DVB-T
Encyclopedia
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television
that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK
in 1998. This system transmits compressed digital audio
, digital video
and other data in an MPEG transport stream, using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
(COFDM or OFDM) modulation.
(RF) carrier, OFDM works by splitting the digital data stream into a large number of slower digital streams, each of which digitally modulate a set of closely spaced adjacent carrier frequencies. In the case of DVB-T, there are two choices for the number of carriers known as 2K-mode or 8K-mode. These are actually 1,705 or 6,817 carriers that are approximately 4 kHz or 1 kHz apart.
DVB-T offers three different modulation schemes (QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM).
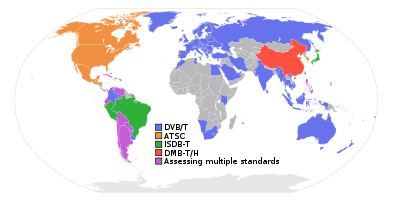
DVB-T has been adopted or proposed for digital television broadcasting by many countries (see map), using mainly VHF 7 MHz and UHF 8 MHz channels whereas Taiwan, Colombia, Panama, Trinidad and Tobago and the Philippines use 6 MHz channels. Examples include the UK's Freeview.
The DVB-T Standard is published as EN 300 744, Framing structure, channel coding and modulation for digital terrestrial television. This is available from the ETSI website, as is ETSI TS 101 154, Specification for the use of Video and Audio Coding in Broadcasting Applications based on the MPEG-2 Transport Stream, which gives details of the DVB use of source coding methods for MPEG-2
and, more recently, H.264/MPEG-4 AVC
as well as audio encoding systems. Many countries that have adopted DVB-T have published standards for their implementation. These include the D-book
in the UK, the Italian DGTVi, the ETSI E-Book and Scandivia NorDig.
DVB-T has been further developed into newer standards such as DVB-H
(Handheld), now in operation, and DVB-T2
, which was recently finalised.
DVB-T as a digital transmission delivers data in a series of discrete blocks at the symbol rate. DVB-T is a COFDM transmission technique which includes the use of a Guard Interval. It allows the receiver to cope with strong multipath situations. Within a geographical area, DVB-T also allows single-frequency network
(SFN) operation, where two or more transmitters carrying the same data operate on the same frequency. In such cases the signals from each transmitter in the SFN needs to be accurately time-aligned, which is done by sync information in the stream and timing at each transmitter referenced to GPS.
The length of the Guard Interval can be chosen. It is a trade off between data rate and SFN
capability. The longer the guard interval the larger is the potential SFN area without creating intersymbol interference
(ISI).
It is possible to operate SFNs which do not fulfill the guard interval condition if the self-interference is properly planned and monitored.
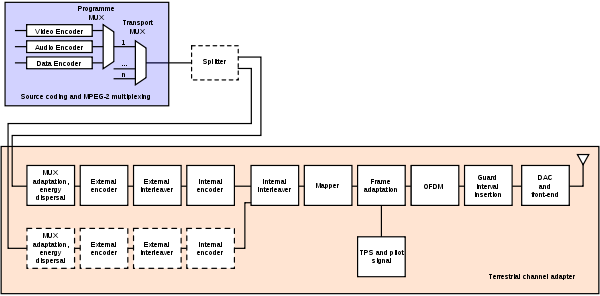 With reference to the figure, a short description of the signal processing blocks follows.
With reference to the figure, a short description of the signal processing blocks follows.
Source coding
and MPEG-2 multiplexing
(MUX): compressed video, compressed audio, and data streams are multiplexed into MPEG program streams (MPEG-PSs). One or more MPEG-PSs are joined together into an MPEG transport stream (MPEG-TS); this is the basic digital stream which is being transmitted and received by TV sets or home Set Top Boxes (STB). Allowed bitrate
s for the transported data depend on a number of coding and modulation parameters: it can range from about 5 to about 32 Mbit/s (see the bottom figure for a complete listing).
Splitter: two different MPEG-TSs can be transmitted at the same time, using a technique called Hierarchical Transmission. It may be used to transmit, for example a standard definition SDTV signal and a high definition HDTV signal on the same carrier
. Generally, the SDTV signal is more robust than the HDTV one. At the receiver, depending on the quality of the received signal, the STB may be able to decode the HDTV stream or, if signal strength lacks, it can switch to the SDTV one (in this way, all receivers that are in proximity of the transmission site can lock the HDTV signal, whereas all the other ones, even the farthest, may still be able to receive and decode an SDTV signal).
