
Symbol rate
Encyclopedia
In digital communications, symbol rate (also known as baud or modulation rate) is the number of symbol changes (waveform changes or signalling events) made to the transmission medium per second using a digitally modulated
signal or a line code
. The Symbol rate is measured in baud
(Bd) or symbols/second. In the case of a line code, the symbol rate is the pulse rate in pulses/second. Each symbol can represent or convey one or several bit
s of data. The symbol rate is related to, but should not be confused with, the gross bitrate expressed in bit/second.
that persists for a fixed period of time. A sending device places symbols on the channel at a fixed and known symbol rate, and the receiving device has the job of detecting the sequence of symbols in order to reconstruct the transmitted data. There may be a direct correspondence between a symbol and a small unit of data
(for example, each symbol may encode one or several binary digits or 'bits') or the data may be represented by the transitions between symbols or even by a sequence of many symbols.
The symbol duration time, also known as unit interval
, can be directly measured as the time between transitions by looking into an eye diagram of an oscilloscope
. The symbol duration time Ts can be calculated as:
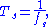
where fs is the symbol rate.
s as well as in the simplest digital communication links using only one bit per symbol, such that binary "0" is represented by one symbol, and binary "1" by another symbol. In more advanced modems and data transmission techniques, a symbol may have more than two states, so it may represent more than one binary digit (a binary digit always represents exactly two states). For this reason, the baud rate value will often be lower than the gross bit rate.
Example of use and misuse of "baud rate": It is correct to write "the baud rate of my COM port is 9,600" if we mean that the bit rate is 9,600 bit/s, since there is one bit per symbol in this case. It is not correct to write "the baud rate of Ethernet is 100 Mbaud" or "the baud rate of my modem is 56,000" if we mean bit rate. See below for more details on these techniques.
The difference between baud (or signalling rate) and the data rate (or bit rate) is like a man using a single semaphore flag
who can move his arm to a new position once each second, so his signalling rate (baud) is one symbol per second. The flag can be held in one of eight distinct positions: Straight up, 45° left, 90° left, 135° left, straight down (which is the rest state, where he is sending no signal), 135° right, 90° right, and 45° right. Each signal (symbol) carries three bits of information. It takes three binary
digits to encode eight states. The data rate is three bits per second. In the Navy, more than one flag pattern and arm can be used at once, so the combinations of these produce many symbols, each conveying several bits, a higher data rate.
If N bits are conveyed per symbol, and the gross bit rate is R, inclusive of channel coding overhead, the symbol rate can be calculated as:
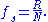
In that case M=2N different symbols are used. In a modem, these may be sinewave tones with unique combinations of amplitude, phase and/or frequency. For example, in a 64QAM modem, M=64. In a line code, these may be M different voltage levels.
By taking information per pulse N in bit/pulse to be the base-2-logarithm
of the number of distinct messages M that could be sent, Hartley
constructed a measure of the gross bitrate R as:

where fs is the baud rate in symbols/second or pulses/second. (See Hartley's law).
filtered channels such as telephone lines, radio channels and other frequency division multiplex (FDM) channels.
In a digital modulation method provided by a modem
, each symbol is typically a sine wave tone with certain frequency, amplitude and phase. The baud rate is the number of transmitted tones per second.
One symbol can carry one or several bits of information. In voiceband modems for the telephone network, it is common for one symbol to carry up to 7 bits.
Conveying more than one bit per symbol or bit per pulse has advantages. It reduces the time required to send a given quantity of data over a limited bandwidth. A high spectral efficiency
in (bit/s)/Hz can be achieved, i.e. a high bit rate in bit/s although the bandwidth in hertz may be low.
The maximum baud rate for a passband for common modulation methods such as QAM, PSK
and OFDM is approximately equal to the passband bandwidth.
Voiceband modem examples:
channel such as a telegraph line, a serial cable or a Local Area Network twisted pair cable, data is transferred using line codes, i.e. pulses
rather than sinewave tones. In this case the baud rate is synonymous to the pulse rate in pulses/second.
The maximum baud rate or pulse rate for a base band channel is called the Nyquist rate
, and is half the bandwidth (half the cut-off frequency).
