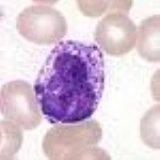
Basophil granulocyte
Encyclopedia
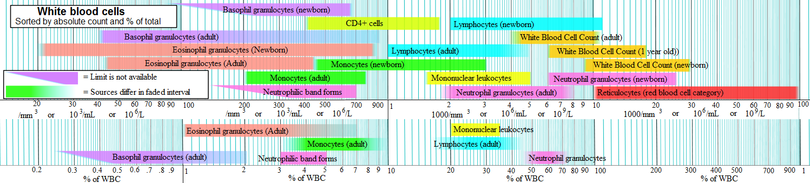
Basophil granulocytes, sometimes referred to as basophils, are the least common of the granulocyte
s, representing about 0.01% to 0.3% of circulating white blood cells.
The name comes from the fact that these leukocytes are basophilic, i.e., they are susceptible to staining by basic
dye
s, as shown in the picture.
Basophils contain large cytoplasm
ic granules which obscure the cell nucleus
under the microscope
. However, when unstained, the nucleus is visible and it usually has 2 lobes. The mast cell
, a cell
in tissues
, has many similar characteristics. For example, both cell types store histamine
, a chemical that is secreted by the cells when stimulated in certain ways (histamine causes some of the symptoms of an allergic
reaction). Like all circulating granulocytes, basophils can be recruited out of the blood
into a tissue when needed.
 Basophils appear in many specific kinds of inflammatory
Basophils appear in many specific kinds of inflammatory
reactions,
particularly those that cause allergic symptoms. Basophils contain anticoagulant heparin
, which prevents blood from clotting too quickly. They also contain the vasodilator histamine, which promotes blood flow to tissues. They can be found in unusually high numbers at sites of ectoparasite infection, e.g., tick
s. Like eosinophils, basophils play a role in both parasitic infections and allergies. They are found in tissues where allergic reactions are occurring and probably contribute to the severity of these reactions. Basophils have protein receptors on their cell surface that bind IgE, an immunoglobulin involved in macroparasite defense and allergy
. It is the bound IgE antibody that confers a selective response of these cells to environmental substances, for example, pollen
protein
s or helminth antigens. Recent studies in mice suggest that basophils may also regulate the behavior of T cell
s and mediate the magnitude of the secondary immune response .
(DX-5)+, CD69
+, Thy-1.2+, 2B4+, CD11bdull, CD117
(c-kit)–, CD24
–, CD19
–, CD80
–, CD14
–, CD23
–, Ly49c–, CD122–, CD11c
–, Gr-1–, NK1.1–, B220–, CD3
–, γδTCR
–, αβTCR
–, α4 and β4-integrin
negative.
to release histamine
, proteoglycan
s (e.g. heparin
and chondroitin
), and proteolytic enzymes (e.g. elastase
and lysophospholipase
). They also secrete lipid
mediators like leukotriene
s, and several cytokine
s. Histamine and proteoglycans are pre-stored in the cell's granules while the other secreted substances are newly generated. Each of these substances contributes to inflammation. Recent evidence suggests that basophils are an important source of the cytokine, interleukin-4, perhaps more important than T cells. Interleukin-4 is considered one of the critical cytokines in the development of allergies and the production of IgE
antibody by the immune system. There are other substances that can activate basophils to secrete which suggests that these cells have other roles in inflammation.
Basopenia
(a low basophil count) is difficult to demonstrate as the normal basophil count is so low; it has been reported in association with autoimmune urticaria
(a chronic itching condition). Basophilia
is also uncommon but may be seen in some forms of leukaemia or lymphoma
.
Granulocyte
Granulocytes are a category of white blood cells characterized by the presence of granules in their cytoplasm. They are also called polymorphonuclear leukocytes because of the varying shapes of the nucleus, which is usually lobed into three segments...
s, representing about 0.01% to 0.3% of circulating white blood cells.
The name comes from the fact that these leukocytes are basophilic, i.e., they are susceptible to staining by basic
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
dye
Dye
A dye is a colored substance that has an affinity to the substrate to which it is being applied. The dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution, and requires a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber....
s, as shown in the picture.
Basophils contain large cytoplasm
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is a small gel-like substance residing between the cell membrane holding all the cell's internal sub-structures , except for the nucleus. All the contents of the cells of prokaryote organisms are contained within the cytoplasm...
ic granules which obscure the cell nucleus
Cell nucleus
In cell biology, the nucleus is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in eukaryotic cells. It contains most of the cell's genetic material, organized as multiple long linear DNA molecules in complex with a large variety of proteins, such as histones, to form chromosomes. The genes within these...
under the microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
. However, when unstained, the nucleus is visible and it usually has 2 lobes. The mast cell
Mast cell
A mast cell is a resident cell of several types of tissues and contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin...
