
Behavior Trees
Encyclopedia
Systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
and software engineering
Software engineering
Software Engineering is the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software, and the study of these approaches; that is, the application of engineering to software...
. Behavior trees employ a well-defined notation to unambiguously represent the hundreds or even thousands of natural language
Natural language
In the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
requirements that are typically used to express the stakeholder needs for a large-scale software-integrated system.
Overview
The amount of detail in the large number of natural languageNatural language
In the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
requirements for a large-scale system causes short-term memory overload and may create a barrier that prevents anyone from gaining a deep, accurate and holistic understanding of the system needs. Also, because of the use of natural language
Natural language
In the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
, there are likely to be many ambiguities, aliases, inconsistencies, redundancies and incompleteness problems associated with the requirement
Requirement
In engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s information. This adds further to the uncertainty and complexity. Generally, at best, a few people understand parts of the system or situation well, but no one has other than a superficial understanding of the whole – that is, the detailed integrated behavior of the system.
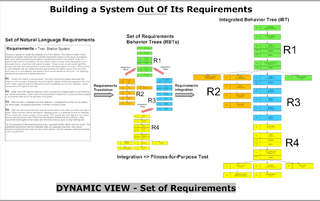
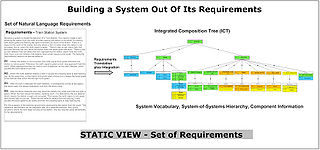
The Behavior Tree representation, (with the help of the Composition Tree representation that resolves alias and other vocabulary problems with large sets of requirements) allows people to avoid short-term memory overload and produce a deep, accurate, holistic representation of system needs that can be understood by all stakeholders because it strictly uses the vocabulary of the original requirements. Because the Behavior Tree Notation uses a formal semantics, for any given example, it already is, or can be made executable
Executable
In computing, an executable file causes a computer "to perform indicated tasks according to encoded instructions," as opposed to a data file that must be parsed by a program to be meaningful. These instructions are traditionally machine code instructions for a physical CPU...
.
Behavior tree forms
Systems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
and software engineering
Software engineering
Software Engineering is the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software, and the study of these approaches; that is, the application of engineering to software...
.
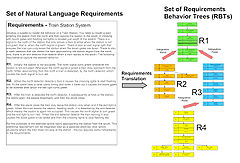
- Requirement Behavior Trees : Initially, individual requirement behavior trees (RBTs) are used to capture all the fragments of behavior in each individual natural languageNatural languageIn the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
requirement by a process of rigorous, intent-preserving and vocabulary-preserving translation. The translation process can uncover a range of defects in original natural language requirementRequirementIn engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s. - Integrated Behavior Tree : Because a set of requirementRequirementIn engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s imply the integrated behavior of a system, all the individual requirement behavior trees can be composed to construct an integrated behavior tree (IBT) that provides a single holistic view of the emergent integrated behavior of the system. This enables the building of the integrated behavior of a system out of its requirements. An analogy to help describe this process is the transition from a randomly arranged set of jigsaw puzzle pieces to putting each of the pieces in its appropriate place. When we do this, we see each piece of information in its intended context and we see the pieces of information as a whole and the emergent properties of the whole.
Having all the requirements converted to behavior trees (RBTs) is similar to having all the pieces for a jigsaw puzzle randomly spread out on a table - until we put all the pieces together we cannot see the emergent picture and whether any pieces are missing or do not fit. Constructing an Integrated Behavior Tree (IBT) allows us to do this.
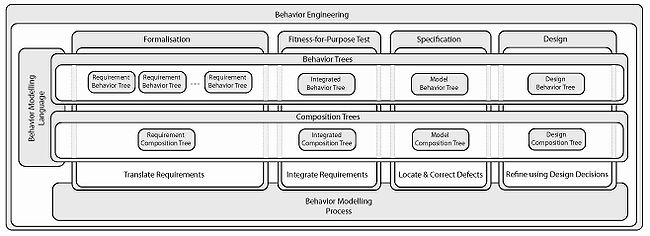
Behavior engineering process
Representation Used - (critical)- BEHAVIOR TREES provide a vehicle for growing a shared understanding of a complex systemComplex systemA complex system is a system composed of interconnected parts that as a whole exhibit one or more properties not obvious from the properties of the individual parts....