The simplest digital communication links (such as individual wires on a motherboard or the RS-232 serial port/COM port) typically have a symbol rate equal to the gross bit rate.
Common communication links such as 10 Mbit/s Ethernet
(10Base-T
), USB, and FireWire typically have a symbol rate slightly higher than the data bit rate, due to the overhead of extra non-data symbols used for self-synchronizing code
and error detection.
J. M. Emile Baudot (1845–1903) worked out a five-level code (five bits per character) for telegraphs which was standardized internationally and is commonly called Baudot code
.
More than two voltage levels are used in advanced techniques such as FDDI and 100/1000 Mbit
/s Ethernet LANs, and others, to achieve high data rates.
1000 Mbit/s Ethernet LAN cables use four wire pairs in full duplex (250 Mbit/s per pair in both directions simultaneously), and many bits per symbol to encode their data payloads.
transmission the symbol rate calculation is:
The 204 is the number of bytes in a packet including the 16 trailing Reed-Solomon error checking and correction
bytes. The 188 is the number of data bytes (187 bytes) plus the leading packet sync byte
(0x47).
The bits per symbol is the (modulation's power of 2)*(Forward Error Correction). So for example in 64-QAM modulation 64 = 26 so the bits per symbol is 6. The Forward Error Correction (FEC) is usually expressed as a fraction, i.e., 1/2, 3/4, etc. In the case of 3/4 FEC, for every 3 bits of data, you are sending out 4 bits, one of which is for error correction.
Example:
then

In digital terrestrial digital television (DVB-T
, DVB-H
and similar techniques) OFDM modulation is used, i.e. multi-carrier modulation. The above symbol rate should then be divided by the number of OFDM sub-carriers in view to achieve the OFDM symbol rate. See the OFDM system comparison table for further numerical details.
links) have a symbol rate much higher than the data rate (they transmit many symbols called chips
per data bit. Representing one bit by a chip sequence of many symbols overcomes co-channel interference
from other transmitters sharing the same frequency channel, including radio jamming
, and is common in military radio and cell phones
. Despite the fact that using more bandwidth to carry the same bit rate gives low channel spectral efficiency in (bit/s)/Hz, it allows many simultaneous users, which results in high system spectral efficiency in (bit/s)/Hz per unit of area.
In these systems, the symbol rate of the physically transmitted high-frequency signal rate is called chip rate, which also is the pulse rate of the equivalent base band signal. However, in spread spectrum systems, the term symbol may also be used at a higher layer and refer to one information bit, or a block of information bits that are modulated using for example conventional QAM modulation, before the CDMA spreading code is applied. Using the latter definition, the symbol rate is equal to or lower than the bit rate.
An optimal symbol set design takes into account channel bandwidth, desired information rate, noise characteristics of the channel and the receiver, and receiver and decoder complexity.
systems operate by the modulation
of a carrier signal
. For example, in frequency-shift keying (FSK)
, the frequency of a tone is varied among a small, fixed set of possible values. In a synchronous
data transmission system, the tone can only be changed from one frequency to another at regular and well-defined intervals. The presence of one particular frequency during one of these intervals constitutes a symbol. (The concept of symbols does not apply to asynchronous data transmission systems.) In a modulated system, the term modulation rate may be used synonymously with symbol rate.
of data (i.e., a 0 or 1) can be transmitted in each symbol. The bit rate
is in this case equal to the symbol rate. For example, a binary FSK system would allow the carrier to have one of two frequencies, one representing a 0 and the other a 1. A more practical scheme is differential binary phase-shift keying
, in which the carrier remains at the same frequency, but can be in one of two phases. During each symbol, the phase either remains the same, encoding a 0, or jumps by 180°, encoding a 1. Again, only one bit
of data (i.e., a 0 or 1) is transmitted by each symbol. This is an example of data being encoded in the transitions between symbols (the change in phase), rather than the symbols themselves (the actual phase). (The reason for this in phase-shift keying is that it is impractical to know the reference phase of the transmitter.)
