
Curitiba
Encyclopedia
Curitiba is the capital of the Brazilian state of Paraná
. It is the largest city with the biggest economy of both Paraná and southern Brazil. The population of Curitiba numbers approximately 1.75 million people (8th largest nationwide) and the latest GDP figures for the city surpass US$61 billion (ranking 4th nationwide) according to IBGE
(2008). Its metropolitan area comprises 26 municipalities with a total population of over 3.2 million (IBGE estimate in 2006).
Curitiba is an important cultural, political and economic centre in the country. The city sits on a plateau
at 932 metres (3,057.7 ft) above sea level
. It is located 105 kilometres (65.2 mi) west of the sea port of Paranaguá
and is served by the Afonso Pena International
and Bacacheri
airports. The city hosts the Federal University of Paraná, established in 1912, one year before electric streetcars were first deployed.
Curitiba's rapid expansion was based on the cattle trade, the city being located half-way between the cattle breeding country to the south and the markets to the north. Waves of European immigrants started arriving after 1850, mainly Germans
, Italians
, Poles
and Ukrainians
, contributing to the economic and cultural development of the city. Nowadays, only smaller numbers of foreign immigrants arrive, mainly from Middle Eastern and South American countries, but there is a substantial inward flow of Brazilians from other states of the country (approximately half the population of Curitiba was not born in the city).
In 2010 Curitiba was awarded the Globe Sustainable City Award which was set up to recognize cities and municipalities which excel in sustainable urban development around the world. According to the American magazine Reader's Digest
, Curitiba is the best place to live in Brazil.
in the region prior to its foundation. The other version, also from the Tupi language, comes from the combination of kurit (pine tree) and yba (large amount).
The Portuguese who founded a village in 1693 gave it the name of "Vila da Nossa Senhora da Luz dos Pinhais" (Village of "Our Lady of the Light" of the Pines). The name was changed to "Curitiba" in 1721. Curitiba officially became a town in 1812, spelling its name as Curityba. An alternative spelling also came up: Coritiba. This spelling looked to become dominant for it was used in press and state documents, but a state decree in 1919 settled the dispute by spelling the city name Curitiba.
 Curitiba has a Maritime Temperate climate or Subtropical highland climate (Cfb), according to the Köppen classification.
Curitiba has a Maritime Temperate climate or Subtropical highland climate (Cfb), according to the Köppen classification.
Located in Southern Brazil, the humid city lies in a temperate zone. It is located on a plateau and the flat terrain with flooded areas contribute to its mild and damp winter, with average temperature of 7 °C (44.6 °F) in the coldest month, sometimes falling below 0 °C (32 °F) on the coldest nights. During summertime, the average temperature is around 18 °C (64.4 °F), but it can get above 30 °C (86 °F) on hottest days. Snowfall was experienced in 1889, 1892, 1912, 1928, 1942, 1955, 1957, 1962, 1975, 1979, 1981, 1984, 1987 and 1988.. Among Brazil's twenty-six state capitals, Curitiba is the coldest due its altitude, despite being 600 kilometres (372.8 mi) north of Porto Alegre
, which is the southernmost state capital in Brazil, but located at sea level. Heat waves during winter and cold wave
s during summer are not uncommon, and even within a single day there can be great variation, a typical feature of subtropical climates. Several factors contribute to the climate's variable nature: the flat terrain surrounded by mountains in a rough circle with radius 40 kilometres (24.9 mi) helps block the winds, allowing the morning mist to cover the city on cold mornings.
The flatness of the terrain hinders quick water drainage after rain, therefore providing a good source of water vapor for the atmosphere. Cold fronts come often from Antarctica and Argentina all year round, bringing tropical storms in summer and cold winds in the winter. They can move very quickly, with no more than one day between the start of the southern winds and the start of rain. Curitiba's weather is also influenced by the dry air masses that dominate Brazil's midwest most of the year, bringing cold and dry weather, sometimes even in winter.
 Curitiba is located in the area of the Ombrophilous Mixed Forest (also known as Araucaria moist forests
Curitiba is located in the area of the Ombrophilous Mixed Forest (also known as Araucaria moist forests
), a sub-type of the Atlantic Forest. In Curitiba it is possible to find steppes, Araucaria forest and other formations. In the local vegetation still appear remnants of the Paraná (or Brazilian) pine (Araucaria angustifolia
), which resisted the effects of modern civilization. The Parana pines are in private and public areas, now protected by environmental legislation which prevents them from being logged. The Municipal Secretariat of the Environment maintains a botanical garden and three green houses for the annual production of 150,000 seedlings of native and exotic tree species, 16,000 seedlings of fruit trees, 260,000 seedlings of flowers, foliage and underbrush, as well as the maintenance of 350,000 seedlings.
The total green area of Curitiba is one of the largest in cities in Brazil. The vegetation of Curitiba is also characterized by the existence of a large quantity of purple and yellow ipês (tabebuia
s), making a beautiful sight during the flowering at the end of winter. Currently, the yellow ipê is the most common tree in the city.
 The catchment area
The catchment area
of Curitiba consists of several rivers and streams that cross the city in different directions, grouped in six river basins. The main rivers that form the watershed
of the city are: Atuba River, Belém River, Barigüi River, Passaúna River, Ribeirão dos Padilhas and the Iguaçu River, all with characteristics of dendritic drainage. Since the 1970s, Curitiba has been working on alternatives to minimize the negative impacts of urbanization on rivers. An example of this was the construction of parks along the rivers with artificial lakes, which retain the water for longer periods of time, minimizing floods.
Currently, after many studies of the local water flows, almost all the rivers are subject to a canalization process. Other alternatives developed to minimize the effects of urbanization are the implementation of the programs for environmental education, inspection and monitoring, elaboration and application of legislation and infrastructure works. The index reaches 1500 millimetres (59.1 in) rainfall on average per year, because the rains are constant in the climate of the city. This happens, among other reasons, because of the deforestation of the Mountain Range of the Sea (Serra do Mar), a natural barrier to moisture.
 The city has surface of 432.17 km² in the First Plateau of Paraná. Curitiba has a topography of smooth rounded hills, giving a relatively regular shape. The municipality of Curitiba has an average altitude of 934.6 metres (3,066.3 ft) above sea level
The city has surface of 432.17 km² in the First Plateau of Paraná. Curitiba has a topography of smooth rounded hills, giving a relatively regular shape. The municipality of Curitiba has an average altitude of 934.6 metres (3,066.3 ft) above sea level
, where the highest point is to the north 1021 metres (3,349.7 ft), and with lower altitude 864 metres (2,834.6 ft) to the south.
There are mountain ranges and sets of rocky
hills practically all around the city, the most remarkable and impressive being the Serra do Mar (Portuguese for "Mountain Range of the Sea"), located in the east that separates the plateau from the coast of Paraná.
 The first ten years of the 16th century marked the beginning of a war of conquest of Europeans (Portuguese colonists) against the indigenous peoples who inhabited the area of the city. Waves of European immigrants started arriving after 1850, mainly Germans, Italians, Poles and Ukrainians. In 1853, the south and southwest of the province of São Paulo were separated, forming the new province of Paraná, and Curitiba became its capital.
The first ten years of the 16th century marked the beginning of a war of conquest of Europeans (Portuguese colonists) against the indigenous peoples who inhabited the area of the city. Waves of European immigrants started arriving after 1850, mainly Germans, Italians, Poles and Ukrainians. In 1853, the south and southwest of the province of São Paulo were separated, forming the new province of Paraná, and Curitiba became its capital.
Curitiba in 1820 received a visit from a French scholar, savant Saint-Hilaire, who was stunned with the city. Some excerpts from his notes state: "... The streets are wide and almost regular (...) the public square is organized, very large and covered with grass ... the churches are three in number, all built of stone ... not in any other part of Brazil I saw so many white people as I saw in Curitiba... they pronounce portuguese without the accent that reveals the race mixtures between the Caucasian race and the red ones... Curitibans are big and beautiful, have brown hair and rosy complexion, pleasing ... women are more delicate than in other parts of the Empire where I traveled . They do not hide and speak with ease. "[36] This description is a reflection of civility, nobility and determination of the people of Curitiba in 1820, which forms the basis of Curitiba in the twenty-first century and so on.
During the 20th century, especially after 1950, the city rapidly increased in population and consolidated its position as regional hub for trade and services, becoming one of the richest cities in Brazil and a pioneer in urban solutions. In the 1940s and 1950s, Alfred Agache
, co-founder of the French Society for Urban Studies, was hired to produce the first city plan
.
It emphasised a "star" of boulevard
s, with public amenities downtown, an industrial district and sanitation. It was followed when possible, but was too expensive to complete.
was the capital of Brazil. The government of the Federative Republic of Brazil was settled in the Iguaçu palace under the presidency of Marshal Arthur da Costa e Silva.
 The executive
The executive
is currently exercised by the mayor Beto Richa (elected in 2004 with a mandate until 2008, and reelected in 2009 to period 2009/2012), by the deputy mayor (vice mayor) Luciano Ducci and the municipal secretaries appointed by the mayor. The City Council
of Curitiba was created in 1693, and has a total of 38 councillors elected since 2004.
Curitiba is divided into nine regional governments (equivalent to subprefecture
), who manage the 75 districts of the municipality. The Rua da Cidadania ("Street of Citizenship") is the symbol of administrative decentralization; it is a reference point and meeting place for the user of municipal utilities, in a regional context, taking into account the needs and rights of the citizen in trade, leisure and services, facilitating the access of the population for different services in the areas of health, justice, policing, education, sport, house, environment, urban planning
, social service and supply, etc. Several units work annexed to the terminals of public transport in Curitiba. Their nuclei offer services in the local, state and federal
areas.