. - The role of the COMPOSITION TREE in the overall process is to provide a vehicle for overcoming the imperfect knowledge associated with the large set of requirements for a system.
Process Used - (critical)
- BEHAVIOR ENGINEERING uses Behavior Trees to control complexity while growing a shared understanding of a complex systemComplex systemA complex system is a system composed of interconnected parts that as a whole exhibit one or more properties not obvious from the properties of the individual parts....
. - That shared, holistic understanding of a complex systemComplex systemA complex system is a system composed of interconnected parts that as a whole exhibit one or more properties not obvious from the properties of the individual parts....
, because it integrates the requirements, shows the emergent behavior of the system implied by requirements.
History
Behavior Trees and the concepts for their application in systemsSystems engineering
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary field of engineering that focuses on how complex engineering projects should be designed and managed over the life cycle of the project. Issues such as logistics, the coordination of different teams, and automatic control of machinery become more...
and software engineering
Software engineering
Software Engineering is the application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of software, and the study of these approaches; that is, the application of engineering to software...
were originally developed by Dromey with first publication of some of the key ideas in 2001. Early publications on this work used the terms “genetic software engineering” and “genetic design” to describe the application of behavior trees. The reason for originally using the word genetic was because sets of genes, sets of jigsaw puzzle pieces and sets of requirements represented as behavior trees all appeared to share several key properties:
- they contained enough information as a set to allow them to be composed – with behavior trees this allows a system to be built out of its requirements
- the order in which the pieces were put together was not important – with requirements this aids coping with complexity
- when all the members of the set were put together the resulting integrated entity exhibited a set of important emergent properties.
For behavior trees important emergent properties include
- the integrated behavior of the system implied by the requirements
- the coherent behavior of each component referred to in the requirements.
These genetic parallels, in another context, were originally spelled by Woolfson, (A. Woolfson, Living Without Genes, Flamingo, 2000)
Further weight for use of the term genetic came from eighteenth century thinker Giambattista Vico
Giambattista Vico
Giovanni Battista ' Vico or Vigo was an Italian political philosopher, rhetorician, historian, and jurist....
, who said, “To understand something, and not merely be able to describe it, or analyse it into its component parts, is to understand how it came into being – its genesis, its growth … true understanding is always genetic”. Despite these legitimate genetic parallels it was felt that this emphasis led to confusion with the concept of genetic algorithms. As a result the term Behavior Engineering was introduced to describe the processes that exploit behavior trees to construct systems. The term "behavior engineering" has previously been used in a specialized area of Artificial Intelligence - robotics research. The present use embraces a much broader rigorous formalization and integration of large sets of behavioral and compositional requirements needed to model large-scale systems.
Since the Behavior Tree Notation was originally conceived a number of people from the DCCS (Dependable Complex Computer-based Systems Group – a joint University of Queensland
University of Queensland
The University of Queensland, also known as UQ, is a public university located in state of Queensland, Australia. Founded in 1909, it is the oldest and largest university in Queensland and the fifth oldest in the nation...
, Griffith University
Griffith University
Griffith University is a public, coeducational, research university located in the southeastern region of the Australian state of Queensland. The university has five satellite campuses located in the Gold Coast, Logan City and in the Brisbane suburbs of Mount Gravatt, Nathan and South Bank. Current...
research group) have made important contributions to the evolution and refinement of the notation and to the use of Behavior Trees. Members of this group include: David Carrington, Rob Colvin, Geoff Dromey, Lars Grunske, Ian Hayes, Diana Kirk, Peter Lindsay, Toby Myers, Dan Powell, John Seagrott, Cameron Smith, Larry Wen, Nisansala Yatapanage, Kirsten Winter, Saad Zafar, Forest Zheng.
Probabilistic Timed Behavior Trees have recently been developed by Colvin, Grunske and Winter so that reliability, performance and other dependability properties can be expressed.
Behavior tree notation
Concurrency (computer science)
In computer science, concurrency is a property of systems in which several computations are executing simultaneously, and potentially interacting with each other...
is admitted, appears abstractly as a set of communicating sequential processes
Communicating sequential processes
In computer science, Communicating Sequential Processes is a formal language for describing patterns of interaction in concurrent systems. It is a member of the family of mathematical theories of concurrency known as process algebras, or process calculi...