). As the bit rate is the product of the symbol rate and the number of bits encoded in each symbol, it is clearly advantageous to increase the latter if the former is fixed. However, for each additional bit encoded in a symbol, the constellation of symbols (the number of states of the carrier) doubles in size. This makes the states less distinct from one another which in turn makes it more difficult for the receiver to detect the symbol correctly in the presence of disturbances on the channel.
The history of modem
s is the attempt at increasing the bit rate over a fixed bandwidth (and therefore a fixed maximum symbol rate), leading to increasing bits per symbol. For example, the V.29 specifies 4 bits per symbol, at a symbol rate of 2,400 baud, giving an effective bit rate of 9,600 bits per second.
The history of spread spectrum
goes in the opposite direction, leading to fewer and fewer data bits per symbol in order to spread the bandwidth. In the case of GPS, we have a data rate of 50 bit/s and a symbol rate of 1.023 Mchips/s. If each chip is considered a symbol, each symbol contains far less than one bit ( 50 bit/s / 1023 ksymbols/s =~= 0.000 05 bits/symbol ).
The complete collection of M possible symbols over a particular channel is called a M-ary modulation
scheme.
Most modulation schemes transmit some integer number of bits per symbol b, requiring the complete collection to contain M = 2^b different symbols.
Most popular modulation schemes can be described by showing each point on a constellation diagram
,
although a few modulation schemes (such as MFSK
, DTMF
, pulse-position modulation
, spread spectrum
modulation) require a different description.
, in the modulation
of a carrier, a significant condition is one of the values of the signal
parameter chosen to represent information
.
A significant condition could be an electrical current (voltage, or power
level), an optical power level, a phase
value, or a particular frequency
or wavelength
. The duration of a significant condition is the time
interval between successive significant instants. A change from one significant condition to another is called a signal transition
. Information can be transmitted either during the given time interval, or encoded as the presence or absence of a change in the received signal.
Significant conditions are recognized by an appropriate device called a receiver, demodulator, or decoder. The decoder translates the actual signal received into its intended logical value such as a binary digit (0 or 1), an alphabetic character, a mark, or a space. Each significant instant is determined when the appropriate device assumes a condition or state usable for performing a specific function, such as recording, processing, or gating
.
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
signal or a line code
Line code
In telecommunication, a line code is a code chosen for use within a communications system for baseband transmission purposes...
. The Symbol rate is measured in baud
Baud
In telecommunications and electronics, baud is synonymous to symbols per second or pulses per second. It is the unit of symbol rate, also known as baud rate or modulation rate; the number of distinct symbol changes made to the transmission medium per second in a digitally modulated signal or a...
(Bd) or symbols/second. In the case of a line code, the symbol rate is the pulse rate in pulses/second. Each symbol can represent or convey one or several bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
s of data. The symbol rate is related to, but should not be confused with, the gross bitrate expressed in bit/second.
Symbols
A symbol can be described as either a pulse (in digital baseband transmission) or a "tone" (in passband transmission using modems) representing an integer number of bits. A theoretical definition of a symbol is a waveform, a state or a significant condition of the communication channelChannel (communications)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
that persists for a fixed period of time. A sending device places symbols on the channel at a fixed and known symbol rate, and the receiving device has the job of detecting the sequence of symbols in order to reconstruct the transmitted data. There may be a direct correspondence between a symbol and a small unit of data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
(for example, each symbol may encode one or several binary digits or 'bits') or the data may be represented by the transitions between symbols or even by a sequence of many symbols.
The symbol duration time, also known as unit interval
Unit interval (data transmission)
The unit interval is the minimum time interval between condition changes of a data transmission signal, also known as the symbol duration time....
, can be directly measured as the time between transitions by looking into an eye diagram of an oscilloscope
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a type of electronic test instrument that allows observation of constantly varying signal voltages, usually as a two-dimensional graph of one or more electrical potential differences using the vertical or 'Y' axis, plotted as a function of time,...
. The symbol duration time Ts can be calculated as:
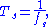
where fs is the symbol rate.
