
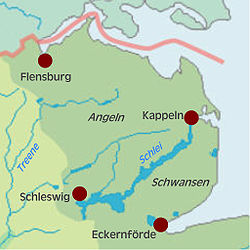
Angeln
Encyclopedia

German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
: Angeln, Danish
Danish language
Danish is a North Germanic language spoken by around six million people, principally in the country of Denmark. It is also spoken by 50,000 Germans of Danish ethnicity in the northern parts of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, where it holds the status of minority language...
: Angel, Latin: Anglia), is a small peninsula
Peninsula
A peninsula is a piece of land that is bordered by water on three sides but connected to mainland. In many Germanic and Celtic languages and also in Baltic, Slavic and Hungarian, peninsulas are called "half-islands"....
(within the larger Jutland
Jutland
Jutland , historically also called Cimbria, is the name of the peninsula that juts out in Northern Europe toward the rest of Scandinavia, forming the mainland part of Denmark. It has the North Sea to its west, Kattegat and Skagerrak to its north, the Baltic Sea to its east, and the Danish–German...
peninsula) in Southern Schleswig
Southern Schleswig
Southern Schleswig denotes the southern half of the former Duchy of Schleswig on the Jutland Peninsula. The geographical area today covers the thirty or forty northernmost kilometers of Germany up to the Flensburg Fjord, where it borders on Denmark...
in the northern Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein is the northernmost of the sixteen states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, protruding into the Bay of Kiel
Bay of Kiel
The Bay of Kiel is a bay in the southwestern Baltic Sea, off the shores of Schleswig-Holstein in Germany and the islands of Denmark. It is connected with the Bay of Mecklenburg in the east, the Little Belt in the northwest, and the Great Belt in the North....
. It is separated from the neighbouring peninsula of Schwansen
Schwansen
Schwansen is a peninsula in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany, protruding into the Baltic Sea. It is located between the Eckernförde Bay in the south and the Schlei inlet in the north....
(Danish: Svans or Svansø) by the Schlei
Schlei
The Schlei is a narrow inlet of the Baltic Sea in Schleswig-Holstein in northern Germany. It stretches for approximately 20 miles from the Baltic near Kappeln and Arnis to the city of Schleswig. Along the Schlei are many small bays and swamps...
inlet, and from the Danish
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
island of Als by the Flensburger Förde ("Firth of Flensburg
Flensburg
Flensburg is an independent town in the north of the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. Flensburg is the centre of the region of Southern Schleswig...
"). Whether ancient Angeln conformed to these borders is uncertain. It may have been somewhat larger; however, the ancient sources mainly concur that it included the territory of modern Angeln.
Angeln has a significance far beyond its current small area and country terrain, in that it is believed to have been the original home of the Angles
Angles
The Angles is a modern English term for a Germanic people who took their name from the ancestral cultural region of Angeln, a district located in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany...
, Germanic immigrants to central
English Midlands
The Midlands, or the English Midlands, is the traditional name for the area comprising central England that broadly corresponds to the early medieval Kingdom of Mercia. It borders Southern England, Northern England, East Anglia and Wales. Its largest city is Birmingham, and it was an important...
and northern England
Northern England
Northern England, also known as the North of England, the North or the North Country, is a cultural region of England. It is not an official government region, but rather an informal amalgamation of counties. The southern extent of the region is roughly the River Trent, while the North is bordered...
, and East Anglia
East Anglia
East Anglia is a traditional name for a region of eastern England, named after an ancient Anglo-Saxon kingdom, the Kingdom of the East Angles. The Angles took their name from their homeland Angeln, in northern Germany. East Anglia initially consisted of Norfolk and Suffolk, but upon the marriage of...
. This migration led to their new homeland being named after them, from which the name "England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
" derives. Both England and the English language
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
, thus, ultimately derive their names from the Angles and Angeln.
Name
In one theory the name of the Angles came from GermanicGermanic languages
The Germanic languages constitute a sub-branch of the Indo-European language family. The common ancestor of all of the languages in this branch is called Proto-Germanic , which was spoken in approximately the mid-1st millennium BC in Iron Age northern Europe...
words for "narrow" (compare German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
eng = "narrow"), and meant "the people who live beside the Narrow [Water]", i.e. beside the Schlei
Schlei
The Schlei is a narrow inlet of the Baltic Sea in Schleswig-Holstein in northern Germany. It stretches for approximately 20 miles from the Baltic near Kappeln and Arnis to the city of Schleswig. Along the Schlei are many small bays and swamps...
estuary
Estuary
An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea....