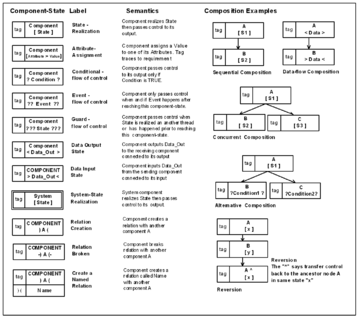
. The Behavior Tree Notation captures these composed component-states in a simple tree-like form.
Behavior is expressed in terms of components realizing states and components creating and breaking relations. Using the logic and graphic forms of conventions found in programming languages, components can support actions, composition, events, control-flow, data-flow, and threads.
Traceability tags (see Section 1.2 of Behavior Tree Notation) in behavior tree nodes link the formal representation to the corresponding natural language
Natural language
In the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
requirement. Behavior trees accurately capture behavior expressed in the natural language representation of functional requirements. Requirements Behavior Trees strictly use the vocabulary of the natural language requirements but employ graphical forms for behavior composition in order to eliminate risk of ambiguity. By doing this they provide a direct and clearly traceable relationship between what is expressed in the natural language representation and its formal specification
Formal specification
In computer science, a formal specification is a mathematical description of software or hardware that may be used to develop an implementation. It describes what the system should do, not how the system should do it...
.
A basis of the notation is that behavior is always associated with some component. Component-states which represent nodes of behavior are composed sequentially or concurrently to construct a behavior tree that represents the behavior expressed in the natural language requirements.
A behavior tree with leaf nodes may revert back (symbolized by adding the caret
Caret
Caret usually refers to the spacing symbol ^ in ASCII and other character sets. In Unicode, however, the corresponding character is , whereas the Unicode character named caret is actually a similar but lowered symbol: ....
operator ^) to an ancestor node to repeat behavior, or start a new thread (symbolized by two carets ^^).
A Behavior Tree specifies state changes in components, how data and control is passed between components and how threads interact. There are constructs for creating and breaking relations. There are also constructs for setting and testing states
State (computer science)
In computer science and automata theory, a state is a unique configuration of information in a program or machine. It is a concept that occasionally extends into some forms of systems programming such as lexers and parsers....
of components as well as mechanisms for inter-process communication
Inter-process communication
In computing, Inter-process communication is a set of methods for the exchange of data among multiple threads in one or more processes. Processes may be running on one or more computers connected by a network. IPC methods are divided into methods for message passing, synchronization, shared...
that include message passing
Message passing
Message passing in computer science is a form of communication used in parallel computing, object-oriented programming, and interprocess communication. In this model, processes or objects can send and receive messages to other processes...
(events), shared variable blocking and synchronization
Synchronization (computer science)
In computer science, synchronization refers to one of two distinct but related concepts: synchronization of processes, and synchronization of data. Process synchronization refers to the idea that multiple processes are to join up or handshake at a certain point, so as to reach an agreement or...
.
For a complete reference to Behavior Tree notation, version 1.0, see: Behavior Tree Notation v1.0 (2007)
Semantics
The formal semantics of Behavior Trees is given via a process algebra and its operational semanticsOperational semantics
In computer science, operational semantics is a way to give meaning to computer programs in a mathematically rigorous way. Operational semantics are classified into two categories: structural operational semantics formally describe how the individual steps of a computation take place in a...
. The semantics has been used as the basis for developing simulation
Simulation
Simulation is the imitation of some real thing available, state of affairs, or process. The act of simulating something generally entails representing certain key characteristics or behaviours of a selected physical or abstract system....
, model checking
Model checking
In computer science, model checking refers to the following problem:Given a model of a system, test automatically whether this model meets a given specification....
and failure modes and effects analysis
Failure mode and effects analysis
A failure modes and effects analysis is a procedure in product development and operations management for analysis of potential failure modes within a system for classification by the severity and likelihood of the failures...
.
Requirements translation
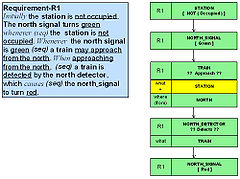
What is clear from the outcome of this process is that apart from pronouns, definite articles etc., essentially all the words in the sentences that contribute to the behavior they describe have been accounted for and used.
