
Chip (CDMA)
Encyclopedia
In digital communications, a chip is a pulse of a direct-sequence spread spectrum
(DSSS) code, such as a pseudo-noise code sequence used in direct-sequence code division multiple access
(CDMA) channel access techniques.
In a binary direct-sequence system, each chip is typically a rectangular pulse of +1 or –1 amplitude, which is multiplied by a data sequence (similarly +1 or –1 representing the message bits) and by a carrier waveform to make the transmitted signal. The chips are therefore just the bit sequence out of the code generator; they are called chips to avoid confusing them with message bits.
The chip rate of a code is the number of pulses per second (chips per second) at which the code is transmitted (or received). The chip rate is larger than the symbol rate
, meaning that one symbol is represented by multiple chips. The ratio is known as the spreading factor (SF) or processing gain: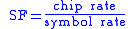
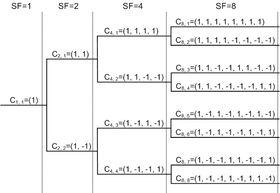 Orthogonal variable spreading factor (OVSF) is an implementation of Code division multiple access
Orthogonal variable spreading factor (OVSF) is an implementation of Code division multiple access
(CDMA) where before each signal is transmitted, the signal is spread over a wide spectrum range
through the use of a user's code. Users' codes are carefully chosen to be mutually orthogonal to each other.
These codes are derived from an OVSF code tree, and each user is given a different, unique code. An OVSF code tree is a complete binary tree
that reflects the construction of Hadamard matrices
.
Direct-sequence spread spectrum
In telecommunications, direct-sequence spread spectrum is a modulation technique. As with other spread spectrum technologies, the transmitted signal takes up more bandwidth than the information signal that is being modulated. The name 'spread spectrum' comes from the fact that the carrier signals...
(DSSS) code, such as a pseudo-noise code sequence used in direct-sequence code division multiple access
Code division multiple access
Code division multiple access is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies. It should not be confused with the mobile phone standards called cdmaOne, CDMA2000 and WCDMA , which are often referred to as simply CDMA, and use CDMA as an underlying channel access...
(CDMA) channel access techniques.
In a binary direct-sequence system, each chip is typically a rectangular pulse of +1 or –1 amplitude, which is multiplied by a data sequence (similarly +1 or –1 representing the message bits) and by a carrier waveform to make the transmitted signal. The chips are therefore just the bit sequence out of the code generator; they are called chips to avoid confusing them with message bits.
The chip rate of a code is the number of pulses per second (chips per second) at which the code is transmitted (or received). The chip rate is larger than the symbol rate
Symbol rate
In digital communications, symbol rate is the number of symbol changes made to the transmission medium per second using a digitally modulated signal or a line code. The Symbol rate is measured in baud or symbols/second. In the case of a line code, the symbol rate is the pulse rate in pulses/second...
, meaning that one symbol is represented by multiple chips. The ratio is known as the spreading factor (SF) or processing gain:
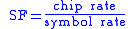
Orthogonal variable spreading factor

Code division multiple access
Code division multiple access is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies. It should not be confused with the mobile phone standards called cdmaOne, CDMA2000 and WCDMA , which are often referred to as simply CDMA, and use CDMA as an underlying channel access...
(CDMA) where before each signal is transmitted, the signal is spread over a wide spectrum range
Spread spectrum
Spread-spectrum techniques are methods by which a signal generated in a particular bandwidth is deliberately spread in the frequency domain, resulting in a signal with a wider bandwidth...
through the use of a user's code. Users' codes are carefully chosen to be mutually orthogonal to each other.
These codes are derived from an OVSF code tree, and each user is given a different, unique code. An OVSF code tree is a complete binary tree
Binary tree
In computer science, a binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two child nodes, usually distinguished as "left" and "right". Nodes with children are parent nodes, and child nodes may contain references to their parents. Outside the tree, there is often a reference to...
that reflects the construction of Hadamard matrices
Hadamard matrix
In mathematics, an Hadamard matrix, named after the French mathematician Jacques Hadamard, is a square matrix whose entries are either +1 or −1 and whose rows are mutually orthogonal...
.

