Airfield traffic pattern
Encyclopedia
An airfield traffic pattern is a standard path followed by aircraft
when taking off
or landing
, while maintaining visual contact with the airfield.
At an airport
, the pattern (or circuit in the Commonwealth
) is a standard path for coordinating air traffic
. It differs from "straight-in approaches" and "direct climb-outs" in that aircraft using a traffic pattern remain close to the airport. Patterns are usually employed at small general aviation
(GA) airfields and military airbase
s. Many large controlled
airports avoid the system, unless there is GA activity as well as commercial flights. However, some kind of a pattern may be used at airports in some cases, such as when an aircraft is required to go around — but this kind of pattern at controlled airports may be very different in form, shape and purpose to the standard traffic pattern as used at GA airports.
The exception to this rule is at alpine airports (altiport
s) where the runway is on a severe slope
. In these instances, takeoffs are usually made downhill and landings uphill, with the slope aiding in acceleration
and deceleration.
Many airfields have runways facing a variety of directions. The purpose of this is to provide arriving aircraft with the best runway to land on, according to the wind direction. Runway orientation is determined from historical data of the prevailing winds in the area. This is especially important for single-runway airports that don't have the option of a second runway pointed in an alternative direction. A common scenario is to have two runways arranged at or close to 90 degrees to one another, so that aircraft can always find a suitable runway. Almost all runways are reversible, and aircraft use whichever runway in whichever direction is best suited to the wind. In light and variable wind conditions, the direction of the runway in use might change several times during the day.
has better visibility out the left window. Right-hand patterns will be set up for parallel runway
s, for noise abatement or because of ground features (such as terrain, towers, etc.). In USA, the non-standard (i.e. right-hand) patterns are noted in the Airport/Facilities Directory or on a sectional chart
, in other countries they may be indicated in that nation's similar document, e.g. Canada Flight Supplement. Unless explicitly indicated otherwise, all traffic patterns at non-towered airport
s are to the left.
Helicopters are encouraged, but not required, to use an opposite pattern from fixed-wing traffic due to their slower speed and greater maneuverability.
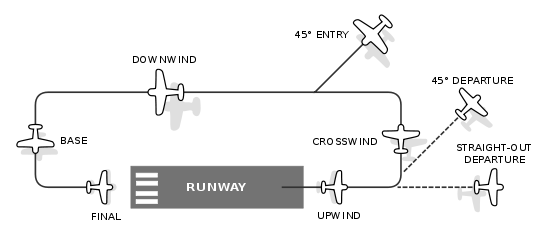
Because the active runway is chosen to meet the wind at the nearest angle (with take-offs and landings upwind), the pattern orientation also depends on wind direction. Patterns are typically rectangular in basic shape, and include the runway along one long side of the rectangle. Each leg of the pattern has a particular name:
The names of the legs are logical and based on the relative wind as seen looking down a runway facing into the wind. An aircraft flying upwind heads into the wind, flying crosswind heads across the wind, flying downwind heads in the direction of the wind just like blown smoke.
 While many airfields operate a completely standard pattern, in other cases it will be modified according to need. For example, military airfields
While many airfields operate a completely standard pattern, in other cases it will be modified according to need. For example, military airfields
often dispense with the crosswind and base legs, but rather fly these as circular arcs directly joining the upwind and downwind sections.
.
There are conventions for joining the pattern, used in different jurisdictions.
Similarly, there are conventions for departing the pattern.
There is also a procedure known as an "orbit", where an aircraft flies a 360° loop either clockwise or anticlockwise. This is usually to allow greater separation with other traffic ahead in the pattern. This can be the result of a controller's instruction. If at the pilot's initiative, the pilot will report e.g. "(tail ID number or flight number) making one left-hand orbit, will advise complete".
in Australia
, then the middle runway(s) can, for obvious reasons, only be used when either a straight in approach is used or when the aircraft joins the pattern from a very wide base leg.
), although a pattern height of 800 feet above ground level is relatively common. Helicopters usually fly their pattern at 500 feet above ground level.
Extreme caution is exercised by pilots flying the published traffic pattern altitude as this may contribute to mid air collisions.
. By using a consistent flight pattern pilots will know from where to expect other air traffic, and be able to see it and avoid it. Pilots flying under Visual Flight Rules
(VFR) may not be separated by air traffic control, so this consistent predictable pattern is a vital way to keep things orderly. At tower-controlled airports air traffic control (ATC) may provide traffic advisories for VFR flights on a work-load permitting basis.