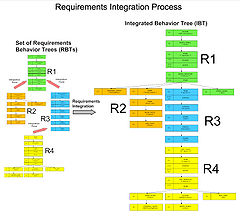
Requirements integration
Once the set of requirementRequirement
In engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s are formalized as individual requirement behavior trees, two joint properties of systems and requirements need to be exploited in order to proceed with composing the integrated behavior tree:
- In general, a fragment of behavior expressed by a requirementRequirementIn engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
always has associated with it a preconditionPreconditionIn computer programming, a precondition is a condition or predicate that must always be true just prior to the execution of some section of code or before an operation in a formal specification....
which needs to be satisfied before the behavior can take place (this precondition may or may not be expressed in the requirement). - If the requirement is really part of the system then some other requirement in the set must establish the precondition needed in (1).
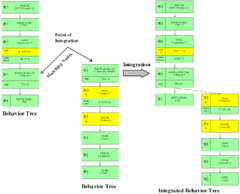
- For requirements represented as behavior trees this amounts to finding where the root node of one tree occurs in some other behavior tree and integrating the two trees at that node.
The example below illustrates requirements integration for two requirements, R1 and R3. In other words, it shows how these two requirements interact.
Operations on integrated behavior trees
Once an integrated behavior tree has been composed, there are a number of important operations that can be performed upon it.Inspection: defect detection and correction
In general, many defects become much more visible when there is an integrated view of the requirementRequirement
In engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s and each requirement has been placed in the behavior context where it needs to execute. For example, it is much easier to tell whether a set of conditions or events emanating from a node is complete and consistent. The traceability tags also make it easy to refer back to the original natural language
Natural language
In the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
requirements. There is also the potential to automate a number of defect and consistency checks on an integrated behavior tree.
When all defects have been corrected and the IBT is logically consistent and complete it becomes a Model Behavior Tree (MBT) which serves as a Formal Specification
Formal specification
In computer science, a formal specification is a mathematical description of software or hardware that may be used to develop an implementation. It describes what the system should do, not how the system should do it...
for the System’s behavior that has been constructed out the original requirements. This is the clearly defined stopping point for the analysis phase. With other modelling notations and methods (for instance, with UML
Unified Modeling Language
Unified Modeling Language is a standardized general-purpose modeling language in the field of object-oriented software engineering. The standard is managed, and was created, by the Object Management Group...
) it is less clear-cut when modelling can stop. In some cases, parts of a Model Behavior Tree may need to be transformed to make the specification executable
Executable
In computing, an executable file causes a computer "to perform indicated tasks according to encoded instructions," as opposed to a data file that must be parsed by a program to be meaningful. These instructions are traditionally machine code instructions for a physical CPU...
. Once an MBT has been made executable it is possible to carry out a number of other dependability checks.
Simulation
A Model Behavior Tree can be readily simulated in order to explore the dynamic properties of the system. Both a symbolic tool and a graphics tool have been constructed to support these activities.Model-checking
A translator has been written to convert a Model Behavior Tree into the “Actions Systems” language. This input can then be fed into the SAL Model-checker in order to allow checks to be made as to whether certain safety and security properties are satisfied.Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
Model-checkingModel checking
In computer science, model checking refers to the following problem:Given a model of a system, test automatically whether this model meets a given specification....
has often been applied to system models to check that hazardous states cannot be reached during normal operation of the system. It is possible to combine model-checking with behavior trees to provide automated support for failure mode and effects analysis
Failure mode and effects analysis
A failure modes and effects analysis is a procedure in product development and operations management for analysis of potential failure modes within a system for classification by the severity and likelihood of the failures...
(FMEA). The advantage of using Behavior Trees for this purpose is that they allow the formal method aspects of the approach to be hidden from non-expert users.
Requirements change
The ideal that is sought when responding to a change in the functional requirementsFunctional requirements
In software engineering, a functional requirement defines a function of a software system or its component. A function is described as a set of inputs, the behavior, and outputs ....
for a system is that it can be quickly determined:
- where to make the change,
- how the change affects the architecture of the existing system,
- which components of the system are affected by the change, and
- what behavioral changes will need to be made to the components (and their interfaces) that are affected by the change of requirements.
Because a system is likely to undergo many sets of changes over its service time, there is also a need to record, manage and optimize the system’s evolution driven by the change sequence.