- A simple example: A baud rate of 1 kBd = 1,000 Bd is synonymous to a symbol rate of 1,000 symbols per second. In case of a modem, this corresponds to 1,000 tones per second, and in case of a line code, this corresponds to 1,000 pulses per second. The symbol duration time is 1/1,000 second = 1 millisecond.
Relationship to gross bitrate
The term baud rate has sometimes incorrectly been used to mean bit rate, since these rates are the same in old modemModem
A modem is a device that modulates an analog carrier signal to encode digital information, and also demodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded to reproduce the original digital data...
s as well as in the simplest digital communication links using only one bit per symbol, such that binary "0" is represented by one symbol, and binary "1" by another symbol. In more advanced modems and data transmission techniques, a symbol may have more than two states, so it may represent more than one binary digit (a binary digit always represents exactly two states). For this reason, the baud rate value will often be lower than the gross bit rate.
Example of use and misuse of "baud rate": It is correct to write "the baud rate of my COM port is 9,600" if we mean that the bit rate is 9,600 bit/s, since there is one bit per symbol in this case. It is not correct to write "the baud rate of Ethernet is 100 Mbaud" or "the baud rate of my modem is 56,000" if we mean bit rate. See below for more details on these techniques.
The difference between baud (or signalling rate) and the data rate (or bit rate) is like a man using a single semaphore flag
Flag semaphore
Semaphore Flags is the system for conveying information at a distance by means of visual signals with hand-held flags, rods, disks, paddles, or occasionally bare or gloved hands. Information is encoded by the position of the flags; it is read when the flag is in a fixed position...
who can move his arm to a new position once each second, so his signalling rate (baud) is one symbol per second. The flag can be held in one of eight distinct positions: Straight up, 45° left, 90° left, 135° left, straight down (which is the rest state, where he is sending no signal), 135° right, 90° right, and 45° right. Each signal (symbol) carries three bits of information. It takes three binary
Binary numeral system
The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, represents numeric values using two symbols, 0 and 1. More specifically, the usual base-2 system is a positional notation with a radix of 2...
digits to encode eight states. The data rate is three bits per second. In the Navy, more than one flag pattern and arm can be used at once, so the combinations of these produce many symbols, each conveying several bits, a higher data rate.
If N bits are conveyed per symbol, and the gross bit rate is R, inclusive of channel coding overhead, the symbol rate can be calculated as:
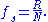
In that case M=2N different symbols are used. In a modem, these may be sinewave tones with unique combinations of amplitude, phase and/or frequency. For example, in a 64QAM modem, M=64. In a line code, these may be M different voltage levels.
By taking information per pulse N in bit/pulse to be the base-2-logarithm
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
of the number of distinct messages M that could be sent, Hartley
Ralph Hartley
Ralph Vinton Lyon Hartley was an electronics researcher. He invented the Hartley oscillator and the Hartley transform, and contributed to the foundations of information theory.-Biography:...
constructed a measure of the gross bitrate R as:

where fs is the baud rate in symbols/second or pulses/second. (See Hartley's law).
Modems for passband transmission
Modulation is used in passbandPassband
A passband is the range of frequencies or wavelengths that can pass through a filter without being attenuated.A bandpass filtered signal , is known as a bandpass signal, as opposed to a baseband signal....
filtered channels such as telephone lines, radio channels and other frequency division multiplex (FDM) channels.
In a digital modulation method provided by a modem
Modem
A modem is a device that modulates an analog carrier signal to encode digital information, and also demodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded to reproduce the original digital data...
, each symbol is typically a sine wave tone with certain frequency, amplitude and phase. The baud rate is the number of transmitted tones per second.
One symbol can carry one or several bits of information. In voiceband modems for the telephone network, it is common for one symbol to carry up to 7 bits.
Conveying more than one bit per symbol or bit per pulse has advantages. It reduces the time required to send a given quantity of data over a limited bandwidth. A high spectral efficiency
Spectral efficiency
Spectral efficiency, spectrum efficiency or bandwidth efficiency refers to the information rate that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth in a specific communication system...
in (bit/s)/Hz can be achieved, i.e. a high bit rate in bit/s although the bandwidth in hertz may be low.
