Hierarchical modulation
Encyclopedia
Hierarchical modulation, also called layered modulation, is one of the signal processing
techniques for multiplexing
and modulating
multiple data streams into one single symbol stream, where base-layer symbols and enhancement-layer symbols are synchronously overplayed before transmission.
Hierarchical modulation is particularly used to mitigate the cliff effect
in digital television
broadcast, particularly mobile TV
, by providing a (lower quality) fallback signal in case of weak signals, allowing graceful degradation instead of complete signal loss. It has been widely proven and included in various standards, such as DVB-T
, MediaFLO
, UMB (Ultra Mobile Broadband
, a new 3.5th generation mobile network standard developed by 3GPP2), and is under study for DVB-H
.
Hierarchical modulation is also taken as one of the practical implementations of superposition precoding, which can help achieve the maximum sum rate of broadcast channels. When hierarchical-modulated signals are transmitted, users with good reception and advanced receivers can demodulate multiple layers. For a user with a conventional receiver or poor reception, it may only demodulate the data stream embedded in the base layer. With hierarchical modulation, a network operator can target users of different types with different services or QoS
.
However, traditional hierarchical modulation suffers from serious inter-layer interference (ILI) with impact on the achievable symbol rate.
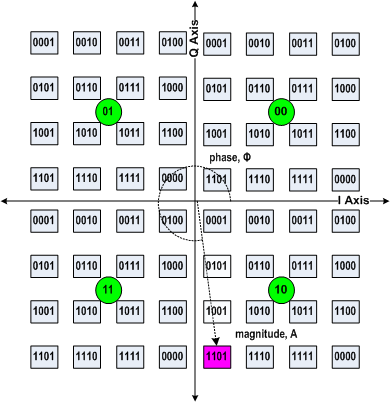 For example, the figure depicts a layering scheme with QPSK
For example, the figure depicts a layering scheme with QPSK
base layer, and a 16QAM
enhancement layer. The first layer is 2 bits (represented by the green circles). The signal detector only needs to establish which quadrant the signal is in, to recover the value (which is '10', the green circle in the lower right corner). In better signal conditions, the detector can establish the phase and amplitude more precisely, to recover four more bits of data ('1101'). Thus, the base layer carries '10', and the enhancement layer carries '1101'.
(SNR) at about 23 dB
, about the minimum needed for the comparable non-hierarchical modulation, 64QAM. But unlayered 16QAM with the same SNR would approach full throughput. This means, due to ILI, about 1.5/4 = 37.5% loss of the base-layer achievable throughput. Furthermore, due to ILI and the imperfect demodulation of base-layer symbols, the demodulation error rate of higher-layer symbols increases too.
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
techniques for multiplexing
Multiplexing
The multiplexed signal is transmitted over a communication channel, which may be a physical transmission medium. The multiplexing divides the capacity of the low-level communication channel into several higher-level logical channels, one for each message signal or data stream to be transferred...
and modulating
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
multiple data streams into one single symbol stream, where base-layer symbols and enhancement-layer symbols are synchronously overplayed before transmission.
Hierarchical modulation is particularly used to mitigate the cliff effect
Cliff effect
In telecommunications, the cliff effect or brickwall effect describes the sudden loss of digital signal reception. Unlike analog signals, which gradually fade when signal strength decreases or electromagnetic interference or multipath increases, a digital signal provides data which is either...
in digital television
Digital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
broadcast, particularly mobile TV
Mobile TV
Mobile television usually means television watched on a small handheld device. It may be a pay TV service broadcast on mobile phone networks or received free-to-air via terrestrial television stations from either regular broadcast or a special mobile TV transmission format...
, by providing a (lower quality) fallback signal in case of weak signals, allowing graceful degradation instead of complete signal loss. It has been widely proven and included in various standards, such as DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
, MediaFLO
MediaFLO
MediaFLO is a technology developed by Qualcomm for transmitting audio, video and data to portable devices such as mobile phones and personal televisions, used for mobile television...
, UMB (Ultra Mobile Broadband
Ultra Mobile Broadband
UMB was the brand name for a project within 3GPP2 to improve the CDMA2000 mobile phone standard for next generation applications and requirements...
, a new 3.5th generation mobile network standard developed by 3GPP2), and is under study for DVB-H
DVB-H
DVB-H is one of three prevalent mobile TV formats. It is a technical specification for bringing broadcast services to mobile handsets. DVB-H was formally adopted as ETSI standard EN 302 304 in November 2004. The DVB-H specification can be downloaded from the official DVB-H website...
.
Hierarchical modulation is also taken as one of the practical implementations of superposition precoding, which can help achieve the maximum sum rate of broadcast channels. When hierarchical-modulated signals are transmitted, users with good reception and advanced receivers can demodulate multiple layers. For a user with a conventional receiver or poor reception, it may only demodulate the data stream embedded in the base layer. With hierarchical modulation, a network operator can target users of different types with different services or QoS
Quality of service
The quality of service refers to several related aspects of telephony and computer networks that allow the transport of traffic with special requirements...
.
However, traditional hierarchical modulation suffers from serious inter-layer interference (ILI) with impact on the achievable symbol rate.
Example

Phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal ....
base layer, and a 16QAM
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
enhancement layer. The first layer is 2 bits (represented by the green circles). The signal detector only needs to establish which quadrant the signal is in, to recover the value (which is '10', the green circle in the lower right corner). In better signal conditions, the detector can establish the phase and amplitude more precisely, to recover four more bits of data ('1101'). Thus, the base layer carries '10', and the enhancement layer carries '1101'.
Inter-layer interference
For a hierarchically-modulated symbol with 16QAM base layer and QPSK enhancement layer, the base-layer throughput loss is up to about 1.5bits/symbol with the total receive signal-to-noise ratioSignal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
(SNR) at about 23 dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
, about the minimum needed for the comparable non-hierarchical modulation, 64QAM. But unlayered 16QAM with the same SNR would approach full throughput. This means, due to ILI, about 1.5/4 = 37.5% loss of the base-layer achievable throughput. Furthermore, due to ILI and the imperfect demodulation of base-layer symbols, the demodulation error rate of higher-layer symbols increases too.
See also
- Link adaptationLink adaptationLink adaptation, or adaptive coding and modulation , is a term used in wireless communications to denote the matching of the modulation, coding and other signal and protocol parameters to the conditions on the radio link Link adaptation, or adaptive coding and modulation (ACM), is a term used in...
- MipmapMipmapIn 3D computer graphics texture filtering, MIP maps are pre-calculated, optimized collections of images that accompany a main texture, intended to increase rendering speed and reduce aliasing artifacts. They are widely used in 3D computer games, flight simulators and other 3D imaging systems. The...
, Pyramid (image processing)Pyramid (image processing)Pyramid or pyramid representation is a type of multi-scale signal representation developed by the computer vision, image processing and signal processing communities, in which a signal or an image is subject to repeated smoothing and subsampling...
– similar techniques in image processing

