 | 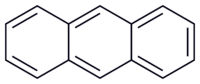 |
| Tetracene Tetracene Tetracene, also called naphthacene, is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. It has the appearance of a pale orange powder. Tetracene is the four-ringed member of the series of acenes, the previous one being anthracene and the next one being pentacene.Tetracene is a molecular organic semiconductor,... |
C18H12 | 4 | 228.29 g/mol Mole (unit) The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value... |
92-24-0 | |
| Pentacene Pentacene Pentacene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon consisting of five linearly-fused benzene rings. This highly conjugated compound is an organic semiconductor. The compound generates excitons upon absorption of ultra-violet or visible light; this makes it very sensitive to oxidation... |
C22H14 | 5 | 278.35 g/mol Mole (unit) The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value... |
135-48-8 | |
| Hexacene Hexacene Hexacene is an aromatic molecule consisting of six linearly-fused benzene rings. Hexacene and its derivatives are investigated for potential applications as organic semiconductor.... |
C26H16 | 6 | 328.41 g/mol Mole (unit) The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value... |
258-31-1 | |
| Heptacene Heptacene Heptacene is an organic compound and a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and the seventh member of the acene or polyacene family of linear fused benzene rings... |
C30H18 | 7 | 378.46 g/mol Mole (unit) The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value... |
The last members, hexacene
Hexacene
Hexacene is an aromatic molecule consisting of six linearly-fused benzene rings. Hexacene and its derivatives are investigated for potential applications as organic semiconductor....
and heptacene
Heptacene
Heptacene is an organic compound and a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and the seventh member of the acene or polyacene family of linear fused benzene rings...
, are very reactive and have only been isolated in a matrix. However, bis(trialkylsilylethynylated) versions of hexacene and heptacene have been isolated as crystalline solids.
Larger acenes
Due to their increased conjugationConjugated system
In chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in compounds with alternating single and multiple bonds, which in general may lower the overall energy of the molecule and increase stability. Lone pairs, radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the...
length the larger acenes are also studied . They are also building blocks for nanotubes
Carbon nanotube
Carbon nanotubes are allotropes of carbon with a cylindrical nanostructure. Nanotubes have been constructed with length-to-diameter ratio of up to 132,000,000:1, significantly larger than for any other material...
and graphene
Graphene
Graphene is an allotrope of carbon, whose structure is one-atom-thick planar sheets of sp2-bonded carbon atoms that are densely packed in a honeycomb crystal lattice. The term graphene was coined as a combination of graphite and the suffix -ene by Hanns-Peter Boehm, who described single-layer...
. Unsubstituted octacene (n=8) and nonacene (n=9) have been detected in matrix isolation. A stable nonacene derivative has also been reported . Due to the electronic effects of the thioaryl substituents the compound is not a diradical
Diradical
A diradical in organic chemistry is a molecular species with two electrons occupying two degenerate molecular orbitals . They are known by their higher reactivities and shorter lifetimes. In a broader definition diradicals are even-electron molecules that have one bond less than the number...
but a closed-shell compound with the lowest HOMO-LUMO gap reported for any acene.
Related compounds
A related group of compounds with 1,2-fused rings and with helical not linear structures are the heliceneHelicene
Helicenes in organic chemistry are ortho-condensed polycyclic aromatic compounds in which benzene rings or other aromatics are angularly annulated to give helically-shaped molecules...
s. Polyquinane
Polyquinane
A polyquinane and polyquinene is a saturated or unsaturated, respectively, polycyclic hydrocarbon consisting of fused five-membered rings . The simplest member is the bicyclic compound bicyclo[3.3.0]octane...
s and quinenes are fused cyclopentane rings.