The maximum baud rate for a passband for common modulation methods such as QAM, PSK
PSK
PSK may refer to:* Partiya Şoreşa Kürdistan, A Kurdish Separatist guerrilla group in Turkey* Property Solutions Korea, a real estate consulting and development company in South Korea* Phase-shift keying, a digital modulation technique...
and OFDM is approximately equal to the passband bandwidth.
Voiceband modem examples:
- A V.22bis modem transmits 2400 bit/s using 1200 Bd (1200 symbol/s), where each quadrature amplitude modulationQuadrature amplitude modulationQuadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
symbol carries two bits of informationInformation theoryInformation theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
. The modem can generate M=22=4 different symbols. It requires a bandwidth of 1200 Hz (equal to the baud rate). The carrier frequency (the central frequency of the generated spectrum) is 1800 Hz, meaning that the lower cut off frequency is 1800 -1200/2 = 1200 Hz, and the upper cutoff frequency is 1800 + 1200/2 = 2400 Hz.
- A V.34 modem may transmit symbols at a baud rate of 3,420 Bd, and each symbol can carry up to ten bits, resulting in a gross bit rate of 3420 * 10 = 34,200 bit/s. However, the modem is said to operate at a net bit rate of 33,800 bit/s, excluding physical layer overhead.
Line codes for baseband transmission
In case of a basebandBaseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is an adjective that describes signals and systems whose range of frequencies is measured from close to 0 hertz to a cut-off frequency, a maximum bandwidth or highest signal frequency; it is sometimes used as a noun for a band of frequencies...
channel such as a telegraph line, a serial cable or a Local Area Network twisted pair cable, data is transferred using line codes, i.e. pulses
Pulse (signal processing)
In signal processing, the term pulse has the following meanings:#A rapid, transient change in the amplitude of a signal from a baseline value to a higher or lower value, followed by a rapid return to the baseline value....
rather than sinewave tones. In this case the baud rate is synonymous to the pulse rate in pulses/second.
The maximum baud rate or pulse rate for a base band channel is called the Nyquist rate
Nyquist rate
In signal processing, the Nyquist rate, named after Harry Nyquist, is two times the bandwidth of a bandlimited signal or a bandlimited channel...
, and is half the bandwidth (half the cut-off frequency).
The simplest digital communication links (such as individual wires on a motherboard or the RS-232 serial port/COM port) typically have a symbol rate equal to the gross bit rate.
Common communication links such as 10 Mbit/s Ethernet
Ethernet
Ethernet is a family of computer networking technologies for local area networks commercially introduced in 1980. Standardized in IEEE 802.3, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies....
(10Base-T
10BASE-T
Ethernet over twisted pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. Other Ethernet cable standards employ coaxial cable or optical fiber. Early versions developed in the 1980s included StarLAN followed by 10BASE-T. By the 1990s, fast, inexpensive...
), USB, and FireWire typically have a symbol rate slightly higher than the data bit rate, due to the overhead of extra non-data symbols used for self-synchronizing code
Self-synchronizing code
In telecommunications, a self-synchronizing code is a line code in which the symbol stream formed by a portion of one code word, or by the overlapped portion of any two adjacent code words, is not a valid code word...
and error detection.
J. M. Emile Baudot (1845–1903) worked out a five-level code (five bits per character) for telegraphs which was standardized internationally and is commonly called Baudot code
Baudot code
The Baudot code, invented by Émile Baudot, is a character set predating EBCDIC and ASCII. It was the predecessor to the International Telegraph Alphabet No 2 , the teleprinter code in use until the advent of ASCII. Each character in the alphabet is represented by a series of bits, sent over a...
.
More than two voltage levels are used in advanced techniques such as FDDI and 100/1000 Mbit
Megabit
The megabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information or computer storage. The prefix mega is defined in the International System of Units as a multiplier of 106 , and therefore...
/s Ethernet LANs, and others, to achieve high data rates.
1000 Mbit/s Ethernet LAN cables use four wire pairs in full duplex (250 Mbit/s per pair in both directions simultaneously), and many bits per symbol to encode their data payloads.
