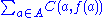Assignment problem
Encyclopedia
The assignment problem is one of the fundamental combinatorial optimization
problems in the branch of optimization
or operations research
in mathematics
. It consists of finding a maximum weight matching in a weighted bipartite graph
.
In its most general form, the problem is as follows:
If the numbers of agents and tasks are equal and the total cost of the assignment for all tasks is equal to the sum of the costs for each agent (or the sum of the costs for each task, which is the same thing in this case), then the problem is called the linear assignment problem. Commonly, when speaking of the assignment problem without any additional qualification, then the linear assignment problem is meant.
is one of many algorithm
s that have been devised that solve the linear assignment problem within time bounded by a polynomial expression of the number of agents.
The assignment problem is a special case of the transportation problem, which is a special case of the minimum cost flow problem
, which in turn is a special case of a linear program. While it is possible to solve any of these problems using the simplex algorithm
, each specialization has more efficient algorithms designed to take advantage of its special structure. If the cost function involves quadratic inequalities it is called the quadratic assignment problem
.
However, the assignment problem can be made rather more flexible than it first appears. In the above example, suppose that there are four taxis available, but still only three customers. Then a fourth dummy task can be invented, perhaps called "sitting still doing nothing", with a cost of 0 for the taxi assigned to it. The assignment problem can then be solved in the usual way and still give the best solution to the problem.
Similar tricks can be played in order to allow more tasks than agents, tasks to which multiple agents must be assigned (for instance, a group of more customers than will fit in one taxi), or maximizing profit rather than minimizing cost.
Usually the weight function is viewed as a square real-valued matrix
C, so that the cost function is written down as:
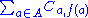
The problem is "linear" because the cost function to be optimized as well as all the constraints contain only linear terms.
The problem can be expressed as a standard linear program with the objective function
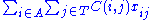
subject to the constraints
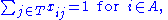
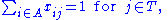
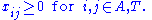
The variable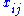 represents the assignment of agent
represents the assignment of agent 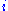 to task
to task 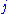 , taking value 1 if the assignment is done and 0 otherwise. This formulation allows also fractional variable values, but there is always an optimal solution where the variables take integer values. This is because the constraint matrix is totally unimodular. The first constraint requires that every agent is assigned to exactly one task, and the second constraint requires that every task is assigned exactly one agent.
, taking value 1 if the assignment is done and 0 otherwise. This formulation allows also fractional variable values, but there is always an optimal solution where the variables take integer values. This is because the constraint matrix is totally unimodular. The first constraint requires that every agent is assigned to exactly one task, and the second constraint requires that every task is assigned exactly one agent.
Combinatorial optimization
In applied mathematics and theoretical computer science, combinatorial optimization is a topic that consists of finding an optimal object from a finite set of objects. In many such problems, exhaustive search is not feasible...
problems in the branch of optimization
Optimization (mathematics)
In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
or operations research
Operations research
Operations research is an interdisciplinary mathematical science that focuses on the effective use of technology by organizations...
in mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
. It consists of finding a maximum weight matching in a weighted bipartite graph
Bipartite graph
In the mathematical field of graph theory, a bipartite graph is a graph whose vertices can be divided into two disjoint sets U and V such that every edge connects a vertex in U to one in V; that is, U and V are independent sets...
.
In its most general form, the problem is as follows:
- There are a number of agents and a number of tasks. Any agent can be assigned to perform any task, incurring some cost that may vary depending on the agent-task assignment. It is required to perform all tasks by assigning exactly one agent to each task in such a way that the total cost of the assignment is minimized.
If the numbers of agents and tasks are equal and the total cost of the assignment for all tasks is equal to the sum of the costs for each agent (or the sum of the costs for each task, which is the same thing in this case), then the problem is called the linear assignment problem. Commonly, when speaking of the assignment problem without any additional qualification, then the linear assignment problem is meant.
Algorithms and generalizations
The Hungarian algorithmHungarian algorithm
The Hungarian method is a combinatorial optimization algorithm which solves the assignment problem in polynomial time and which anticipated later primal-dual methods...
is one of many algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
s that have been devised that solve the linear assignment problem within time bounded by a polynomial expression of the number of agents.
The assignment problem is a special case of the transportation problem, which is a special case of the minimum cost flow problem
Minimum cost flow problem
The minimum-cost flow problem is finding the cheapest possible way of sending a certain amount of flow through a flow network.- Definition :Given a flow network \,G with source s \in V and sink t \in V, where edge \in E has capacity \,c, flow \,f and cost \,a. The cost of sending this flow is f...
