
Augmented Dickey-Fuller test
Encyclopedia
In statistics
and econometrics
, an augmented Dickey–Fuller test (ADF) is a test for a unit root
in a time series
sample
. It is an augmented version of the Dickey–Fuller test for a larger and more complicated set of time series models.
The augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) statistic, used in the test, is a negative number. The more negative it is, the stronger the rejection of the hypothesis that there is a unit root at some level of confidence.
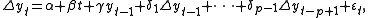
where is a constant,
is a constant, 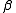 the coefficient on a time trend and
the coefficient on a time trend and 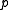 the lag order of the autoregressive process. Imposing the constraints
the lag order of the autoregressive process. Imposing the constraints  and
and 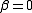 corresponds to modelling a random walk and using the constraint
corresponds to modelling a random walk and using the constraint 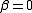 corresponds to modelling a random walk with a drift. Consequently, there are three main versions of the test, analogous to the ones discussed on the Wikipedia page for the Dickey-Fuller test
corresponds to modelling a random walk with a drift. Consequently, there are three main versions of the test, analogous to the ones discussed on the Wikipedia page for the Dickey-Fuller test
. See that page for a discussion on dealing with uncertainty about including the intercept and deterministic time trend terms in the test equation.
By including lags of the order p (greek for 'rho') the ADF formulation allows for higher-order autoregressive processes. This means that the lag length p has to be determined when applying the test. One possible approach is to test down from high orders and examine the t-values on coefficients. An alternative approach is to examine information criteria such as the Akaike information criterion
, Bayesian information criterion or the Hannan-Quinn information criterion
.
The unit root test is then carried out under the null hypothesis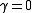 against the alternative hypothesis of
against the alternative hypothesis of 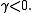 Once a value for the test statistic
Once a value for the test statistic
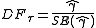
is computed it can be compared to the relevant critical value for the Dickey–Fuller Test. If the test statistic is less (this test is non symmetrical so we do not consider an absolute value) than (a larger negative) the critical value, then the null hypothesis of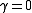 is rejected and no unit root is present.
is rejected and no unit root is present.
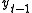 ) will provide no relevant information in predicting the change in
) will provide no relevant information in predicting the change in 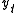 besides the one obtained in the lagged changes (
besides the one obtained in the lagged changes (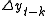 ). In that case the
). In that case the 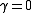 null hypothesis is not rejected.
null hypothesis is not rejected.
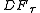 statistic of −4.57. This is more negative than the tabulated critical value of −3.50, so at the 95 per cent level the null hypothesis of a unit root will be rejected.
statistic of −4.57. This is more negative than the tabulated critical value of −3.50, so at the 95 per cent level the null hypothesis of a unit root will be rejected.
s such as the Phillips–Perron test or the ADF-GLS procedure developed by Elliot, Rothenberg and Stock (1996).
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
and econometrics
Econometrics
Econometrics has been defined as "the application of mathematics and statistical methods to economic data" and described as the branch of economics "that aims to give empirical content to economic relations." More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on...
, an augmented Dickey–Fuller test (ADF) is a test for a unit root
Unit root
In time series models in econometrics , a unit root is a feature of processes that evolve through time that can cause problems in statistical inference if it is not adequately dealt with....
in a time series
Time series
In statistics, signal processing, econometrics and mathematical finance, a time series is a sequence of data points, measured typically at successive times spaced at uniform time intervals. Examples of time series are the daily closing value of the Dow Jones index or the annual flow volume of the...
sample
Sample (statistics)
In statistics, a sample is a subset of a population. Typically, the population is very large, making a census or a complete enumeration of all the values in the population impractical or impossible. The sample represents a subset of manageable size...
. It is an augmented version of the Dickey–Fuller test for a larger and more complicated set of time series models.
The augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) statistic, used in the test, is a negative number. The more negative it is, the stronger the rejection of the hypothesis that there is a unit root at some level of confidence.
Testing Procedure
The testing procedure for the ADF test is the same as for the Dickey–Fuller test but it is applied to the model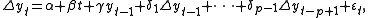
where
 is a constant,
is a constant, 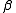 the coefficient on a time trend and
the coefficient on a time trend and 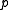 the lag order of the autoregressive process. Imposing the constraints
the lag order of the autoregressive process. Imposing the constraints  and
and 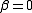 corresponds to modelling a random walk and using the constraint
corresponds to modelling a random walk and using the constraint 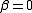 corresponds to modelling a random walk with a drift. Consequently, there are three main versions of the test, analogous to the ones discussed on the Wikipedia page for the Dickey-Fuller test
corresponds to modelling a random walk with a drift. Consequently, there are three main versions of the test, analogous to the ones discussed on the Wikipedia page for the Dickey-Fuller testDickey-Fuller test
In statistics, the Dickey–Fuller test tests whether a unit root is present in an autoregressive model. It is named after the statisticians D. A. Dickey and W. A. Fuller, who developed the test in 1979.- Explanation :A simple AR model is...