Digital television and OFDM example
In digital televisionDigital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
transmission the symbol rate calculation is:
- symbol rate in symbols per second = (Data rate in bits per second * 204) / (188 * bits per symbol)
The 204 is the number of bytes in a packet including the 16 trailing Reed-Solomon error checking and correction
Error detection and correction
In information theory and coding theory with applications in computer science and telecommunication, error detection and correction or error control are techniques that enable reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communication channels...
bytes. The 188 is the number of data bytes (187 bytes) plus the leading packet sync byte
Syncword
In computer networks, a syncword, sync character or preamble is used to synchronize a transmission by indicating the end of header information and the start of data.-Examples:For example an audio receiver is receiving a bit stream of data...
(0x47).
The bits per symbol is the (modulation's power of 2)*(Forward Error Correction). So for example in 64-QAM modulation 64 = 26 so the bits per symbol is 6. The Forward Error Correction (FEC) is usually expressed as a fraction, i.e., 1/2, 3/4, etc. In the case of 3/4 FEC, for every 3 bits of data, you are sending out 4 bits, one of which is for error correction.
Example:
- given bit rate = 18096263
- Modulation type = 64-QAM
- FEC = 3/4
then

In digital terrestrial digital television (DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
, DVB-H
DVB-H
DVB-H is one of three prevalent mobile TV formats. It is a technical specification for bringing broadcast services to mobile handsets. DVB-H was formally adopted as ETSI standard EN 302 304 in November 2004. The DVB-H specification can be downloaded from the official DVB-H website...
and similar techniques) OFDM modulation is used, i.e. multi-carrier modulation. The above symbol rate should then be divided by the number of OFDM sub-carriers in view to achieve the OFDM symbol rate. See the OFDM system comparison table for further numerical details.
Relationship to chip rate
Some communication links (such as GPS transmissions, CDMA cell phones, and other spread spectrumSpread spectrum
Spread-spectrum techniques are methods by which a signal generated in a particular bandwidth is deliberately spread in the frequency domain, resulting in a signal with a wider bandwidth...
links) have a symbol rate much higher than the data rate (they transmit many symbols called chips
Chip (CDMA)
In digital communications, a chip is a pulse of a direct-sequence spread spectrum code, such as a pseudo-noise code sequence used in direct-sequence code division multiple access channel access techniques....
per data bit. Representing one bit by a chip sequence of many symbols overcomes co-channel interference
Co-channel interference
Co-channel interference or CCI is crosstalk from two different radio transmitters using the same frequency. There can be several causes of co-channel radio interference; four examples are listed here....
from other transmitters sharing the same frequency channel, including radio jamming
Radio jamming
Radio jamming is the transmission of radio signals that disrupt communications by decreasing the signal to noise ratio. Unintentional jamming occurs when an operator transmits on a busy frequency without first checking whether it is in use, or without being able to hear stations using the frequency...
, and is common in military radio and cell phones
Mobile phone
A mobile phone is a device which can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile network operator...
. Despite the fact that using more bandwidth to carry the same bit rate gives low channel spectral efficiency in (bit/s)/Hz, it allows many simultaneous users, which results in high system spectral efficiency in (bit/s)/Hz per unit of area.
In these systems, the symbol rate of the physically transmitted high-frequency signal rate is called chip rate, which also is the pulse rate of the equivalent base band signal. However, in spread spectrum systems, the term symbol may also be used at a higher layer and refer to one information bit, or a block of information bits that are modulated using for example conventional QAM modulation, before the CDMA spreading code is applied. Using the latter definition, the symbol rate is equal to or lower than the bit rate.
Relationship to bit error rate
The disadvantage of conveying many bits per symbol is that the receiver has to distinguish many signal levels or symbols from each other, which may be difficult and cause bit errors in case of a poor phone line that suffers from low signal-to-noise ratio. In that case, a modem or network adapter may automatically choose a slower and more robust modulation scheme or line code, using fewer bits per symbol, in view to reduce the bit error rate.An optimal symbol set design takes into account channel bandwidth, desired information rate, noise characteristics of the channel and the receiver, and receiver and decoder complexity.