A pilot undergoing training will often fly many patterns, one after another. Usually, each landing is followed immediately by a take off and further pattern; this is called a touch and go. Pilots executing Touch and Go landings should declare the intention to do so when calling the final approach leg. After landing and once airborne again the Touch and Go pilot should declare that the aircraft is On the Go. The pilot should not declare that the aircraft is on an Upwind as that term is not applicable to non-towered airports and is not appropriate for aircraft departing from a runway end.
pilots also prefer to land facing the wind and are often asked to fly a pattern on arrival or departure. Many airfields operate a special pattern for helicopters to take account of their low airspeed. This is usually a mirror image of the fixed-wing pattern, and often at a slightly lower standard height above surface level; as noted above this altitude is usually 500 feet above ground level. However due to helicopters' unique maneuverability, helicopter pilots often choose not to enter the pattern, and make a direct approach to the helipad or apron they wish to land on.
(ATC) may decide to place it in a holding pattern until the airport is prepared to permit the landing. Commercial aircraft on hold will generally fly slow, racetrack-shaped patterns which differ considerably from the airfield traffic pattern that will be commenced once the approval has been given to land. Although an aircraft in a holding pattern may similarly circle the airport, ATC may designate a distant location in which to circle.
Aircraft
An aircraft is a vehicle that is able to fly by gaining support from the air, or, in general, the atmosphere of a planet. An aircraft counters the force of gravity by using either static lift or by using the dynamic lift of an airfoil, or in a few cases the downward thrust from jet engines.Although...
when taking off
Takeoff
Takeoff is the phase of flight in which an aerospace vehicle goes from the ground to flying in the air.For horizontal takeoff aircraft this usually involves starting with a transition from moving along the ground on a runway. For balloons, helicopters and some specialized fixed-wing aircraft , no...
or landing
Landing
thumb|A [[Mute Swan]] alighting. Note the ruffled feathers on top of the wings indicate that the swan is flying at the [[Stall |stall]]ing speed...
, while maintaining visual contact with the airfield.
At an airport
Airport
An airport is a location where aircraft such as fixed-wing aircraft, helicopters, and blimps take off and land. Aircraft may be stored or maintained at an airport...
, the pattern (or circuit in the Commonwealth
Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, normally referred to as the Commonwealth and formerly known as the British Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of fifty-four independent member states...
) is a standard path for coordinating air traffic
Air traffic control
Air traffic control is a service provided by ground-based controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and in the air. The primary purpose of ATC systems worldwide is to separate aircraft to prevent collisions, to organize and expedite the flow of traffic, and to provide information and other...
. It differs from "straight-in approaches" and "direct climb-outs" in that aircraft using a traffic pattern remain close to the airport. Patterns are usually employed at small general aviation
General aviation
General aviation is one of the two categories of civil aviation. It refers to all flights other than military and scheduled airline and regular cargo flights, both private and commercial. General aviation flights range from gliders and powered parachutes to large, non-scheduled cargo jet flights...
(GA) airfields and military airbase
Airbase
An airbase is a military airfield that provides basing and support of military aircraft....
s. Many large controlled
Air traffic control
Air traffic control is a service provided by ground-based controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and in the air. The primary purpose of ATC systems worldwide is to separate aircraft to prevent collisions, to organize and expedite the flow of traffic, and to provide information and other...
airports avoid the system, unless there is GA activity as well as commercial flights. However, some kind of a pattern may be used at airports in some cases, such as when an aircraft is required to go around — but this kind of pattern at controlled airports may be very different in form, shape and purpose to the standard traffic pattern as used at GA airports.
Wind direction
Pilots prefer to take off and land facing into the wind. This has the effect of reducing the aircraft's speed over the ground (for the same given airspeed) and hence reducing the distance required to perform either maneuver.The exception to this rule is at alpine airports (altiport
Altiport
An altiport is an aerodrome for small airplanes and helicopters, situated on a high mountain. It is characterised by having an extremely sloping runway, where all landings are uphill and all takeoffs are downhill....
s) where the runway is on a severe slope
Slope
In mathematics, the slope or gradient of a line describes its steepness, incline, or grade. A higher slope value indicates a steeper incline....
. In these instances, takeoffs are usually made downhill and landings uphill, with the slope aiding in acceleration
Acceleration
In physics, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with time. In one dimension, acceleration is the rate at which something speeds up or slows down. However, since velocity is a vector, acceleration describes the rate of change of both the magnitude and the direction of velocity. ...
and deceleration.
Many airfields have runways facing a variety of directions. The purpose of this is to provide arriving aircraft with the best runway to land on, according to the wind direction. Runway orientation is determined from historical data of the prevailing winds in the area. This is especially important for single-runway airports that don't have the option of a second runway pointed in an alternative direction. A common scenario is to have two runways arranged at or close to 90 degrees to one another, so that aircraft can always find a suitable runway. Almost all runways are reversible, and aircraft use whichever runway in whichever direction is best suited to the wind. In light and variable wind conditions, the direction of the runway in use might change several times during the day.