. The root would be *angh-, "tight".
The word Engel in German means "angel", but is used as a way to designate the area they occupied (Anglia). The most common theory is that the name Angeln itself means "hook", as in angling
Angling
Angling is a method of fishing by means of an "angle" . The hook is usually attached to a fishing line and the line is often attached to a fishing rod. Fishing rods are usually fitted with a fishing reel that functions as a mechanism for storing, retrieving and paying out the line. The hook itself...
for fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
. Many reputable etymological dictionaries are silent on its root. Julius Pokorny
Julius Pokorny
Julius Pokorny was an Austrian linguist and scholar of the Celtic languages, particularly Irish, and a supporter of Irish nationalism. He held academic posts in Austrian and German universities.-Life:...
, a major Indo-European linguist, derives it from *ang-, "bend". The meaning would be Anwohner der Holsteiner Bucht, "residents at the Bay of Holstein". The problem with this derivation is that Grimm's Law
Grimm's law
Grimm's law , named for Jacob Grimm, is a set of statements describing the inherited Proto-Indo-European stops as they developed in Proto-Germanic in the 1st millennium BC...
does not appear to apply to it. The theory that "Angeln" refers to a landform
Landform
A landform or physical feature in the earth sciences and geology sub-fields, comprises a geomorphological unit, and is largely defined by its surface form and location in the landscape, as part of the terrain, and as such, is typically an element of topography...
resembling a hook would have required advanced mapmaking abilities by its people, and is thus misleading.
Angeln is situated on the large bight
Bight (geography)
In geography, bight has two meanings. A bight can be simply a bend or curve in any geographical feature—usually a bend or curve in the line between land and water....
linking the Baltic coast to Jutland, which is mainly the Bay of Kiel (Kieler Bucht), but might be seen as Holsteiner Bucht.
The Angles were part of the Federation of the Ingaevones
Ingaevones
The Ingaevones or, as Pliny has it, apparently more accurately, Ingvaeones , as described in Tacitus's Germania, written c. 98 AD, were a West Germanic cultural group living along the North Sea coast in the areas of Jutland, Holstein, Frisia and the Danish islands, where they had by the 1st...
, with their mythical ancestor and god of fertility
Fertility
Fertility is the natural capability of producing offsprings. As a measure, "fertility rate" is the number of children born per couple, person or population. Fertility differs from fecundity, which is defined as the potential for reproduction...
Yngvi
Yngvi
Yngvi, Yngvin, Ingwine, Inguin are names that relate to an older theonym Ing and which appears to have been the older name for the god Freyr ....
, and both terms might well share the same root (inglish -> anglish), say as the origin of the federation. Pokorny points out the possible use of this etymological root in other ancient names, such as Hardanger
Hardanger
Hardanger is a traditional district in the western part of Norway, dominated by the Hardangerfjord. It consists of the municipalities of Odda, Ullensvang, Eidfjord, Ulvik, Granvin, Kvam and Jondal, and is located inside the county of Hordaland....
and Angrivarii
Angrivarii
The Angrivarii were a Germanic tribe of the early Roman Empire mentioned briefly in Ptolemy as the Angriouarroi , which transliterates into Latin Angrivari. They are believed to be the source of the 8th century identity, Angrarii, which was one of three subdivisions of Saxony...
.
Early history
The region was home to the Germanic people, the AnglesAngles
The Angles is a modern English term for a Germanic people who took their name from the ancestral cultural region of Angeln, a district located in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany...
, who, together with Saxons
Saxons
The Saxons were a confederation of Germanic tribes originating on the North German plain. The Saxons earliest known area of settlement is Northern Albingia, an area approximately that of modern Holstein...
and Jutes
Jutes
The Jutes, Iuti, or Iutæ were a Germanic people who, according to Bede, were one of the three most powerful Germanic peoples of their time, the other two being the Saxons and the Angles...
, left their home to migrate to Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
in the 5th-6th centuries. For the years 449-455, the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The Anglo-Saxon Chronicle is a collection of annals in Old English chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the Chronicle was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alfred the Great...
, written c. 890, describes how King Vortigern
Vortigern
Vortigern , also spelled Vortiger and Vortigen, was a 5th-century warlord in Britain, a leading ruler among the Britons. His existence is considered likely, though information about him is shrouded in legend. He is said to have invited the Saxons to settle in Kent as mercenaries to aid him in...
