
Binary offset carrier
Encyclopedia
Binary Offset Carrier modulation currently used in Galileo is a square sub-carrier modulation
, where a signal is multiplied by a rectangular sub-carrier of frequency equal or higher to the chip (CDMA)
equal or higher to the chip (CDMA)
rate. Following this sub-carrier multiplication
, the spectrum
of the signal is divided into two parts, therefore BOC modulation is also known as a split-spectrum modulation.
The main idea behind BOC modulation is to reduce the interference with BPSK-modulated signal, which has a sinc function shaped spectrum. Therefore, BPSK-modulated signals such as C/A GPS codes have most of their spectral energy concentrated around the carrier frequency, while BOC-modulated signals (used in Galileo system) have low energy around the carrier frequency and two main spectral lobes further away from the carrier (thus, the name of split-spectrum).
BOC modulation has several variants: sine BOC (SinBOC), cosine BOC (CosBOC) Alternative BOC (AltBOC),, multiplexed BOC (MBOC
), Double BOC (DBOC) etc. and some of them have been currently selected for Galileo GNSS signals.
A BOC waveform is typically denoted via BOC(m,n) or BOC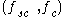 , where
, where  is the sub-carrier frequency,
is the sub-carrier frequency,  is the chip frequency,
is the chip frequency, 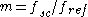 ,
, 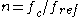 , and
, and  Mcps is the reference chip frequency of C/A GPS signal.
Mcps is the reference chip frequency of C/A GPS signal.
A sine BOC(1,1) modulation is similar to Manchester code
, that is, in digital domain, a '+1' is encoded as a '+1 −1' sequence, and a '0' is encoded as a '−1 +1' sequence.
For an arbitrary modulation order, in sine BOC(m,n) case, a '+1' is encoded as an alternating sequence of '+1 −1 +1 −1 +1 ...', having
modulation order, in sine BOC(m,n) case, a '+1' is encoded as an alternating sequence of '+1 −1 +1 −1 +1 ...', having  elements, and a '0' (or '−1') is encoded as an alternating '−1 +1 ...' sequence, also having
elements, and a '0' (or '−1') is encoded as an alternating '−1 +1 ...' sequence, also having 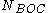 elements.
elements.
BOC modulation is typically applied on CDMA signals, where each chip of the pseudorandom code is split into BOC sub-intervals, as explained above (i.e., there are BOC intervals per chip).
BOC intervals per chip).
The power spectral density
of a BOC-modulated signal depends on the BOC modulation order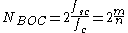 and its derivation can be found, for example, in
and its derivation can be found, for example, in
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
, where a signal is multiplied by a rectangular sub-carrier of frequency
 equal or higher to the chip (CDMA)
equal or higher to the chip (CDMA)Chip (CDMA)
In digital communications, a chip is a pulse of a direct-sequence spread spectrum code, such as a pseudo-noise code sequence used in direct-sequence code division multiple access channel access techniques....
rate. Following this sub-carrier multiplication
Multiplication
Multiplication is the mathematical operation of scaling one number by another. It is one of the four basic operations in elementary arithmetic ....
, the spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
of the signal is divided into two parts, therefore BOC modulation is also known as a split-spectrum modulation.
The main idea behind BOC modulation is to reduce the interference with BPSK-modulated signal, which has a sinc function shaped spectrum. Therefore, BPSK-modulated signals such as C/A GPS codes have most of their spectral energy concentrated around the carrier frequency, while BOC-modulated signals (used in Galileo system) have low energy around the carrier frequency and two main spectral lobes further away from the carrier (thus, the name of split-spectrum).
BOC modulation has several variants: sine BOC (SinBOC), cosine BOC (CosBOC) Alternative BOC (AltBOC),, multiplexed BOC (MBOC
MBOC
Multiplexed binary offset carrier modulation is a modulation proposed for Galileo and modernized GPS signals, which combines a sine binary offset carrier SinBOC signal with a SinBOC signal, either via weighted sum/difference or via time-multiplexing...
), Double BOC (DBOC) etc. and some of them have been currently selected for Galileo GNSS signals.
A BOC waveform is typically denoted via BOC(m,n) or BOC
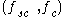 , where
, where  is the sub-carrier frequency,
is the sub-carrier frequency,  is the chip frequency,
is the chip frequency, 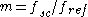 ,
, 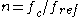 , and
, and  Mcps is the reference chip frequency of C/A GPS signal.
Mcps is the reference chip frequency of C/A GPS signal.A sine BOC(1,1) modulation is similar to Manchester code
Manchester code
In telecommunication and data storage, Manchester code is a line code in which the encoding of each data bit has at least one transition and occupies the same time...
, that is, in digital domain, a '+1' is encoded as a '+1 −1' sequence, and a '0' is encoded as a '−1 +1' sequence.
For an arbitrary
 modulation order, in sine BOC(m,n) case, a '+1' is encoded as an alternating sequence of '+1 −1 +1 −1 +1 ...', having
modulation order, in sine BOC(m,n) case, a '+1' is encoded as an alternating sequence of '+1 −1 +1 −1 +1 ...', having  elements, and a '0' (or '−1') is encoded as an alternating '−1 +1 ...' sequence, also having
elements, and a '0' (or '−1') is encoded as an alternating '−1 +1 ...' sequence, also having  elements.
elements.BOC modulation is typically applied on CDMA signals, where each chip of the pseudorandom code is split into BOC sub-intervals, as explained above (i.e., there are
 BOC intervals per chip).
BOC intervals per chip).The power spectral density
Spectral density
In statistical signal processing and physics, the spectral density, power spectral density , or energy spectral density , is a positive real function of a frequency variable associated with a stationary stochastic process, or a deterministic function of time, which has dimensions of power per hertz...
of a BOC-modulated signal depends on the BOC modulation order
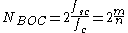 and its derivation can be found, for example, in
and its derivation can be found, for example, inExternal links
- Binary Offset Carrier (BOC) signal generator in Matlab, http://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/12829