Layout
Traffic patterns can be defined as left-hand or right-hand, according to which way the turns in the pattern are performed. They are usually left-hand turns because most small airplanes are piloted from the left seat (or the senior pilot or pilot-in-command sits in the left seat), and so the pilotAviator
An aviator is a person who flies an aircraft. The first recorded use of the term was in 1887, as a variation of 'aviation', from the Latin avis , coined in 1863 by G. de la Landelle in Aviation Ou Navigation Aérienne...
has better visibility out the left window. Right-hand patterns will be set up for parallel runway
Runway
According to ICAO a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and take-off of aircraft." Runways may be a man-made surface or a natural surface .- Orientation and dimensions :Runways are named by a number between 01 and 36, which is generally one tenth...
s, for noise abatement or because of ground features (such as terrain, towers, etc.). In USA, the non-standard (i.e. right-hand) patterns are noted in the Airport/Facilities Directory or on a sectional chart
Sectional Chart
In United States aviation, a sectional chart, often called sectional for short, is a type of aeronautical chart designed for navigation under visual flight rules.-Overview:...
, in other countries they may be indicated in that nation's similar document, e.g. Canada Flight Supplement. Unless explicitly indicated otherwise, all traffic patterns at non-towered airport
Non-towered airport
A non-towered airport, sometimes referred to as an uncontrolled airport, is an airport with no operating tower, or air traffic control unit...
s are to the left.
Helicopters are encouraged, but not required, to use an opposite pattern from fixed-wing traffic due to their slower speed and greater maneuverability.
Because the active runway is chosen to meet the wind at the nearest angle (with take-offs and landings upwind), the pattern orientation also depends on wind direction. Patterns are typically rectangular in basic shape, and include the runway along one long side of the rectangle. Each leg of the pattern has a particular name:
- Upwind leg. A flight path parallel to and in the direction of the landing runway. This can be above the runway, as in a "low and over" or when practicing a "missed [instrument] approach," or offset to the upwind side as when inspecting the field prior to landing.
- Crosswind leg. A short climbing flight path at right angles to the departure end of the runway.
- Downwind leg. A long level flight path parallel to but in the opposite direction of the landing runway. (Some consider it to have "sub-legs" of early, mid and late. Certainly a plane giving a position report of "mid-downwind" can be visually located easily.)
- Base leg. A short descending flight path at right angles to the approach end extended centerline of the landing runway.
- Final approach. A descending flight path in the direction of landing along the extended runway centerline from the base leg to the runway. The last section of the final approach is sometimes referred to as short final.
- Departure leg. The climbing flight path along the extended runway centerline which begins at takeoff and continues to at least 1/2 mile beyond the runway's departure end and not less than 300 feet below the traffic pattern altitude. It is a special case of an upwind leg.
The names of the legs are logical and based on the relative wind as seen looking down a runway facing into the wind. An aircraft flying upwind heads into the wind, flying crosswind heads across the wind, flying downwind heads in the direction of the wind just like blown smoke.

Military aviation
Military aviation is the use of aircraft and other flying machines for the purposes of conducting or enabling warfare, including national airlift capacity to provide logistical supply to forces stationed in a theater or along a front. Air power includes the national means of conducting such...
often dispense with the crosswind and base legs, but rather fly these as circular arcs directly joining the upwind and downwind sections.
Procedures in the pattern
Aircraft are expected to join and leave the pattern, following the pattern already in use. Sometimes this will be at the discretion of the pilot, while at other times the pilot will be directed by air traffic controlAir traffic control
Air traffic control is a service provided by ground-based controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and in the air. The primary purpose of ATC systems worldwide is to separate aircraft to prevent collisions, to organize and expedite the flow of traffic, and to provide information and other...
.
There are conventions for joining the pattern, used in different jurisdictions.
- In the United StatesUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, aircraft usually join the pattern at a 45° angle to the downwind leg and abeam midfield. Although aircraft may legally join the pattern at any point, the AIM clearly states that the only approved pattern entry is the 45. - In CanadaCanadaCanada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, aircraft at uncontrolled airports usually cross the airport at midfield at pattern altitude from the upwind side, turning onto the downwind leg. At controlled airports, the tower typically directs aircraft to join the downwind leg, base leg, or straight in to the final leg. - In the UK and South AfricaSouth AfricaThe Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
, a Standard Overhead JoinOverhead joinAn overhead join is a conventional method for an aircraft to approach and safely land at an airfield. It helps a pilot to integrate with any air traffic pattern near an airfield, join any circuit, and land....
is recommended. - In EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, aircraft usually join the pattern at a 45° angle to the downwind leg, in the beginning of the downwind leg. - Fast aircraft, for example military jets, may enter the pattern with a run-and-breakRun-and-breakIn aviation, a run-and-break is a procedure used by high-performance aircraft to join an airfield traffic pattern without requiring the aircraft to spend a long time flying at low speed...