A traceability model, which uses behavior trees as a formal notation to represent functional requirements, reveals change impacts on different types of design constructs (documents) caused by the changes of the requirements. The model introduces the concept of evolutionary design documents that record the change history of the designs. From these documents, any version of a design document as well as the difference between any two versions can be retrieved. An important advantage of this model is that the major part of the procedure to generate these evolutionary design documents can be supported by automated tools.
Code generation and execution
The Behavior Tree representation of the integrated behavior of the system affords several important advantages as an executable model. It clearly separates the tasks of component integration from the task of individual component implementation. The integrated behavior of the system that emerges from integrating the requirementRequirement
In engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s can be used as a foundation to create a design by applying design decisions. The result is a Design Behavior Tree (DBT): an executable multithreaded component integration specification that has been built out of the original requirements.
Behavior Tree models are executed in a virtual machine called the Behavior Run-time Environment (BRE). The BRE links together components using middleware, allowing components to be independent programs written in one of several languages that can be executed in a distributed environment
Distributed computing
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. A distributed system consists of multiple autonomous computers that communicate through a computer network. The computers interact with each other in order to achieve a common goal...
. The BRE also contains an expression parser that automatically performs simple operations to minimize the amount of code required to be manually implemented in the component.
The implementation of components is supported by views that are automatically extractable from the DBT. These views provide the component behavior trees (CBTs) of individual components together with the interfaces of individual components. This information, together with the information in the integrated composition tree (ICT) captured about each individual component, provides the information that is needed to implement each individual component.
Several BRE’s can be linked together to form complex systems using a system-of-systems construct and the Behavior Engineering Component Integration Environment (BECIE). BECIE is also used to monitor and control the Behavior Tree models being executed within a BRE, similar to supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA)
SCADA
SCADA generally refers to industrial control systems : computer systems that monitor and control industrial, infrastructure, or facility-based processes, as described below:...
systems used in industrial process control.
Executable Behavior Trees have been developed for case studies including automated train protection, mobile robots with dynamic object following, an ambulatory infusion pump and traffic light management systems. A version of the BRE suited for embedded systems (eBRE) is also available that has reduced functionality to tailor it to small-footprint microcontrollers.
Applications
Behavior Tree modelling can and has been applied to a diverse range of applications over a number of years. Some of the main application areas are described below.Large-scale systems
Modeling large-scale systems with large sets of natural languageNatural language
In the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
requirement
Requirement
In engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s has always been the major focus for trialling Behavior Trees and the overall Behavior Engineering process. Conducting these evaluations and trials of the method has involved work with a number of industry partners and government departments in Australia. The systems studied have included a significant number of defense systems, enterprise systems, transportation systems, information systems, health systems and sophisticated control systems with stringent safety requirements. The results of these studies have all been commercial-in-confidence. However the results of the extensive industry trails with Raytheon
Raytheon
Raytheon Company is a major American defense contractor and industrial corporation with core manufacturing concentrations in weapons and military and commercial electronics. It was previously involved in corporate and special-mission aircraft until early 2007...
Australia are presented below in the Industry Section.
What all this work has consistently shown is that by translating requirements and creating dynamic and static integrated views of requirements a very significant number major defects are discovered early, over and above the defects that are found by current industry best-practice.
Embedded systems
Failure of a design to satisfy a system’s requirementRequirement
In engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s can result in schedule and cost overruns. If there are also critical dependability issues, not satisfying system requirements can have life threatening consequences. However in current approaches, ensuring requirements are satisfied is often delayed until late in the development process during a cycle of testing and debugging. This work describes how the system development approach, Behavior Engineering, can be used to develop software for embedded system
Embedded system
An embedded system is a computer system designed for specific control functions within a larger system. often with real-time computing constraints. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including hardware and mechanical parts. By contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a personal...
s. The result is a model-driven development approach that can create embedded system software that satisfies its requirements, as a result of applying the development process.
Hardware-software systems
Many large-scale systems consist of a mixture of co-dependent software and hardware. The different nature of software and hardware means they are often modelled separately using different approaches. This can subsequently lead to integration problems due to incompatible assumptions about hardware/software interactions. These problems can be overcome by integrating Behavior Trees with the ModelicaModelica
Modelica is an object-oriented, declarative, multi-domain modeling language for component-oriented modeling of complex systems, e.g., systems containing mechanical, electrical, electronic, hydraulic, thermal, control, electric power or process-oriented subcomponents.The free Modelica languageis...