MUX adaptation and energy dispersal: the MPEG-TS is identified as a sequence of data packets, of fixed length (188 bytes). With a technique called energy dispersal, the byte sequence is decorrelated
.
External encoder: a first level of error correction is applied to the transmitted data, using a non-binary block code
, a Reed-Solomon RS (204, 188) code, allowing the correction of up to a maximum of 8 wrong bytes for each 188-byte packet.
External interleaver: convolutional interleaving is used to rearrange the transmitted data sequence, in such a way that it becomes more rugged to long sequences of errors.
Internal encoder: a second level of error correction is given by a punctured convolutional code
, which is often denoted in STBs menus as FEC (Forward error correction
). There are five valid coding rates: 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, and 7/8.
Internal interleaver: data sequence is rearranged again, aiming to reduce the influence of burst errors. This time, a block interleaving technique is adopted, with a pseudo-random assignment scheme (this is really done by two separate interleaving processes, one operating on bits and another one operating on groups of bits).
Mapper: the digital bit sequence is mapped into a base band modulated sequence of complex symbols. There are three valid modulation
schemes: QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM.
Frame adaptation: the complex symbols are grouped in blocks of constant length (1512, 3024, or 6048 symbols per block). A frame
is generated, 68 blocks long, and a superframe is built by 4 frames.
Pilot and TPS signals: in order to simplify the reception of the signal being transmitted on the terrestrial radio channel, additional signals are inserted in each block. Pilot signals are used during the synchronization and equalization phase, while TPS signals (Transmission Parameters Signalling) send the parameters of the transmitted signal and to unequivocally identify the transmission cell. The receiver must be able to synchronize, equalize, and decode the signal to gain access to the information held by the TPS pilots. Thus, the receiver must know this information beforehand, and the TPS data is only used in special cases, such as changes in the parameters, resynchronizations, etc.
 OFDM Modulation: the sequence of blocks is modulated according to the OFDM
OFDM Modulation: the sequence of blocks is modulated according to the OFDM
technique, using 2048, 4096, or 8192 carriers (2k, 4k, 8k mode, respectively). Increasing the number of carriers does not modify the payload bit rate, which remains constant.
Guard interval insertion: to decrease receiver complexity, every OFDM block is extended, copying in front of it its own end (cyclic prefix
). The width of such guard interval can be 1/32, 1/16, 1/8, or 1/4 that of the original block length. Cyclic prefix is required to operate single frequency networks, where there may exist an ineliminable interference coming from several sites transmitting the same program on the same carrier frequency.
DAC and front-end: the digital signal is transformed into an analogue signal, with a digital-to-analogue converter (DAC), and then modulated to radio frequency (VHF
, UHF
) by the RF front-end. The occupied bandwidth is designed to accommodate each single DVB-T signal into 5, 6, 7, or 8 MHz wide channels. The base band sample rate provided at the DAC input depends on the channel bandwidth: it is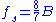 samples/s, where
samples/s, where  is the channel bandwidth expressed in Hz.
is the channel bandwidth expressed in Hz.
for SD and HD. Is considering moving to DVB-T2/H.264/MPEG-4
) (decided on May 12, 2009) (Uses DVB-T/MPEG-2
for SD and DVB-T
/H.264/MPEG-4
for HD transmissions.) (Experimental DVB-T MPEG2)
(experimental - MPEG-4, FEC=2/3, 16 QAM.) (See DVB-T in Croatia.) (MPEG-2, MPEG-4 experimental in Prague and surroundings) (MPEG-4 video)
(Uses MPEG-2
/MPEG-4
) for SD and MPEG-4
for HD transmissions. See DVB-T in Denmark.)