Modulation
Many data transmissionData transmission
Data transmission, digital transmission, or digital communications is the physical transfer of data over a point-to-point or point-to-multipoint communication channel. Examples of such channels are copper wires, optical fibres, wireless communication channels, and storage media...
systems operate by the modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
of a carrier signal
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
. For example, in frequency-shift keying (FSK)
Frequency-shift keying
Frequency-shift keying is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier wave. The simplest FSK is binary FSK . BFSK uses a pair of discrete frequencies to transmit binary information. With this scheme, the "1" is called...
, the frequency of a tone is varied among a small, fixed set of possible values. In a synchronous
Synchronization
Synchronization is timekeeping which requires the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. The familiar conductor of an orchestra serves to keep the orchestra in time....
data transmission system, the tone can only be changed from one frequency to another at regular and well-defined intervals. The presence of one particular frequency during one of these intervals constitutes a symbol. (The concept of symbols does not apply to asynchronous data transmission systems.) In a modulated system, the term modulation rate may be used synonymously with symbol rate.
Binary Modulation
If the carrier signal has only two states, then only one bitBit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
of data (i.e., a 0 or 1) can be transmitted in each symbol. The bit rate
Bit rate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
is in this case equal to the symbol rate. For example, a binary FSK system would allow the carrier to have one of two frequencies, one representing a 0 and the other a 1. A more practical scheme is differential binary phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal ....
, in which the carrier remains at the same frequency, but can be in one of two phases. During each symbol, the phase either remains the same, encoding a 0, or jumps by 180°, encoding a 1. Again, only one bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
of data (i.e., a 0 or 1) is transmitted by each symbol. This is an example of data being encoded in the transitions between symbols (the change in phase), rather than the symbols themselves (the actual phase). (The reason for this in phase-shift keying is that it is impractical to know the reference phase of the transmitter.)
N-ary Modulation, N greater than 2
By increasing the number of states that the carrier signal can take, the number of bits encoded in each symbol can be greater than one. The bit rate can then be greater than the symbol rate. For example, a differential phase-shift keying system might allow four possible jumps in phase between symbols. Then two bits could be encoded at each symbol interval, achieving a data rate of double the symbol rate. In a more complex scheme such as 16-QAM, four bits of data are transmitted in each symbol, resulting in a bit rate of four times the symbol rate.Data Rate versus Error Rate
Modulating a carrier increases the frequency range, or bandwidth, it occupies. Transmission channels are generally limited in the bandwidth they can carry. The bandwidth depends on the symbol (modulation) rate (not directly on the bit rateBit rate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
). As the bit rate is the product of the symbol rate and the number of bits encoded in each symbol, it is clearly advantageous to increase the latter if the former is fixed. However, for each additional bit encoded in a symbol, the constellation of symbols (the number of states of the carrier) doubles in size. This makes the states less distinct from one another which in turn makes it more difficult for the receiver to detect the symbol correctly in the presence of disturbances on the channel.
The history of modem
Modem
A modem is a device that modulates an analog carrier signal to encode digital information, and also demodulates such a carrier signal to decode the transmitted information. The goal is to produce a signal that can be transmitted easily and decoded to reproduce the original digital data...
s is the attempt at increasing the bit rate over a fixed bandwidth (and therefore a fixed maximum symbol rate), leading to increasing bits per symbol. For example, the V.29 specifies 4 bits per symbol, at a symbol rate of 2,400 baud, giving an effective bit rate of 9,600 bits per second.
The history of spread spectrum
Spread spectrum
Spread-spectrum techniques are methods by which a signal generated in a particular bandwidth is deliberately spread in the frequency domain, resulting in a signal with a wider bandwidth...
goes in the opposite direction, leading to fewer and fewer data bits per symbol in order to spread the bandwidth. In the case of GPS, we have a data rate of 50 bit/s and a symbol rate of 1.023 Mchips/s. If each chip is considered a symbol, each symbol contains far less than one bit ( 50 bit/s / 1023 ksymbols/s =~= 0.000 05 bits/symbol ).
The complete collection of M possible symbols over a particular channel is called a M-ary modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
scheme.
Most modulation schemes transmit some integer number of bits per symbol b, requiring the complete collection to contain M = 2^b different symbols.