 According to the IBGE of 2008, there were 3,225,000 people residing in the Metropolitan Region of Curitiba. The population density was 4159.4 PD/sqkm (in the urban area). The last PNAD (National Research for Sample of Domiciles) census revealed the following percentage: 2,459,000 White
According to the IBGE of 2008, there were 3,225,000 people residing in the Metropolitan Region of Curitiba. The population density was 4159.4 PD/sqkm (in the urban area). The last PNAD (National Research for Sample of Domiciles) census revealed the following percentage: 2,459,000 White
people (76.27%), 640,000 Brown (Multiracial) people (19.84%), 92,000 Black
people (2.86%), 26,000 Asian
people (0.80%), 6,000 Amerindian
people (0.18%).
As most of Southern Brazil's population, Curitiba is mostly inhabited by Brazilians of European descent. The first Europeans to arrive in the region were of Portuguese origin, during the 17th century. They intermarried
with the native people
and with the African slaves.
In the 19th century, the influx of immigrants from Europe increased. In 1828, the first German immigrants
settled in Paraná. However, large numbers of immigrants from Germany only arrived in Curitiba during the 1870s, most of them coming from Santa Catarina
or Volga German
s from Russia.
Immigrants from Poland first arrived in 1871, settling in rural areas close to Curitiba. They largely influenced the agriculture of the region. Curitiba has the second largest Polish diaspora
in the world, second only to Chicago.
The Memorial of Polish Immigration was inaugurated on 13 December 1980, after the visit of the Pope John Paul II
to the city of Curitiba, in June, in the same year. Its area is 46 thousand square meters and was part of the former Candles plant. The seven wooden log houses are parts of this memorial area, as a souvenir of the Polish immigrants, and their struggles and faith. Objects like the old wagon, the pipe of cabbage and the print of the black virgin of Częstochowa, who is the patron saint of Polish people, form parts of the memorial.
Italian immigrants
started arriving in Brazil in 1875 and in Curitiba in 1878. They came mostly from the Veneto
and Trento
regions, in Northern Italy
and settled mostly in the Santa Felicidade neighborhood, still today the center of the large Italian community of Curitiba.
Large numbers of Ukrainian
immigrants settled in Curitiba, mostly between 1895 and 1897, when some 20,000 arrived. They were peasants from Galicia, who emigrated to Brazil to become farmers. Nowadays there are around 300,000 Ukrainian-Brazilians living in Paraná. The State of Paraná has the largest Ukrainian community
and Slavic community of the country.
Curitiba has a well established Jewish community originally established in the 1870s. Much of the early Jewish congregation has been assimilated. In 1937 with the conquest of power by the Nazis in Germany, several notable German Jewish academics were allowed into Brazil, some of them settling in Curitiba.
Physicist César Lattes
and former mayors Jaime Lerner
, and Saul Raiz were Jewish. A monument in memory of the Holocaust has been erected in the city. There is also a community center
, a Habad house (Beit Chabad) in Curitiba as well as at least two synagogues and two Jewish cemeteries, one of which was defiled in 2004.
Japanese immigrants began arriving in the region in 1915. Most Japanese settled in the State of São Paulo, but many settled in Northern Paraná, cities such as Maringá
and Londrina
. Curitiba also received significant numbers of immigrants from Japan. Nowadays, there are about 40,000 Japanese-Brazilians living in the city.
Other immigrants, such as Lebanese
, Syrians
, Palestinians
, Russians
and other Eastern Europeans also settled in Curitiba.
 Since it was declared the capital of the State of Paraná in 1853, the city has gone through several major urban planning projects to avoid uncontrolled growth and thus has become an international role model in dealing with such sensitive issues as transportation and the environment. The city is the second largest car manufacturer in the country, and its economy is based on industry, commerce and services. For that reason, Curitiba is considered by many specialists of the financial sector to be the best location for investors in Brazil. At the moment, the city receives more than two million tourists every year. Most arrive via Afonso Pena International Airport, where almost sixty thousand airplanes land annually.
Since it was declared the capital of the State of Paraná in 1853, the city has gone through several major urban planning projects to avoid uncontrolled growth and thus has become an international role model in dealing with such sensitive issues as transportation and the environment. The city is the second largest car manufacturer in the country, and its economy is based on industry, commerce and services. For that reason, Curitiba is considered by many specialists of the financial sector to be the best location for investors in Brazil. At the moment, the city receives more than two million tourists every year. Most arrive via Afonso Pena International Airport, where almost sixty thousand airplanes land annually.
According to IPEA data, the GDP in 2006 at real 32 billion, without recording activities in the agriculture and livestock farming (0.03%) sectors. Industry represented 34.13% and the commerce and service sectors 65.84%. Cidade Industrial de Curitiba, the industrial district of Curitiba, is home to many multinational industries, such as Nissan, Renault
, Volkswagen
, Audi
, Volvo
, HSBC
, Siemens
, ExxonMobil
, Electrolux
and Kraft Foods
, as well as many well known national industries, such as Sadia
, O Boticário, Positivo Informática. Curitiba's infrastructure makes bus travel fast and convenient, effectively creating demand for bus use in the same way that the infrastructure of traditional cities creates demand for private motor vehicles. In July 2001, Curitiba has become the first city in the country to receive the prize "Pole of Information Technology", granted by InfoExame magazine, because the performance of their companies of technology. According to the magazine, the number of companies of "Technology and Information Technology" based in Curitiba submitted in 2001 a turnover of US$ 1.2 billion, representing a growth of 21% over the previous year.
 In the early 1970s, when Brazil was welcoming industry with open arms, Curitiba accepted only non-polluters and constructed an industrial district
In the early 1970s, when Brazil was welcoming industry with open arms, Curitiba accepted only non-polluters and constructed an industrial district
with so much green space that it was derided as a "golf course" until it filled up with major businesses while its counterparts in other Latin American cities flagged. The city's 30-year economic growth rate is 7.1%, higher than the national average of 4.2%, and per capita income is 66% higher than the Brazilian average. Between 1975 and 1995, Curitiba's domestic product grew by some 75% more than the entire State of Paraná, and 48% more than Brazil as a whole. In 1994, tourism generated US$ 280 million, 4% of the city's net income. Curitiba has municipal health, education and day care networks, neighbourhood libraries shared by schools and citizens, and Citizenship Streets, where buildings provide essential public services, sports and cultural facilities near mass transportation terminals. At the Open University, residents can take courses in subjects such as mechanics, hair styling and environmental protection for a small fee. Policies for job creation and income generation also became part of the city's strategic planning
in the '90s, for the metropolitan area as well as the city.
Since 1990, the Municipal Housing Fund has been providing financial support to housing for lower income populations. After national housing finance collapsed in 1985, just as people from the countryside poured into Curitiba, the city's public housing program bought one of the few remaining large plots of land, "Novo Bairro" (New Neighborhood), as home for 50,000 families. While landowners built the houses themselves, each received a pair of trees and an hour's consultation with an architect to help them develop their plan. COHAB also built Technology Street, an avenue of 24 homes in the centre of Novo Bairro, each built using different construction techniques.
There are also six massive shopping malls in Curitiba shopping: Mueller, Estação, Curitiba, Crystal, Palladium and Park Barigüi. The Mueller is one of the best shopping malls, coupled with Crystal, which is a high class, haute-couture based mall. Curitiba and Estação are smaller, while less expensive kinds of shopping malls, and the newer one, Palladium, is one of the biggest. The Rua das Flores (Flower's Street) is the home of the majority of stores in Curitiba, and this is so for a very good reason. The area is pedestrianized, thus there are no cars around the centre. An essential element of Curitiba shopping is the Feira do Largo da Ordem, or Largo da Ordem Street Fair, where Paraná fashion, Curitiba gemstones, Brazil furniture Curitiba-made, Curitiba Brazil leather equipment, crafts, arts etc. can be found.
The GDP for the city is R$ 32,153,307,000 (2006).
The per capita income for the city was R$ 17,977 (2006).