, mathematical modelling approach. The environment and hardware components are modelled using Modelica and integrated with an executable software model that uses Behavior Trees.
Role-based access control
To ensure correct implementation of complex access controlAccess control
Access control refers to exerting control over who can interact with a resource. Often but not always, this involves an authority, who does the controlling. The resource can be a given building, group of buildings, or computer-based information system...
requirements, it is important that the validated and verified requirement
Requirement
In engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s are effectively integrated with the rest of the system. It is also important that the system can be validated and verified early in the development process. An integrated, role-based access control model has been developed. The model is based on the graphical Behavior Tree notation, and can be validated by simulation
Simulation
Simulation is the imitation of some real thing available, state of affairs, or process. The act of simulating something generally entails representing certain key characteristics or behaviours of a selected physical or abstract system....
, as well as verified using a model checker. Using this model, access control requirements can be integrated with the rest of the system from the outset, because: a single notation is used to express both access control and functional requirements
Functional requirements
In software engineering, a functional requirement defines a function of a software system or its component. A function is described as a set of inputs, the behavior, and outputs ....
; a systematic and incremental approach to constructing a formal Behavior Tree specification can be adopted; and the specification can be simulated and model checked. The effectiveness of the model has been evaluated using a case study with distributed access control requirements.
Biological systems
Because Behavior Trees describe complex behavior, they can be used for describing a range of systems not limited to those that arecomputer-based. In a biological context, BTs can be used to piece together a procedural interpretation of biological functions
described in research papers, treating the papers as the requirements documents as described above. This can help to construct a more concrete description of the process than is possible from reading only, and can also be used as the basis for comparing competing theories in alternative papers. In ongoing research, the Behavior Trees notation is being used to develop models of the brain function in rats under fear conditioning
Fear conditioning
Fear conditioning is a behavioral paradigm in which organisms learn to predict aversive events. It is a form of learning in which an aversive stimulus is associated with a particular neutral context or neutral stimulus , resulting in the expression of fear responses to the originally neutral...
.
Game A.I Modeling
While BTs have become popular for modeling the Artificial Intelligence in computer games such as Halo and Spore, these types of trees are very different than the ones described on this page, and are closer to a combination of hierarchical finite state machines or hierarchical task network planners. Soccer-player modeling has also been a successful application of BTs.Scalability and industry applications
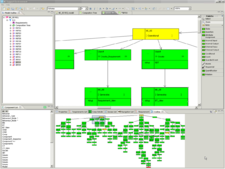
An important part of this work with industry has involved applying the analysis part of the method to six large-scale defence projects for Raytheon
Raytheon
Raytheon Company is a major American defense contractor and industrial corporation with core manufacturing concentrations in weapons and military and commercial electronics. It was previously involved in corporate and special-mission aircraft until early 2007...
Australia. They see the method as “a key risk mitigation strategy, of use in both solution development and as a means of advising the customer on problems with acquisition documentation”. An outcome of these industry trials has been the joint development with Raytheon Australia of an industry-strength tool to support the analysis, editing and display of large integrated sets of requirements. More extensive details of industry findings can be found on the Behavior Engineering website.
Dr Terry Stevenson (Chief Technical Officer, Raytheon
Raytheon
Raytheon Company is a major American defense contractor and industrial corporation with core manufacturing concentrations in weapons and military and commercial electronics. It was previously involved in corporate and special-mission aircraft until early 2007...
Australia) and Mr. Jim Boston (Senior Project Manager Raytheon
Raytheon
Raytheon Company is a major American defense contractor and industrial corporation with core manufacturing concentrations in weapons and military and commercial electronics. It was previously involved in corporate and special-mission aircraft until early 2007...
Australia), Mr. Adrian Pitman from the Australian Defence Materiel Organization
Defence Materiel Organisation
The Defence Materiel Organisation is the Australian Government agency responsible for the acquisition, through-life support and disposal of equipment for the Australian Defence Force...