(MPEG2 for SD, MPEG 4 AVC for HD) (uses H.264/MPEG-4 AVC) (uses H.264/MPEG-4 AVC) (DVB-T in Macedonia) (uses MPEG-2
. MPEG-4
is being tested.) (MPEG-2
SD, operated by Digitenne) (Uses MPEG-4
) for SD and MPEG-4
for HD transmissions. See DVB-T in Norway.) (Uses MPEG-4/H.264 video; see DVB-T in Poland
) (Uses MPEG-4/H.264 video;) (uses MPEG-2
for SD and MPEG-4
for HD transmissions.) (experimental) (testing, will use MPEG-4
video and DVB-T2
) (Use MPEG-4
video since 2007. See DVB-T in Slovenia) (Uses DVB-T/MPEG-2
for SD and DVB-T/H.264/MPEG-4
for HD transmissions.) (Uses MPEG-2
/MPEG-4
) for SD and DVB-T2
with MPEG-4
for HD transmissions. See DVB-T in Sweden.) (experimental) (Uses DVB-T/MPEG-2
for SD and DVB-T2
/H.264/MPEG-4
for HD transmissions. See DVB-T in United Kingdom
.) (uses DVB-T2
/MPEG-4
for all nationwide broadcasts)
for both SD and HD transmissions.) (In Assessment) (Uses MPEG-4
and MPEG-2
Video) (Experimental target in 2015 full covered all city) (uses MPEG-4/H.264/AAC SD video and DVB-T/H.264/MPEG-4
for HD transmissions)
(In Assessment) (uses MPEG-4/H.264 video) (In Assessment) (Will use MPEG-2 for SD and MPEG-4 for HD transmissions.) (In Assessment) (experimental, may also adopt DMB-T/H, also experimenting with DVB-T2 as of 2011) (see Freeview New Zealand) (In Assessment) (In Assessment) (In Assessment) (Will use MPEG-2 for SD and MPEG-4 for HD transmissions.) (Will use DVB-T , MPEG-2 and MPEG-4.) (pilot service ) (Uses DVB-T/MPEG-2
for SD and DVB-T/H.264/MPEG-4
for HD transmissions.) (Confirm to uses DVB-T2
) (Will use MPEG-2 for SD and MPEG-4 for HD transmissions.) (In Assessment)
) (Will use DVB-T2, after briefly considering ISDB-T) (experimental)
Digital terrestrial television
Digital terrestrial television is the technological evolution of broadcast television and advance from analog television, which broadcasts land-based signals...
that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
in 1998. This system transmits compressed digital audio
Digital audio
Digital audio is sound reproduction using pulse-code modulation and digital signals. Digital audio systems include analog-to-digital conversion , digital-to-analog conversion , digital storage, processing and transmission components...
, digital video
Digital video
Digital video is a type of digital recording system that works by using a digital rather than an analog video signal.The terms camera, video camera, and camcorder are used interchangeably in this article.- History :...
and other data in an MPEG transport stream, using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing is a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital communication, whether wireless or over copper wires, used in applications such as digital television and audio...
(COFDM or OFDM) modulation.
Basics of DVB-T
Rather than carrying the data on a single radio frequencyRadio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
(RF) carrier, OFDM works by splitting the digital data stream into a large number of slower digital streams, each of which digitally modulate a set of closely spaced adjacent carrier frequencies. In the case of DVB-T, there are two choices for the number of carriers known as 2K-mode or 8K-mode. These are actually 1,705 or 6,817 carriers that are approximately 4 kHz or 1 kHz apart.
DVB-T offers three different modulation schemes (QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM).
DVB-T has been adopted or proposed for digital television broadcasting by many countries (see map), using mainly VHF 7 MHz and UHF 8 MHz channels whereas Taiwan, Colombia, Panama, Trinidad and Tobago and the Philippines use 6 MHz channels. Examples include the UK's Freeview.
The DVB-T Standard is published as EN 300 744, Framing structure, channel coding and modulation for digital terrestrial television. This is available from the ETSI website, as is ETSI TS 101 154, Specification for the use of Video and Audio Coding in Broadcasting Applications based on the MPEG-2 Transport Stream, which gives details of the DVB use of source coding methods for MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
and, more recently, H.264/MPEG-4 AVC
H.264/MPEG-4 AVC
H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video...
as well as audio encoding systems. Many countries that have adopted DVB-T have published standards for their implementation. These include the D-book
D-book
The D-Book is the UK technical specification for Digital terrestrial television .The Digital TV Group has published and maintained the D-Book for over a decade and the specification is updated annually to keep up with the pace of development in UK DTT...
in the UK, the Italian DGTVi, the ETSI E-Book and Scandivia NorDig.