 Botanic Gardens
Botanic Gardens
Curitiba's trademark, created to resemble French gardens, rolls out its flower carpet to the visitors right at the entrance. The greenhouse, with a metallic structure, has botanic species that are national symbols, and also a water fountain.
The native forest is filled with paths for walking. The Botanic Museum attracts researchers from all over the world, and has library and a theatre as well as a space for exhibitions.
The city recycles 70 percent of its paper and 60 percent of metal, glass and plastic.The previous garbage dump has become a botanical garden.:(from oxford university press,environmental studies from crisis to cure)
German Woods
The wood has various features to celebrate and promote the German
traditions. There are 38 thousand square meters of native forest, which was part of the old farm from the Schaffer family. The replica of an old wooden church, built in 1933 at the Seminário neighbourhood, with neo-gothic decorative elements, shelters a concert hall called Bach's Oratorium.
Other attractions are the John and Mary path, which tells the Grimm brothers tale, a children's library, the Philosophers Tower, a wooden observatory allowing a panoramic view of the city and the Ocean Ridge, and the German Poetry Square, with a reproduction of the Casa Mila façade, a German building from the beginning of the last century, originally located in the city centre.
It's closed for remodeling at the present time.
Italian Woods
A place for the typical parties of the Italian community in the district, such as the Grape
Party, the Wine Party and the 4 Giorni in Italy. It has structure for food and drink stalls, space for shows and folkloric presentations and a polenta pot.
Japan Square
Homage to Japanese immigrants who settled there dedicating themselves to agriculture. Scattered around the square are 30 cherry trees sent from Japan and artificial lakes. In 1993 the Japanese Portal, the Culture House and the Tea House were built.
Tingüi Park
Part of the biggest linear environmental park in the Country, established at the Barigüi river margins, it reminds us of the Indians who used to live there, with the statue of Tindiqüera Chieftain. The Ukrainian Memorial is also there, homage to the immigrants, in a replica of an orthodox church, originally built in inland Paraná State, hosting a pêssankas and icons exhibition.
Wire Opera House
It is one of the emblematic symbols of Curitiba, with tubular structure and transparent ceiling, of great beauty. Inaugurated in 1992, it caters for all types of shows, between lakes, typical vegetation and cascades, on a unique landscape. The Wire Opera House
is part of the Pedreiras Park, together with the Paulo Leminski Cultural Space, where the Passion of Christ was enacted, and hosted many other big events since 1989, and can hold, in the open air, 10 thousand people seated or 50 thousand standing.
Tanguá Park
This park was inaugurated in 1996, the Tanguá Park surprises with its beauty as an example of urban space being re-utilized, on one old complex of disactivated quarries, and it is part of the Barigüi river preservation project joining Tingüi and Barigüi parks. This park with an area of 450 thousand square meters has two quarries connected by a 45 meter tunnel that may be crossed on foot by a path over the water. It can be visited on boat or on foot (hiking).
The park has a cooper and bicycle track, snack bar, belvedere and Poty Lazzaroto garden.
Portugal Wood
Homage to the Portuguese-Brazilian
bonds, this space is highlighted by a track following a small brook, where one can see drawn on tiles excerpts from famous Portuguese language poets, as well as a tribute to the great Portuguese navigators and their discoveries.
Curitiba International Ecological Marathon
The Maratona Ecológica Internacional de Curitiba ("Curitiba International Ecological marathon
")is held in November and is known as the hardest in Brazil, because it happens in the end of the year in the summer heat, and because of the hilly course. To compensate the hard course, runners count with good structure and enthusiastic fans cheering along the course.
Tourism Line
Every year, tourism grows in Curitiba. To attend this demand, the Linha Turismo ("Tourism Line") started in 1994. Its a special city tour that visits the principal tourist attractions in Curitiba, featuring comfortable green with big windows and a shape similar to that of streetcars. The vehicles are equipped with a sound system that plays recorded messages describing sites in three different languages: Portuguese, English and Spanish. It is possible to visit the parks, town squares and the rest of the city's tourist attractions. Considered one of the best in the country, the Linha Turismo is available every thirty minutes and has a two and a half-hour tour, which travels around forty-four kilometers. To go on the tour you must buy a ticket with five tickets that give you the right to get on and off bus four times. Users can therefore choose the touristic point where they want to stay longer. Then, they can embark again to complete the remaining part of the itinerary. Today the line goes to 25 key reference points in Curitiba, completing 44 km (27 mi) in 2 and ½ hours.

s are free educational centers which include libraries
, Internet access, and other cultural resources. This community libraries works with municipal schools, have a collection of approximately 5000 books, and be cultural reference and leisure for the community, and are designed to diversify the opportunities of access to knowledge
, expanding the area of formal education.
In each quarter of the city these "Lighthouses of Knowledge" have been implanted containing library and room of computer science, to public use, mainly by students; job training, social welfare and educational programs are coordinated, and often supply labor to improve the city's amenities or services, as well as education and income. Among the Brazilian capitals, Curitiba has the lowest rate of illiteracy, and also number 1 in education between the Brazilian capitals.