. The aircraft flies at speed along the final leg, and makes a sharp, high-G turn above midfield to lose speed and arrive on the downwind leg at pattern altitude and in landing configuation.
Similarly, there are conventions for departing the pattern.
- In the United States, aircraft usually depart the pattern either straight out along the runway heading, or with a 45° turn in the direction of the crosswind leg.
- In Canada, aircraft usually depart straight out along the runway heading until at circuit altitude, at which point they may turn as desired. At controlled airports, the tower typically gives instructions for what turn to make on departure.
There is also a procedure known as an "orbit", where an aircraft flies a 360° loop either clockwise or anticlockwise. This is usually to allow greater separation with other traffic ahead in the pattern. This can be the result of a controller's instruction. If at the pilot's initiative, the pilot will report e.g. "(tail ID number or flight number) making one left-hand orbit, will advise complete".
Contra-rotating circuit patterns
In cases where two or more parallel runways are in operation concurrently, the aircraft operating on the outermost runways are required to perform their patterns in a direction which will not conflict with the other runways. Thus, one runway may be operating with a left-hand pattern direction, and the other one will be operating with a right-hand pattern direction. This allows aircraft to maintain maximum separation during their patterns, however it is important that the aircraft do not stray past the centerline of the runway when joining the final leg, so as to avoid potential collisions. If three or more parallel runways exist, as is the case at Bankstown AirportBankstown Airport
Bankstown Airport is a general aviation airport and business park located in the City of Bankstown, from the central business district of Sydney, Australia...
in Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, then the middle runway(s) can, for obvious reasons, only be used when either a straight in approach is used or when the aircraft joins the pattern from a very wide base leg.
Altitudes
An airfield will define a circuit height or pattern altitude, that is, a nominal level above the field at which pilots are required (recommended in the US, FAA AC90-66A Para. 8c )to fly while in the circuit. Unless otherwise specified, the standard recommended pattern height is 1000 ft AGL (above ground levelAbove ground level
In aviation and atmospheric sciences, an altitude is said to be above ground level when it is measured with respect to the underlying ground surface. This is as opposed to above mean sea level , or in broadcast engineering, height above average terrain...
), although a pattern height of 800 feet above ground level is relatively common. Helicopters usually fly their pattern at 500 feet above ground level.
Extreme caution is exercised by pilots flying the published traffic pattern altitude as this may contribute to mid air collisions.
Benefits
The use of a pattern at airfields is for air safetyAir safety
Air safety is a term encompassing the theory, investigation and categorization of flight failures, and the prevention of such failures through regulation, education and training. It can also be applied in the context of campaigns that inform the public as to the safety of air travel.-United...
. By using a consistent flight pattern pilots will know from where to expect other air traffic, and be able to see it and avoid it. Pilots flying under Visual Flight Rules
Visual flight rules
Visual flight rules are a set of regulations which allow a pilot to operate an aircraft in weather conditions generally clear enough to allow the pilot to see where the aircraft is going. Specifically, the weather must be better than basic VFR weather minimums, as specified in the rules of the...
(VFR) may not be separated by air traffic control, so this consistent predictable pattern is a vital way to keep things orderly. At tower-controlled airports air traffic control (ATC) may provide traffic advisories for VFR flights on a work-load permitting basis.
A pilot undergoing training will often fly many patterns, one after another. Usually, each landing is followed immediately by a take off and further pattern; this is called a touch and go. Pilots executing Touch and Go landings should declare the intention to do so when calling the final approach leg. After landing and once airborne again the Touch and Go pilot should declare that the aircraft is On the Go. The pilot should not declare that the aircraft is on an Upwind as that term is not applicable to non-towered airports and is not appropriate for aircraft departing from a runway end.
Helicopters
HelicopterHelicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by one or more engine-driven rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forwards, backwards, and laterally...
pilots also prefer to land facing the wind and are often asked to fly a pattern on arrival or departure. Many airfields operate a special pattern for helicopters to take account of their low airspeed. This is usually a mirror image of the fixed-wing pattern, and often at a slightly lower standard height above surface level; as noted above this altitude is usually 500 feet above ground level. However due to helicopters' unique maneuverability, helicopter pilots often choose not to enter the pattern, and make a direct approach to the helipad or apron they wish to land on.
Other patterns
If an aircraft intending to land must be delayed, the air traffic controlAir traffic control
Air traffic control is a service provided by ground-based controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and in the air. The primary purpose of ATC systems worldwide is to separate aircraft to prevent collisions, to organize and expedite the flow of traffic, and to provide information and other...
(ATC) may decide to place it in a holding pattern until the airport is prepared to permit the landing. Commercial aircraft on hold will generally fly slow, racetrack-shaped patterns which differ considerably from the airfield traffic pattern that will be commenced once the approval has been given to land. Although an aircraft in a holding pattern may similarly circle the airport, ATC may designate a distant location in which to circle.