, which in turn is a special case of a linear program. While it is possible to solve any of these problems using the simplex algorithm
Simplex algorithm
In mathematical optimization, Dantzig's simplex algorithm is a popular algorithm for linear programming. The journal Computing in Science and Engineering listed it as one of the top 10 algorithms of the twentieth century....
, each specialization has more efficient algorithms designed to take advantage of its special structure. If the cost function involves quadratic inequalities it is called the quadratic assignment problem
Quadratic assignment problem
The quadratic assignment problem is one of fundamental combinatorial optimization problems in the branch of optimization or operations research in mathematics, from the category of the facilities location problems....
.
Example
Suppose that a taxi firm has three taxis (the agents) available, and three customers (the tasks) wishing to be picked up as soon as possible. The firm prides itself on speedy pickups, so for each taxi the "cost" of picking up a particular customer will depend on the time taken for the taxi to reach the pickup point. The solution to the assignment problem will be whichever combination of taxis and customers results in the least total cost.However, the assignment problem can be made rather more flexible than it first appears. In the above example, suppose that there are four taxis available, but still only three customers. Then a fourth dummy task can be invented, perhaps called "sitting still doing nothing", with a cost of 0 for the taxi assigned to it. The assignment problem can then be solved in the usual way and still give the best solution to the problem.
Similar tricks can be played in order to allow more tasks than agents, tasks to which multiple agents must be assigned (for instance, a group of more customers than will fit in one taxi), or maximizing profit rather than minimizing cost.
Formal mathematical definition
The formal definition of the assignment problem (or linear assignment problem) is- Given two sets, A and T, of equal size, together with a weight functionWeight functionA weight function is a mathematical device used when performing a sum, integral, or average in order to give some elements more "weight" or influence on the result than other elements in the same set. They occur frequently in statistics and analysis, and are closely related to the concept of a...
C : A × T → RReal numberIn mathematics, a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuum, such as -5 , 4/3 , 8.6 , √2 and π...
. Find a bijectionBijectionA bijection is a function giving an exact pairing of the elements of two sets. A bijection from the set X to the set Y has an inverse function from Y to X. If X and Y are finite sets, then the existence of a bijection means they have the same number of elements...
f : A → T such that the cost function:
-
- is minimized.
Usually the weight function is viewed as a square real-valued matrix
Matrix (mathematics)
In mathematics, a matrix is a rectangular array of numbers, symbols, or expressions. The individual items in a matrix are called its elements or entries. An example of a matrix with six elements isMatrices of the same size can be added or subtracted element by element...
C, so that the cost function is written down as:
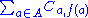
The problem is "linear" because the cost function to be optimized as well as all the constraints contain only linear terms.
The problem can be expressed as a standard linear program with the objective function

subject to the constraints
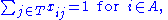
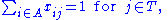
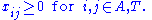
The variable
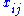 represents the assignment of agent
represents the assignment of agent 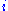 to task
to task 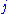 , taking value 1 if the assignment is done and 0 otherwise. This formulation allows also fractional variable values, but there is always an optimal solution where the variables take integer values. This is because the constraint matrix is totally unimodular. The first constraint requires that every agent is assigned to exactly one task, and the second constraint requires that every task is assigned exactly one agent.
, taking value 1 if the assignment is done and 0 otherwise. This formulation allows also fractional variable values, but there is always an optimal solution where the variables take integer values. This is because the constraint matrix is totally unimodular. The first constraint requires that every agent is assigned to exactly one task, and the second constraint requires that every task is assigned exactly one agent.See also
- Stable marriage problemStable marriage problemIn mathematics and computer science, the stable marriage problem is the problem of finding a stable matching between two sets of elements given a set of preferences for each element. A matching is a mapping from the elements of one set to the elements of the other set...
- Auction algorithmAuction algorithmThe term "auction algorithm" applies to several variations of a combinatorial optimization algorithm which solves assignment problems, and network optimization problems with linear and convex/nonlinear cost. An auction algorithm has been used in a business setting to determine the best prices on a...
- Generalized assignment problemGeneralized assignment problemIn applied mathematics, the maximum generalized assignment problem is a problem in combinatorial optimization. This problem is a generalization of the assignment problem in which both tasks and agents have a size...
- Linear bottleneck assignment problemLinear bottleneck assignment problemIn combinatorial optimization, a field within mathematics, the linear bottleneck assignment problem is similar to the linear assignment problem. In plain words the problem is stated as follows:...
- Quadratic assignment problemQuadratic assignment problemThe quadratic assignment problem is one of fundamental combinatorial optimization problems in the branch of optimization or operations research in mathematics, from the category of the facilities location problems....
- Weapon target assignment problemWeapon target assignment problemThe weapon target assignment problem is a class of combinatorial optimization problems present in the fields of optimization and operations research...