 Curitiba has a planned transportation system, which includes lanes on major streets devoted to a bus rapid transit
Curitiba has a planned transportation system, which includes lanes on major streets devoted to a bus rapid transit
system. The buses are long, split into three sections (bi-articulated
), and stop at designated elevated tubes, complete with disabled access. There is only one price no matter how far you travel and you pay at the bus stop.
The system, used by 85% of Curitiba's population, is the source of inspiration for the TransMilenio
in Bogotá
, Colombia; Metrovia
in Guayaquil
, Ecuador; Transmetro
in Guatemala City
, Guatemala; Metrobus
in Mexico City
; as well as the Orange Line
of Los Angeles, U.S. State of California
, and for a future transportation system in Panama City
, Panama, Cebu City
, Philippines and the latest, Kuala Lumpur
, Malaysia.
The city has also paid careful attention to preserving and caring for its green areas, boasting 51.5 square metres (554.3 sq ft) of green space per inhabitant.
In the 1940s and 1950s, Alfred Agache
, cofounder of the French Society for Urban Studies, was hired to produce the first city plan. It emphasised a star of boulevards, with public amenities downtown, an industrial district and sanitation. It was followed when possible, but was too expensive to complete.
By the 1960s, Curitiba's population had ballooned to 430,000, and some residents feared that the growth in population threatened to drastically change the character of the city. In 1964, Mayor Ivo Arzua solicited proposals for urban design. Architect Jaime Lerner
, who later became mayor, led a team from the Universidade Federal do Paraná
that suggested strict controls on urban sprawl, a reduction of traffic in the downtown area, preservation of Curitiba's Historic Sector, and a convenient and affordable public transit system.
This plan, known as the Curitiba Master Plan, was adopted in 1968. Lerner closed XV de Novembro St.
to vehicles, because it had very high pedestrian traffic. The plan had a new road design to minimise traffic: the Trinary Road System. This uses two one-way streets moving in opposite directions which surround a smaller, two-lane street where the express buses have their exclusive lane. Five of these roads form a star that converges on the city centre. Land farther from these roads is zoned for lower density developments, to reduce traffic away from the main roads. In a number of areas subject to floods, buildings were condemned and the land became parks.
Today, Curitiba is considered one of the best examples of urban planning worldwide. In June 1996, the chairman of the Habitat II
summit of mayors and urban planners in Istanbul
praised Curitiba as "the most innovative city in the country."
Curitiba was recently recommended by UNESCO
as a model for the reconstruction of the cities of Afghanistan
, after the U.S invaded in 2001.
In the 1980s, the RIT (Rede Integrada de Transporte
, Integrated Transport Network) was created, allowing transit between any point in the city by paying just one fare. At the same time, the city began a project called the "Faróis de Saber" (Lighthouses of Knowledge). These Lighthouses are free educational centers which include libraries
, Internet access, and other cultural resources. Job training, social welfare and educational programs are coordinated, and often supply labor to improve the city's amenities or services, as well as education and income.
Curitiba is referred to as the ecological capital of Brazil, with a network of 28 parks and wooded areas. In 1970, there was less than 1 square meter of green space per person; now there are 52 square meters for each person. Residents planted 1.5 million trees along city streets. Builders get tax breaks if their projects include green space. Flood waters diverted into new lakes in parks solved the problem of dangerous flooding, while also protecting valley floors and riverbanks, acting as a barrier to illegal occupation, and providing aesthetic and recreational value to the thousands of people who use city parks.
In 2007, the city was placed third in a list of "15 Green Cities" in the world, according the U.S. magazine "Grist", after Reykjavik
in Iceland and Portland, Oregon
in the United States. As a result, according to one survey, 99% of Curitibans are happy with their hometown. The "green exchange" employment program focuses on social inclusion, benefiting both those in need and the environment. Low-income families living in shantytowns unreachable by truck bring their trash bags to neighborhood centers, where they exchange them for bus tickets and food. This means less city litter and less disease, less garbage dumped in sensitive areas such as rivers and a better life for the undernourished poor. There's also a program for children where they can exchange recyclable garbage for school supplies, chocolate, toys and tickets for shows.
Jaime Lerner suggests urban acupuncture
as the future solution for contemporary urban issues; by focusing on very narrow pressure points in cities, we can initiate positive ripple effects for the greater society. Urban acupuncture reclaims the ownership of land to the public and emphasizes the importance of community development through small interventions in design of cities.It involves pinpointed interventions that can be accomplished quickly to release energy and create a positive ripple effect.
He described in 2007:
I believe that some medicinal “magic” can and should be applied to cities, as many are sick and some nearly terminal. As with the medicine needed in the interaction between doctor and patient, in urban planning it is also necessary to make the city react; to poke an area in such a way that it is able to help heal, improve, and create positive chain reactions. It is indispensable in revitalizing interventions to make the organism work in a different way.
Under the "garbage that's not garbage" program, 70% of the city's trash is recycled by its residents. Once a week, a truck collects paper, cardboard, metal, plastic and glass that has been sorted in the city's homes. The city's paper recycling
alone saves the equivalent of 1,200 trees a day. As well as the environmental benefits, money raised from selling materials goes into social programs, and the city employs the homeless and recovering alcoholics in its garbage separation plant. Open University, created by the city, lets residents take courses in many subjects such as mechanics, hair styling and environmental protection for a small fee. Retired city buses are often used as mobile schools or offices. Downtown areas were transformed into pedestrian streets, including a 24-hour mall with shops, restaurants and cafes, and a street of flowers with gardens tended by street kids.
The "capacity building job line" was created to generate a better quality of life
for people in the region surrounding a new economic development axis of Curitiba. Key initiatives include the South-Circular bus line, which links the southern and eastern regions of town; Entrepreneurial Sheds, business incubators designed to help small companies get established and prosper; and the Crafts Lycée, which trains people for profession
s such as marketing and finance so that they can find employment in new companies that emerge from the business incubator
. Specifically, the goal is to provide jobs and income for the unemployed among 400,000 people living in 15 peripheral towns, and to structure and develop the region according to integrated planning principles. About 15,000 new jobs have been generated so far, and 15,000 more are expected.
There's a model, inexpensive, speedy transit service used by more than 2 million people a day. There are more car owners per capita than anywhere else in Brazil, and the population has doubled since 1974, yet auto traffic has declined by 30%, and atmospheric pollution is the lowest in Brazil.


It is in the Palladium Shopping Center which is the biggest mall in Southern Brazil. Curitiba also has many theaters. The biggest and most important one is the Guaíra Theater. Every year, in April, it hosts the Curitiba Theater Festival, with various artists playing in Curitiba Theaters and even on the squares.
Curitiba became the home to his extravagantly designed museum, the state museum of Curitiba. Its design includes a gravity defying construction that was intended to look like a Paraná Pine
, one of the city's symbols, but is widely interpreted by locals as an eye which gave the Museum its nickname – Museu do Olho, or Museum of the Eye. In keeping with the Curitiba history and culture of science, the museum offers many science exhibitions, including Curitiba biennal/Curitiba biennial, twice-yearly exhibitions. The Curitiba museum also includes the Oscar Niemeyer Curitiba auditorium.
Curitiba is unique and, as a result, extremely different from the carnivals held elsewhere in the country, and especially the ones that are so prevalent on any TV coverage of the carnival that occurs in Rio de Janeiro
, Salvador
, and Recife
every single year. Carnival Curitiba is in fact non-existent in terms of the way that it is done elsewhere. The carnival in Curitiba that does occur every year, in March to be precise to coincide with the Rio de Janeiro carnival, consists of a small celebration
on the coast. The beaches that are an hour away via car in Paranaguá
host the miniature carnival Curitiba celebrations. There is usually traditional Brazilian food like "Feijoada
", their special hotdog
s and a variety of salads on offer from stalls. The revellers will usually dance the "samba
" and mingle before heading home after the party in the early hours of the morning. The carnival Curitiba offers is therefore out of the town and gives those that do not wish to attend a break. Three clubs are renowned for their carnival Curitiba celebrations: Santa Mônica, Paraná and Curitibano (the most traditional one). They are all located within easy distance of the Central area. The costumes are readily available from most of the cheaper clothes stores and can be hired out from a variety of shops, as well as smaller independent ones in the weeks leading up to the celebrations for less than $20 for the night.
 On 20–31 March 2006 an important world gathering of the United Nations on biodiversity
On 20–31 March 2006 an important world gathering of the United Nations on biodiversity
took place in Pinhais (a city near Curitiba), addressing items of the 1993 Convention on Biological Diversity adopted by 188 countries. This convention seeks to discuss strategies to safeguard life from the threats to its existence. Starting with the Summit of the Earth or Rio de Janeiro
Eco-92 the topic has been gaining centrality and has been the subject of numerous official documents, especially the 2000 and 2003 Cartagena Protocols on biosecurity
. The Curitiba preparatory document, developed by specialists of the UN and of the Brazilian Ministry of the Environment for issues from Brazil, defines biodiversity
as follows: including all the different species
of plants, animals and microorganism
s (estimated at more than 10 million species), all the genetic variability within the species (10 to 100 genes per species) and all the diverse ecosystems formed by different combinations of species. Biodiversity includes the environmental services responsible for maintenance of life on Earth, for the interaction between living beings and for the offer of goods and services that sustain human societies and their economies.

, developed locally and causing much interest worldwide. This Bus Rapid Transit
system is very simple and practical. Public transportation consists entirely of buses. There are several different types of bus, each with a different function. All stations are easily accessed and enclosed. The buses have been changed to make for easier entry and exit. Together with other low-cost changes, this bus system aims at becoming a comfortable and preferred transportation choice for the public.
The popularity of Curitiba's BRT has effected a modal shift from automobile travel to bus travel. Based on 1991 traveller survey results, it was estimated that the introduction of the BRT had caused a reduction of about 27 million auto trips per year, saving about 27 million liters of fuel annually. In particular, 28 percent of BRT riders previously traveled by car. Compared to eight other Brazilian cities of its size, Curitiba uses about 30 percent less fuel per capita, resulting in one of the lowest rates of ambient air pollution in the country. Today about 1,100 buses make 12,500 trips every day, serving more than 1.3 million passengers, 50 times the number from 20 years ago. Eighty percent of travelers use the express or direct bus services. Best of all, Curitibanos spend only about 10 percent of their income on travel, much below the national average.
Curitiba's Master Plan integrated transportation with land use planning, calling for a cultural, social, and economic transformation of the city. It limited central area growth, while encouraging commercial growth along the transport arteries radiating out from the city center. The city center was partly closed to vehicular traffic, and pedestrian
streets were created. Linear development along the arteries reduced the traditional importance of the downtown area as the primary focus of day-to-day transport activity, thereby minimizing congestion and the typical morning and afternoon flows of traffic. Instead, rush hour in Curitiba has heavy commuter movements in both directions along the public transportation arteries.
Other policies have also contributed to the success of the transit system. Land within two blocks of the transit arteries is zoned for high density, since it generates more transit ridership per square foot. Beyond the two blocks, zoned residential densities taper in proportion to distance from transitways. Planners discourage auto-oriented centers and channel new retail growth to transit corridors. Very limited public parking is available in the downtown area, and most employers offer transportation subsidies, especially to low-skilled and low-paid employees.