. See that page for a discussion on dealing with uncertainty about including the intercept and deterministic time trend terms in the test equation.
By including lags of the order p (greek for 'rho') the ADF formulation allows for higher-order autoregressive processes. This means that the lag length p has to be determined when applying the test. One possible approach is to test down from high orders and examine the t-values on coefficients. An alternative approach is to examine information criteria such as the Akaike information criterion
Akaike information criterion
The Akaike information criterion is a measure of the relative goodness of fit of a statistical model. It was developed by Hirotsugu Akaike, under the name of "an information criterion" , and was first published by Akaike in 1974...
, Bayesian information criterion or the Hannan-Quinn information criterion
Hannan-Quinn information criterion
In statistics, the Hannan-Quinn information criterion is a criterion for model selection. It is an alternative to Akaike information criterion and Bayesian information criterion...
.
The unit root test is then carried out under the null hypothesis
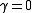 against the alternative hypothesis of
against the alternative hypothesis of 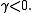 Once a value for the test statistic
Once a value for the test statistic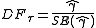
is computed it can be compared to the relevant critical value for the Dickey–Fuller Test. If the test statistic is less (this test is non symmetrical so we do not consider an absolute value) than (a larger negative) the critical value, then the null hypothesis of
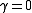 is rejected and no unit root is present.
is rejected and no unit root is present.Intuition
The intuition behind the test is that if the series is integrated then the lagged level of the series (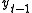 ) will provide no relevant information in predicting the change in
) will provide no relevant information in predicting the change in 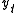 besides the one obtained in the lagged changes (
besides the one obtained in the lagged changes (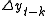 ). In that case the
). In that case the 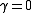 null hypothesis is not rejected.
null hypothesis is not rejected.Examples
A model that includes a constant and a time trend is estimated using sample of 50 observations and yields the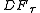 statistic of −4.57. This is more negative than the tabulated critical value of −3.50, so at the 95 per cent level the null hypothesis of a unit root will be rejected.
statistic of −4.57. This is more negative than the tabulated critical value of −3.50, so at the 95 per cent level the null hypothesis of a unit root will be rejected.Alternatives
There are alternative unit root testUnit root test
In statistics, a unit root test tests whether a time series variable is non-stationary using an autoregressive model. A well-known test that is valid in large samples is the augmented Dickey–Fuller test. The optimal finite sample tests for a unit root in autoregressive models were developed by John...
s such as the Phillips–Perron test or the ADF-GLS procedure developed by Elliot, Rothenberg and Stock (1996).
Implementations in statistics packages
- In RR (programming language)R is a programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics. The R language is widely used among statisticians for developing statistical software, and R is widely used for statistical software development and data analysis....
, the tseries package includes an adf.test function.. - GretlGretlgretl is an open-source statistical package, mainly for econometrics. The name is an acronym for Gnu Regression, Econometrics and Time-series Library. It has a graphical user interface and can be used together with X-12-ARIMA, TRAMO/SEATS, R, Octave, and Ox. It is written in C, uses GTK as widget...
includes the Augmented Dickey–Fuller test. - In MatlabMATLABMATLAB is a numerical computing environment and fourth-generation programming language. Developed by MathWorks, MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages,...
, the adftest function is part of the Econometrics Toolbox , and a free version is available as part of the 'Spatial Econometrics' toolbox, available at http://www.spatial-econometrics.com/ - In SAS, "PROC ARIMA" can perform ADF tests.
- In StataStataStata is a general-purpose statistical software package created in 1985 by StataCorp. It is used by many businesses and academic institutions around the world...
, the "dfuller" command is used for ADF tests. - In EviewsEViewsEViews is a statistical package for Windows, used mainly for time-series oriented econometric analysis. It is developed by Quantitative Micro Software , now a part of IHS. Version 1.0 was released in March 1994, and replaced MicroTSP...
, the "Augmented Dickey-Fuller" is available under "Unit Root Test."
See also
- Elliot–Rothenberg–Stock test
- Kwiatkowski–Phillips–Schmidt–Shin testKPSS testIn econometrics, Kwiatkowski–Phillips–Schmidt–Shin tests are used for testing a null hypothesis that an observable time series is stationary around a deterministic trend. Such models were proposed in 1982 by Alok Bhargava in his Ph.D. thesis where several John von Neumann or Durbin–Watson type...

