
Cliff effect
Encyclopedia
Digital
A digital system is a data technology that uses discrete values. By contrast, non-digital systems use a continuous range of values to represent information...
signal reception
Reception
Reception is a noun form of receiving, or to receive something, such as information, art, experience, or people. It is often used in the following contexts:...
. Unlike analog signal
Analog signal
An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are...
s, which gradually fade when signal strength
Signal strength
In telecommunications, particularly in radio, signal strength refers to the magnitude of the electric field at a reference point that is a significant distance from the transmitting antenna. It may also be referred to as received signal level or field strength. Typically, it is expressed in...
decreases or electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
or multipath
Multipath interference
Multipath interference is a phenomenon in the physics of waves whereby a wave from a source travels to a detector via two or more paths and, under the right condition, the two components of the wave interfere...
increases, a digital signal provides data which is either perfect or non-existent at the receiving
Receiver (Information Theory)
The receiver in information theory is the receiving end of a communication channel. It receives decoded messages/information from the sender, who first encoded them. Sometimes the receiver is modeled so as to include the decoder. Real-world receivers like radio receivers or telephones can not be...
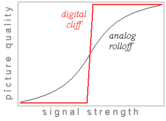
end. It is named for a graph (shown at right) of reception quality versus signal quality, where the digital signal "falls off a cliff" instead of having a gradual rolloff.
The phenomenon is primarily seen in broadcasting, where signal strength is liable to vary, rather than in recorded media, which generally have a good signal. However, it may be seen in significantly damaged media, which is at the edge of readability.
The term is also used in economics for an unrelated phenomenon.
Digital television
This effect can most easily be seen on digital televisionDigital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
, including both satellite TV and over-the-air
Over-the-air
Over-the-air has several meanings, depending on context. *Generally, over-the-air is synonymous for wireless.*Specifically, over-the-air can have the following meanings or is used in the following contexts:...
terrestrial TV. While forward error correction
Forward error correction
In telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, forward error correction or channel coding is a technique used for controlling errors in data transmission over unreliable or noisy communication channels....
is applied to the broadcast
Broadcasting
Broadcasting is the distribution of audio and video content to a dispersed audience via any audio visual medium. Receiving parties may include the general public or a relatively large subset of thereof...
, when a minimum threshold of signal quality (a maximum bit error rate) is reached it is no longer enough for the decoder
Decoder
A decoder is a device which does the reverse operation of an encoder, undoing the encoding so that the original information can be retrieved. The same method used to encode is usually just reversed in order to decode...
to recover. The picture may break up (pixellation), lock on a freeze frame
Freeze frame television
Freeze frame television: Television in which fixed images are transmitted sequentially at a rate far too slow to be perceived as continuous motion by human vision...
, or go blank. Causes include rain fade
Rain fade
Rain fade refers primarily to the absorption of a microwave radio frequency signal by atmospheric rain, snow or ice, and losses are especially prevalent at frequencies above 11 GHz. It also refers to the degradation of a signal caused by the electromagnetic interference of the leading edge of a...
or solar transit
Solar transit
In astronomy, a solar transit is when any object passes between the Sun and the Earth. This mainly includes the planets Mercury and Venus. A solar eclipse is also a solar transit of the Moon, but technically only if it does not cover the entire disc of the Sun , as "transit" counts only objects...
on satellites, and temperature inversions and other weather or atmospheric conditions causing anomalous propagation
Anomalous propagation
Anomalous propagation includes different forms of electromagnetic wave propagation that are not encountered in a standard atmosphere. While technically the term includes propagation with larger losses than in standard atmosphere, in practical applications it is most often meant to refer to cases...
on the ground.
Three particular issues particularly manifest the cliff effect. Firstly, anomalous conditions will cause occasional signal degradation. Secondly, if one is located in a fringe area, where the signal is just barely strong enough to receive the signal, then usual variation in signal quality will cause relatively frequent signal degradation, and a very small change in overall signal quality can have a dramatic impact on the frequency of signal degradation – one incident per hour (not significantly affecting watchability) versus problems every few seconds or continuous problems. Thirdly, in some cases, where the signal is beyond the cliff (in unwatchable territory), viewers who were once able to receive a degraded signal from analog stations will find after digital transition that there is no available signal in rural, fringe or mountainous regions.
The cliff effect is a particularly serious issue for mobile TV
Mobile TV
Mobile television usually means television watched on a small handheld device. It may be a pay TV service broadcast on mobile phone networks or received free-to-air via terrestrial television stations from either regular broadcast or a special mobile TV transmission format...