 Moving around in a car can be difficult in and around the city centre because of the many one-way streets and frequent traffic jams. This makes the public transportation system more attractive if one wants to go there. The Trinary Road System allows quick access to the city centre for car drivers. Some avenues are spacious and laid out in a grid and apart from some points around the city centre, Munhoz da Rocha Street and Batel Avenue, traffic jams are not thus severe.Coming from São Paulo
Moving around in a car can be difficult in and around the city centre because of the many one-way streets and frequent traffic jams. This makes the public transportation system more attractive if one wants to go there. The Trinary Road System allows quick access to the city centre for car drivers. Some avenues are spacious and laid out in a grid and apart from some points around the city centre, Munhoz da Rocha Street and Batel Avenue, traffic jams are not thus severe.Coming from São Paulo
use BR-116 South. From Florianópolis
use BR-101. From Porto Alegre
use BR-116 North.
Recently, the city installed around 140 traffic radars
, causing much discontent among drivers in general.
It has perhaps the best world's public transport system,with clean and efficient buses carrying 1.9 million passengers(75 percent of all commuters) every day at low cost.The bus runs on high speed,dedicated lanes.
Five major roads penetrate into the heart of the city,with two bus lanes.The bus stops are connected to bicycle paths,which extended to 160 km (99.42 mi) into the city.
is Curitiba's main airport. It is located in the nearby city of São José dos Pinhais
and all commercial flights operate from this airport. It is integrated into Curitiba's transportation system, with rapid buses and shuttle service connecting the airport to the city.
Bacacheri Airport
is a smaller facility used for general aviation.
s are issued yearly, even though there are more than 40,000 existing traffic signs in all the city.
play at Estádio Major Antônio Couto Pereira, Clube Atlético Paranaense
at Estádio Joaquim Américo Guimarães and Paraná Clube
at Estádio Durival Britto e Silva
. Both Coritiba and Atlético Paranaense have won Campeonato Brasileiro Série A
, in 1985 and 2001, respectively. Estádio Joaquim Américo Guimarães will be one of the 12 stadia to host games of the 2014 FIFA World Cup
to be held in Brazil.
The Autódromo Internacional de Curitiba
(Curitiba International Raceway) is located in nearby Pinhais
.
Curitiba house one of the most famous Vale Tudo training camps in the world since the late 1990s and early years of the millennium named Chute Boxe Academy. Noted fighters to come from Chute Boxe include Wanderlei Silva, Anderson Silva, Murilo and Mauricio Rua.
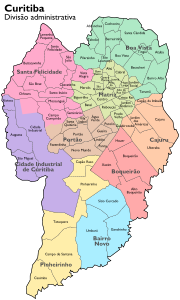 Bairros (neighbourhoods) of Curitiba are geographical divisions of the city. There is no delegation of administrative powers to neighborhoods, although there are several neighborhood associations devoted to improve their own standards of living.
Bairros (neighbourhoods) of Curitiba are geographical divisions of the city. There is no delegation of administrative powers to neighborhoods, although there are several neighborhood associations devoted to improve their own standards of living.
Curitiba is divided into 9 regional governments (boroughs) covering the 75 neighbourhoods of the city. All districts are served by the system of integrated urban transport.
Most districts of Curitiba was born of colonial groups formed by families of European immigrants in the second half of the nineteenth century.
The centro ("Downtown" in American English
or "CBD" – central business district – in other English use), place of foundation of the city, is the most bustling area, which concentrates most of the financial institutions of Curitiba.
List of neighborhoods by regional:
with:
 Curitiba is mostly known for some of its famous places:
Curitiba is mostly known for some of its famous places:




Mixed martial arts
Motorsports
Basketball
Beach Volleyball
Poker
Official homepage
Paraná (state)
Paraná is one of the states of Brazil, located in the South of the country, bordered on the north by São Paulo state, on the east by the Atlantic Ocean, on the south by Santa Catarina state and the Misiones Province of Argentina, and on the west by Mato Grosso do Sul and the republic of Paraguay,...
. It is the largest city with the biggest economy of both Paraná and southern Brazil. The population of Curitiba numbers approximately 1.75 million people (8th largest nationwide) and the latest GDP figures for the city surpass US$61 billion (ranking 4th nationwide) according to IBGE
IBGE
The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics or IBGE , is the agency responsible for statistical, geographic, cartographic, geodetic and environmental information in Brazil...
(2008). Its metropolitan area comprises 26 municipalities with a total population of over 3.2 million (IBGE estimate in 2006).
Curitiba is an important cultural, political and economic centre in the country. The city sits on a plateau
Plateau
In geology and earth science, a plateau , also called a high plain or tableland, is an area of highland, usually consisting of relatively flat terrain. A highly eroded plateau is called a dissected plateau...
at 932 metres (3,057.7 ft) above sea level
Above mean sea level
The term above mean sea level refers to the elevation or altitude of any object, relative to the average sea level datum. AMSL is used extensively in radio by engineers to determine the coverage area a station will be able to reach...
. It is located 105 kilometres (65.2 mi) west of the sea port of Paranaguá
Paranaguá
Paranaguá is a city in the state of Paraná in Brazil. Founded in 1648, it is Paraná's oldest city.It is known for its excellent port facilities, being the sea port for Curitiba, the capital of Paraná....
and is served by the Afonso Pena International
Afonso Pena International Airport
Afonso Pena International Airport is the main airport serving Curitiba, Brazil, located in the adjoining municipality of São José dos Pinhais. It is named after Afonso Augusto Moreira Pena , the 6th President of Brazil....
and Bacacheri
Bacacheri Airport
Bacacheri Airport is an airport in Curitiba, Brazil. It is named after the neighborhood where it is located.It is operated by Infraero.-History:The history of Bacacheri airport begins in 1930 as an air field for Military Aviation...
airports. The city hosts the Federal University of Paraná, established in 1912, one year before electric streetcars were first deployed.
Curitiba's rapid expansion was based on the cattle trade, the city being located half-way between the cattle breeding country to the south and the markets to the north. Waves of European immigrants started arriving after 1850, mainly Germans
German Brazilian
A German Brazilian is a Brazilian person of ethnic German ancestry or origin...
, Italians
Italian Brazilian
-Italian immigration to Brazil:The Italian government claims there are 25 million Brazilians of Italian descent, which would be the largest population of Italian background outside of Italy itself. There are no actual surveys, or even verifiable calculations supporting such claims. According to...
, Poles
Polish Brazilian
A Polish Brazilian is a Brazilian person of full or partial Polish ancestry, who is aware of such ancestry and remains connected, in some degree, to Polish culture, or a Polish-born person permanently residing in Brazil. The number of Polish descendants in Brazil is estimated at 1.8 million...
and Ukrainians
Ukrainians of Brazil
Ukrainians of Brazil are Brazilian citizens born in Ukraine, or Brazilians of Ukrainian descent who remain connected, in some degree, to Ukrainian culture...
, contributing to the economic and cultural development of the city. Nowadays, only smaller numbers of foreign immigrants arrive, mainly from Middle Eastern and South American countries, but there is a substantial inward flow of Brazilians from other states of the country (approximately half the population of Curitiba was not born in the city).
In 2010 Curitiba was awarded the Globe Sustainable City Award which was set up to recognize cities and municipalities which excel in sustainable urban development around the world. According to the American magazine Reader's Digest
Reader's Digest
Reader's Digest is a general interest family magazine, published ten times annually. Formerly based in Chappaqua, New York, its headquarters is now in New York City. It was founded in 1922, by DeWitt Wallace and Lila Bell Wallace...
, Curitiba is the best place to live in Brazil.
Name
One theory about the name "Curitiba" comes from the Tupi words kurí tyba, "many pine seeds" due to the large number of pinecones of Paraná pinesAraucaria angustifolia
Araucaria angustifolia, the Paraná pine or Brazilian pine , is a species in the conifer genus Araucaria. Covering an original area of 233000 km², it is native to southern Brazil Araucaria angustifolia, the Paraná pine or Brazilian pine , is a species in the conifer genus Araucaria. Covering an...
in the region prior to its foundation. The other version, also from the Tupi language, comes from the combination of kurit (pine tree) and yba (large amount).
The Portuguese who founded a village in 1693 gave it the name of "Vila da Nossa Senhora da Luz dos Pinhais" (Village of "Our Lady of the Light" of the Pines). The name was changed to "Curitiba" in 1721. Curitiba officially became a town in 1812, spelling its name as Curityba. An alternative spelling also came up: Coritiba. This spelling looked to become dominant for it was used in press and state documents, but a state decree in 1919 settled the dispute by spelling the city name Curitiba.
Climate