Most popular modulation schemes can be described by showing each point on a constellation diagram
Constellation diagram
A constellation diagram is a representation of a signal modulated by a digital modulation scheme such as quadrature amplitude modulation or phase-shift keying. It displays the signal as a two-dimensional scatter diagram in the complex plane at symbol sampling instants...
,
although a few modulation schemes (such as MFSK
Multiple frequency-shift keying
Multiple frequency-shift keying is a variation of frequency-shift keying that uses more than two frequencies. MFSK is a form of M-ary orthogonal modulation, where each symbol consists of one element from an alphabet of orthogonal waveforms...
, DTMF
Dual-tone multi-frequency
Dual-tone multi-frequency signaling is used for telecommunication signaling over analog telephone lines in the voice-frequency band between telephone handsets and other communications devices and the switching center. The version of DTMF that is used in push-button telephones for tone dialing is...
, pulse-position modulation
Pulse-position modulation
Pulse-position modulation is a form of signal modulation in which M message bits are encoded by transmitting a single pulse in one of 2^M possible time-shifts. This is repeated every T seconds, such that the transmitted bit rate is M/T bits per second...
, spread spectrum
Spread spectrum
Spread-spectrum techniques are methods by which a signal generated in a particular bandwidth is deliberately spread in the frequency domain, resulting in a signal with a wider bandwidth...
modulation) require a different description.
Significant condition
In telecommunicationTelecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information over significant distances to communicate. In earlier times, telecommunications involved the use of visual signals, such as beacons, smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs, or audio messages via coded...
, in the modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
of a carrier, a significant condition is one of the values of the signal
Signalling (telecommunications)
In telecommunication, signaling has the following meanings:*the use of signals for controlling communications...
parameter chosen to represent information
Information
Information in its most restricted technical sense is a message or collection of messages that consists of an ordered sequence of symbols, or it is the meaning that can be interpreted from such a message or collection of messages. Information can be recorded or transmitted. It can be recorded as...
.
A significant condition could be an electrical current (voltage, or power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
level), an optical power level, a phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
value, or a particular frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
or wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
. The duration of a significant condition is the time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
interval between successive significant instants. A change from one significant condition to another is called a signal transition
Signal transition
Signal transition: In the modulation of a carrier, a change from one significant condition to another.Examples of signal transitions are a change from one electrical current, voltage, or power level to another; a change from one optical power level to another; a phase shift; or a change from one...
. Information can be transmitted either during the given time interval, or encoded as the presence or absence of a change in the received signal.
Significant conditions are recognized by an appropriate device called a receiver, demodulator, or decoder. The decoder translates the actual signal received into its intended logical value such as a binary digit (0 or 1), an alphabetic character, a mark, or a space. Each significant instant is determined when the appropriate device assumes a condition or state usable for performing a specific function, such as recording, processing, or gating
Gating
-Neurobiology:*Gating , the opening or closing of ion channels*Sensory gating, an automatic process by which the brain adjusts to stimuli*Synaptic gating, neural circuits suppressing inputs through synapses...
.
See also
- Chip rate
- Gross bit rate, also known as data signaling rateData signaling rateIn telecommunication, data signaling rate , also known as gross bit rate, is the aggregate rate at which data pass a point in the transmission path of a data transmission system.Notes:#The DSR is usually expressed in bits per second....
or line rate. - bandwidthBandwidth (computing)In computer networking and computer science, bandwidth, network bandwidth, data bandwidth, or digital bandwidth is a measure of available or consumed data communication resources expressed in bits/second or multiples of it .Note that in textbooks on wireless communications, modem data transmission,...
- BitrateBitrateIn telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
- Constellation diagramConstellation diagramA constellation diagram is a representation of a signal modulated by a digital modulation scheme such as quadrature amplitude modulation or phase-shift keying. It displays the signal as a two-dimensional scatter diagram in the complex plane at symbol sampling instants...
, which shows (on a graph or 2D oscilloscope image) how a given signal state (a symbol) can represent three or four bits at once. - List of device bandwidths
- PCM