, a cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
in tissues
Biological tissue
Tissue is a cellular organizational level intermediate between cells and a complete organism. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning...
, has many similar characteristics. For example, both cell types store histamine
Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogen compound involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter. Histamine triggers the inflammatory response. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by...
, a chemical that is secreted by the cells when stimulated in certain ways (histamine causes some of the symptoms of an allergic
Allergy
An Allergy is a hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system. Allergic reactions occur when a person's immune system reacts to normally harmless substances in the environment. A substance that causes a reaction is called an allergen. These reactions are acquired, predictable, and rapid...
reaction). Like all circulating granulocytes, basophils can be recruited out of the blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
into a tissue when needed.
Function

Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
reactions,
particularly those that cause allergic symptoms. Basophils contain anticoagulant heparin
Heparin
Heparin , also known as unfractionated heparin, a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan, is widely used as an injectable anticoagulant, and has the highest negative charge density of any known biological molecule...
, which prevents blood from clotting too quickly. They also contain the vasodilator histamine, which promotes blood flow to tissues. They can be found in unusually high numbers at sites of ectoparasite infection, e.g., tick
Tick
Ticks are small arachnids in the order Ixodida, along with mites, constitute the subclass Acarina. Ticks are ectoparasites , living by hematophagy on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians...
s. Like eosinophils, basophils play a role in both parasitic infections and allergies. They are found in tissues where allergic reactions are occurring and probably contribute to the severity of these reactions. Basophils have protein receptors on their cell surface that bind IgE, an immunoglobulin involved in macroparasite defense and allergy
Allergy
An Allergy is a hypersensitivity disorder of the immune system. Allergic reactions occur when a person's immune system reacts to normally harmless substances in the environment. A substance that causes a reaction is called an allergen. These reactions are acquired, predictable, and rapid...
. It is the bound IgE antibody that confers a selective response of these cells to environmental substances, for example, pollen
Pollen
Pollen is a fine to coarse powder containing the microgametophytes of seed plants, which produce the male gametes . Pollen grains have a hard coat that protects the sperm cells during the process of their movement from the stamens to the pistil of flowering plants or from the male cone to the...
protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s or helminth antigens. Recent studies in mice suggest that basophils may also regulate the behavior of T cell
T cell
T cells or T lymphocytes belong to a group of white blood cells known as lymphocytes, and play a central role in cell-mediated immunity. They can be distinguished from other lymphocytes, such as B cells and natural killer cells , by the presence of a T cell receptor on the cell surface. They are...
s and mediate the magnitude of the secondary immune response .
Immunophenotyping of basophils
Basophils of mouse and human have consistent immunophenotypes as follows: FcεRI+, CD123, CD49bCD49b
CD49b is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CD49b gene.The CD49b protein is an integrin alpha subunit. It makes up half of the α2β1 integrin duplex. Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane glycoproteins composed of a distinct alpha chain and a common beta chain...
(DX-5)+, CD69
CD69
CD69 is a human transmembrane C-Type lectin protein encoded by the gene.-Further reading:...
+, Thy-1.2+, 2B4+, CD11bdull, CD117
CD117
Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor also known as proto-oncogene c-Kit or tyrosine-protein kinase Kit or CD117 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIT gene...
(c-kit)–, CD24
CD24
Signal transducer CD24 also known as cluster of differentiation 24 or heat stable antigen CD24 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD24 gene. CD24 is a cell adhesion molecule.- Function :...
–, CD19
CD19
B-lymphocyte antigen CD19 also known as CD19 , is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD19 gene.- Function :...
–, CD80
CD80
Cluster of Differentiation 80 is a protein found on activated B cells and monocytes that provides a costimulatory signal necessary for T cell activation and survival...
–, CD14
CD14
Cluster of differentiation 14 also known as CD14 is a human gene.The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the innate immune system. CD14 exists in two forms. Either it is anchored into the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol tail or it appears in a soluble form...
–, CD23
CD23
CD23, also known as Fc epsilon RII, or FcεRII, is the "low-affinity" receptor for IgE, an antibody isotype involved in allergy and resistance to parasites, and is important in regulation of IgE levels. Unlike many of the antibody receptors, CD23 is a C-type lectin...
–, Ly49c–, CD122–, CD11c
CD11c
CD11c, also known as Integrin, alpha X , is a human gene.CD11c is a type I transmembrane protein found at high levels on most human dendritic cells, but also on monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, and some B cells that induces cellular activation and helps trigger neutrophil respiratory burst;...