Located in Southern Brazil, the humid city lies in a temperate zone. It is located on a plateau and the flat terrain with flooded areas contribute to its mild and damp winter, with average temperature of 7 °C (44.6 °F) in the coldest month, sometimes falling below 0 °C (32 °F) on the coldest nights. During summertime, the average temperature is around 18 °C (64.4 °F), but it can get above 30 °C (86 °F) on hottest days. Snowfall was experienced in 1889, 1892, 1912, 1928, 1942, 1955, 1957, 1962, 1975, 1979, 1981, 1984, 1987 and 1988.. Among Brazil's twenty-six state capitals, Curitiba is the coldest due its altitude, despite being 600 kilometres (372.8 mi) north of Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre is the tenth most populous municipality in Brazil, with 1,409,939 inhabitants, and the centre of Brazil's fourth largest metropolitan area . It is also the capital city of the southernmost Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul. The city is the southernmost capital city of a Brazilian...
, which is the southernmost state capital in Brazil, but located at sea level. Heat waves during winter and cold wave
Cold wave
A cold wave is a weather phenomenon that is distinguished by a cooling of the air. Specifically, as used by the U.S. National Weather Service, a cold wave is a rapid fall in temperature within a 24 hour period requiring substantially increased protection to agriculture, industry, commerce, and...
s during summer are not uncommon, and even within a single day there can be great variation, a typical feature of subtropical climates. Several factors contribute to the climate's variable nature: the flat terrain surrounded by mountains in a rough circle with radius 40 kilometres (24.9 mi) helps block the winds, allowing the morning mist to cover the city on cold mornings.
The flatness of the terrain hinders quick water drainage after rain, therefore providing a good source of water vapor for the atmosphere. Cold fronts come often from Antarctica and Argentina all year round, bringing tropical storms in summer and cold winds in the winter. They can move very quickly, with no more than one day between the start of the southern winds and the start of rain. Curitiba's weather is also influenced by the dry air masses that dominate Brazil's midwest most of the year, bringing cold and dry weather, sometimes even in winter.
Vegetation

Araucaria moist forests
The Araucaria moist forests are a subtropical moist forest ecoregion of southern Brazil and northeastern Argentina.-Setting:The Araucaria moist forests cover an area of , encompassing a region of mountains and plateaus in the Brazilian states of São Paulo, Paraná, Santa Catarina, and Rio Grande do...
), a sub-type of the Atlantic Forest. In Curitiba it is possible to find steppes, Araucaria forest and other formations. In the local vegetation still appear remnants of the Paraná (or Brazilian) pine (Araucaria angustifolia
Araucaria angustifolia
Araucaria angustifolia, the Paraná pine or Brazilian pine , is a species in the conifer genus Araucaria. Covering an original area of 233000 km², it is native to southern Brazil Araucaria angustifolia, the Paraná pine or Brazilian pine , is a species in the conifer genus Araucaria. Covering an...
), which resisted the effects of modern civilization. The Parana pines are in private and public areas, now protected by environmental legislation which prevents them from being logged. The Municipal Secretariat of the Environment maintains a botanical garden and three green houses for the annual production of 150,000 seedlings of native and exotic tree species, 16,000 seedlings of fruit trees, 260,000 seedlings of flowers, foliage and underbrush, as well as the maintenance of 350,000 seedlings.
The total green area of Curitiba is one of the largest in cities in Brazil. The vegetation of Curitiba is also characterized by the existence of a large quantity of purple and yellow ipês (tabebuia
Tabebuia
Tabebuia is a neotropical genus of about 100 species in the tribe Tecomeae of the family Bignoniaceae. The species range from northern Mexico and southern Florida south to northern Argentina, including the Caribbean islands of Hispaniola and Cuba...
s), making a beautiful sight during the flowering at the end of winter. Currently, the yellow ipê is the most common tree in the city.
Hydrography and pluviometry

Drainage basin
A drainage basin is an extent or an area of land where surface water from rain and melting snow or ice converges to a single point, usually the exit of the basin, where the waters join another waterbody, such as a river, lake, reservoir, estuary, wetland, sea, or ocean...
of Curitiba consists of several rivers and streams that cross the city in different directions, grouped in six river basins. The main rivers that form the watershed
Drainage basin
A drainage basin is an extent or an area of land where surface water from rain and melting snow or ice converges to a single point, usually the exit of the basin, where the waters join another waterbody, such as a river, lake, reservoir, estuary, wetland, sea, or ocean...
of the city are: Atuba River, Belém River, Barigüi River, Passaúna River, Ribeirão dos Padilhas and the Iguaçu River, all with characteristics of dendritic drainage. Since the 1970s, Curitiba has been working on alternatives to minimize the negative impacts of urbanization on rivers. An example of this was the construction of parks along the rivers with artificial lakes, which retain the water for longer periods of time, minimizing floods.
Currently, after many studies of the local water flows, almost all the rivers are subject to a canalization process. Other alternatives developed to minimize the effects of urbanization are the implementation of the programs for environmental education, inspection and monitoring, elaboration and application of legislation and infrastructure works. The index reaches 1500 millimetres (59.1 in) rainfall on average per year, because the rains are constant in the climate of the city. This happens, among other reasons, because of the deforestation of the Mountain Range of the Sea (Serra do Mar), a natural barrier to moisture.
Relief

Above mean sea level
The term above mean sea level refers to the elevation or altitude of any object, relative to the average sea level datum. AMSL is used extensively in radio by engineers to determine the coverage area a station will be able to reach...
, where the highest point is to the north 1021 metres (3,349.7 ft), and with lower altitude 864 metres (2,834.6 ft) to the south.
There are mountain ranges and sets of rocky
Rocky
Rocky is a 1976 American sports drama film directed by John G. Avildsen and both written by and starring Sylvester Stallone. It tells the rags to riches American Dream story of Rocky Balboa, an uneducated but kind-hearted debt collector for a loan shark in the city of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania...
hills practically all around the city, the most remarkable and impressive being the Serra do Mar (Portuguese for "Mountain Range of the Sea"), located in the east that separates the plateau from the coast of Paraná.
History

Curitiba in 1820 received a visit from a French scholar, savant Saint-Hilaire, who was stunned with the city. Some excerpts from his notes state: "... The streets are wide and almost regular (...) the public square is organized, very large and covered with grass ... the churches are three in number, all built of stone ... not in any other part of Brazil I saw so many white people as I saw in Curitiba... they pronounce portuguese without the accent that reveals the race mixtures between the Caucasian race and the red ones... Curitibans are big and beautiful, have brown hair and rosy complexion, pleasing ... women are more delicate than in other parts of the Empire where I traveled . They do not hide and speak with ease. "[36] This description is a reflection of civility, nobility and determination of the people of Curitiba in 1820, which forms the basis of Curitiba in the twenty-first century and so on.
During the 20th century, especially after 1950, the city rapidly increased in population and consolidated its position as regional hub for trade and services, becoming one of the richest cities in Brazil and a pioneer in urban solutions. In the 1940s and 1950s, Alfred Agache
Alfred Agache (architect)
Alfred Hubert Donat Agache , sometimes called Alfredo Agache, formally planned the Brazilian cities of Rio de Janeiro, Recife, Porto Alegre and Curitiba in the 1940s and 1950s, supported by the Estado Novo fascist regime in Brazil...
, co-founder of the French Society for Urban Studies, was hired to produce the first city plan
Plan
A plan is typically any diagram or list of steps with timing and resources, used to achieve an objective. See also strategy. It is commonly understood as a temporal set of intended actions, through which one expects to achieve a goal...
.
It emphasised a "star" of boulevard
Boulevard
A Boulevard is type of road, usually a wide, multi-lane arterial thoroughfare, divided with a median down the centre, and roadways along each side designed as slow travel and parking lanes and for bicycle and pedestrian usage, often with an above-average quality of landscaping and scenery...
s, with public amenities downtown, an industrial district and sanitation. It was followed when possible, but was too expensive to complete.
Curitiba as the capital of Brazil
From 24 to 27 March 1969, CuritibaCuritiba
Curitiba is the capital of the Brazilian state of Paraná. It is the largest city with the biggest economy of both Paraná and southern Brazil. The population of Curitiba numbers approximately 1.75 million people and the latest GDP figures for the city surpass US$61 billion according to...
was the capital of Brazil. The government of the Federative Republic of Brazil was settled in the Iguaçu palace under the presidency of Marshal Arthur da Costa e Silva.
Government

