
Administrative division of Second Polish Republic
Encyclopedia
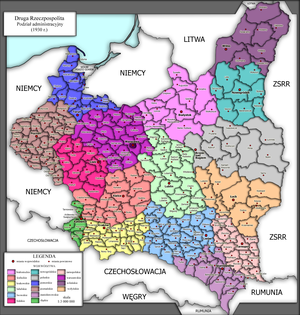
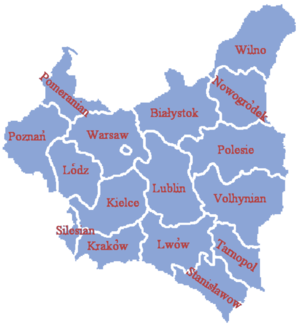
Administrative division
An administrative division, subnational entity, or country subdivision is a portion of a country or other political division, established for the purpose of government. Administrative divisions are each granted a certain degree of autonomy, and are required to manage themselves through their own...
of Second Polish Republic
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, Second Commonwealth of Poland or interwar Poland refers to Poland between the two world wars; a period in Polish history in which Poland was restored as an independent state. Officially known as the Republic of Poland or the Commonwealth of Poland , the Polish state was...
became an issue immediately after Poland regained independence in the aftermath of the First World War, 1918. Poland had been partitioned
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
in the late 18th century, and various parts of new Polish territory had belonged to different administrative structures of Austrian Empire
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
, Imperial Germany and Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
.
In 1919 the first voivodeships
Voivodeships of Poland
The voivodeship, or province, called in Polish województwo , has been a high-level administrative subdivision of Poland since the 14th century....
of interwar Poland were created; in addition the capital of Warsaw
Warsaw
Warsaw is the capital and largest city of Poland. It is located on the Vistula River, roughly from the Baltic Sea and from the Carpathian Mountains. Its population in 2010 was estimated at 1,716,855 residents with a greater metropolitan area of 2,631,902 residents, making Warsaw the 10th most...
had a status of an independent city-voivodeship. In the years 1919–1921 additional voivodeships were created, as borders of Poland were still fluid, with events such as the Silesian Uprisings
Silesian Uprisings
The Silesian Uprisings were a series of three armed uprisings of the Poles and Polish Silesians of Upper Silesia, from 1919–1921, against German rule; the resistance hoped to break away from Germany in order to join the Second Polish Republic, which had been established in the wake of World War I...
in the West and Polish-Soviet War
Polish-Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War was an armed conflict between Soviet Russia and Soviet Ukraine and the Second Polish Republic and the Ukrainian People's Republic—four states in post–World War I Europe...
in the East. Eventually by 1921 Poland would have 15 voivodeships, Warsaw capital city-voivodeship and the Autonomous Silesian Voivodeship
Autonomous Silesian Voivodeship
The Silesian Voivodeship was an autonomous province of the interwar Second Polish Republic. It consisted of territory which came into Polish possession as a result of the 1921 Upper Silesia plebiscite, the Geneva Conventions, three Upper Silesian Uprisings, and the eventual partition of Upper...
(the system known as 15+1+1). Additionally, creation of the new Sandomierz Voivodeship
Sandomierz Voivodeship (1939)
Sandomierz Voivodeship , , was a proposed voivodeship of the Second Polish Republic, which was never created because of the Nazi and Soviet invasion of Poland in September 1939...
was planned for late 1939.
The lower level of administration, below voivodeships, were powiat
Powiat
A powiat is the second-level unit of local government and administration in Poland, equivalent to a county, district or prefecture in other countries. The term powiat is most often translated into English as "county", although other terms are also sometimes used...
s (counties). They were subject to several reforms, particularly in early and late 1930s. Below them were gmina
Gmina
The gmina is the principal unit of administrative division of Poland at its lowest uniform level. It is often translated as "commune" or "municipality." As of 2010 there were 2,479 gminas throughout the country...
s and gromada
Gromada
Gromada is a Polish word meaning "gathering", "group", or "assembly". In the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, the term referred to a village organization which embraced all the inhabitants of a village and acted as a local authority, as well as overseeing tax payments. In this sense the gromada...
s. Shortly before the Second World War, in April 1939, Poland had 264 powiats, 611 urban and 3195 rural gminas and 40533 gromads.