–, Gr-1–, NK1.1–, B220–, CD3
CD3
CD3 or CD-3 may be:* CD3 , an antigen, cluster of differentiation protein , part of the T cell receptor complex on a mature T lymphocyte* Ford CD3 platform* MediaMax CD-3, copy protection scheme* MiniCD, a 3-inch CD...
–, γδTCR
TCR
TCR can mean:*Time Code Reading, a method of accounting for video or film footage and frames in media editing*T cell receptor*Tobacco Control Research*Toronto Civic Railways...
–, αβTCR
TCR
TCR can mean:*Time Code Reading, a method of accounting for video or film footage and frames in media editing*T cell receptor*Tobacco Control Research*Toronto Civic Railways...
–, α4 and β4-integrin
Integrin
Integrins are receptors that mediate attachment between a cell and the tissues surrounding it, which may be other cells or the ECM. They also play a role in cell signaling and thereby regulate cellular shape, motility, and the cell cycle....
negative.
Secretions
When activated, basophils degranulateDegranulation
Degranulation is a cellular process that releases antimicrobial cytotoxic molecules from secretory vesicles called granules found inside some cells...
to release histamine
Histamine
Histamine is an organic nitrogen compound involved in local immune responses as well as regulating physiological function in the gut and acting as a neurotransmitter. Histamine triggers the inflammatory response. As part of an immune response to foreign pathogens, histamine is produced by...
, proteoglycan
Proteoglycan
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan chain. The point of attachment is a Ser residue to which the glycosaminoglycan is joined through a tetrasaccharide bridge...
s (e.g. heparin
Heparin
Heparin , also known as unfractionated heparin, a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan, is widely used as an injectable anticoagulant, and has the highest negative charge density of any known biological molecule...
and chondroitin
Chondroitin
Chondroitin is a chondrin derivative.Types include:* Chondroitin sulfate* Dermatan sulfate...
), and proteolytic enzymes (e.g. elastase
Elastase
In molecular biology, elastase is an enzyme from the class of proteases that break down proteins.- Forms and classification:There exist eight human genes for elastase:Bacterial forms: Organisms such as P...
and lysophospholipase
Lysophospholipase
In enzymology, a lysophospholipase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are 2-lysophosphatidylcholine and H2O, whereas its two products are glycerophosphocholine and carboxylate....
). They also secrete lipid
Lipid
Lipids constitute a broad group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins , monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, and others...
mediators like leukotriene
Leukotriene
Leukotrienes are fatty signaling molecules. They were first found in leukocytes . One of their roles is to trigger contractions in the smooth muscles lining the trachea; their overproduction is a major cause of inflammation in asthma and allergic rhinitis...
s, and several cytokine
Cytokine
Cytokines are small cell-signaling protein molecules that are secreted by the glial cells of the nervous system and by numerous cells of the immune system and are a category of signaling molecules used extensively in intercellular communication...
s. Histamine and proteoglycans are pre-stored in the cell's granules while the other secreted substances are newly generated. Each of these substances contributes to inflammation. Recent evidence suggests that basophils are an important source of the cytokine, interleukin-4, perhaps more important than T cells. Interleukin-4 is considered one of the critical cytokines in the development of allergies and the production of IgE
IGE
IGE was one of the largest services company buying and selling virtual currencies and accounts for MMORPG. During its peak time, it had offices in Los Angeles, China , and headquarters & customer service centre in Hong Kong. IGE was one of the main monopoly in virtual economy services, also known...
antibody by the immune system. There are other substances that can activate basophils to secrete which suggests that these cells have other roles in inflammation.
Basopenia
Basopenia
Basopenia is a form of agranulocytosis associated with a deficiency of basophils.One cause is urticaria.It has been proposed as an indicator of ovulation....
(a low basophil count) is difficult to demonstrate as the normal basophil count is so low; it has been reported in association with autoimmune urticaria
Urticaria
Urticaria is a kind of skin rash notable for pale red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives is frequently caused by allergic reactions; however, there are many non-allergic causes...
(a chronic itching condition). Basophilia
Basophilia
Basophilia is a condition where the basophil quantity is abnormally elevated .-Causes:Basophilia as an isolated finding is uncommon. However it is a common feature of myeloproliferative disorders and particularly prominent in chronic myelogenous leukemia....
is also uncommon but may be seen in some forms of leukaemia or lymphoma
Lymphoma
Lymphoma is a cancer in the lymphatic cells of the immune system. Typically, lymphomas present as a solid tumor of lymphoid cells. Treatment might involve chemotherapy and in some cases radiotherapy and/or bone marrow transplantation, and can be curable depending on the histology, type, and stage...
.