Executive (government)
Executive branch of Government is the part of government that has sole authority and responsibility for the daily administration of the state bureaucracy. The division of power into separate branches of government is central to the idea of the separation of powers.In many countries, the term...
is currently exercised by the mayor Beto Richa (elected in 2004 with a mandate until 2008, and reelected in 2009 to period 2009/2012), by the deputy mayor (vice mayor) Luciano Ducci and the municipal secretaries appointed by the mayor. The City Council
City council
A city council or town council is the legislative body that governs a city, town, municipality or local government area.-Australia & NZ:Because of the differences in legislation between the States, the exact definition of a City Council varies...
of Curitiba was created in 1693, and has a total of 38 councillors elected since 2004.
Curitiba is divided into nine regional governments (equivalent to subprefecture
Subprefecture
Subprefecture is an administrative division of a country that is below prefecture or province.-Albania:There are twelve Albanian counties or prefectures, each of which is subdivided into several districts, sometimes translated as subprefectures.-Brazil:...
), who manage the 75 districts of the municipality. The Rua da Cidadania ("Street of Citizenship") is the symbol of administrative decentralization; it is a reference point and meeting place for the user of municipal utilities, in a regional context, taking into account the needs and rights of the citizen in trade, leisure and services, facilitating the access of the population for different services in the areas of health, justice, policing, education, sport, house, environment, urban planning
Urban planning
Urban planning incorporates areas such as economics, design, ecology, sociology, geography, law, political science, and statistics to guide and ensure the orderly development of settlements and communities....
, social service and supply, etc. Several units work annexed to the terminals of public transport in Curitiba. Their nuclei offer services in the local, state and federal
Federal republic
A federal republic is a federation of states with a republican form of government. A federation is the central government. The states in a federation also maintain the federation...
areas.
Demographics



White Brazilian
White Brazilians make up 48.4% of Brazil's population, or around 92 million people, according to the IBGE's 2008 PNAD . Whites are present in the entire territory of Brazil, although the main concentrations are found in the South and Southeastern parts of the country...
people (76.27%), 640,000 Brown (Multiracial) people (19.84%), 92,000 Black
Afro-Brazilian
In Brazil, the term "preto" is one of the five categories used by the Brazilian Census, along with "branco" , "pardo" , "amarelo" and "indígena"...
people (2.86%), 26,000 Asian
Asian Brazilian
An Asian Brazilian is is a Brazilian citizen of full or partial Asian ancestry, who remains culturally connected to Asia, or an Asian-born person permanently residing in Brazil. Brazil received many immigrants from Asia, both from Middle East and East Asia...
people (0.80%), 6,000 Amerindian
Indigenous peoples in Brazil
The Indigenous peoples in Brazil comprise a large number of distinct ethnic groups who inhabited the country prior to the European invasion around 1500...
people (0.18%).
As most of Southern Brazil's population, Curitiba is mostly inhabited by Brazilians of European descent. The first Europeans to arrive in the region were of Portuguese origin, during the 17th century. They intermarried
Interracial marriage
Interracial marriage occurs when two people of differing racial groups marry. This is a form of exogamy and can be seen in the broader context of miscegenation .-Legality of interracial marriage:In the Western world certain jurisdictions have had regulations...
with the native people
Indigenous peoples in Brazil
The Indigenous peoples in Brazil comprise a large number of distinct ethnic groups who inhabited the country prior to the European invasion around 1500...
and with the African slaves.
In the 19th century, the influx of immigrants from Europe increased. In 1828, the first German immigrants
German Brazilian
A German Brazilian is a Brazilian person of ethnic German ancestry or origin...
settled in Paraná. However, large numbers of immigrants from Germany only arrived in Curitiba during the 1870s, most of them coming from Santa Catarina
Santa Catarina (state)
Santa Catarina is a state in southern Brazil with one of the highest standards of living in Latin America. Its capital is Florianópolis, which mostly lies on the Santa Catarina Island. Neighbouring states are Rio Grande do Sul to the south and Paraná to the north. It is bounded on the east by...
or Volga German
Volga German
The Volga Germans were ethnic Germans living along the River Volga in the region of southern European Russia around Saratov and to the south. Recruited as immigrants to Russia in the 18th century, they were allowed to maintain German culture, language, traditions and churches: Lutherans, Reformed,...
s from Russia.
Immigrants from Poland first arrived in 1871, settling in rural areas close to Curitiba. They largely influenced the agriculture of the region. Curitiba has the second largest Polish diaspora
Polonia
The Polish diaspora refers to people of Polish origin who live outside Poland. The Polish diaspora is also known in modern Polish language as Polonia, which is the name for Poland in Latin and in many other Romance languages....
in the world, second only to Chicago.
The Memorial of Polish Immigration was inaugurated on 13 December 1980, after the visit of the Pope John Paul II
Pope John Paul II
Blessed Pope John Paul II , born Karol Józef Wojtyła , reigned as Pope of the Catholic Church and Sovereign of Vatican City from 16 October 1978 until his death on 2 April 2005, at of age. His was the second-longest documented pontificate, which lasted ; only Pope Pius IX ...
to the city of Curitiba, in June, in the same year. Its area is 46 thousand square meters and was part of the former Candles plant. The seven wooden log houses are parts of this memorial area, as a souvenir of the Polish immigrants, and their struggles and faith. Objects like the old wagon, the pipe of cabbage and the print of the black virgin of Częstochowa, who is the patron saint of Polish people, form parts of the memorial.
Italian immigrants
Italian Brazilian
-Italian immigration to Brazil:The Italian government claims there are 25 million Brazilians of Italian descent, which would be the largest population of Italian background outside of Italy itself. There are no actual surveys, or even verifiable calculations supporting such claims. According to...
started arriving in Brazil in 1875 and in Curitiba in 1878. They came mostly from the Veneto
Veneto
Veneto is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about 5 million, ranking 5th in Italy.Veneto had been for more than a millennium an independent state, the Republic of Venice, until it was eventually annexed by Italy in 1866 after brief Austrian and French rule...
and Trento
Trento
Trento is an Italian city located in the Adige River valley in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. It is the capital of Trentino...
regions, in Northern Italy
Northern Italy
Northern Italy is a wide cultural, historical and geographical definition, without any administrative usage, used to indicate the northern part of the Italian state, also referred as Settentrione or Alta Italia...
and settled mostly in the Santa Felicidade neighborhood, still today the center of the large Italian community of Curitiba.
Large numbers of Ukrainian
Ukrainians of Brazil
Ukrainians of Brazil are Brazilian citizens born in Ukraine, or Brazilians of Ukrainian descent who remain connected, in some degree, to Ukrainian culture...
immigrants settled in Curitiba, mostly between 1895 and 1897, when some 20,000 arrived. They were peasants from Galicia, who emigrated to Brazil to become farmers. Nowadays there are around 300,000 Ukrainian-Brazilians living in Paraná. The State of Paraná has the largest Ukrainian community
Ukrainians of Brazil
Ukrainians of Brazil are Brazilian citizens born in Ukraine, or Brazilians of Ukrainian descent who remain connected, in some degree, to Ukrainian culture...
and Slavic community of the country.
Curitiba has a well established Jewish community originally established in the 1870s. Much of the early Jewish congregation has been assimilated. In 1937 with the conquest of power by the Nazis in Germany, several notable German Jewish academics were allowed into Brazil, some of them settling in Curitiba.
Physicist César Lattes
César Lattes
Cesare Mansueto Giulio Lattes , also known as Cesar Lattes, was a Brazilian experimental physicist, one of the discoverers of the pion, a composite subatomic particle made of a quark and an antiquark.-Life:Lattes was born to a family of Italian Jewish immigrants in Curitiba, Southern Brazil...
and former mayors Jaime Lerner
Jaime Lerner
Jaime Lerner was governor of the state of Paraná, in southern Brazil. He is renowned as an architect and urban planner, having been mayor of Curitiba, capital of Paraná, three times...
, and Saul Raiz were Jewish. A monument in memory of the Holocaust has been erected in the city. There is also a community center
Centro Israelita do Paraná
The Centro Israelita do Paraná is the main gathering place for Jews in the city of Curitiba, Brazil.- History :The first Jew to arrive in Curitiba was José Flaks, who in 1889 arrived with his wife Roni and their children Michael and Frederick. Shortly thereafter came Max Rosenamn. Both were...
, a Habad house (Beit Chabad) in Curitiba as well as at least two synagogues and two Jewish cemeteries, one of which was defiled in 2004.
Japanese immigrants began arriving in the region in 1915. Most Japanese settled in the State of São Paulo, but many settled in Northern Paraná, cities such as Maringá
Maringá
Maringá is a city in southern Brazil that was founded on May 10, 1947. Maringá is the third largest city in the state of Paraná. The city has a population of 357,117 , 612,617 in its metropolitan area...
and Londrina
Londrina
Londrina is a city located in the northern region of the state of Paraná, Brazil, and is 369 km away from the capital, Curitiba. Londrina was originally founded by British settlers. The city exerts great influence on Paraná and Brazil's south region...
. Curitiba also received significant numbers of immigrants from Japan. Nowadays, there are about 40,000 Japanese-Brazilians living in the city.
Other immigrants, such as Lebanese
Lebanese Brazilian
A Lebanese Brazilian is a Brazilian person of full, partial, or predominantly Lebanese ancestry, or a Lebanese-born person immigrant in Brazil....
, Syrians
Syrian Brazilian
Syrian Brazilian is a Brazilian person of full, partial, or predominantly Syrian ancestry, or a Syrian-born person immigrant in Brazil....
, Palestinians
Palestinian Brazilian
Palestinian Brazilian is a Brazilian person of full, partial, or predominantly Palestinian ancestry, or a Palestinian-born person immigrant in Brazil.The group that headed to Rio Grande do Sul is distributed throughout six cities...
, Russians
Russian Brazilian
Russian Brazilian is a Brazilian person of full, partial, or predominantly Russian ancestry, or a Russian-born person residing in Brazil. The term can also refer to somomeone with a Brazilian mother and Russian father, or vice versa....
and other Eastern Europeans also settled in Curitiba.
Economy