The division was based on the three tier system. On the lowest rung were the gminy, which were little more than local town and village governments. These were then grouped together into powiaty which were then arranged into wojewodztwa.
| Polish voivodeships in the interbellum (data as per April 1, 1937) |
||||
| car plates (since 1937) |
Voivodeship Separate city |
Capital | Area in 1000 km² (1930) |
Population in 1000 (1931) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00-19 | City of Warsaw Warsaw Warsaw is the capital and largest city of Poland. It is located on the Vistula River, roughly from the Baltic Sea and from the Carpathian Mountains. Its population in 2010 was estimated at 1,716,855 residents with a greater metropolitan area of 2,631,902 residents, making Warsaw the 10th most... |
Warsaw | 0,14 | 1179,5 |
| 85-89 | warszawskie | Warsaw Warsaw Warsaw is the capital and largest city of Poland. It is located on the Vistula River, roughly from the Baltic Sea and from the Carpathian Mountains. Its population in 2010 was estimated at 1,716,855 residents with a greater metropolitan area of 2,631,902 residents, making Warsaw the 10th most... |
31,7 | 2460,9 |
| 20-24 | białostockie | Białystok | 26,0 | 1263,3 |
| 25-29 | kieleckie | Kielce Kielce Kielce ) is a city in central Poland with 204,891 inhabitants . It is also the capital city of the Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship since 1999, previously in Kielce Voivodeship... |
22,2 | 2671,0 |
| 30-34 | krakowskie | Kraków Kraków Kraków also Krakow, or Cracow , is the second largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in the Lesser Poland region, the city dates back to the 7th century. Kraków has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life... |
17,6 | 2300,1 |
| 35-39 | lubelskie | Lublin Lublin Lublin is the ninth largest city in Poland. It is the capital of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 350,392 . Lublin is also the largest Polish city east of the Vistula river... |
26,6 | 2116,2 |
| 40-44 | lwowskie Lwów Voivodeship Lwów Voivodeship was an administrative unit of interwar Poland . According to Nazis and Soviets it ceased to exist in September 1939, following German and Soviet aggression on Poland . The Polish underground administration existed till August 1944.-Population:Its capital, biggest and most... |
Lwów | 28,4 | 3126,3 |
| 45-49 | łódzkie | Łódź | 20,4 | 2650,1 |
| 50-54 | nowogródzkie | Nowogródek | 23,0 | 1057,2 |
| 55-59 | poleskie Polesie Voivodeship Polesie Voivodeship was an administrative unit of interwar Poland . It ceased to exist in September 1939, following German and Soviet aggression on Poland .-Population:... |
Brześć nad Bugiem | 36,7 | 1132,2 |
| 60-64 | pomorskie | Toruń Torun Toruń is an ancient city in northern Poland, on the Vistula River. Its population is more than 205,934 as of June 2009. Toruń is one of the oldest cities in Poland. The medieval old town of Toruń is the birthplace of the astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus.... |
25,7 | 1884,4 |
| 65-69 | poznańskie | Poznań Poznan Poznań is a city on the Warta river in west-central Poland, with a population of 556,022 in June 2009. It is among the oldest cities in Poland, and was one of the most important centres in the early Polish state, whose first rulers were buried at Poznań's cathedral. It is sometimes claimed to be... |
28,1 | 2339,6 |
| 70-74 | stanisławowskie | Stanisławów Ivano-Frankivsk Ivano-Frankivsk is a historic city located in the western Ukraine. It is the administrative centre of the Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast , and is designated as its own separate raion within the oblast, municipality.... |
16,9 | 1480,3 |
| 75-79 ? | śląskie Autonomous Silesian Voivodeship The Silesian Voivodeship was an autonomous province of the interwar Second Polish Republic. It consisted of territory which came into Polish possession as a result of the 1921 Upper Silesia plebiscite, the Geneva Conventions, three Upper Silesian Uprisings, and the eventual partition of Upper... (autonomous) |
Katowice Katowice Katowice is a city in Silesia in southern Poland, on the Kłodnica and Rawa rivers . Katowice is located in the Silesian Highlands, about north of the Silesian Beskids and about southeast of the Sudetes Mountains.It is the central district of the Upper Silesian Metropolis, with a population of 2... |
5,1 | 1533,5 |
| 80-84 | tarnopolskie Tarnopol Voivodeship Tarnopol Voivodeship was an administrative region of interwar Poland with an area of 16,500 km², 17 counties, and capital in Tarnopol... |
Tarnopol | 16,5 | 1600,4 |
| 90-94 | wileńskie | Wilno | 29,0 | 1276,0 |
| 95-99 | wołyńskie | Łuck Lutsk Lutsk is a city located by the Styr River in northwestern Ukraine. It is the administrative center of the Volyn Oblast and the administrative center of the surrounding Lutskyi Raion within the oblast... |
35,7 | 2085,6 |
On April 1, 1938, borders of several western Voivodeships changed considerably. For more information, see Territorial changes of Polish Voivodeships on April 1, 1938
Territorial changes of Polish Voivodeships on April 1, 1938
On April 1, 1938, borders of several western and central Voivodeships changed considerably. This included such Voivodeships as Pomerania, Poznan, Warsaw, Lodz, Bialystok, Lublin and Kielce. Pomerania gained most, while Bialystok lost most...