(a British tribal king) invited the Angles to come and receive land in return for helping him defend against marauding Picts
Picts
The Picts were a group of Late Iron Age and Early Mediaeval people living in what is now eastern and northern Scotland. There is an association with the distribution of brochs, place names beginning 'Pit-', for instance Pitlochry, and Pictish stones. They are recorded from before the Roman conquest...
. Those successful Angles sent word back that good land was available and that the British were worthless (it is presumed as soldiers). A wholesale emigration of Angles and kindred German peoples followed.
The Chronicle, commissioned by King Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great was King of Wessex from 871 to 899.Alfred is noted for his defence of the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of southern England against the Vikings, becoming the only English monarch still to be accorded the epithet "the Great". Alfred was the first King of the West Saxons to style himself...
, drew on earlier oral traditions and on the few written fragments available. The best of these, written around 730, was by the monk Bede whose history of English Christianity had the following brief account of the origin and distribution of the Angles:
- "...from the Angles, that is, the country which is called Anglia, and which is said, from that time, to remain desert to this day, between the provinces of the Jutes and the Saxons, are descended the East Angles, the Midland Angles, Mercians, all the race of the Northumbrians, that is, of those nations that dwell on the north side of the river Humber, and the other nations of the English." (Bede's Ecclesiastical History of the English Nation, Book I, Chapter XV, 731 A.D.)
The phrase "north of the Humber" refers to the northern kingdom of Northumbria
Northumbria
Northumbria was a medieval kingdom of the Angles, in what is now Northern England and South-East Scotland, becoming subsequently an earldom in a united Anglo-Saxon kingdom of England. The name reflects the approximate southern limit to the kingdom's territory, the Humber Estuary.Northumbria was...
, which includes what is now north and north-eastern England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
and part of southern Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
. Mercia
Mercia
Mercia was one of the kingdoms of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy. It was centred on the valley of the River Trent and its tributaries in the region now known as the English Midlands...
was located in central England and broadly corresponds to what is now known as the English Midlands
English Midlands
The Midlands, or the English Midlands, is the traditional name for the area comprising central England that broadly corresponds to the early medieval Kingdom of Mercia. It borders Southern England, Northern England, East Anglia and Wales. Its largest city is Birmingham, and it was an important...
.
It had long been suspected from all the Germanic sources that this report is too simple, a suspicion confirmed by the archaeology; namely, the fibulae, or brooches, worn by the women. In essence, there are two kinds, the saucer brooch and the cruciform brooch. East coastal and northern Britain were settled by women wearing cruciform brooches, which came from coastal Scandinavia
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
, all of Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
, and Schleswig-Holstein all the way south to the lower Elbe
Elbe
The Elbe is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Krkonoše Mountains of the northwestern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia , then Germany and flowing into the North Sea at Cuxhaven, 110 km northwest of Hamburg...
and all the way east to the Oder
Oder
The Oder is a river in Central Europe. It rises in the Czech Republic and flows through western Poland, later forming of the border between Poland and Germany, part of the Oder-Neisse line...
, as well as a pocket in coastal Friesland
Friesland
Friesland is a province in the north of the Netherlands and part of the ancient region of Frisia.Until the end of 1996, the province bore Friesland as its official name. In 1997 this Dutch name lost its official status to the Frisian Fryslân...
, the embarkation point.
South central Britain was settled by women wearing the saucer brooch, which came from Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a German state situated in north-western Germany and is second in area and fourth in population among the sixteen states of Germany...
, the south side of the lower Elbe, and pockets among the then Franks
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
up the Rhine and along the coast to the mouth of the Seine
Seine
The Seine is a -long river and an important commercial waterway within the Paris Basin in the north of France. It rises at Saint-Seine near Dijon in northeastern France in the Langres plateau, flowing through Paris and into the English Channel at Le Havre . It is navigable by ocean-going vessels...
. These are the areas of England that are labeled explicitly as Saxon: Sussex
Sussex
Sussex , from the Old English Sūþsēaxe , is an historic county in South East England corresponding roughly in area to the ancient Kingdom of Sussex. It is bounded on the north by Surrey, east by Kent, south by the English Channel, and west by Hampshire, and is divided for local government into West...