DVB-T has been further developed into newer standards such as DVB-H
DVB-H
DVB-H is one of three prevalent mobile TV formats. It is a technical specification for bringing broadcast services to mobile handsets. DVB-H was formally adopted as ETSI standard EN 302 304 in November 2004. The DVB-H specification can be downloaded from the official DVB-H website...
(Handheld), now in operation, and DVB-T2
DVB-T2
DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television....
, which was recently finalised.
DVB-T as a digital transmission delivers data in a series of discrete blocks at the symbol rate. DVB-T is a COFDM transmission technique which includes the use of a Guard Interval. It allows the receiver to cope with strong multipath situations. Within a geographical area, DVB-T also allows single-frequency network
Single-frequency network
A single-frequency network or SFN is a broadcast network where several transmitters simultaneously send the same signal over the same frequency channel.-Overview:...
(SFN) operation, where two or more transmitters carrying the same data operate on the same frequency. In such cases the signals from each transmitter in the SFN needs to be accurately time-aligned, which is done by sync information in the stream and timing at each transmitter referenced to GPS.
The length of the Guard Interval can be chosen. It is a trade off between data rate and SFN
Single-frequency network
A single-frequency network or SFN is a broadcast network where several transmitters simultaneously send the same signal over the same frequency channel.-Overview:...
capability. The longer the guard interval the larger is the potential SFN area without creating intersymbol interference
Intersymbol interference
In telecommunication, intersymbol interference is a form of distortion of a signal in which one symbol interferes with subsequent symbols. This is an unwanted phenomenon as the previous symbols have similar effect as noise, thus making the communication less reliable...
(ISI).
It is possible to operate SFNs which do not fulfill the guard interval condition if the self-interference is properly planned and monitored.
Technical description of a DVB-T transmitter

Source coding
Source coding
In information theory, Shannon's source coding theorem establishes the limits to possible data compression, and the operational meaning of the Shannon entropy....
and MPEG-2 multiplexing
Multiplexing
The multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel, which may be a physical transmission medium. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the low-level communication channel into several higher-level logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred...
(MUX): compressed video, compressed audio, and data streams are multiplexed into MPEG program streams (MPEG-PSs). One or more MPEG-PSs are joined together into an MPEG transport stream (MPEG-TS); this is the basic digital stream which is being transmitted and received by TV sets or home Set Top Boxes (STB). Allowed bitrate
Bitrate
In telecommunications and computing, bit rate is the number of bits that are conveyed or processed per unit of time....
s for the transported data depend on a number of coding and modulation parameters: it can range from about 5 to about 32 Mbit/s (see the bottom figure for a complete listing).
Splitter: two different MPEG-TSs can be transmitted at the same time, using a technique called Hierarchical Transmission. It may be used to transmit, for example a standard definition SDTV signal and a high definition HDTV signal on the same carrier
Carrier wave
In telecommunications, a carrier wave or carrier is a waveform that is modulated with an input signal for the purpose of conveying information. This carrier wave is usually a much higher frequency than the input signal...
. Generally, the SDTV signal is more robust than the HDTV one. At the receiver, depending on the quality of the received signal, the STB may be able to decode the HDTV stream or, if signal strength lacks, it can switch to the SDTV one (in this way, all receivers that are in proximity of the transmission site can lock the HDTV signal, whereas all the other ones, even the farthest, may still be able to receive and decode an SDTV signal).
MUX adaptation and energy dispersal: the MPEG-TS is identified as a sequence of data packets, of fixed length (188 bytes). With a technique called energy dispersal, the byte sequence is decorrelated
Correlation
In statistics, dependence refers to any statistical relationship between two random variables or two sets of data. Correlation refers to any of a broad class of statistical relationships involving dependence....
.
External encoder: a first level of error correction is applied to the transmitted data, using a non-binary block code
Block code
In coding theory, block codes refers to the large and important family of error-correcting codes that encode data in blocks.There is a vast number of examples for block codes, many of which have a wide range of practical applications...
, a Reed-Solomon RS (204, 188) code, allowing the correction of up to a maximum of 8 wrong bytes for each 188-byte packet.
External interleaver: convolutional interleaving is used to rearrange the transmitted data sequence, in such a way that it becomes more rugged to long sequences of errors.
Internal encoder: a second level of error correction is given by a punctured convolutional code
Convolutional code
In telecommunication, a convolutional code is a type of error-correcting code in which* each m-bit information symbol to be encoded is transformed into an n-bit symbol, where m/n is the code rate and...
, which is often denoted in STBs menus as FEC (Forward error correction
Forward error correction
In telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, forward error correction or channel coding is a technique used for controlling errors in data transmission over unreliable or noisy communication channels....
). There are five valid coding rates: 1/2, 2/3, 3/4, 5/6, and 7/8.
Internal interleaver: data sequence is rearranged again, aiming to reduce the influence of burst errors. This time, a block interleaving technique is adopted, with a pseudo-random assignment scheme (this is really done by two separate interleaving processes, one operating on bits and another one operating on groups of bits).
Mapper: the digital bit sequence is mapped into a base band modulated sequence of complex symbols. There are three valid modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
schemes: QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM.
Frame adaptation: the complex symbols are grouped in blocks of constant length (1512, 3024, or 6048 symbols per block). A frame
Frame synchronization
While receiving a stream of framed data, frame synchronization is the process by which incoming frame alignment signals, i.e., distinctive bit sequences , are identified, i.e., distinguished from data bits, permitting the data bits within the frame to be extracted for decoding or retransmission...
is generated, 68 blocks long, and a superframe is built by 4 frames.
Pilot and TPS signals: in order to simplify the reception of the signal being transmitted on the terrestrial radio channel, additional signals are inserted in each block. Pilot signals are used during the synchronization and equalization phase, while TPS signals (Transmission Parameters Signalling) send the parameters of the transmitted signal and to unequivocally identify the transmission cell. The receiver must be able to synchronize, equalize, and decode the signal to gain access to the information held by the TPS pilots. Thus, the receiver must know this information beforehand, and the TPS data is only used in special cases, such as changes in the parameters, resynchronizations, etc.

Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing is a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital communication, whether wireless or over copper wires, used in applications such as digital television and audio...
technique, using 2048, 4096, or 8192 carriers (2k, 4k, 8k mode, respectively). Increasing the number of carriers does not modify the payload bit rate, which remains constant.
Guard interval insertion: to decrease receiver complexity, every OFDM block is extended, copying in front of it its own end (cyclic prefix
Cyclic prefix
In telecommunications, the term cyclic prefix refers to the prefixing of a symbol with a repetition of the end. Although the receiver is typically configured to discard the cyclic prefix samples, the cyclic prefix serves two purposes....
). The width of such guard interval can be 1/32, 1/16, 1/8, or 1/4 that of the original block length. Cyclic prefix is required to operate single frequency networks, where there may exist an ineliminable interference coming from several sites transmitting the same program on the same carrier frequency.
DAC and front-end: the digital signal is transformed into an analogue signal, with a digital-to-analogue converter (DAC), and then modulated to radio frequency (VHF
Very high frequency
Very high frequency is the radio frequency range from 30 MHz to 300 MHz. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted High frequency , and the next higher frequencies are known as Ultra high frequency...
, UHF
Ultra high frequency
Ultra-High Frequency designates the ITU Radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz , also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres...
) by the RF front-end. The occupied bandwidth is designed to accommodate each single DVB-T signal into 5, 6, 7, or 8 MHz wide channels. The base band sample rate provided at the DAC input depends on the channel bandwidth: it is
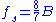 samples/s, where
samples/s, where  is the channel bandwidth expressed in Hz.
is the channel bandwidth expressed in Hz.| Available bitrates (Mbit/s) for a DVB-T system in 8 MHz channels | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modulation | Coding rate | Guard interval Guard interval In telecommunications, guard intervals are used to ensure that distinct transmissions do not interfere with one another. These transmissions may belong to different users or to the same user .... |
|||
| 1/4 | 1/8 | 1/16 | 1/32 | ||
| QPSK | 1/2 | 4.976 | 5.529 | 5.855 | 6.032 |
| 2/3 | 6.635 | 7.373 | 7.806 | 8.043 | |
| 3/4 | 7.465 | 8.294 | 8.782 | 9.048 | |
| 5/6 | 8.294 | 9.216 | 9.758 | 10.053 | |
| 7/8 | 8.709 | 9.676 | 10.246 | 10.556 | |
| 16-QAM Quadrature amplitude modulation Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog... |
1/2 | 9.953 | 11.059 | 11.709 | 12.064 |
| 2/3 | 13.271 | 14.745 | 15.612 | 16.086 | |
| 3/4 | 14.929 | 16.588 | 17.564 | 18.096 | |
| 5/6 | 16.588 | 18.431 | 19.516 | 20.107 | |
| 7/8 | 17.418 | 19.353 | 20.491 | 21.112 | |
| 64-QAM Quadrature amplitude modulation Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog... |
1/2 | 14.929 | 16.588 | 17.564 | 18.096 |
| 2/3 | 19.906 | 22.118 | 23.419 | 24.128 | |
| 3/4 | 22.394 | 24.882 | 26.346 | 27.144 | |
| 5/6 | 24.882 | 27.647 | 29.273 | 30.160 | |
| 7/8 | 26.126 | 29.029 | 30.737 | 31.668 | |
Technical description of the receiver
The receiving STB adopts techniques which are dual to those ones used in the transmission.- Front-end and ADC: the analogue RF signal is converted to base-band and transformed into a digital signal, using an analogue-to-digital converter (ADC).
- Time and frequency synchronization: the digital base band signal is searched to identify the beginning of frames and blocks. Any problems with the frequency of the components of the signal are corrected, too. The property that the guard interval at the end of the symbol is placed also at the beginning is exploited to find the beginning of a new OFDM symbol. On the other hand, continual pilots (whose value and position is determined in the standard and thus known by the receiver) determine the frequency offset suffered by the signal. This frequency offset might have been caused by Doppler effectDoppler effectThe Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
, inaccuracies in either the transmitter or receiver clock, and so on.
- Guard interval disposal: the cyclic prefix is removed.
- OFDM demodulation
- Frequency equalizationEqualizationEqualization, is the process of adjusting the balance between frequency components within an electronic signal. The most well known use of equalization is in sound recording and reproduction but there are many other applications in electronics and telecommunications. The circuit or equipment used...
: the pilot signals equalize the received signal. - Demapping
- Internal deinterleaving
- Internal decoding: uses the Viterbi algorithmViterbi algorithmThe Viterbi algorithm is a dynamic programming algorithm for finding the most likely sequence of hidden states – called the Viterbi path – that results in a sequence of observed events, especially in the context of Markov information sources, and more generally, hidden Markov models...
. - External deinterleaving
- External decoding
- MUX adaptation
- MPEG-2 demultiplexing and source decoding
Countries and territories using DVB-T

America
(decided on August 28, 2008) (Uses DVB-T/H.264/MPEG-4MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for SD and HD. Is considering moving to DVB-T2/H.264/MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
) (decided on May 12, 2009) (Uses DVB-T/MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
for SD and DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
/H.264/MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for HD transmissions.) (Experimental DVB-T MPEG2)
Europe
(uses MPEG-4 AVC /H.264 for SD transmission.)(experimental - MPEG-4, FEC=2/3, 16 QAM.) (See DVB-T in Croatia.) (MPEG-2, MPEG-4 experimental in Prague and surroundings) (MPEG-4 video)
(Uses MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
/MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
) for SD and MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for HD transmissions. See DVB-T in Denmark.)
-
 Faroe Islands
Faroe Islands -
 Greenland (Nuuk tv) (uses MPEG-4MPEG-4MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
Greenland (Nuuk tv) (uses MPEG-4MPEG-4MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
video) (uses MPEG-2MPEG-2MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
for SD and MPEG-4MPEG-4MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for HD transmissions.) (usually MPEG-2MPEG-2MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
, SD only, Überallfernsehen) (ERT Digital and Digital Union use MPEG-2MPEG-2MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
but will shift to MPEG-4MPEG-4MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
. Digea and ERT / ERT HD use MPEG-4MPEG-4MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
) (branded MinDigTV, uses H.264/MPEG-4 AVCH.264/MPEG-4 AVCH.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video...
video exclusively.) (Will use MPEG-4MPEG-4MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
video, see DVB-T in Ireland.)