, as signal quality may vary significantly, particularly if the receiver is moving rapidly, as in a car.
Hierarchical modulation
Hierarchical modulation
Hierarchical modulation, also called layered modulation, is one of the signal processing techniques for multiplexing and modulating multiple data streams into one single symbol stream, where base-layer symbols and enhancement-layer symbols are synchronously overplayed before...
and coding can provide a compromise by supporting two or more streams with different robustness parameters and allowing receivers to scale back to a lower definition (usually from HDTV to SDTV, or possibly from SDTV to LDTV) before dropping out completely. Two-level hierarchical modulation is supported in principle by the European DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
digital terrestrial television standard. However, layered source coding
Source coding
In information theory, Shannon's source coding theorem establishes the limits to possible data compression, and the operational meaning of the Shannon entropy....
, such as provided by Scalable Video Coding
Scalable Video Coding
Scalable Video Coding is the name for the Annex G extension of the H.264/MPEG-4 AVC video compression standard. SVC standardizes the encoding of a high-quality video bitstream that also contains one or more subset bitstreams. A subset video bitstream is derived by dropping packets from the...
, is not supported.
Digital radio
HD RadioHD Radio
HD Radio, which originally stood for "Hybrid Digital", is the trademark for iBiquity's in-band on-channel digital radio technology used by AM and FM radio stations to transmit audio and data via a digital signal in conjunction with their analog signals...
broadcasting, officially used only in the United States, is one system designed to have an analog fallback. Receivers are designed to immediately switch to the analog signal upon losing a lock on digital, but only as long as the tuned station operates in hybrid
In-band on-channel
In-band on-channel is a hybrid method of transmitting digital radio and analog radio broadcast signals simultaneously on the same frequency....
digital mode (the official meaning of "HD"). In the future all-digital mode, there is no analog to fallback to at the edge of the digital cliff. This applies only to the main channel simulcast
Simulcast
Simulcast, shorthand for "simultaneous broadcast", refers to programs or events broadcast across more than one medium, or more than one service on the same medium, at the same time. For example, Absolute Radio is simulcast on both AM and on satellite radio, and the BBC's Prom concerts are often...
, and not to any subchannels, because they have nothing to fall back to. It is also important for the station's broadcast engineer to make sure that the audio signal
Audio signal
An audio signal is an analog representation of sound, typically as an electrical voltage. Audio signals may be synthesized directly, or may originate at a transducer such as a microphone, musical instrument pickup, phonograph cartridge, or tape head. Loudspeakers or headphones convert an electrical...
is synchronized between analog and digital, or the cliff effect will still cause a jump slightly forward or backward in the radio program.
Mobile phones
The cliff effect is also heard on mobile phoneMobile phone
A mobile phone is a device which can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile network operator...
s, where one or both sides of the conversation may break up, possibly resulting in a dropped call. Other forms of digital radio
Digital radio
Digital radio has several meanings:1. Today the most common meaning is digital radio broadcasting technologies, such as the digital audio broadcasting system, also known as Eureka 147. In these systems, the analog audio signal is digitized into zeros and ones, compressed using formats such as...
also suffer from this.
Economics
In economicsEconomics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
, the "cliff effect" refers to a positive feedback
Positive feedback
Positive feedback is a process in which the effects of a small disturbance on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A. In contrast, a system that responds to a perturbation in a way that reduces its effect is...
loop, where downgrading a single security can have a disproportionate cascading effect. This has become pronounced with respect to the assessment of credit risk
Credit risk
Credit risk is an investor's risk of loss arising from a borrower who does not make payments as promised. Such an event is called a default. Other terms for credit risk are default risk and counterparty risk....
in a bank's portfolio. If a Credit Rating Agency
Credit rating agency
A Credit rating agency is a company that assigns credit ratings for issuers of certain types of debt obligations as well as the debt instruments themselves...
has the expectation that the credit risk of a position rises, it will downgrade its rating
Rating
A rating is the evaluation or assessment of something, in terms of quality , quantity , or some combination of both.Rating may also refer to:...
. As a consequence, a bank faces additional capital charges in order to comply with national capital requirements. Especially during the subprime mortgage crisis
Subprime mortgage crisis
The U.S. subprime mortgage crisis was one of the first indicators of the late-2000s financial crisis, characterized by a rise in subprime mortgage delinquencies and foreclosures, and the resulting decline of securities backed by said mortgages....
banks had to increase their capital substantially, because many ratings were considerably downgraded. In a time banks needed their capital most to cope with high losses, this term emerged in the consultative process on reforms regarding existing capital requirements, namely criticizing the procyclical "cliff effect".

