
Additive smoothing
Encyclopedia
In statistics
, additive smoothing, also called Laplace
smoothing (not to be confused with Laplacian smoothing
), or Lidstone
smoothing, is a technique used to smooth
categorical data. Given an observation x = (x1, …, xd) from a multinomial distribution with N trials and parameter vector θ = (θ1, …, θd), a "smoothed" version of the data gives the estimator
:
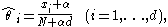
where α > 0 is the smoothing parameter (α = 0 corresponds to no smoothing). Additive smoothing is a type of shrinkage estimator
, as the resulting estimate will be between the empirical estimate xi/n, and the uniform probability 1/d. Using Laplace's rule of succession
, some authors have argued that α should be 1 (in which case the term add-one smoothing is also used), though in practice a smaller value is typically chosen.
From a Bayesian
point of view, this corresponds to the expected value
of the posterior distribution, using a Dirichlet distribution with parameter α as a prior.
of natural language processing and information retrieval, the data consists of the number of occurrences of each word in a document. Additive smoothing allows the assignment of non-zero probabilities to words which do not occur in the sample.
Chen & Goodman (1996) empirically compare additive smoothing to a variety of other techniques, using both α fixed at one and a more general value.
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, additive smoothing, also called Laplace
Pierre-Simon Laplace
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace was a French mathematician and astronomer whose work was pivotal to the development of mathematical astronomy and statistics. He summarized and extended the work of his predecessors in his five volume Mécanique Céleste...
smoothing (not to be confused with Laplacian smoothing
Laplacian smoothing
Laplacian smoothing is an algorithm to smooth a polygonal mesh. For each vertex in a mesh, a new position is chosen based on local information and the vertex is moved there...
), or Lidstone
George James Lidstone
George James Lidstone was a British actuary who made several contributions to the field of statistics. He is known for Lidstone smoothing and Lidstone series.- References :...
smoothing, is a technique used to smooth
Smoothing
In statistics and image processing, to smooth a data set is to create an approximating function that attempts to capture important patterns in the data, while leaving out noise or other fine-scale structures/rapid phenomena. Many different algorithms are used in smoothing...
categorical data. Given an observation x = (x1, …, xd) from a multinomial distribution with N trials and parameter vector θ = (θ1, …, θd), a "smoothed" version of the data gives the estimator
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on observed data: thus the rule and its result are distinguished....
:
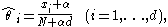
where α > 0 is the smoothing parameter (α = 0 corresponds to no smoothing). Additive smoothing is a type of shrinkage estimator
Shrinkage estimator
In statistics, a shrinkage estimator is an estimator that, either explicitly or implicitly, incorporates the effects of shrinkage. In loose terms this means that a naïve or raw estimate is improved by combining it with other information. The term relates to the notion that the improved estimate is...
, as the resulting estimate will be between the empirical estimate xi/n, and the uniform probability 1/d. Using Laplace's rule of succession
Rule of succession
In probability theory, the rule of succession is a formula introduced in the 18th century by Pierre-Simon Laplace in the course of treating the sunrise problem....
, some authors have argued that α should be 1 (in which case the term add-one smoothing is also used), though in practice a smaller value is typically chosen.
From a Bayesian
Bayesian inference
In statistics, Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference. It is often used in science and engineering to determine model parameters, make predictions about unknown variables, and to perform model selection...
point of view, this corresponds to the expected value
Expected value
In probability theory, the expected value of a random variable is the weighted average of all possible values that this random variable can take on...
of the posterior distribution, using a Dirichlet distribution with parameter α as a prior.
Statistical language modelling
In a bag of words modelBag of words model
The bag-of-words model is a simplifying assumption used in natural language processing and information retrieval. In this model, a text is represented as an unordered collection of words, disregarding grammar and even word order.The bag-of-words model is used in some methods of document...
of natural language processing and information retrieval, the data consists of the number of occurrences of each word in a document. Additive smoothing allows the assignment of non-zero probabilities to words which do not occur in the sample.
Chen & Goodman (1996) empirically compare additive smoothing to a variety of other techniques, using both α fixed at one and a more general value.
External links
- SF Chen, J Goodman (1996). "An empirical study of smoothing techniques for language modeling". Proceedings of the 34th annual meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics.