, Wessex
Wessex
The Kingdom of Wessex or Kingdom of the West Saxons was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the West Saxons, in South West England, from the 6th century, until the emergence of a united English state in the 10th century, under the Wessex dynasty. It was to be an earldom after Canute the Great's conquest...
, and Essex
Essex
Essex is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East region of England, and one of the home counties. It is located to the northeast of Greater London. It borders with Cambridgeshire and Suffolk to the north, Hertfordshire to the west, Kent to the South and London to the south west...
. The settlement of Kent
Kent
Kent is a county in southeast England, and is one of the home counties. It borders East Sussex, Surrey and Greater London and has a defined boundary with Essex in the middle of the Thames Estuary. The ceremonial county boundaries of Kent include the shire county of Kent and the unitary borough of...
is attributed to Jutes (from the north of the Angles).
This leads to a conclusion that the "Angles" described by Bede included all the people who populated modern Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein
Schleswig-Holstein is the northernmost of the sixteen states of Germany, comprising most of the historical duchy of Holstein and the southern part of the former Duchy of Schleswig...
and Western Pomerania south to the first big bend in the Elbe
Elbe
The Elbe is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Krkonoše Mountains of the northwestern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia , then Germany and flowing into the North Sea at Cuxhaven, 110 km northwest of Hamburg...
, and potentially members of any of the other language related groups that were recorded under different names grouped by late ethnologists as Ingaevones
Ingaevones
The Ingaevones or, as Pliny has it, apparently more accurately, Ingvaeones , as described in Tacitus's Germania, written c. 98 AD, were a West Germanic cultural group living along the North Sea coast in the areas of Jutland, Holstein, Frisia and the Danish islands, where they had by the 1st...
. A more complete presentation is given under Angles
Angles
The Angles is a modern English term for a Germanic people who took their name from the ancestral cultural region of Angeln, a district located in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany...
.
Later history

Hedeby
Hedeby |heath]]land, and býr = yard, thus "heath yard"), mentioned by Alfred the Great as aet Haethe , in German Haddeby and Haithabu, a modern spelling of the runic Heiðabý was an important trading settlement in the Danish-northern German borderland during the Viking Age...
.
Later Angeln's history is subsumed in that of the larger surrounding region, which came to be known as Southern Jutland
Southern Jutland
Southern Jutland is the name for the region south of the Kongeå in Jutland, Denmark. The region north of the Kongeå is called Nørrejylland . Both territories had their own ting assemblies in the Middle Ages . South Jutland is mentioned for the first time in the Knýtlinga saga.In the 13th century...
or Schleswig
Schleswig
Schleswig or South Jutland is a region covering the area about 60 km north and 70 km south of the border between Germany and Denmark; the territory has been divided between the two countries since 1920, with Northern Schleswig in Denmark and Southern Schleswig in Germany...
(Danish: Slesvig). Until the 19th century, the area belonged primarily to Denmark. But, in terms of ethnic and linguistic heritage, a mixed German/Danish population evolved. Denmark lost Schleswig to Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
and Prussia
Prussia
Prussia was a German kingdom and historic state originating out of the Duchy of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia shaped the history...
in 1864 as a result of the second war of Schleswig
Second War of Schleswig
The Second Schleswig War was the second military conflict as a result of the Schleswig-Holstein Question. It began on 1 February 1864, when Prussian forces crossed the border into Schleswig.Denmark fought Prussia and Austria...
. In 1920, following Germany's defeat in World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, a plebiscite
Schleswig Plebiscites
The Schleswig Plebiscites were two plebiscites, organized according to section XII, articles 109 to 114 of the Treaty of Versailles of June 28, 1919, in order to determine the future border between Denmark and Germany through the former duchy of Schleswig...
was held to determine which areas should return to Danish control. As a result of the plebiscite, much of Schleswig returned to Denmark, but Angeln remained in Germany. See Schleswig-Holstein Question
Schleswig-Holstein Question
The Schleswig-Holstein Question was a complex of diplomatic and other issues arising in the 19th century from the relations of two duchies, Schleswig and Holstein , to the Danish crown and to the German Confederation....
for a detailed history.
External links
- Bede, ca 731 A.D., Ecclesiastical History of the English Nation
- Anglo-Saxon Chronicle, ca 890 A.D.
- Angeln cattle
- Tourism in Angeln
- Cinarchea (Archaeological films of Schleswig-Holstein)
- County and Municipal Flags (Schleswig-Holstein, Germany)
- Genealogy in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany

