Digital terrestrial television
Encyclopedia
Analog television
Analog television is the analog transmission that involves the broadcasting of encoded analog audio and analog video signal: one in which the message conveyed by the broadcast signal is a function of deliberate variations in the amplitude and/or frequency of the signal...
, which broadcasts land-based (terrestrial) signals. The purposes of digital terrestrial television, similar to digital versus analogue in other platforms such as cable, satellite, and telecommunications, are reduced use of spectrum and more capacity than analogue, better-quality picture, and lower operating costs for broadcast and transmission after the initial upgrade costs. A terrestrial implementation of digital television
Digital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
(DTV) technology uses aerial broadcasts to a conventional television antenna
Television antenna
A television antenna, or TV aerial, is an antenna specifically designed for the reception of over the air broadcast television signals, which are transmitted at frequencies from about 41 to 250 MHz in the VHF band, and 470 to 960 MHz in the UHF band in different countries...
(or aerial) instead of a satellite dish
Satellite dish
A satellite dish is a dish-shaped type of parabolic antenna designed to receive microwaves from communications satellites, which transmit data transmissions or broadcasts, such as satellite television.-Principle of operation:...
or cable television
Cable television
Cable television is a system of providing television programs to consumers via radio frequency signals transmitted to televisions through coaxial cables or digital light pulses through fixed optical fibers located on the subscriber's property, much like the over-the-air method used in traditional...
connection.
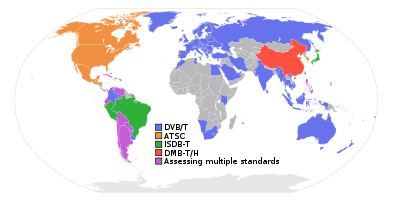
Competing variants of broadcast television system
Broadcast television system
Broadcast television systems are encoding or formatting standards for the transmission and reception of terrestrial television signals. There are three main analog television systems in current use around the world: NTSC, PAL, and SECAM...
s are used around the world. Advanced Television Standards Committee created the ATSC standards that use an ATSC tuner
ATSC tuner
An ATSC tuner, often called an ATSC receiver or HDTV tuner is a type of television tuner that allows reception of digital television television channels transmitted by television stations in North America, parts of Central America and South Korea that use ATSC standards...
in North America and South Korea, an evolution from the analogue National Television Standards Committee (NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
) standard. Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting (ISDB-T) is used in Japan, with a variation of it used in most of South America, while DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
is the most prevalent, covering Europe, Australia, New Zealand, Colombia and some countries of Africa. DMB-T/H
DMB-T/H
DTMB is the TV standard for mobile and fixed terminals used in the People's Republic of China, Hong Kong and Macau. Although at first this standard was called DMB-T/H , the official name is DTMB.DTT broadcasting systems...
is China's own standard (including Hong Kong, though Hong Kong's cable operators use DVB); the rest of the world remains mostly undecided, many evaluating multiple standards. ISDB-T is very similar to DVB-T and can share front-end receiver and demodulator components. Several European countries have switched from analogue to digital terrestrial television, with the rest hoping to have completed the switchover mostly by 2012.
Transmission
DTTV is transmitted on radio frequenciesRadio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
through terrestrial space in the same way as standard analog television
Analog television
Analog television is the analog transmission that involves the broadcasting of encoded analog audio and analog video signal: one in which the message conveyed by the broadcast signal is a function of deliberate variations in the amplitude and/or frequency of the signal...
, with the primary difference being the use of multiplex
Multiplexing
The multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel, which may be a physical transmission medium. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the low-level communication channel into several higher-level logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred...
transmitters to allow reception of multiple channels on a single frequency range (such as a UHF
Ultra high frequency
Ultra-High Frequency designates the ITU Radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz , also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres...
or VHF
Very high frequency
Very high frequency is the radio frequency range from 30 MHz to 300 MHz. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted High frequency , and the next higher frequencies are known as Ultra high frequency...
channel) known as subchannels.
The amount of data
Data
The term data refers to qualitative or quantitative attributes of a variable or set of variables. Data are typically the results of measurements and can be the basis of graphs, images, or observations of a set of variables. Data are often viewed as the lowest level of abstraction from which...
that can be transmitted (and therefore the number of channels) is directly affected by channel capacity
Channel capacity
In electrical engineering, computer science and information theory, channel capacity is the tightest upper bound on the amount of information that can be reliably transmitted over a communications channel...
and the modulation
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
method of the channel. The modulation method in DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
is COFDM with either 64 or 16-state Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
(QAM). In general, a 64QAM channel is capable of transmitting a greater bit rate, but is more susceptible to interference. 16 and 64QAM constellations can be combined in a single multiplex, providing a controllable degradation for more important program stream
Program stream
Program stream is a container format for multiplexing digital audio, video and more. The PS format is specified in MPEG-1 Part 1 and MPEG-2 Part 1, Systems...
s. This is called hierarchical modulation
Hierarchical modulation
Hierarchical modulation, also called layered modulation, is one of the signal processing techniques for multiplexing and modulating multiple data streams into one single symbol stream, where base-layer symbols and enhancement-layer symbols are synchronously overplayed before...
.
New developments in video compression have resulted in the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC
H.264/MPEG-4 AVC
H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video...
standard which enable three high-definition television
High-definition television
High-definition television is video that has resolution substantially higher than that of traditional television systems . HDTV has one or two million pixels per frame, roughly five times that of SD...
services to be coded into a 24 Mbit/s European terrestrial transmission channel.
The DVB-T standard is not used for terrestrial digital television in North America. Instead, the ATSC standard calls for 8VSB
8VSB
8VSB is the modulation method used for broadcast in the ATSC digital television standard. ATSC and 8VSB modulation is used primarily in North America; in contrast, the DVB-T standard uses COFDM....
modulation, which has similar characteristics to the vestigial sideband
Sideband
In radio communications, a sideband is a band of frequencies higher than or lower than the carrier frequency, containing power as a result of the modulation process. The sidebands consist of all the Fourier components of the modulated signal except the carrier...
modulation used for analogue television. This provides considerably more immunity to interference, but is not immune — as DVB-T is — to multipath distortion and also does not provide for single-frequency network operation (which is in any case not relevant in the United States).
Both systems use the MPEG transport stream and H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2
H.262/MPEG-2 Part 2
H.262 or MPEG-2 Part 2 is a digital video compression and encoding standard developed and maintained jointly by ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group and ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group . It is the second part of the ISO/IEC MPEG-2 standard...
video codec
Video codec
A video codec is a device or software that enables video compression and/or decompression for digital video. The compression usually employs lossy data compression. Historically, video was stored as an analog signal on magnetic tape...
specified in MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
; they differ significantly in how related services (such as multichannel audio, captions, and program guides) are encoded.
Advantages
- Digital presentation tends to be better overall, particularly with a good signal, due to the elimination of visible interference and other effects such as ghostingGhosting (television)In television, a ghost is a replica of the transmitted image, offset in position, that is super-imposed on top of the main image on an analogue broadcast.-Common causes:Common causes of ghosts are:...
. - With a weaker signal there is little perceptible difference in digital presentations.
- It is easier to obtain the optimum digital picture than the optimum analogue picture.
- Many more channels can fit on the same spectrum under digital transmission.
- Interactive (red button) services can be provided.
Disadvantages
- It can be quite difficult to adjust the antenna, because of the lack of feedback that would be provided by a gradually degraded analog picture. The picture is usually either totally on or totally off, providing no information about which direction to move the antenna. A signal meter provided on most tuners helps considerably with this problem, but some televisions lack a signal meter. The same problem can also make it very difficult to select and test antennas.
- New equipment (set-top boxSet-top boxA set-top box or set-top unit is an information appliance device that generally contains a tuner and connects to a television set and an external source of signal, turning the signal into content which is then displayed on the television screen or other display device.-History:Before the...
) may be required. - Increased electricity consumption by the digital receiving equipment if both TV and additional set-top box is plugged.
- An upgraded antenna installation may be required.
- Analogue requires lower signal strength to get a viewable picture. By extension, digital does not degrade as gracefully as analogue. This is because digital signal transmission suffers from the cliff effectCliff effectIn telecommunications, the cliff effect or brickwall effect describes the sudden loss of digital signal reception. Unlike analog signals, which gradually fade when signal strength decreases or electromagnetic interference or multipath increases, a digital signal provides data which is either...
; meaning that once the signal degrades beyond a certain point, the receiver fails to decode the signal and cannot present the expected output. - Switching channels is slower because of the time delays in decoding digital signals.
Reception
DTTV is received either via a digital set-top boxSet-top box
A set-top box or set-top unit is an information appliance device that generally contains a tuner and connects to a television set and an external source of signal, turning the signal into content which is then displayed on the television screen or other display device.-History:Before the...
(STB) or integrated tuner included with television set
Television set
A television set is a device that combines a tuner, display, and speakers for the purpose of viewing television. Television sets became a popular consumer product after the Second World War, using vacuum tubes and cathode ray tube displays...
s, that decodes the signal received via a standard television antenna
Television antenna
A television antenna, or TV aerial, is an antenna specifically designed for the reception of over the air broadcast television signals, which are transmitted at frequencies from about 41 to 250 MHz in the VHF band, and 470 to 960 MHz in the UHF band in different countries...
. However, due to frequency planning issues, an aerial capable of receiving a different channel group (usually a wideband) may be required if the DTTV multiplexes lie outside the reception capabilities of the originally installed aerial. This is quite common in the UK; see external links.
Indoor aerials are even more likely to be affected by these issues and possibly need replacing.
DTT around the world and digital television transition
- Main articles: List of digital television deployments by country, Digital television transitionDigital television transitionThe digital television transition is the process in which analog television broadcasting is converted to and replaced by digital television. This primarily involves both TV stations and over-the-air viewers; however it also involves content providers like TV networks, and cable television...
(aka Analog Switchoff (ASO) or Digital Switchover (DSO))
Japan
The Japanese Ministry of Internal Affairs and CommunicationsMinistry of Internal Affairs and Communications
The ' or Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is a cabinet-level ministry in the Government of Japan. The English name Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications was used prior to 2004...
and DPA (The Association for Promotion of Digital Broadcasting-Japan) jointly set the specification
Specification (technical standard)
A specification is an explicit set of requirements to be satisfied by a material, product, or service. Should a material, product or service fail to meet one or more of the applicable specifications, it may be referred to as being out of specification;the abbreviation OOS may also be used...
and announced a guideline for "simplified DTT tuner
Antenna tuner
An antenna tuner, transmatch or antenna tuning unit is a device connected between a radio transmitter or receiver and its antenna to improve the efficiency of the power transfer between them by matching the impedance of the equipment to the antenna...
s" with price under 5,000 Japanese yen
Japanese yen
The is the official currency of Japan. It is the third most traded currency in the foreign exchange market after the United States dollar and the euro. It is also widely used as a reserve currency after the U.S. dollar, the euro and the pound sterling...
on 25 December 2007. MIAC officially solicited manufactures to put it on the market by end of March 2010 (end of fiscal year 2009). MIAC is estimating that 14 million, at maximum, traditional non-digital TV
Analog television
Analog television is the analog transmission that involves the broadcasting of encoded analog audio and analog video signal: one in which the message conveyed by the broadcast signal is a function of deliberate variations in the amplitude and/or frequency of the signal...
sets remain and need the "simplified DTT tuner" to be adapted even after complete transition to DTT after July 2011; it is aiming to avoid the disposal of large numbers of useless TV sets without such a tuner at one time.
On 20 December 2007, the Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association
Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association
The is a Japanese trade organization for the electronics and IT industries. It was formed in 2000 from two earlier organizations, the Electronic Industries Association of Japan and the Japan Electronic Industries Development Association.-See also:...
set rules for Digital Rights Management for DTT broadcasting, allowing consumers up to 10 time of dubbing
Dubbing (music)
In sound recording, dubbing is the transfer or copying of previously recorded audio material from one medium to another of the same or a different type. It may be done with a machine designed for this purpose, or by connecting two different machines: one to play back and one to record the signal...
of entire TV program with video and audio into Blu-ray Disc
Blu-ray Disc
Blu-ray Disc is an optical disc storage medium designed to supersede the DVD format. The plastic disc is 120 mm in diameter and 1.2 mm thick, the same size as DVDs and CDs. Blu-ray Discs contain 25 GB per layer, with dual layer discs being the norm for feature-length video discs...
recorder etc. by naming "Dubbing 10"(:ja:ダビング10) (actually up to 9 times of copy, then 1 time or last time of move). The broadcasting with "Dubbing 10" was supposed to start at about 4:00 a.m. on 2 June 2008, but was postponed after long talks with the Japanese Society for Rights of Authors, Composers and Publishers
Japanese Society for Rights of Authors, Composers and Publishers
, often referred to as the is a Japanese copyright collection society. It was founded in 1939 as a non-profit making organization, and is the largest musical copyright administration society in Japan....
, then confirmed to start about 4:00 a.m. on 4 July 2008. The manufacturers of DVD recorders and associated DTT recorders will make unit conforming to the "Dubbing 10" rule, and some manufacturers will create firmware downloads to update their recorders' internal software for existing users.
On 3 April 2008, DPA (The Association for Promotion of Digital Broadcasting-Japan) announced that a total of 32.71 million of DTT (ISDB-T) receiving TV sets (except 1seg
1seg
is a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
receiver) are installed in Japan as of the end of March 2008. DPA also announced a guideline for manufacturers who make the DTT receive, record and replay unit which operate with Personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s on 8 April 2008. This add-on
Peripheral
A peripheral is a device attached to a host computer, but not part of it, and is more or less dependent on the host. It expands the host's capabilities, but does not form part of the core computer architecture....
unit operates on USB
Universal Serial Bus
USB is an industry standard developed in the mid-1990s that defines the cables, connectors and protocols used in a bus for connection, communication and power supply between computers and electronic devices....
or PCI
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Conventional PCI is a computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer...
BUS, and started to sell on reservation basis from late April and put on retail store in mid. May 2008.
On 8 May 2008, the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
The ' or Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is a cabinet-level ministry in the Government of Japan. The English name Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications was used prior to 2004...
announced that 43.7% of homes have DTT (ISDB-T) receiving TV and/or Tuner with DVD recorder
DVD recorder
A DVD recorder , is an optical disc recorder that uses Optical disc recording technologies to digitally record analog signal or digital signals onto blank writable DVD media...
by end of March 2008, which was 27.8% in one year before, and expecting 100% by April 2011.
On 27 April 2009, National Association of Commercial Broadcasters in Japan (NAB) revealed its official mascot, Chidejika
Chidejika
Chidejika is the official mascot of National Association of Commercial Broadcasters in Japan , revealed on April 27, 2009 to promote transition from analogue television to digital terrestrial television in Japan.Voiced by Megumi Urawa.-See also:*Tsuyoshi Kusanagi - Digital terrestrial...
, to replace Tsuyoshi Kusanagi
Tsuyoshi Kusanagi
is a Japanese entertainer. Kusanagi is a member of the popular Japanese idol group SMAP and has also appeared in a number of television dramas, variety shows and movies.-Background:Kusanagi grew up in Kasukabe, Saitama, Japan....
as the face of NAB after he was arrested on suspicion of public indecency.
On 3 September 2009, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
The ' or Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is a cabinet-level ministry in the Government of Japan. The English name Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications was used prior to 2004...
announced the procurement under bidding 5,000-8,000 sets of "simplified DTT tuners
Antenna tuner
An antenna tuner, transmatch or antenna tuning unit is a device connected between a radio transmitter or receiver and its antenna to improve the efficiency of the power transfer between them by matching the impedance of the equipment to the antenna...
" with remote control
Remote control
A remote control is a component of an electronics device, most commonly a television set, used for operating the television device wirelessly from a short line-of-sight distance.The remote control is usually contracted to remote...
to apply "Analog to digital transition rehearsal
Rehearsal
For other uses, see Rehearsal or Dress rehearsal A rehearsal is a preparatory event in music and theatre that is performed before the official public performance, as a form of practice, and to ensure that all details of the performance are adequately prepared and coordinated for professional...
program" in Suzu, Ishikawa
Suzu, Ishikawa
is a city located at the northeasternmost tip of the Noto Peninsula in Ishikawa, Japan. The city is the proposed site of the Suzu Nuclear Power Plant; however, in 2003 the proposal was "frozen" until further notice....
, citywide transition practice. The set should be delivered until 30 November 2009. The program is aiming to examine the transition problem at individuals home in countrywide such as senior and non-technical families. Based on this rehearsal plan, analog TV transmission was interrupted in Suzu and parts of Noto
Noto, Ishikawa
Noto was a town located in Fugeshi District, Ishikawa, Japan.On March 1, 2005 Noto was merged with the village of Yanagida, both from Fugeshi District, and the town of Uchiura, from Suzu District, to form the new town of Noto, in the newly-created Hōsu District, Ishikawa and no longer exists as...
for 48 hours, between noon on 2010-01-22 and noon on 2010-01-24.
On 4 September 2009, ÆON
ÆON
, commonly written AEON Co., Ltd., is the holding company of Æon Group. It has its headquarters in Mihama-ku, Chiba, Chiba Prefecture.It operates JUSCO supermarkets directly in Japan.Æon is the largest retailer in Asia...
announced the low cost "simplified DTT tuners
Antenna tuner
An antenna tuner, transmatch or antenna tuning unit is a device connected between a radio transmitter or receiver and its antenna to improve the efficiency of the power transfer between them by matching the impedance of the equipment to the antenna...
" with remote control
Remote control
A remote control is a component of an electronics device, most commonly a television set, used for operating the television device wirelessly from a short line-of-sight distance.The remote control is usually contracted to remote...
for ISDB-T to sell at JUSCO
JUSCO
is the acronym for Japan United Stores Company, a chain of "general merchandise stores" and the largest of its type in Japan. The various JUSCO companies are subsidiaries of ÆON Co., Ltd.....
from 19 September 2009. Tuner is produced by Pixela
Pixela Corporation
-Overview:Pixela Corporation is a Japanese manufacturer of PC peripheral hardware and multimedia software. The company is known for its software series, ImageMixer, which is currently bundled with some camcorders...
and the first one meeting retail price under 5,000 Japanese yen
Japanese yen
The is the official currency of Japan. It is the third most traded currency in the foreign exchange market after the United States dollar and the euro. It is also widely used as a reserve currency after the U.S. dollar, the euro and the pound sterling...
which is solicited target price to industry by Dpa . Tuner connects to old fashion TV though RCA connector
RCA connector
An RCA connector, sometimes called a phono connector or cinch connector, is a type of electrical connector commonly used to carry audio and video signals...
with SDTV
Standard-definition television
Sorete-definition television is a television system that uses a resolution that is not considered to be either enhanced-definition television or high-definition television . The term is usually used in reference to digital television, in particular when broadcasting at the same resolution as...
quality and some other minimal function.
On 7 September 2009, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
The ' or Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is a cabinet-level ministry in the Government of Japan. The English name Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications was used prior to 2004...
appointed two manufacture I-O Data
I-O Data
is a Japanese computer peripheral manufacturer. They manufacture hard disk drives, Ethernet hubs, USB cables, etc. It gained fame for its durable external hard disk which survived the 122 cm drop test, which is used in some military equipment tests. Other than its headquarters in Tokyo, I-O...
and Melco
Melco
Melco Holdings Inc. is a family business founded by Makoto Maki in 1975. The name stands for Maki Engineering Laboratory COmpany...
among 12 bidder for minimal functioning "simplified DTT tuners
Antenna tuner
An antenna tuner, transmatch or antenna tuning unit is a device connected between a radio transmitter or receiver and its antenna to improve the efficiency of the power transfer between them by matching the impedance of the equipment to the antenna...
" with remote control
Remote control
A remote control is a component of an electronics device, most commonly a television set, used for operating the television device wirelessly from a short line-of-sight distance.The remote control is usually contracted to remote...
for ISDB-T of free supply to Japanese Temporary Assistance for Needy Families
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families is one of the United States of America's federal assistance programs. It began on July 2, 1997, and succeeded the Aid to Families with Dependent Children program, providing cash assistance to indigent American families with dependent children through the...
. Tuner connects to old fashion TV though RCA connector
RCA connector
An RCA connector, sometimes called a phono connector or cinch connector, is a type of electrical connector commonly used to carry audio and video signals...
with SDTV
Standard-definition television
Sorete-definition television is a television system that uses a resolution that is not considered to be either enhanced-definition television or high-definition television . The term is usually used in reference to digital television, in particular when broadcasting at the same resolution as...
quality and some other minimal function.
On 24 July 2010 noon, analog TV transmission officially stopped in Suzu and parts of Noto (approximately 8,800 homes) as the rehearsal plan one year ahead of nationwide stop scheduled on 24 July 2011. Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
The ' or Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is a cabinet-level ministry in the Government of Japan. The English name Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications was used prior to 2004...
shall watch what type of problem arise in transition to DTT which might apply to nationwide stop.
On 20 April 2011, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
The ' or Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is a cabinet-level ministry in the Government of Japan. The English name Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications was used prior to 2004...
confirmed, and made the resolution
Resolution (law)
A resolution is a written motion adopted by a deliberative body. The substance of the resolution can be anything that can normally be proposed as a motion. For long or important motions, though, it is often better to have them written out so that discussion is easier or so that it can be...
by House of Councillors
House of Councillors
The is the upper house of the Diet of Japan. The House of Representatives is the lower house. The House of Councillors is the successor to the pre-war House of Peers. If the two houses disagree on matters of the budget, treaties, or designation of the prime minister, the House of Representatives...
on 8 June 2011, the analog terrestrial TV closedown schedule on 24 July 2011 unchanged, except closedown postponed maximum one year, but rescheduled closedown on 31 March 2012 in Iwate
Iwate Prefecture
is the second largest prefecture of Japan after Hokkaido. It is located in the Tōhoku region of Honshū island and contains the island's easternmost point. The capital is Morioka. Iwate has the lowest population density of any prefecture outside Hokkaido...
, Miyagi
Miyagi Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan in the Tōhoku Region on Honshu island. The capital is Sendai.- History :Miyagi Prefecture was formerly part of the province of Mutsu. Mutsu Province, on northern Honshu, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the...
and Fukushima
Fukushima Prefecture
is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region on the island of Honshu. The capital is the city of Fukushima.-History:Until the Meiji Restoration, the area of Fukushima prefecture was known as Mutsu Province....
prefectures where heavily damaged by 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami
2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami
The 2011 earthquake off the Pacific coast of Tohoku, also known as the 2011 Tohoku earthquake, or the Great East Japan Earthquake, was a magnitude 9.0 undersea megathrust earthquake off the coast of Japan that occurred at 14:46 JST on Friday, 11 March 2011, with the epicenter approximately east...
.
Malaysia
In 2005, the Ministry of Information announced their plan to digitalise nationwide free-to-airFree-to-air
Free-to-air describes television and radio services broadcast in clear form, allowing any person with the appropriate receiving equipment to receive the signal and view or listen to the content without requiring a subscription or one-off fee...
TV broadcasts led by Radio Televisyen Malaysia
Radio Televisyen Malaysia
The Department of Broadcasting, Malaysia, DBA Radio Televisyen Malaysia , is a Malaysian state-owned public broadcaster. It owns and operates a number of radio and television stations in Malaysia, based in Kuala Lumpur...
(RTM). Trial broadcasts were undertaken, involving one thousand households in the Klang Valley
Klang Valley
Klang Valley is an area in Malaysia comprising Kuala Lumpur and its suburbs, and adjoining cities and towns in the state of Selangor. An alternative reference to this would be Kuala Lumpur Metropolitan Area or Greater Kuala Lumpur. It is geographically delineated by Titiwangsa Mountains to the...
from September 2006 till February 2007. According to the then-Deputy Minister of Information, Chia Kwang Chye, the trial received "very positive" feedback, i.e. "more than 60 percent said the quality of the signal ranged from good to very good. Over 88 percent said the picture quality improved, while 70 percent said the sound quality was better."
According to Information Minister Datuk Ahmad Shabery Cheek
Ahmad Shabery Cheek
YB. Dato' Sri Ahmad Shabery Cheek is a Malaysian politician. He is the Minister of Youth and Sports in the Barisan Nasional coalition government, and sits in Parliament as the member for Kemaman, Terengganu...
, RTM is expected to fully complete its digitalization in 2012 as part of its three-year restructuring process. Each household, once equipped with the necessary equipment (set-top box
Set-top box
A set-top box or set-top unit is an information appliance device that generally contains a tuner and connects to a television set and an external source of signal, turning the signal into content which is then displayed on the television screen or other display device.-History:Before the...
or iDTV
Integrated Digital Television
An Integrated Digital Television set is a television set with a built in digital tuner, be it for DVB-T, DVB-S, DVB-C, DMB-T/H, ATSC or ISDB. Most of them also allow reception of analogue signals . They do away with the need for a set top box for converting those signals for reception on a...
set) is expected to receive up to 19 channels, seven of which fall under RTM and the rest for private broadcasters such as Media Prima which owns its channels such as TV3
TV3 (Malaysia)
Sistem Televisyen Malaysia Berhad or TV3 began broadcasting on 1 June 1984 as Malaysia’s first commercial television station. It is part of Media Prima Berhad group of companies. It now transmits opened broadcasting business private 24-hours a day, 7 days a week since 1 January 2010...
, ntv7
Ntv7
Natseven TV Sdn Bhd or better known as ntv7 is a terrestrial television channel in Malaysia. It was launched nationwide on 7 April 1998 and was the country's third private free-to-air TV station after TV3 and Astro. Its mission is to promote a happier and more enlightened Malaysia...
, 8TV
8TV (Malaysia)
8TV is a private Malaysian Chinese television station, previously known as MetroVision Channel 8. Metrovision closed on 1 November 1999. 8TV was officially launched on Thursday, 8 January 2004 as 8TV after being acquired by Media Prima Berhad....
and TV9
TV9 (Malaysia)
TV9 is a free-to-air private television station in Malaysia. TV9 began broadcasting on 22 April 2006, as a subsidiary of Media Prima Berhad. It formerly existed as Channel 9, which began airing on 9 September 2003 and ceased transmission on 1 February 2005 due to financial difficulties faced by the...
. Thus far, besides simulcast
Simulcast
Simulcast, shorthand for "simultaneous broadcast", refers to programs or events broadcast across more than one medium, or more than one service on the same medium, at the same time. For example, Absolute Radio is simulcast on both AM and on satellite radio, and the BBC's Prom concerts are often...
ing TV1 and TV2
TV2 (Malaysia)
RTM2, also known as TV2 is a television station in Malaysia owned and operated by the Radio Television Malaysia, a division of the Malaysian Government. RTM2 is now broadcasting for 24 hours a day effective January 2006.- History :...
, RTM is test-airing RTMi
RTMi
RTMi was a digital television channel fully owned by Radio Televisyen Malaysia. It is also known as Digital Terrestrial Television Broadcasting . Its test broadcast began in 2000 chosen residential homes surrounding Klang Valley for 6 months starting in September 2006, using the DVB-T standard...
, Muzik Aktif and Arena exclusively on the digital TV platform, transmitted at UHF channel 44, modulated at 64QAM
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
. RTM was also expected to launch regional channels for each state and/or territory in Malaysia, making it 20 RTM television channels. Media Prima was expected to commence trials on March 2009.
Malaysia and all other ASEAN nations have selected DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
as the final DTV standard, and are expected to switch off analogue broadcasts completely by 2015. On June 2008, participants of the 6th ASEAN Digital Broadcast Meeting from seven south-east Asian countries (including Malaysia) agreed to finalise the specifications of the DTV set-top box for use within ASEAN, and also set up an ASEAN HD Centre to provide training on HDTV content to broadcasters in the region.
Even though RTM's trial was a success, the future of the digital terrestrial television transition has become uncertain, especially after the end of Abdullah Badawi's tenure as the Prime Minister
Prime minister
A prime minister is the most senior minister of cabinet in the executive branch of government in a parliamentary system. In many systems, the prime minister selects and may dismiss other members of the cabinet, and allocates posts to members within the government. In most systems, the prime...
and the beginning of successor Najib Tun Razak
Najib Tun Razak
Dato' Sri Haji Mohd Najib bin Tun Haji Abdul Razak is the sixth, and since 2009, Prime Minister of Malaysia. He previously held the post of Deputy Prime Minister from 7 January 2004 until he succeeded Tun Abdullah Ahmad Badawi as Prime Minister on 3 April 2009. Najib is President of the United...
's reign in favor of his 1Malaysia
1Malaysia
1Malaysia is an on-going programme designed by Malaysian Prime Minister Najib Tun Razak on September 16, 2010, calling for the cabinet, government agencies, and civil servants to more strongly emphasize ethnic harmony, national unity, and efficient governance....
concept.
On March 2011, RTM announced that it is also possible that RTM may be planning to switch to DVB-T2
DVB-T2
DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television....
some time in the future to replace DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
.
Philippines
June 11, 2010, National Telecommunications Commission of the PhilippinesNational Telecommunications Commission (Philippines)
The Philippines' National Telecommunications Commission , abbreviated as NTC, is an agency of the Philippine government under the Commission on Information and Communications Technology responsible for the supervision, adjudication and control over all telecommunications services throughout the...
announced that the country will use the Japanese ISDB-T standard. The first fully operational Digital TV is GEM-TV49
DZCE-TV
GEMNET is the first to test broadcast on DTV channel 49 is the flagship station of the Philippine Television Network GEMNET. It is currently the UHF television station of Christian Era Broadcasting Service, a broadcast ministry of the independent Philippine Christian church, the Iglesia ni Cristo,...
of the religious group Iglesia ni Cristo
Iglesia ni Cristo
Iglesia ni Cristo also known as INC, is the largest entirely indigenous Christian religious organization that originated from the Philippines and the largest independent church in Asia. Due to a number of similarities, some Protestant writers describe the INC's doctrines as restorationist in...
.
Australia
Australia uses DVB-TDVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
. A transition to digital television and a phaseout of analogue television will be completed by December 2013.
Bulgaria
Bulgaria launched a free-to-air platform on Sofia region, starting in November 2004. Standards chosen are DVB-T/DVB-T2 and MPEG4 AVC/H.264 compression format. The Communications Regulatory Commission (CRC) has said that it received 6 bids for the licence to build and operate Bulgaria's two nationwide DTT networks. A second licence tender for the operation of 3 DTT multiplexes was open until 27 May 2009. Following the closing of this process, Hannu Pro, part of Silicon Group, and with Baltic Operations has secured the license to operate three DTT multiplexes in Bulgaria by the country's Communications Regulatory Commission (CRC) Bulgaria is aiming to complete the transition to digital broadcasting in December 2012.European Union
The EU recommended in May 2005 that its Member States cease all analogue television transmissions by Jan 01, 2012. Some EU member states decided to complete the transition as early as 2006 for Luxembourg and the Netherlands, and 2007 for Finland. Latvia stopped broadcasting analogue television from June 1, 2010. While Poland and Bulgaria had been looking towards 2015, Poland has now decided for June 2013 and Bulgaria 2012. See section on Poland above. Malta switched on the 1st of November, 2011. It looks likely that ASO will be completed in Europe in 2013 though small hilly underpopulated isolated terrain areas will be awaiting DTT rollout beyond that date.Finland
Finland launched DTT in 2001, and terminated analogue transmissions nationwide on 1 September 2007. Finland has successfully launched a mixture of pay and free-to-air DTT services. Digita operates the DTT and Mobile Terrestrial networks and rents capacity to broadcasters on its network on a neutral market basis. DigitaDigita
Digita is a genus of moths of the Micronoctuidae family.-Species:*Digita biuncus Fibiger, 2008*Digita ampullai Fibiger, 2008-References: 2008: Revision of the Micronoctuidae . Part 2, Taxonomy of the Belluliinae, Magninae and Parachrostiinae. 1867: 1-136....
is owned by TDF
TDF Group
TDF is a French company which provides radio and television transmission services, services for telecoms operators, and other multimedia services: digitization of content, encoding, storage, etc.Its headquarters are located in Paris.It is the dominant partner in the HDRR WiMAX consortium...
(France). The pay-DTT service provider Boxer has acquired a majority stake in the leading Finnish pay DTT operator PlusTV which offers a number of commercial channels for a subscription. It started in October 2006. Boxer already provides pay-DTT services in Sweden and Denmark.
Three nationwide multiplexes are granted to DNA and Anvia for DVB-T2 for High Definition and Standard Definition channel (MPEG4).
France
France's TNT (Télévision Numérique TerrestreTélévision Numérique Terrestre
TNT is the national digital terrestrial service for France. It formally arrived on 31 March 2005 after a short testing period. Like Freeview in the United Kingdom it will support many new channels as well as the current terrestrial television stations...
) offers 19 free national channels and 9 pay channels, plus up to 4 local free channels. An 89% DTT penetration rate is expected by December 2008. Free-to-view satellite services offering the same DTT offer were made available in June 2007.
Since 30-10-2008 France has four free HD channel (TF1 HD, France2 HD, Arte HD, M6 HD) and one pay TNT HD channel (Canal+ HD) on TNT using the MPEG4 AVC/H.264 compression format. French video website which rate 10/10 the Blu-ray image, rated 8/10 the TNT HD image.
Typically :
- free TNT channels are broadcast 720×576 MPEG-2 with a VBR of 3.9 Mbits (2.1 to 6.8 as measured)or a CBR of 4.6 Mbits
- pay TNT channels are broadcast 720×576 MPEG4 AVC/H.264 with a VBR of 3.0 Mbits (1.1 to 6.0 as measured)
- free TNT-HD and pay TNT-HD are broadcast 1920×1080 (1080i50) MPEG4 AVC/H.264 with a VBR of 7.6 Mbits (3 to max 15M), but were previously broadcast at the lower definition of 1440x1080.
For the audio part AC3 and AAC are used in 192 kbits for 2.0 and 384 kbits for 5.1.
Typically up to four audio part can be used:
French 5.1
VO 5.1
French 2.0
Audivision 5.1
The Prime Minister François Fillon has confirmed that the final analogue switch-off date will be 30 November 2011. DTT coverage must reach 91% of a given before analogue transmissions can be switched off. CSA announced a call to tender for more local DTT licences on 15 June 2009 and 66 new DTT sites went up since May 2009 to expand coverage to cover low population areas.
Freesat began broadcasts from the Eutelsat Atlantic Bird 3 satellite from June 2009 as Fransat, providing for those unable to receive DTT signals for terrain reasons in preparation for ASO in 2011. Eighteen channels will be broadcast initially and although free to watch, viewers will need to buy a set top box with smart card for €99 according to DVB.org article.
The end dates of analogue shutdown are as follows: 2 February 2010: Alsace, 9 March 2010: Lower Normandy, 18 May 2010: Pays de la Loire, 8 June 2010: Bretagne, 28 September 2010: Lorraine and Champagne-Ardenne, 19 October 2010: Poitou-Charentes and the middle of the country, November 2010: Franche-Comté and Bourgogne, 7 December 2010: North of the country, First quarter 2011: Picardie and Haute-Normandie, Île-de-France, Aquitaine and Limousin, Auvergne, Côte d'Azur and Corsica, Rhône, Second quarter 2011 (before November 30): Provence, Alpes, Midi-Pyrénées, Languedoc-Roussillon.
Germany
Germany launched a free-to-air platform region-by-region, starting in Berlin in November 2002. The analogue broadcasts were planned to cease soon after digital transmissions are started. Berlin became completely digital on 4 August 2003 with other regions completing between then and 2008. Digital switchover has been completed throughout Germany as of 2 December 2008 and services are now available to 100% of the population following the update of infill for the remaining 10% of transmitters by Media Broadcast who set up broadcast antennas at 79 transmission sites and installed 283 new transmitter stations. More services are to be launched on DTT and some pay DTT channels are or have been launched in various areas such as Stuttgart and soon Leipzig.Greece
ERT:- January 16, 2006: Started its first pilot DTT broadcasts of 1st DTT package using five transmitters in AtticaAtticaAttica is a historical region of Greece, containing Athens, the current capital of Greece. The historical region is centered on the Attic peninsula, which projects into the Aegean Sea...
(Hymettus, Parnitha, Aegina): 48 UHF, Central MacedoniaCentral MacedoniaCentral Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the region of Macedonia. With a population of over 1.8 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.- Administration :...
(Chortiatis): 56 UHF and ThessalyThessalyThessaly is a traditional geographical region and an administrative region of Greece, comprising most of the ancient region of the same name. Before the Greek Dark Ages, Thessaly was known as Aeolia, and appears thus in Homer's Odyssey....
(Pelion): 53 UHF to distribute the stations Prisma+Prisma+Prisma+ is a digital terrestrial commercial-free channel provided by ERT, the public broadcaster in Greece. It is the first digital channel in Greece . It is also the only channel in Greece, which is fully accessible for people with disabilities.-Programming:Prisma+ broadcasts a programme with a...
, Cine+Cine+Cine+ was a digital-only terrestrial channel, provided by ERT. Cine+ was a commercial-free 24-hour free-to-air channel. It started broadcasting April 25 2006 and it was the second digital terrestrial channel which opened in Greece.-Programming:...
, Sport+Sport+ (Greece)Sport+ was a digital terrestrial television station by ERT, which was a 20-hour commercial-free channel. It was the third digital terrestrial channel launched in Greece on . It broadcasted in Attica, Central Macedonia and Thessaly....
and RIK SatCyprus Broadcasting CorporationThe Cyprus Broadcasting Corporation ) or CyBC is Cyprus's public broadcasting service, transmitting island-wide on four radio and two television channels. CyBC is a non-profit organization that utilises its entire income for the promotion of its main mission, which is the objective provision of...
via its ERT DigitalERT DigitalERT Digital is a pilot project from ERT, the Hellenic Broadcasting Corporation. It is the first legal attempt of DVB-T broadcasting in Greece, featuring 4 all new digital television channels: Cine+, Prisma+ Sport+ and Info+...
subsidiary, transmitting digitally terrestrial for first time in Greece. - September 26, 2007: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package from 26 UHF added in Central MacedoniaCentral MacedoniaCentral Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the region of Macedonia. With a population of over 1.8 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.- Administration :...
region from Chortiatis, Central MacedoniaCentral MacedoniaCentral Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the region of Macedonia. With a population of over 1.8 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.- Administration :...
(Chortiatis): 26, 56 UHF. - October 13, 2007: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package from 42 UHF added in Thessaly region from Pelion, Thessaly (Pelion): 42, 53 UHF.
- October 31, 2008: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package commenced in South West ThraceThraceThrace is a historical and geographic area in southeast Europe. As a geographical concept, Thrace designates a region bounded by the Balkan Mountains on the north, Rhodope Mountains and the Aegean Sea on the south, and by the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara on the east...
(Plaka): 64 UHF. - May 6, 2009: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package from Styra added to Attica region, Attica (Hymettus, Parnitha, Aegina, Styra): 48 UHF.
- October 7, 2009: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package commenced in ArcadiaArcadiaArcadia is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Peloponnese. It is situated in the central and eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. It takes its name from the mythological character Arcas. In Greek mythology, it was the home of the god Pan...
and ArgolisArgolisArgolis is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Peloponnese. It is situated in the eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula.-Geography:...
(Doliana): 21 UHF. - September 27, 2010: Started broadcast of 2nd DTT package in Attica (Hymettus): 52 UHF, Central MacedoniaCentral MacedoniaCentral Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the region of Macedonia. With a population of over 1.8 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.- Administration :...
(Chortiatis): 26 UHF (switching off 1st DTT package from 26 UHF in Central MacedoniaCentral MacedoniaCentral Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the region of Macedonia. With a population of over 1.8 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.- Administration :...
region from Chortiatis), 1st DTT package in Central MacedoniaCentral MacedoniaCentral Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the region of Macedonia. With a population of over 1.8 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.- Administration :...
(Chortiatis): 56 UHF only consisting of television stations ET1, NETNew Hellenic TelevisionNew Hellenic Television , branded as NET, is the second television network of the Hellenic Broadcasting Corporation , the public broadcaster of Greece. It is mainly a news and information channel that broadcasts daily newscasts with national and international news, documentaries, talkshows, current...
, ET3, Vouli TileorasiVouli TileorasiVouli Tileorasi is a Greek network dedicated to airing non-stop coverage of government proceedings and public affairs programming. The name comes from Greek Βουλή Vouli, meaning ‘assembly’, ‘council’, or ‘parliament’; and Tileorasi, meaning television.The primary aim of the channel is to give...
, and radio stations NET, Deftero, Trito, ERA Sport, KOSMOS. - November 19, 2010: Broadcasting of 2nd DTT package commenced in South West Thrace (Plaka): 58 UHF.
- December 14, 2010: Broadcasting of 2nd DTT package from Aegina added to Attica region, Attica (Hymettus, Aegina): 52 UHF.
- January 14, 2011: Broadcasting of 2nd DTT package moved frequency in Central MacedoniaCentral MacedoniaCentral Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the region of Macedonia. With a population of over 1.8 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.- Administration :...
region from 26 UHF (switching off 26 UHF) to 23 UHF and added broadcasting also from Philippion from 23 UHF, Central MacedoniaCentral MacedoniaCentral Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the region of Macedonia. With a population of over 1.8 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.- Administration :...
(Chortiatis, Philippion): 23 UHF. - April 26, 2011: 1st DTT package consists from now on with television stations Vouli TileorasiVouli TileorasiVouli Tileorasi is a Greek network dedicated to airing non-stop coverage of government proceedings and public affairs programming. The name comes from Greek Βουλή Vouli, meaning ‘assembly’, ‘council’, or ‘parliament’; and Tileorasi, meaning television.The primary aim of the channel is to give...
, Prisma+Prisma+Prisma+ is a digital terrestrial commercial-free channel provided by ERT, the public broadcaster in Greece. It is the first digital channel in Greece . It is also the only channel in Greece, which is fully accessible for people with disabilities.-Programming:Prisma+ broadcasts a programme with a...
, CineSport+ continiuing Sport+Sport+ (Greece)Sport+ was a digital terrestrial television station by ERT, which was a 20-hour commercial-free channel. It was the third digital terrestrial channel launched in Greece on . It broadcasted in Attica, Central Macedonia and Thessaly....
created from the merge of Cine+Cine+Cine+ was a digital-only terrestrial channel, provided by ERT. Cine+ was a commercial-free 24-hour free-to-air channel. It started broadcasting April 25 2006 and it was the second digital terrestrial channel which opened in Greece.-Programming:...
and Sport+Sport+ (Greece)Sport+ was a digital terrestrial television station by ERT, which was a 20-hour commercial-free channel. It was the third digital terrestrial channel launched in Greece on . It broadcasted in Attica, Central Macedonia and Thessaly....
stations and RIK SatCyprus Broadcasting CorporationThe Cyprus Broadcasting Corporation ) or CyBC is Cyprus's public broadcasting service, transmitting island-wide on four radio and two television channels. CyBC is a non-profit organization that utilises its entire income for the promotion of its main mission, which is the objective provision of...
, all stations with temporarily MPEG-2 Compression. 2nd DTT package consists from now on with television stations ET1, NETNew Hellenic TelevisionNew Hellenic Television , branded as NET, is the second television network of the Hellenic Broadcasting Corporation , the public broadcaster of Greece. It is mainly a news and information channel that broadcasts daily newscasts with national and international news, documentaries, talkshows, current...
, ET3 and a new Full High Definition television station ERT HDERT HDERT HD is a high definition television channel by the Hellenic Broadcasting Corporation, or ERT. It is the first high definition TV channel in Greece and started broadcasting on April 27, 2011 in several large Greek cities such as Athens, Thessaloniki and Alexandroupolis...
, all stations with H.264/MPEG-4 AVC Compression along with radio stations NET, Deftero, Trito, ERA Sport, KOSMOS. - April 27, 2011: ERT HDERT HDERT HD is a high definition television channel by the Hellenic Broadcasting Corporation, or ERT. It is the first high definition TV channel in Greece and started broadcasting on April 27, 2011 in several large Greek cities such as Athens, Thessaloniki and Alexandroupolis...
started pilot High Definition transmissions. - May 2, 2011: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package moved frequency in ArcadiaArcadiaArcadia is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Peloponnese. It is situated in the central and eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. It takes its name from the mythological character Arcas. In Greek mythology, it was the home of the god Pan...
and ArgolisArgolisArgolis is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Peloponnese. It is situated in the eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula.-Geography:...
from 21 UHF to 39 UHF, ArcadiaArcadiaArcadia is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the administrative region of Peloponnese. It is situated in the central and eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula. It takes its name from the mythological character Arcas. In Greek mythology, it was the home of the god Pan...
and ArgolisArgolisArgolis is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Peloponnese. It is situated in the eastern part of the Peloponnese peninsula.-Geography:...
(Doliana): 39 UHF. - May 27, 2011: Broadcasting of 1st DTT package commenced in Central Thessaly (Dovroutsi): 43 UHF
- July 29, 2011: Broadcasting commenced in the Gulf of CorinthGulf of CorinthThe Gulf of Corinth or the Corinthian Gulf is a deep inlet of the Ionian Sea separating the Peloponnese from western mainland Greece...
(Xylokastro): 55 & 61 UHF - October 27, 2011: Broadcasting will commence in Aetolia-AcarnaniaAetolia-AcarnaniaAetolia-Acarnania is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of West Greece. It is located in the western part of Greece; the regional unit is a combination of the geographic regions Aetolia and Acarnania. Its capital is Missolonghi for historical reasons, with its biggest...
. - November 2011: Broadcasting will commence in CorfuCorfuCorfu is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea. It is the second largest of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the edge of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The island is part of the Corfu regional unit, and is administered as a single municipality. The...
. - January 5, 2012: Broadcasting will commence in PatraPatrasPatras , ) is Greece's third largest urban area and the regional capital of West Greece, located in northern Peloponnese, 215 kilometers west of Athens...
.
DIGEA
DIGEA
Digea, the company established by the private national scale television stations , has undertaken digital broadcasting of television programs for private stations of national range as well as for any other stations choosing to use its services.The name Digea was not a haphazard choice...
:
- 24 September 2009: The first digital broadcasting of Digea consisting of television stations Alpha TVAlpha TVAlpha TV is a Greek terrestrial channel . The station features a mix of Greek and foreign shows with an emphasis on entertainment programs. The studios are located near Athens...
, Alter ChannelAlter ChannelAlter Channel better known as Alter, is a private TV network in Greece. It launched in 1994 and is owned by Eleftheri Tileorasi S.A, which is headed by Andreas Kouris. Programming mainly consists of news & current affairs shows and entertainment programmes...
, ANT1ANT1Antenna, better known as ANT1, is a television network airing in Greece and Cyprus. The alternate spelling is play on words in Greek; ena is the Greek number 1, thus ANT1 is pronounced the same as Antenna . It launched on 31 December 1989, the same year as rival Mega Channel, and is owned by...
, Makedonia TV, Mega ChannelMega ChannelMega Channel, also known as Mega TV or just Mega, is a major television network in Greece. Teletypos S.A. was founded in 1989 under the name Teletypos Television Programmes S.A...
, Skai TVSkai TVSkai TV is a Greek TV station, based in Pireus, Athens. It is part of the Skai Group one of the largest media groups in Greece. It was relaunched in its present form on April 1, 2006 in Athens and gradually managed to spread its coverage nationwide. Besides analog over-the-air transmission, it is...
and Star ChannelStar ChannelStar Channel is a Greek television network that broadcasts a mix of foreign and Greek programming. It launched in December 1993 and is owned by Nea Tileorasi A.E.. The main news bulletin is called Star Eidiseis, which is currently hosted by Aimilios Liatsos...
was carried out in the Gulf of CorinthGulf of CorinthThe Gulf of Corinth or the Corinthian Gulf is a deep inlet of the Ionian Sea separating the Peloponnese from western mainland Greece...
from the transmitting site of Xylokastro. - 14 January 2010: Digital broadcasting began in ThessalonikiThessalonikiThessaloniki , historically also known as Thessalonica, Salonika or Salonica, is the second-largest city in Greece and the capital of the region of Central Macedonia as well as the capital of the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace...
- Central MacedoniaCentral MacedoniaCentral Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the region of Macedonia. With a population of over 1.8 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.- Administration :...
from the transmitting sites of Chortiatis and Philippion. - 18 June 2001: Digital broadcasting began in AthensAthensAthens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
- Attica from the transmitting sites of Hymettus and Aegina. - 1 September 2010: Digital broadcasting of regional scale channels 0-6 TVTV 0-60-6 TV is a channel on television in Greece which broadcasts cartoons and other shows for children....
, ATTICA TV, Extra 3, High TV, MAD TV, MTV GreeceMTV GreeceMTV Greece is the Greek version of MTV, launched on September 1, 2008.MTV Greece broadcasts mainly English, American and Greek music, MTV's shows like Date My Mom, Made, Nitro Circus, RoomRaiders, America's Most Smartest Model, etc. subtitled in Greek, as well as three Greek shows...
, Nickelodeon (Greece)Nickelodeon (Greece)Nickelodeon ' is the Greek version of Nickelodeon. It launched on 3 September 2010. It is available free-to-air in the Athens area on 35 UHF signal broadcast from Hymettus, while it is also available through the DIGEA DVB-T2 digital consortium on 54 UHF signal broadcast from Aegina.. Nickelodeon HD...
and SPORT TVSport TVSportTV is the brand name for a group of seven Portuguese sports-oriented television channels. SportTV is the dominant subscription television sports brand in Portugal. The first channel, then known as only SportTV, was launched on 16 September 1998 and is produced by ZON Multimédia and...
added in Athens - Attica from the transmitting site of Aegina. - 19 November 2010: Digital broadcasting began in AlexandroupoliAlexandroupoliAlexandroupoli , is a city of Greece and the capital of the Evros peripheral unit in Thrace. Named after King Alexander, it is an important port and commercial center of northeastern Greece.-Name:...
- South West Thrace from the transmitting site of Plaka. - 8 February 2011: Digital broadcasting of regional scale channels BLUE SKY, CHANNEL 9Channel 9 (Greece)Channel 9 is a Greek TV channel that broadcasts in the region of Attica. It is considered as an informational channel although a significant part of its broadcasting are cartoons from the Nickelodeon TV network.- Cartoon shows :...
, KONTRA Channel and ΤELEASTY added in Athens - Attica from the transmitting site of Aegina. - 25 February 2011: Digital broadcasting began in Rhodes (city) from the transmitting site of Monte Smith.
- 27 May 2011: Digital broadcasting began in Central Thessaly from the transmitting site of Dovroutsi.
- 27 October 2011: Digital broadcasting will begin in Aetolia-AcarnaniaAetolia-AcarnaniaAetolia-Acarnania is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of West Greece. It is located in the western part of Greece; the regional unit is a combination of the geographic regions Aetolia and Acarnania. Its capital is Missolonghi for historical reasons, with its biggest...
. - November 2011: Digital broadcasting will begin in CorfuCorfuCorfu is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea. It is the second largest of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the edge of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The island is part of the Corfu regional unit, and is administered as a single municipality. The...
. - 5 January 2012: Digital broadcasting will begin in PatraPatrasPatras , ) is Greece's third largest urban area and the regional capital of West Greece, located in northern Peloponnese, 215 kilometers west of Athens...
.
ERT - NOVA
NOVA Greece
NOVA Greece is a Greek digital satellite pay TV platform owned by Multichoice Hellas. It was launched in December 1999.NOVA offers Greek subscribers an array of international and domestic programmes plus the majority of popular Greek terrestrial TV channels along with a number of Greek...
(pay TV platform):
- July 22, 2011: Broadcasting consisting of television stations NovaCinema1, NovaSports1 and two more satellite TV channels, that ERT will decide in the future, commenced in AtticaAtticaAttica is a historical region of Greece, containing Athens, the current capital of Greece. The historical region is centered on the Attic peninsula, which projects into the Aegean Sea...
(Hymettus): 22 UHF - Autumn 2011: Broadcasting will commence in ThessalonikiThessalonikiThessaloniki , historically also known as Thessalonica, Salonika or Salonica, is the second-largest city in Greece and the capital of the region of Central Macedonia as well as the capital of the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace...
- Central MacedoniaCentral MacedoniaCentral Macedonia is one of the thirteen regions of Greece, consisting of the central part of the region of Macedonia. With a population of over 1.8 million, it is the second most populous in Greece after Attica.- Administration :...
.
TV1 Syros started its first pilot broadcasts on November 1, 2008 in Cyclades
Cyclades
The Cyclades is a Greek island group in the Aegean Sea, south-east of the mainland of Greece; and a former administrative prefecture of Greece. They are one of the island groups which constitute the Aegean archipelago. The name refers to the islands around the sacred island of Delos...
(Syros
Syros
Syros , or Siros or Syra is a Greek island in the Cyclades, in the Aegean Sea. It is located south-east of Athens. The area of the island is . The largest towns are Ermoupoli, Ano Syros, and Vari. Ermoupoli is the capital of the island and the Cyclades...
): 60 UHF.
Republic of Ireland
In the Republic of Ireland DTT has been somewhat problematic. Responsibility for DTT following from the plans of Raidió Teilifís ÉireannRaidió Teilifís Éireann
Raidió Teilifís Éireann is a semi-state company and the public service broadcaster of Ireland. It both produces programmes and broadcasts them on television, radio and the Internet. The radio service began on January 1, 1926, while regular television broadcasts began on December 31, 1961, making...
was divided between two government Departments with differing views on its running. This delayed the project, took away its momentum and the economic situation deteriorated so that the opportunity to launch in good conditions was lost. When legislation finally arrived after two years to enable DTT to proceed a private sector model was envisaged similar to the UK. It's TV was the sole applicant for a digital terrestrial television license under the provisions of the Irish Broadcasting Act 2001. It proposed a triple play deployment with Broadband, TV and Digital Radio services. RTÉ was to have a minority stake in its network and sell its majority share. Legislative delays and economic changes however made it financially difficult for RTÉ to get a good price for the network stake and for It's TV to raise the necessary funding to proceed the license. Other DTT deployments, most particularly in the neighbouring UK and in Spain and Portugal in operation around that time also went bust. It's TV failed to get its license conditions varied or to get a time extension to securing funding and its license was eventually withdrawn for non performance.
Under subsequent legislation in May 2007, RTÉ and the spectrum regulator (ComReg)and the broadcasting regulator BCI (now BAI) were mandated to invite applications during 2008 under the Broadcasting (Amendment) Act 2007
Broadcasting (Amendment) Act 2007
The Broadcasting Act 2007 is an Act of the Oireachtas .It deals with Irish Analogue broadcasting systems and the amendment of legislation on Digital Terrestrial Television dating back to 2001. This act amends previous acts, in particular the Broadcasting Act 2001...
and RTÉ and the BCI received licenses from ComReg for spectrum to establish DTT. The BAI, then BCI advertised and invited multiplex submissions by 2 May 2008. RTÉ Networks was required to broadcast in digital terrestrial TV (aerial TV) under the that and the more recent Broadcasting Act 2009 and received an automatic license through the RTÉ Authority. It has been expanding its upgrading its transmission network to digital terrestrial during 2009 which will culimate in 98% coverage by 31 December 2011 with ASO to begin in Summer 2012 in concert with Northern Ireland under the MOU signed with the UK & Irish Governments.
It is also making this network available to the commercial multiplex winner for rental of capacity once negotiations are concluded, rental agreed and a security bond received. <. It has been testing the BAI multiplexes since November 2009 across the network which is publicly receivable with the correct DTT receivers. 1 Mux (group of channel radio wave space) will provide the services of the public service broadcaster and have a 98% population coverage by 31 December 2011. The other three multiplexes will have between 90% and 92% population coverage. Following Analogue Switchover 1 addition PSB mux and 1 or more commercial muxes will be made available for DTT, mobile television, broadband and other services.
The BCI (now BAI) received 3 conditional applications to operate the 3 muxes which were presented in public on 12 May 2008. It decided in principle to allocate the license to Boxer DTT Ltd, a consortium made up of the Swedish pay-DTT operator Boxer and the media group Communicorp at its board meeting on 21 July 2008.
On 20 April 2009, the BCI revealed that Boxer had withdrawn their license, and it was instead given to the runner up applicant OneVision. At the end of April 2010 the negotiations with Onevision ended and they also decided to return the license. On April 29, 2010 the contract was offered to the only remaining applicant, Easy TV. The Easy TV consortium informed the BAI on 12 May 2010 that it was declining their offer to pursue negotiations regarding the Commercial DTT Multiplex Licence.
A Houses of the Oireachtas Channel
Houses of the Oireachtas Channel
Houses of the Oireachtas Channel or informally Oireachtas TV is a public service broadcaster for the two houses of the Oireachtas . The channel was created under the Broadcasting Act 2009 for broadcast on the proposed roll out of Irish Digital Terrestrial Television...
(reportedly shelved in December 2008) and the Irish Film Channel (status unclear though company formed for channel) are enabled for establishment as public service broadcasters on Irish DTT.
The Broadcasting Authority of Ireland replaced the Broadcasting Complaints Commission, the Broadcasting Commission of Ireland and the RTÉ Authority and include Awards and Advisory Committees under statutory instrument 389 that gave effect to the provisions of the Broadcasting Act 2009 which dissolved the BCI vesting it and new responsibilities, assets & liabilities and so forth in a new Broadcasting Authority of Ireland
Broadcasting Authority of Ireland
The Broadcasting Authority of Ireland was established on 1 October 2009 effectively replacing the Broadcasting Commission of Ireland ....
on October 1, 2009. That act deals with Analogue switchover.
A DTT Information Campaign was announced by the Department of Communications, Energy & Natural Resources Irish Government Department to launch in March 2009 ahead of the September 2009 launch of Irish DTT. AS of December 2009, the information campaign has not launched and has been postponed until after Saorview launches in public testing phase. The Information Campaign is to be undertaken by the BAI, with support of the Department.
As of October 30, 2010 FTA DTT, which will be known as Saorview
Saorview
Saorview is the national free-to-air digital terrestrial television service in Republic of Ireland.The service began operation on 29 October 2010 on a trial basis with full launch on 26 May 2011. By legislation it was required to be available to approximately 90% of the population by end of...
, has launched following a direction from the Minister for Communications, Energy & Natural Resources, to RTÉ and signing of the RTÉ (National Television Multiplex) Order 2010 (S.I. No. 85 of 2010) on February 26, 2010. The rollout of FTA Saorview DTT will now proceed, and a commercial DTT competition may well be deferred until the economic situation improves.
On 1 July 2010 RTÉ announced that Mary Curtis their current deputy head of TV programming would take on the role of Director of Digital Switchover (DSO).
Italy
Gradual switching from analog to digital TV is in progress. A few regions are already completely digital, others are in a transition state (with only a few programs being digital and the others still analog) and some other regions still have to begin switching off analog transmitters.The selected broadcasting standard is DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
with MPEG2 video for SD and H.264 video for HD, audio is usually MPEG1. The whole frequency spectrum has been allocated with SFN
Single-frequency network
A single-frequency network or SFN is a broadcast network where several transmitters simultaneously send the same signal over the same frequency channel.-Overview:...
in mind.
Along the original analog free to air channels that will be switched to digital, a few new pay per view platforms came around with the advent of DTT.
Worth mentioning is the addition of an experimental free to air HD 1080i
1080i
1080i is the shorthand name for a high-definition television mode. The i means interlaced video; 1080i differs from 1080p, in which the p stands for progressive scan. The term 1080i assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a frame size of 1920×1080 pixels...
channel from RAI
RAI
RAI — Radiotelevisione italiana S.p.A. known until 1954 as Radio Audizioni Italiane, is the Italian state owned public service broadcaster controlled by the Ministry of Economic Development. Rai is the biggest television company in Italy...
which is set to broadcast important sport events like the olympic games
Olympic Games
The Olympic Games is a major international event featuring summer and winter sports, in which thousands of athletes participate in a variety of competitions. The Olympic Games have come to be regarded as the world’s foremost sports competition where more than 200 nations participate...
or the FIFA world cup
FIFA World Cup
The FIFA World Cup, often simply the World Cup, is an international association football competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of Fédération Internationale de Football Association , the sport's global governing body...
.
Luxembourg
Luxembourg launched DTT services in April 2006. The national service launched in June 2006. On 1 September 2006, Luxembourg became the first European country to transition completely to DTT. Luxe TV, a niche theme based station, will soon begin broadcasting on the Luxembourg DTT platform, transmitted from the Dudelange transmitter.The aim is to reach audiences in some parts of Germany as well as in Luxembourg.Republic of Macedonia
DTT was successfully launched in November, 2009. It uses MPEG-2 for SD and MPEG-4 for HD. The service was launched by ONE, and the platform is called BoomTV. It offers 42 channels including all national networks and it is available to 95% of the population.Netherlands
The Netherlands launched its DTT service 23 April 2003, and terminated analogue transmissions nationwide on 11 December 2006. KPN own Digitenne which provides a mix of FTA public channels and paid DTT services. It also provides a mobile broadcast DVB-H service as well as an IPTV service, with DTT the most popular of its products.Poland
DTT launch in Poland is scheduled for Autumn 2009. Regulatory disagreements delayed its tender and approach until resolved recently and the multiplexes available for DTT were reduced to 3 and the 2nd is to be licensed in the Autumn of 2009. The reduction from 5 to 3 enable mobile TV and broadband to get more spectrum allocation. Muxes 2 and 3 may therefore have limited coverage until ASO. Polsat, TVN, TV4 and TV Puls have officially applied to reserve space on the countries first multiplex set to start in September. Wirtualne Media is given as the source of the story. The public broadcaster's three main channels TVP1, TVP2 and TVP Info have already been allocated capacity on the multiplex.Poland is to switch off analogue transmissions by 31 July 2013. A mobile TV license has also been awarded in Poland to Info TV FM to use DVB-H standard.
Portugal
Portugal launched its DTT service on 29 April 2009 available to around 20% of the Portuguese population and Portugal Telecom expects to reach 80% of the population by the end of the 2009. Airplus TV Portugal that was set up to compete for a licence to manage Portugal's pay-TV DTT multiplexes, will dissolve as it didn't get the license and a Portuguese court ruled not to suspend the process for the awarding of a licence to Portugal Telecom, based on a complaint submitted by Airplus TV Portugal. Surprisingly (or maybe not), after Airplus TV Portugal has been dissolved, Portugal Telecom informed that will not honour the pay-TV DTT multiplexes licence obligations. ANACOM, the Portuguese communications authority, has accepted. Portugal will thus haveonly one active multiplexer.Romania
In Romania, broadcasting regulations have been amended so that DTT service providers have only a single licence rather than the two previously required by the National Audiovisual Council (CNA). DTT services are set to launch in December 2009 using the MPEG-4 (H.264 AVC) compression format following the Ministry of Communications publication of a strategic plan for the transition to digital broadcasting. According to Media Express, it envisages a maximum of five national UHF multiplexes, a national VHF multiplex and a multiplex allocated to regional and local services, all in accordance with the ITU Geneva Conference RRC-06 reports BroadbandTVNews.The Ministry of Communications (MCSI) estimates that 49% of Romania's 7.5 million households get TV from cable and 27% from DTH services in Romania while terrestrial TV is used by 18% of the TV households. 6% are reported as not able to receive TV transmissions. Subsidies may be offered for those below a certain income to assist switchover for them. Switchover is scheduled for January 2012.
Romkatel, the local representative of Kathrein, have since been awarded the commercial Romanian DTT services license. ZF reports that Romkatel has signed a 12-month contract worth €710,420, having beaten off a challenge from France's TDF. The tender was organised by Romania's National Society for Radiocommunications (SNR).
Meanwhile the National Audiovisual Council, in charge of the public service broadcasting sector has awarded digital licences to the public channels TVR1 and TVR2.
According to Media Express, this followed a short debate at the National Audiovisual Council (CNA) about whether to also award licences to the nine remaining public channels, one of which transmits in HD and five are regional.
Romania's first DTT multiplex is likely to have the five leading commercial channels — Pro TV
Pro TV
Launched in December 1995, Pro TV reaches almost 99% of Romania’s 21.5 million people and has 48% of its broadcast schedule comprising locally-produced programs...
, Antena 1 (Romania), Prima TV
Prima TV
Prima TV is a Romanian commercial TV channel, famous mainly for the Cronica Cârcotaşilor show and various reality shows.-Start:Prima TV was launched as one of the first commercial television stations in Romania in December 1997...
, Kanal D Romania
Kanal D Romania
Kanal D Romania is a nation-wide television channel in Romania and part of Doğan Holding which is owned by the Turkish media tycoon Aydın Doğan. The channel was launched on 18 February 2007.-External links:* *...
and Realitatea TV
Realitatea TV
Realitatea TV is a Romanian news television network. The channel is distributed by many cable operators in Romania and Moldova. Its main owner is Romanian businessman Elan Schwartzenberg....
— as well as TVR1 and TVR2.
The National Audiovisual Council (ANCOM), will most probably award the transmission network contract for this to the national transmission company Radiocommunicatii.
Spain
In Spain most multiplexes closed after the failure of Quiero TVQuiero Television
Quiero Television was one of the first companies to provide Digital Terrestrial Television in Spain. The company collapsed in April 2002, shortly before the United Kingdom's DTT provider ITV Digital ceased broadcasting....
, the country's original pay DTT platform. DTT was relaunched on 30 November 2005, with 20 free-to-air national TV services as well as numerous regional and local services. Nearly 11 million DTT receivers had been sold as of July 2008. Positive approval for pay DTT services have reportedly been given by Spain's Ministry of Industry in a surprise move on 17 June of the Advisory Council on Telecommunications and the Information Society (Catsi). IT will now be included in a Royal Decree. A number of leading Spanish media players including Sogecable, Telefónica, Ono, Orange and Vodafone have apparently criticised that as according to Prisa, Sogecable's owner, "it caps a series of policy changes that benefits only a few audiovisual operators, those of terrestrial TV, to the detriment of satellite operators, cable and DSL." There may be appeals lodged against the government's decision.
Sweden
In Sweden, DTT was launched in 1999 solely as a paid service. As of 2007, there are 38 channels in 5 MUXs. 11 of those are free-to-air channels from a number of different broadcasters. Switch-off of the analogue TV service started on 19 September 2005 and finished on 29 October 2007. Boxer began the deployment of MPEG-4 receivers to new subscribers. Over the next six years from 2008 Sweden will gradually migrate from MPEG-2 visual coding to using MPEG-4, H.264.The Swedish Radio and TV Authority (RTVV) recently announced eight new national channels that will broadcast in the MPEG-4 format.
From 1 April 2008 Boxer is also responsible for approving devices to use on the network, will no longer accept MPEG-2 receivers for test and approval. Set Top Boxes must be backward compatible so that they can decode both MPEG-2 and MPEG-4 coded transmissions.
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom (1998), Sweden (1999) and Spain (2000) were the first to launch DTT with platforms heavily reliant on pay television. All platforms experienced many starter problems, in particular the British and Spanish platforms which failed financially. Nevertheless, Boxer, the Swedish pay platform which started in October 1999, proved to be very successful.DTT in the United Kingdom
Digital terrestrial television in the United Kingdom
Digital terrestrial television in the United Kingdom encompasses over 100 television, radio and interactive services broadcast via the UK's terrestrial television network and receivable with a standard television aerial...
was launched in November 1998 as a primarily subscription service branded as ONdigital, a joint venture between Granada Television
Granada Television
Granada Television is the ITV contractor for North West England. Based in Manchester since its inception, it is the only surviving original ITA franchisee from 1954 and is ITV's most successful....
and Carlton Communications
Carlton Communications
Carlton Communications was a British media company. It was led by Michael Green and listed on the London Stock Exchange from 1983 until 2 February 2004, when it taken over by Granada plc to form ITV plc with Carlton gaining 32% of the new company....
, with only a few channels being available free to air. ONdigital soon ran into financial difficulties with subscriber numbers below expectations, and in order to attempt to reverse their fortunes, it was decided that the ITV and ONdigital brands should align, and the service was rebranded ITV Digital in 2001. Despite an expensive advertising campaign, ITV Digital struggled to attract sufficient new subscribers and in 2002 closed the service. After commercial failure of the Pay TV proposition it was relaunched as the free-to-air
Free-to-air
Free-to-air describes television and radio services broadcast in clear form, allowing any person with the appropriate receiving equipment to receive the signal and view or listen to the content without requiring a subscription or one-off fee...
Freeview platform in 2002. Top Up TV
Top Up TV
Top Up TV is a pay television service in the UK launched in March 2004, operating on the digital terrestrial platform. The aim of the service is to "Top Up" Freeview customers by providing additional channels and services....
, a lite pay DTT service, became available in 2004. There is a possibility that a 2nd pay DTT service may launch during 2010/2011 from Sky
Sky Picnic
Sky Picnic is a proposed pay television service to launch from BSkyB. It would sit alongside Freeview and Top Up TV on the digital terrestrial television platform in the United Kingdom.-History:...
.
DSO has begun in some areas of the UK and will begin soon in others, spanning over the next few years and reaching completion by the end of 2012. One multiplex for public service broadcasters has been freed up and given over to HD on DTT and some areas will be able to receive Freeview HD in advance of digital switchover using the new 2nd generation DVB-T2 and MPEG4 set top boxes according to Freeview.
Canada
In Canada, analogue switch-off was mandated by regulatory authorities for all provincial capital cities and all multi-station markets. Analogue would continue in single-station markets and remote areas. With an exception, analogue switch-off in the mandated areas took place on 31 August 2011. The CBC was granted an exception in many smaller multi-station markets, due to the cost of conversion, otherwise the CBC services would have gone dark in many such markets. Most network stations are already broadcasting high-definition digital signals in Toronto, with partial network digital coverage in Ottawa, Montreal, Calgary, Edmonton and Vancouver. Most networks had been concerned about the August 2011 deadline as not all parts of the country were equipped to receive DTTV by the scheduled date.Mexico
In MexicoMexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
, digital signals are as 2010 currently on-air in the largest cities, with more cities to be added in descending order of population size, until full national coverage is reached on December 31, 2015. At that point analogue broadcasts will officially end.
United States
In the United States on 12 June 2009, all full power U.S. television broadcasts became exclusively digital, under the Digital Television and Public Safety Act of 2005. Furthermore, from 1 March 2007, new television sets that receive signals over-the-air, including pocket sized portable televisions, include ATSCATSC
ATSC standards are a set of standards developed by the Advanced Television Systems Committee for digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable, and satellite networks....
digital tuners for digital broadcasts. Prior to 12 June, most U.S. broadcasters were transmitting in both analogue and digital formats; a few were digital-only. Most U.S. stations were not permitted to shut down their analogue transmissions prior to 16 February 2009, unless doing so was required in order to complete work on a station's permanent digital facilities. In 2009, the FCC will finish auctioning channels 52–59 (the lower half of the 700 MHz band) for other communications services, completing the reallocation of broadcast channels 52–69 that began in the late 1990s.
The analogue switch-off will render all non-digital television sets unable to receive most over-the-air television channels, without an external setbox receiver; however, low-power television stations and cable TV systems are not required to convert to digital until 2011 or later. Beginning 1 January 2008, consumers could request coupons to help cover most of the cost of these converters by calling a toll free number or via a website. Some television stations have also been licensed to operate "nightlights", analogue signals which consist only of a brief repeated announcement advising remaining analogue viewers how to switch to digital reception.
Costa Rica
Costa RicaCosta Rica
Costa Rica , officially the Republic of Costa Rica is a multilingual, multiethnic and multicultural country in Central America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the west and the Caribbean Sea to the east....
chose Japanese-Brazilian standard ISDB-T as 7th country on 25 May 2010.
Cuba
CubaCuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
has announced recently that it will decide on the norm to use, within the current year. According to official sources of the MIC (Ministry of Computer science and Telecommunications) the Caribbean island is deciding DVB format used by Europe. At the moment, Cuban specialists are performing tests in both formats but an "analogical blackout" is far away.
Argentina
Argentine President Cristina Fernández signed on August 28, 2009 an agreement to adopt the ISDB-Tb system, joining Brazil, which has already implemented the standard in its big cities. On air service started from 28 April 2010.Bolivia
On July 5, 2010 the Bolivian Chancellor signed an agreement with the Japanese Ambassador,selecting the Japanese system with the Brazilian modifications ISDB-T (Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting Terrestial)Brazil
In Brazil, they chose a modified version of the Japanese ISDB-T standard, called ISDB-Tb (or SBTVD) in June, 2006. Digital broadcast started in 2 December 2007 in São PauloSão Paulo
São Paulo is the largest city in Brazil, the largest city in the southern hemisphere and South America, and the world's seventh largest city by population. The metropolis is anchor to the São Paulo metropolitan area, ranked as the second-most populous metropolitan area in the Americas and among...
and now it is under expansion all over the country. As of 15 September 2009, metro areas of São Paulo
São Paulo
São Paulo is the largest city in Brazil, the largest city in the southern hemisphere and South America, and the world's seventh largest city by population. The metropolis is anchor to the São Paulo metropolitan area, ranked as the second-most populous metropolitan area in the Americas and among...
, Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro , commonly referred to simply as Rio, is the capital city of the State of Rio de Janeiro, the second largest city of Brazil, and the third largest metropolitan area and agglomeration in South America, boasting approximately 6.3 million people within the city proper, making it the 6th...
, Belo Horizonte
Belo Horizonte
Belo Horizonte is the capital of and largest city in the state of Minas Gerais, located in the southeastern region of Brazil. It is the third largest metropolitan area in the country...
, Brasilia
Brasília
Brasília is the capital city of Brazil. The name is commonly spelled Brasilia in English. The city and its District are located in the Central-West region of the country, along a plateau known as Planalto Central. It has a population of about 2,557,000 as of the 2008 IBGE estimate, making it the...
, Goiânia
Goiânia
-Climate:The city has a tropical wet and dry climate with an average temperature of . There's a wet season, from October to April, and a dry one, from May to September. Annual rainfall is around 1,520 mm....
, Curitiba
Curitiba
Curitiba is the capital of the Brazilian state of Paraná. It is the largest city with the biggest economy of both Paraná and southern Brazil. The population of Curitiba numbers approximately 1.75 million people and the latest GDP figures for the city surpass US$61 billion according to...
, Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre is the tenth most populous municipality in Brazil, with 1,409,939 inhabitants, and the centre of Brazil's fourth largest metropolitan area . It is also the capital city of the southernmost Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul. The city is the southernmost capital city of a Brazilian...
, Salvador, Campinas
Campinas
Campinas is a city and municipality located in the coastal interior of the state of São Paulo, Brazil. is the administrative center of the meso-region of the same name, with 3,783,597 inhabitants as of the 2010 Census, consisting of 49 cities....
, Vitória, Florianópolis
Florianópolis
-Climate:Florianópolis experiences a warm humid subtropical climate, falling just short of a true tropical climate. The seasons of the year are distinct, with a well-defined summer and winter, and characteristic weather for autumn and spring. Frost is infrequent, but occurs occasionally in the winter...
, Uberlândia
Uberlândia
Uberlândia is the main town in the Triangle region, west of the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. With a population of 604,013 inhabitants, according to 2010 estimates, the city is the second largest in the state second only to Belo Horizonte...
, São José do Rio Preto
São José do Rio Preto
São José do Rio Preto is a city and municipality in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Is located at the north/northwest portion of the state, 450 km from the city of São Paulo and 700 km from Brasília....
, Teresina
Teresina
Teresina is the capital and most populous municipality in the Brazilian state of Piauí. It is located in North-central Piauí 366 km from the coast.It is therefore, the only capital in the Northeast that is not located on the shores of the Atlantic Ocean. With 814 439 inhabitants, it is the 19th...
, Santos
Santos (São Paulo)
-Sister cities: Shimonoseki, Japan Nagasaki, Japan Funchal, Portugal Trieste, Italy Coimbra, Portugal Ansião, Portugal Arouca, Portugal Ushuaia, Argentina Havana, Cuba Taizhou. China Ningbo. China Constanţa, Romania Ulsan, South Korea Colón, Panama* Cadiz, Spain...
, Campo Grande
Campo Grande
-Climate:Campo Grande has a highland tropical climate, semi-humid, hot, and notably seasonal, with a dry winter season from May through September or October. Under the Koppen climate classification Campo Grande features a tropical wet and dry climate, albeit a noticeably cooler version of the...
, Fortaleza
Fortaleza
Fortaleza is the state capital of Ceará, located in Northeastern Brazil. With a population close to 2.5 million , Fortaleza is the 5th largest city in Brazil. It has an area of and one of the highest demographic densities in the country...
, Recife
Recife
Recife is the fifth-largest metropolitan area in Brazil with 4,136,506 inhabitants, the largest metropolitan area of the North/Northeast Regions, the 5th-largest metropolitan influence area in Brazil, and the capital and largest city of the state of Pernambuco. The population of the city proper...
, João Pessoa
João Pessoa
João Pessoa , is the capital city of the state of Paraíba, was founded in 1585 and sometimes called the city where the sun rises first, is a Brazilian city and the easternmost city in the Americas at 34º47'38"W, 7º9'28"S. Local residents call its easternmost point Ponta do Seixas. It is also...
, Sorocaba
Sorocaba
Sorocaba is a city in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Sorocaba is the fourth largest city in the state of São Paulo. Outside the Greater São Paulo region, it ranks behind only Campinas, Sao Jose dos Campos and Ribeirão Preto...
, Manaus
Manaus
Manaus is a city in Brazil, the capital of the state of Amazonas. It is situated at the confluence of the Negro and Solimões rivers. It is the most populous city of Amazonas, according to the statistics of Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics, and is a popular ecotourist destination....
, Belém
Belém
Belém is a Brazilian city, the capital and largest city of state of Pará, in the country's north region. It is the entrance gate to the Amazon with a busy port, airport and bus/coach station...
, Aracaju
Aracaju
-Vegetation:Aracaju lies in tropical forest. Rainforests are characterized by high rainfall, with minimum normal annual rainfall between 2,000 mm and 1,700 mm...
, Ribeirão Preto
Ribeirão Preto
Ribeirão Preto is a municipality and city in the Northeastern region of the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is nicknamed Brazilian California, because of a combination of an economy based on agrobusiness plus high technology, wealth and sunny weather all year long. With 605,114 inhabitants,...
, Boa Vista
Boa Vista, Roraima
Boa Vista is the capital of the Brazilian state of Roraima. Situated on the western bank of the River Branco, the city lies 220 km away from Brazil's border with Venezuela. It is the only Brazilian capital located entirely above the Equator...
, Macapá
Macapá
Macapá is a Brazilian city, capital of Amapá state. Located in the North Region, it is the only state capital that has no highway connections with other capitals...
, Porto Velho
Porto Velho
Porto Velho is the capital of the Brazilian state of Rondônia, in the upper Amazon River basin. The population is estimated to be 426,558 people...
, Rio Branco
Rio Branco
Rio Branco is a Brazilian city, capital of Acre. Located in the Valley of Acre in northern Brazil, it is the most populous county in the state, with 305,954 inhabitants, according to a 2009 estimate - almost half the state population....
, São Carlos
São Carlos
São Carlos is a city of 221,950 inhabitants in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. It is located at , at about 231 km from the city of São Paulo.-History:...
, São José do Rio Preto
São José do Rio Preto
São José do Rio Preto is a city and municipality in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Is located at the north/northwest portion of the state, 450 km from the city of São Paulo and 700 km from Brasília....
, São Luís, Pirassununga
Pirassununga
Pirassununga is a municipality in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. The population in 2010 was 70.081 and the area is 728.78 km². The elevation is 627 m. This place name comes from the Tupi language....
, São José dos Campos
São José dos Campos
São José dos Campos is a municipality and a major city in the state of São Paulo, Brazil and one of the most important industrial and research centers in Latin America. It is located in the Paraíba Valley, between the two most active production and consumption regions in the country, São Paulo ...
, Taubaté
Taubaté
Taubaté is a city in the State of São Paulo, in southeastern Brazil. Its strategic geographical location, between the two most important Brazilian cities , being crossed by Presidente Dutra Highway which connects the two megacities, and between high, cold mountains and the Atlantic Ocean has...
, Ituiutaba
Ituiutaba
Ituiutaba is a city and municipality in the western part of Minas Gerais state, Brazil. Elevated to city status in 1901, it had a population in 2007 of 100,316 and a total area in the municipality of 2,694 km²...
, Araraquara
Araraquara
Not to be confused with Araracuara, a town, region, genus of trees in ColombiaAraraquara is a city in the state of São Paulo in Brazil. It is also known as "the abode of the sun," because of its impressive sunset and because of its hazy temperature, especially in summer.More than 200,000 people...
, Feira de Santana
Feira de Santana
Feira de Santana is a city in Bahia, Brazil. It is the second-most populous city in the state, with a population of 700,000 according to IBGE's estimate. It is located 115 km northwest of Salvador, Bahia's capital city. These cities are connected by BR-324, a four-lane divided highway...
, Itapetininga
Itapetininga
Itapetininga is a municipality in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. The name comes from the Tupi languageIt is situated in the southwestern region of the state, and is known as cidade das escolas, meaning city of schools in Portuguese....
, Sorocaba
Sorocaba
Sorocaba is a city in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Sorocaba is the fourth largest city in the state of São Paulo. Outside the Greater São Paulo region, it ranks behind only Campinas, Sao Jose dos Campos and Ribeirão Preto...
, Presidente Prudente
Presidente Prudente
Presidente Prudente is a municipality in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. The city has a population of 207,610 inhabitants and area of 562.8 km². The city is named after president Prudente de Morais. Prudente is located 558 km from the city of São Paulo.Presidente Prudente is considered the...
, Bauru
Bauru
Bauru is a Brazilian city and municipality in midwestern region of the state of São Paulo. It is also the capital of the micro-region of Bauru...
, Campos dos Goytacazes
Campos dos Goytacazes
Campos dos Goytacazes is a municipality and city located in the northern area of Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil, with a population of 463,545 inhabitants. Its area is 4,031.910 km², which makes it the largest municipality in the state and its elevation is 14 m...
, Londrina
Londrina
Londrina is a city located in the northern region of the state of Paraná, Brazil, and is 369 km away from the capital, Curitiba. Londrina was originally founded by British settlers. The city exerts great influence on Paraná and Brazil's south region...
, Juiz de Fora
Juiz de Fora
-Industry, Trade, and Culture:Juiz de Fora is the second most important industrial center in the state of Minas Gerais, despite being the fourth largest in terms of population. It was once the state's largest city, position which was held up until the beginning of the 20th century...
, Campina Grande
Campina Grande
Campina Grande is the second most populous Brazilian city in the State of Paraíba after João Pessoa, the capital. It is considered to be the most important city of the Northeastern Brazilian subregion called agreste. It is considered one of the main industrial, technological and educational...
, Caxias do Sul
Caxias do Sul
Caxias do Sul is a city in Rio Grande do Sul, Southern Brazil, situated in the state's mountainous Serra Gaúcha region. Coordinates: 29°10′0″ S, 51°11′0″ W....
, Franca
Franca
-Demography:*Total: 328.473 inhabitants on July 1, 2006.** Urban: 324.138** Rural: 6.999*Demographic density : 473,80*Child mortality until 1 year : 12,66 = 1,26%*Life expectancy : 73,03*Fertility : 2,26...
, Rio Claro
Rio Claro
Rio Claro may refer to:-Cities:*Rio Claro, Trinidad and Tobago, the largest town in southeastern Trinidad and Tobago...
and Cuiabá
Cuiabá
Under the Koppen climate classification, Cuiaba features a tropical wet and dry climate. Cuiabá is famous for its searing heat, although temperatures in winter can arrive sporadically at 10 degrees, indeed atypical, caused by cold fronts coming from the south, and that may only last one or two...
have digital terrestrial broadcasting.
By 2013 the digital signal will be available in the whole country.
Analogue shut-off is scheduled for 29 June 2016.
Chile
On September 14, 2009, president Michelle Bachelet announced that the government had finally decided, after prolonged delays, on a digital television standard. Chile will be adopting the ISDB-T Japanese standard (with the custom modifications made by Brazil). Simulcasting is expected to begin in 2010, with a projected analog switch-off in 2017.Colombia
ColombiaColombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the...
has chosen the European DVB-T standard on 28 August 2008 It is expected that by year end 2009 some 42% of the Colombian population would be able to receive digital TV coverage.
On December 28, 2010, private networks Caracol TV
Caracol TV
Caracol Televisión is a Colombian private national television network, owned by Julio Mario Santo Domingo.- History :Caracol Televisión started in 1954 when Organización de Radiodifusora Caracol offered to afford national television costs, then state-run, through commercial spots...
and RCN TV
RCN TV
RCN Televisión , is a Colombian private television network. It started as a production company in 1967...
officially started digital broadcasts for Bogotá, Medellín and surrounding areas on channels 14 and 15 UHF, respectively. State-run Señal Colombia
Señal Colombia
Señal Colombia is a Colombian national television channel established and funded by the government, launched in 1970 as Canal 11. It uses its current name since 1995....
and Canal Institucional
Canal Institucional
Canal Institucional is a Colombian state-run national television channel launched 2 February 2004.It broadcasts programmes produced by state institutions in order to promote and publicize their activities to the public...
had started test digital broadcasts earlier in 2010.
Peru
PeruPeru
Peru , officially the Republic of Peru , is a country in western South America. It is bordered on the north by Ecuador and Colombia, on the east by Brazil, on the southeast by Bolivia, on the south by Chile, and on the west by the Pacific Ocean....
has chosen on 23 April 2009 the Brazilian modified version of the Japanese standard ISDB-T. Agreed with Japan to cooperate for resource exchange and technical transfer on 21 August 2009, and On air service started on Channel 7 of TV Perú from 30 March 2010.
Uruguay
UruguayUruguay
Uruguay ,officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay,sometimes the Eastern Republic of Uruguay; ) is a country in the southeastern part of South America. It is home to some 3.5 million people, of whom 1.8 million live in the capital Montevideo and its metropolitan area...
had chosen the European DVB-T standard in August 2007, however disproved it and decided to adopt ISDB-T on 27 December 2010 to follow neighbouring countries.
Venezuela
In Venezuela, tests are being performed with full deployment to start 2008–2009. DTT will coexist with analogue standard television for some time, until full deployment of the system on a nationwide level is accomplished. 30 September 2009, decided to employ Japanese ISDB-T system under cooperation with Japan, and officially be agreed with Japan in early October 2009.On October 6, 2009, Venezuela has officially adopted ISDB-T with Brazilian modifications. Transition from analog to digital is expected to take place in the next 10 years.
Africa
On the African continent is still the worldwide trend the European standard "DVB-T2DVB-T2
DVB-T2 is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting – Second Generation Terrestrial; it is the extension of the television standard DVB-T, issued by the consortium DVB, devised for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television....
" being the most modern system of broadcasting. Countries that have adopted the standard are: Angola, Botswana, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Seychelles, South Africa, Swaziland, Tanzania, Zambia and Zimbabwe.
Analogue to digital transition by country
- Official launch: The official launch date of digital terrestrial television in the country, not the start for trial broadcasts.
- Start of closedown: The date for the first major closedown of analogue transmitters.
- End of closedown: The date when analogue television is definitely closed down.
- System: Transmission system, e. g. DVB-TDVB-TDVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
, ATSC or ISDB-T. - Interactive: System used for interactive services, such as MHPMultimedia Home PlatformMultimedia Home Platform is an open middleware system standard designed by the DVB project for interactive digital television. The MHP enables the reception and execution of interactive, Java-based applications on a TV-set. Interactive TV applications can be delivered over the broadcast channel,...
and MHEG-5MHEG-5MHEG-5, or ISO/IEC 13522-5, is part of a set of international standards relating to the presentation of multimedia information, standardised by the Multimedia and Hypermedia Experts Group...
. - Compression: Video compression standard used. Most systems use MPEG-2MPEG-2MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
, but the more efficient H.264/MPEG-4 AVCH.264/MPEG-4 AVCH.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video...
has become increasingly popular among networks launching later on. Some countries use both MPEG-2 and H.264, for example France which uses MPEG-2 for standard definition free content but MPEG-4 for HD broadcasts and pay services.
| Country |
Official launch |
Start of closedown |
End of closedown |
System |
Interactive |
Compression |
References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Albania | 2004-07-15 | 2012/2015 | DVB-T | MPEG-2 | |||
| Andorra | 2007-09-25 | DVB-T | MHP | MPEG-2 | |||
| Australia | 2001-01-01 | Regional ASO started 30 June 2010 | 2013 | DVB-T (7 MHz channels 6~12 VHF and 29~69 UHF) |
MHP | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Austria | 2006-10-26 | 2007-03-05 | 2010 | DVB-T | MHP | MPEG-2 | |
| Belgium | 2002/2003 | 2008-11-03 (Flemish Community) | 2011 (Francophone Community) | DVB-T | None | MPEG-2 | |
| Argentina Digital television in Argentina Argentine television broadcasting began in 1951 with the inaugural of then state-owned Canal 7, developed by Radio Belgrano executive Jaime Yankelevich. Color television broadcasting, however, was not widely available until after 1978, when the government launched Argentina Televisora Color , now... |
2010-04-28 | — | 2019-09-01 | ISDB-Tb ISDB-Tb ISDB-Tb is the short for International System for Digital Broadcast, Terrestrial, Brazilian version.It is a Digital TV system based on Japanese ISDB-T . ISDB-Tb system is also known as SBTVD and is used in Brazil... |
Ginga Ginga (SBTVD Middleware) Ginga is the middleware specification for the Brazilian Digital TV System . Ginga was developed based on a set of standardized technologies, such as ITU-T J.200, and also adding innovations developed by Brazilian researchers... |
H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Brazil | 2007-12-03 | — | 2016-06-29 | ISDB-T | Ginga Ginga (SBTVD Middleware) Ginga is the middleware specification for the Brazilian Digital TV System . Ginga was developed based on a set of standardized technologies, such as ITU-T J.200, and also adding innovations developed by Brazilian researchers... |
H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Bulgaria | 2004-11 | 2009-03 | 2012, end | DVB-T | MHP | MPEG-4 | |
| Canada Digital television in Canada Digital television in Canada is transmitted using the ATSC standards developed for and in use in the United States. Because Canada and the U.S... |
2003-01 | 2011-08-31 | ATSC ATSC ATSC standards are a set of standards developed by the Advanced Television Systems Committee for digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable, and satellite networks.... |
MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... (ATSC 2.0) |
|||
| China | 2006 | 2006 | 2015 (SARFT reported August 2005) | DMB-T/H DMB-T/H DTMB is the TV standard for mobile and fixed terminals used in the People's Republic of China, Hong Kong and Macau. Although at first this standard was called DMB-T/H , the official name is DTMB.DTT broadcasting systems... |
MPEG-2 | ||
| Colombia | 2008-08-28 | 2019-12-31 | DVB-T DVB-T DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998... ( 6 MHz ) |
MHP Multimedia Home Platform Multimedia Home Platform is an open middleware system standard designed by the DVB project for interactive digital television. The MHP enables the reception and execution of interactive, Java-based applications on a TV-set. Interactive TV applications can be delivered over the broadcast channel,... |
H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
||
| Costa Rica | 2010-05-04 | — | 2018 | ISDB-T | Ginga Ginga (SBTVD Middleware) Ginga is the middleware specification for the Brazilian Digital TV System . Ginga was developed based on a set of standardized technologies, such as ITU-T J.200, and also adding innovations developed by Brazilian researchers... |
H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Croatia | 2002-07-09 | 2002-07-09 | 2011-01-01 | DVB-T | MPEG-2 | ||
| Czech Republic | 2005-10-21 | 2005-10-21 | 2010-10 | DVB-T | MHP | MPEG-2 | |
| Denmark Digital terrestrial television in Denmark Digital terrestrial television in Denmark was officially launched in March 2006 after some years of public trials. The analogue broadcasts shut down nationwide at midnight on November 1, 2009.... |
2006-03-31 | 2009-02-01 | 2009-11-01 | DVB-T | MHP | MPEG-2, H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| El Salvador | 2009-04-22 | 2018-12-31 | 2019-01-01 | ATSC | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... (ATSC 2.0) |
||
| Estonia Digital terrestrial television in Estonia Digital terrestrial television in Estonia, was officially launched on December 15, when the operator Zuum TV launched its pay service on two multiplexes. Transmissions are made with MPEG-4 AVC compression using the DVB-T standard.... |
2006-12-15 | 2008-03-31 (Ruhnu Ruhnu Ruhnu is an island situated in the Gulf of Riga in the Baltic Sea. It belongs to Estonia and is an administrative part of Saare County. At 11.9 km2 it has currently less than 100, mostly ethnic Estonian permanent inhabitants... island) |
2010-07-01 | DVB-T | MHP planned | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Faroe Islands Digital terrestrial television in Denmark Digital terrestrial television in Denmark was officially launched in March 2006 after some years of public trials. The analogue broadcasts shut down nationwide at midnight on November 1, 2009.... |
2002-12 | 2002-12 | 2003 | DVB-T | None | MPEG-2 | |
| Finland Digital terrestrial television in Finland Digital terrestrial television in Finland was launched on August 21, 2001. The analogue networks continued its broadcasts alongside the digital ones until September 1, 2007, when they were shut down nationwide.... |
2001-08-27 | 2007-09-01 | 2007-09-01 | DVB-T | MHP (abandoned) | MPEG-2 | |
| France Télévision Numérique Terrestre TNT is the national digital terrestrial service for France. It formally arrived on 31 March 2005 after a short testing period. Like Freeview in the United Kingdom it will support many new channels as well as the current terrestrial television stations... |
2005-03-31 FTA/2006/03/01 Pay DTT | 2009-02-04 | 2011 (before November 30) | DVB-T | MHP | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Germany | 2003-03 | 2003-03 Regional rollout | 2008-12-02 completed | DVB-T | MPEG-2 / H.264 (Stuttgart for non public channels) | ||
| Greece | 2006-01-16 Tests | 2008-11-01 | 2015 | DVB-T | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... (ERT) H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... (ERT, DIGEA) |
||
| Hong Kong | 2007-12-31 | 2015 | DMB-T/H DMB-T/H DTMB is the TV standard for mobile and fixed terminals used in the People's Republic of China, Hong Kong and Macau. Although at first this standard was called DMB-T/H , the official name is DTMB.DTT broadcasting systems... |
MHEG-5 (TVB) | MPEG-2, H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
||
| Hungary | 2008-12-01 | 2014-12-31 | DVB-T | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|||
| Indonesia | 2010 | 2014 | 2018 | DVB-T | MPEG-2 | ||
| Iran | 2009 | 2015 | DVB-T | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|||
| Ireland | 1999–2002 Licensing abandoned; 2006–2008 Trial; 31 October 2010 (90%) DTT launch, 31 December 2011(98%) Network testing, publicly receivable with MPEG4 compatible equipment pre October 31, 2010. |
2011-12-31-coincide with NI | 2012, By Q4 likely co-timed with NI(MOU) | DVB-T | RCT abandoned, MHEG5, | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Israel | 2009-08-02 | June 2011 | DVB-T | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... , AAC+ V2 |
|||
| Italy | 2004-01-01 | 2012-12-31 | DVB-T | MHP | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
||
| Japan | 2003-12-01 | 2011-07-24 Postpone 2012-03-31 in Iwate Iwate Prefecture is the second largest prefecture of Japan after Hokkaido. It is located in the Tōhoku region of Honshū island and contains the island's easternmost point. The capital is Morioka. Iwate has the lowest population density of any prefecture outside Hokkaido... , Miyagi Miyagi Prefecture is a prefecture of Japan in the Tōhoku Region on Honshu island. The capital is Sendai.- History :Miyagi Prefecture was formerly part of the province of Mutsu. Mutsu Province, on northern Honshu, was one of the last provinces to be formed as land was taken from the indigenous Emishi, and became the... and Fukushima Fukushima Prefecture is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region on the island of Honshu. The capital is the city of Fukushima.-History:Until the Meiji Restoration, the area of Fukushima prefecture was known as Mutsu Province.... |
ISDB-T | BML Broadcast Markup Language Broadcast Markup Language, or BML, is an XML-based standard developed by Japanese ARIB association as a data broadcasting specification for digital television broadcasting... |
MPEG-2 | ||
| Lithuania | 2006 | Now expanded nationwide at January 2009 | 2012-10-29 | DVB-T | MPEG-4 | ||
| Luxembourg | 2006-04-04 | 2006-04-04 | 2006-09-01 | DVB-T | None | MPEG-2 | |
| Republic of Macedonia | 2004-05-04 | 2010-01-01 | 2012, May | DVB-T | MHP | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Malaysia Digital television in Malaysia In Malaysia, digital television broadcasts, or DTV, can be received via cable, internet, satellite, or via free over-the-air digital terrestrial television - much like analog television broadcasts have been... |
2006-09 (trials) abandoned | 2010 abandoned | 2015 | DVB-T abandoned | MHEG-5 abandoned | H.264 abandoned | |
| Mexico Digital television in Mexico Television in Mexico first began in August 19, 1946 in Mexico City when Guillermo González Camarena transmitted the first television signal in Latin America from his home’s bathroom. On September 7, 1946 at 8:30 PM Mexico’s and Latin America’s first experimental television station was established... |
2004-07-05 | 2015-31-12 | ATSC | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... (ATSC 2.0) |
|||
| Morocco | 2007-06-01 | 2007-03-05 | 2015 | DVB-T | |||
| Netherlands Digital television in the Netherlands The Netherlands now has three major forms of broadcast digital television. Terrestrial , Cable , and Satellite . In addition IPTV services are available... |
2003 | 2003-11 | 2006-12-11 | DVB-T | MPEG-2 | ||
| New Zealand | April 2008 | 2012-09-30 | 2013-12-01 | DVB-T | MHEG-5 | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Norway | 2007-09 | 2008-03 | 2009-12-01 | DVB-T | MHP | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Peru | 2010-03-30 | 2023-03-01 | ISDB-T | Ginga Ginga (SBTVD Middleware) Ginga is the middleware specification for the Brazilian Digital TV System . Ginga was developed based on a set of standardized technologies, such as ITU-T J.200, and also adding innovations developed by Brazilian researchers... |
H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
||
| Philippines Digital television in the Philippines The digital television broadcast transition in the Philippines also known locally, the Digital Terrestrial Television was the switchover from analog signals to digital transmission of free-to-air television programs... |
October 2008 | 2010 | 2015-12-31 | ISDB-T | BML | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Poland Digital television in Poland First efforts to introduce DVB-T in Poland was made in 1997 in Gdańsk on initiative of TVP . First test DVB-T emission was carried in Warsaw at 9 November 2001.... |
2004 (trials) 2009-09-20 DTT Launch |
2011-05 | 2013-07-31 | DVB-T | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
||
| Portugal | 2009-04-29 | 2011 | 2012-04-26 | DVB-T | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
||
| Romania | 2005-12-01, Full:2009-12 | 2012-12-31 (planned) | DVB-T | MPEG-4 | |||
| Russia Digital television in Russia Different alternatives were considered in the process of preparing proposals on shifting the country to digital broadcasting , but the Ministry of IT and Communication decided to focus solely on terrestrial broadcasting as the object of digital TV implementation... |
2010 | 2015 | DVB-T | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|||
| Slovakia | 1999–2004,2005–2009 | 2010 | 2012 | DVB-T | MHEG-5 | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Slovenia | 2007 | 2010-12-01 | 2011-06-30 | DVB-T | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
||
| South Africa | 2006-03 | 2008-11-01 | 2011-11-01 | DVB-T | MHEG-5 (Future use planned) | H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| South Korea | 2001 | 2010-09-01 14:00 (Uljin) | 2012-12-31 | ATSC | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... (ATSC 2.0) |
||
| Spain | 2000–2005 (Previous and relaunch) | 2009 | 2010-04-03 | DVB-T | MHP | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Sweden Digital terrestrial television in Sweden Digital terrestrial television was launched in Sweden in 1999. The shutdown of the analogue equivalent started on September 19, 2005, and was finalized on October 29, 2007.... |
1999-04-01 | 2005-09-19 | 2007-10-29 | DVB-T, DVB-T2 (HDTV) | MHP | MPEG-2/H.264 | |
| Switzerland | 2001 | 2002-03 | 2008-02-25 | DVB-T | |||
| Taiwan | 2004-01 | 2010-07 (Pinglin) | 2012-06 | DVB-T | MHP | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Thailand | 2011 (trial) 2012 |
2012 | 2015–2020 | DVB-T2 | MHEG-5 | H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| Turkey Digital television in Turkey -Pay-TV Services:Current Pay-TV services in Turkey are Digiturk, D-Smart, TeleDünya and Türksat KabloTV.- First Digital Transmissions :The first digital television transmissions in Turkey were made by the Uzan Group with Turkey's first television channel Star TV... |
2006-02 (trial services) | 2007 | DVB-T | ||||
| Ukraine | 2009-04-01 | 2012 | 2015 | DVB-T | none | MPEG-4 | |
| United Kingdom Digital terrestrial television in the United Kingdom Digital terrestrial television in the United Kingdom encompasses over 100 television, radio and interactive services broadcast via the UK's terrestrial television network and receivable with a standard television aerial... |
1998-11-15 | 2007 (Whitehaven) | 2012 | DVB-T, DVB-T2 (HDTV) | MHEG-5 | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... |
|
| United States | 1998-10-29 | 2007 | ATSC | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... , H.264 H.264/MPEG-4 AVC H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video... (ATSC 2.0) |
|||
| Vietnam | 2011 | Probably not | Probably not |
See also
- Common InterfaceCommon InterfaceIn Digital Video Broadcasting, the Common Interface is an extensible digital interconnect found in the digital TV market. It is also known as DVB-CI for Digital Video Broadcast Common Interface....
(CI) - Conditional-Access Module (CAM)
- Digital television transitionDigital television transitionThe digital television transition is the process in which analog television broadcasting is converted to and replaced by digital television. This primarily involves both TV stations and over-the-air viewers; however it also involves content providers like TV networks, and cable television...
- List of digital television deployments by country
- 1seg1segis a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
- USB stick
External links
- Future of Broadcast Television Summit Declares Global Goals for Future of Broadcasting Nov. 11, 2011
- IEEE Spectrum - Does China Have the Best Digital Television Standard on the Planet?
- DigiTAG
- The DVB Project - including data on DTT deployments worldwide
- European Audiovisual Observatory
- MAVISE database on TV channels and TV companies in the European Union
- Worldwide overview of the digital terrestrial systems ATSC, DMB-T/H, DVB-T and ISDB-T Status DTT in the world.
- Digital Broadcasting, the Launching by Country Digital Broadcasting Experts Group (DiBEG)
- Research in DTT
- Schedule for the implementation of Digital TV in the world