.
Polish Voivodeships 1919–1939
Total number of Voivodeships - 16, plus the capital city of Warsaw, which was regarded as a separate unit.Biggest Voivodeships (as for August 1, 1939)
- Polesie Voivodeship - area 36 668 km²
- Volhynian Voivodeship - area 35 754 km²
- Warszawa Voivodeship - area 31 656 km²
Smallest Voivodeships (as for August 1, 1939)
- miasto stoleczne Warszawa (the capital city of Warsaw) - area 141 km²
- Silesian Voivodeship - area 5 122 km²
- Tarnopol Voivodeship - area 16 533 km²
Most populous Voivodeships
- Lwów Voivodeship - pop. 3 126 300,
- Kielce Voivodeship - pop. 2 671 000,
- Łódź Voivodeship - pop. 2 650 100.
Least populous Voivodeships
- Nowogródek Voivodeship - pop. 1 057 200,
- Polesie Voivodeship - pop. 1 132 200
- miasto stoleczne Warszawa (the capital city of Warsaw) - pop. 1 179 500.
Polish Counties 1919–1939
Total number of counties (as for August 1, 1939) - 264, including 23 urban counties.Biggest counties (as for August 1, 1939)
- Wilno – Troki county (area 5 967 km²),
- LuniniecLuniniecLuninets is a town and administrative centre for the Luninets district in Brest Province, Belarus, before which it was in Poland and Russia and the Soviet Union . It has a population of some 24,000, and is immediately east of the Pinsk district within Brest...
county (area 5 722 km²), - Kowel county (area 5 682 km²).
Smallest counties (as for August 1, 1939)
- Warszawa-Srodmiescie (mid-Warsaw) (area 10 km²),
- city of BielskoBielskoBielsko was until 1950 an independent town situated in Cieszyn Silesia, Poland. In 1951 it was joined with Biała Krakowska to form the new town of Bielsko-Biała. Bielsko constitutes the western part of that town....
(area 10 km²), - city of GnieznoGnieznoGniezno is a city in central-western Poland, some 50 km east of Poznań, inhabited by about 70,000 people. One of the Piasts' chief cities, it was mentioned by 10th century A.D. sources as the capital of Piast Poland however the first capital of Piast realm was most likely Giecz built around...
(area 18 km²).
Most populous counties
- city of Łódź county (pop. 604 600),
- Warszawa-North county (pop. 478 200),
- KatowiceKatowiceKatowice is a city in Silesia in southern Poland, on the Kłodnica and Rawa rivers . Katowice is located in the Silesian Highlands, about north of the Silesian Beskids and about southeast of the Sudetes Mountains.It is the central district of the Upper Silesian Metropolis, with a population of 2...
county, (pop. 357 300).
Least populous counties
- city of Bielsko county, (pop. 25 400),
- city of Gniezno, (pop. 30 700),
- MiędzychódMiedzychódMiędzychód is a town in Greater Poland Voivodeship, Poland, about 75 km west of Poznań. It is the capital of Międzychód County. Population is 10,920 .-Notable residents:* Manuel Joël , philosopher...
county, (pop. 31 000).
Source
- Maly rocznik statystyczny 1939, Nakladem Glownego Urzedu Statystycznego, Warszawa 1939 (Concise Statistical Year-Book of Poland, Warsaw 1939).