(MPEG2 for SD, MPEG 4 AVC for HD) (uses H.264/MPEG-4 AVC) (uses H.264/MPEG-4 AVC) (DVB-T in Macedonia) (uses MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
. MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
is being tested.) (MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
SD, operated by Digitenne) (Uses MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
) for SD and MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for HD transmissions. See DVB-T in Norway.) (Uses MPEG-4/H.264 video; see DVB-T in Poland
Digital television in Poland
First efforts to introduce DVB-T in Poland was made in 1997 in Gdańsk on initiative of TVP . First test DVB-T emission was carried in Warsaw at 9 November 2001....
) (Uses MPEG-4/H.264 video;) (uses MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
for SD and MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for HD transmissions.) (experimental) (testing, will use MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
video and DVB-T2
DVB-T2
DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television....
) (Use MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
video since 2007. See DVB-T in Slovenia) (Uses DVB-T/MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
for SD and DVB-T/H.264/MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for HD transmissions.) (Uses MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
/MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
) for SD and DVB-T2
DVB-T2
DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television....
with MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for HD transmissions. See DVB-T in Sweden.) (experimental) (Uses DVB-T/MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
for SD and DVB-T2
DVB-T2
DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television....
/H.264/MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for HD transmissions. See DVB-T in United Kingdom
Digital terrestrial television in the United Kingdom
Digital terrestrial television in the United Kingdom encompasses over 100 television, radio and interactive services broadcast via the UK's terrestrial television network and receivable with a standard television aerial...
.) (uses DVB-T2
DVB-T2
DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television....
/MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for all nationwide broadcasts)
Asia & Australia
(Uses DVB-T/MPEG-2MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
for both SD and HD transmissions.) (In Assessment) (Uses MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
and MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
Video) (Experimental target in 2015 full covered all city) (uses MPEG-4/H.264/AAC SD video and DVB-T/H.264/MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for HD transmissions)
(In Assessment) (uses MPEG-4/H.264 video) (In Assessment) (Will use MPEG-2 for SD and MPEG-4 for HD transmissions.) (In Assessment) (experimental, may also adopt DMB-T/H, also experimenting with DVB-T2 as of 2011) (see Freeview New Zealand) (In Assessment) (In Assessment) (In Assessment) (Will use MPEG-2 for SD and MPEG-4 for HD transmissions.) (Will use DVB-T , MPEG-2 and MPEG-4.) (pilot service ) (Uses DVB-T/MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
for SD and DVB-T/H.264/MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
for HD transmissions.) (Confirm to uses DVB-T2
DVB-T2
DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television....
) (Will use MPEG-2 for SD and MPEG-4 for HD transmissions.) (In Assessment)
Africa
(Will use DVB-T2MPEG-4MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
) (Will use DVB-T2, after briefly considering ISDB-T) (experimental)
See also
- ATSC (Advanced Television Systems Committee, North American Standard)
- Digital audio broadcastingDigital audio broadcastingDigital Audio Broadcasting is a digital radio technology for broadcasting radio stations, used in several countries, particularly in Europe. As of 2006, approximately 1,000 stations worldwide broadcast in the DAB format....
(low bitrate video suitable for moving receivers) - DTV channel protection ratios
- DVB over IP
- DVB-T2DVB-T2DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television....
- Digital terrestrial televisionDigital terrestrial televisionDigital terrestrial television is the technological evolution of broadcast television and advance from analog television, which broadcasts land-based signals...
- DMB-T - Digital Multimedia Broadcast-Terrestrial
- Interactive televisionInteractive televisionInteractive television describes a number of techniques that allow viewers to interact with television content as they view it.- Definitions :...
- ISDBISDBIntegrated Services Digital Broadcasting is a Japanese standard for digital television and digital radio used by the country's radio and television stations. ISDB replaced the previously used MUSE "Hi-vision" analogue HDTV system...
- Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting- ISDB-T International
- OFDM system comparison table
- Personal video recorder
- Spectral efficiency comparison table
- TeletextTeletextTeletext is a television information retrieval service developed in the United Kingdom in the early 1970s. It offers a range of text-based information, typically including national, international and sporting news, weather and TV schedules...