, Dr Kelvin Ross (CEO, K.J.Ross & Associates) and Christine Cornish (Bushell & Cornish) have provided the special opportunities needed to support this research and to conduct the industry trials and live project work. This work has been supported by the Australian Research Council
Australian Research Council
The Australian Research Council is the Australian Government’s main agency for allocating research funding to academics and researchers in Australian universities. Its mission is to advance Australia’s capacity to undertake research that brings economic, social and cultural benefit to the...
– ARC Centre for Complex Systems
ARC Centre for Complex Systems
The ARC Centre for Complex Systems was established in 2004 from a consortium of Australian universities, led by The University of Queensland. The objective of ACCS was to conduct basic and applied research in the field of complex systems. It conducted research into both the science and engineering...
and funds received from industry.
Benefits, advantages
As a behavior modelling representation, Behavior Trees have a number of significant benefits and advantages:- They employ a well-defined and effective strategy for dealing with requirements complexity, particularly where the initial needs of a system are expressed using hundreds or thousands of requirementRequirementIn engineering, a requirement is a singular documented physical and functional need that a particular product or service must be or perform. It is most commonly used in a formal sense in systems engineering, software engineering, or enterprise engineering...
s written in natural languageNatural languageIn the philosophy of language, a natural language is any language which arises in an unpremeditated fashion as the result of the innate facility for language possessed by the human intellect. A natural language is typically used for communication, and may be spoken, signed, or written...
. This significantly reduces the risk on large-scale projects. - By rigorously translating then integrating requirements at the earliest possible time they provide a more effective means for uncovering requirements defects than competing methods.
- They employ a single, simple notation for analysisAnalysisAnalysis is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle , though analysis as a formal concept is a relatively recent development.The word is...
, specification and to represent the behavior design of a system. - They represent the system behavior as an executableExecutableIn computing, an executable file causes a computer "to perform indicated tasks according to encoded instructions," as opposed to a data file that must be parsed by a program to be meaningful. These instructions are traditionally machine code instructions for a physical CPU...
integrated whole. - They build the behavior of a system out of its functional requirementsFunctional requirementsIn software engineering, a functional requirement defines a function of a software system or its component. A function is described as a set of inputs, the behavior, and outputs ....
in a directly traceable way which aids verification and validationVerification and ValidationIn software project management, software testing, and software engineering, verification and validation is the process of checking that a software system meets specifications and that it fulfills its intended purpose...
. - They can be understood by stakeholders without the need for formal methodsFormal methodsIn computer science and software engineering, formal methods are a particular kind of mathematically-based techniques for the specification, development and verification of software and hardware systems...
training. By strictly retaining the vocabulary of the original requirements this eases the burden of understanding. - They have a formal semantics, they support concurrencyConcurrency (computer science)In computer science, concurrency is a property of systems in which several computations are executing simultaneously, and potentially interacting with each other...
, they are executableExecutableIn computing, an executable file causes a computer "to perform indicated tasks according to encoded instructions," as opposed to a data file that must be parsed by a program to be meaningful. These instructions are traditionally machine code instructions for a physical CPU...
and they can be simulated, model-checkedModel checkingIn computer science, model checking refers to the following problem:Given a model of a system, test automatically whether this model meets a given specification....
and used to undertake failure mode and effects analysisFailure mode and effects analysisA failure modes and effects analysis is a procedure in product development and operations management for analysis of potential failure modes within a system for classification by the severity and likelihood of the failures...
. - They can be used equally well to model human processes, to analyse contracts, to represent forensic information, to represent biological systems, and numerous other applications. In each case they deliver the same benefits in terms of managing complexity, and seeing things as a whole. They can also be used for safety critical systems, embedded systems and real-time systems.
Criticisms, disadvantages
- For small textbook level examples, their tree-like nature means that the graphic models produced are sometimes not as compact as StatechartState diagramA state diagram is a type of diagram used in computer science and related fields to describe the behavior of systems. State diagrams require that the system described is composed of a finite number of states; sometimes, this is indeed the case, while at other times this is a reasonable abstraction...
or State Machine behavior specifications. - The process of requirements translation is very demanding. It is not possible to spend more than three or four hours in a day doing translation even with good tool support.
- Tool support is needed to navigate the very large integrated behavior trees for systems that have hundreds or thousands of requirements.
- For group walkthroughs of very large systems good display facilities are needed.
- There is a need to provide additional sophisticated tool support to fully exploit integrated behavior tree models.