According to IPEA data, the GDP in 2006 at real 32 billion, without recording activities in the agriculture and livestock farming (0.03%) sectors. Industry represented 34.13% and the commerce and service sectors 65.84%. Cidade Industrial de Curitiba, the industrial district of Curitiba, is home to many multinational industries, such as Nissan, Renault
Renault
Renault S.A. is a French automaker producing cars, vans, and in the past, autorail vehicles, trucks, tractors, vans and also buses/coaches. Its alliance with Nissan makes it the world's third largest automaker...
, Volkswagen
Volkswagen
Volkswagen is a German automobile manufacturer and is the original and biggest-selling marque of the Volkswagen Group, which now also owns the Audi, Bentley, Bugatti, Lamborghini, SEAT, and Škoda marques and the truck manufacturer Scania.Volkswagen means "people's car" in German, where it is...
, Audi
Audi
Audi AG is a German automobile manufacturer, from supermini to crossover SUVs in various body styles and price ranges that are marketed under the Audi brand , positioned as the premium brand within the Volkswagen Group....
, Volvo
Volvo
AB Volvo is a Swedish builder of commercial vehicles, including trucks, buses and construction equipment. Volvo also supplies marine and industrial drive systems, aerospace components and financial services...
, HSBC
HSBC
HSBC Holdings plc is a global banking and financial services company headquartered in Canary Wharf, London, United Kingdom. it is the world's second-largest banking and financial services group and second-largest public company according to a composite measure by Forbes magazine...
, Siemens
Siemens
Siemens may refer toSiemens, a German family name carried by generations of telecommunications industrialists, including:* Werner von Siemens , inventor, founder of Siemens AG...
, ExxonMobil
ExxonMobil
Exxon Mobil Corporation or ExxonMobil, is an American multinational oil and gas corporation. It is a direct descendant of John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil company, and was formed on November 30, 1999, by the merger of Exxon and Mobil. Its headquarters are in Irving, Texas...
, Electrolux
Electrolux
The Electrolux Group is a Swedish appliance maker.As of 2010 the 2nd largest home appliance manufacturer in the world after Whirlpool, its products sell under a variety of brand names including its own and are primarily major appliances and vacuum cleaners...
and Kraft Foods
Kraft Foods
Kraft Foods Inc. is an American confectionery, food and beverage conglomerate. It markets many brands in more than 170 countries. 12 of its brands annually earn more than $1 billion worldwide: Cadbury, Jacobs, Kraft, LU, Maxwell House, Milka, Nabisco, Oscar Mayer, Philadelphia, Trident, Tang...
, as well as many well known national industries, such as Sadia
Sadia
This Food Company was created in Concórdia, Santa Catarina, Brazil. Its headquarters are also located in the same city.Sadia S.A. is a major Brazilian food producer...
, O Boticário, Positivo Informática. Curitiba's infrastructure makes bus travel fast and convenient, effectively creating demand for bus use in the same way that the infrastructure of traditional cities creates demand for private motor vehicles. In July 2001, Curitiba has become the first city in the country to receive the prize "Pole of Information Technology", granted by InfoExame magazine, because the performance of their companies of technology. According to the magazine, the number of companies of "Technology and Information Technology" based in Curitiba submitted in 2001 a turnover of US$ 1.2 billion, representing a growth of 21% over the previous year.

Industrial district
Industrial district was initially introduced as a term to describe an area where workers of a monolithic heavy industry live within walking-distance of their places of work...
with so much green space that it was derided as a "golf course" until it filled up with major businesses while its counterparts in other Latin American cities flagged. The city's 30-year economic growth rate is 7.1%, higher than the national average of 4.2%, and per capita income is 66% higher than the Brazilian average. Between 1975 and 1995, Curitiba's domestic product grew by some 75% more than the entire State of Paraná, and 48% more than Brazil as a whole. In 1994, tourism generated US$ 280 million, 4% of the city's net income. Curitiba has municipal health, education and day care networks, neighbourhood libraries shared by schools and citizens, and Citizenship Streets, where buildings provide essential public services, sports and cultural facilities near mass transportation terminals. At the Open University, residents can take courses in subjects such as mechanics, hair styling and environmental protection for a small fee. Policies for job creation and income generation also became part of the city's strategic planning
Strategic planning
Strategic planning is an organization's process of defining its strategy, or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this strategy. In order to determine the direction of the organization, it is necessary to understand its current position and the possible avenues...
in the '90s, for the metropolitan area as well as the city.
Since 1990, the Municipal Housing Fund has been providing financial support to housing for lower income populations. After national housing finance collapsed in 1985, just as people from the countryside poured into Curitiba, the city's public housing program bought one of the few remaining large plots of land, "Novo Bairro" (New Neighborhood), as home for 50,000 families. While landowners built the houses themselves, each received a pair of trees and an hour's consultation with an architect to help them develop their plan. COHAB also built Technology Street, an avenue of 24 homes in the centre of Novo Bairro, each built using different construction techniques.
There are also six massive shopping malls in Curitiba shopping: Mueller, Estação, Curitiba, Crystal, Palladium and Park Barigüi. The Mueller is one of the best shopping malls, coupled with Crystal, which is a high class, haute-couture based mall. Curitiba and Estação are smaller, while less expensive kinds of shopping malls, and the newer one, Palladium, is one of the biggest. The Rua das Flores (Flower's Street) is the home of the majority of stores in Curitiba, and this is so for a very good reason. The area is pedestrianized, thus there are no cars around the centre. An essential element of Curitiba shopping is the Feira do Largo da Ordem, or Largo da Ordem Street Fair, where Paraná fashion, Curitiba gemstones, Brazil furniture Curitiba-made, Curitiba Brazil leather equipment, crafts, arts etc. can be found.
The GDP for the city is R$ 32,153,307,000 (2006).
The per capita income for the city was R$ 17,977 (2006).
Tourism and recreation





Curitiba's trademark, created to resemble French gardens, rolls out its flower carpet to the visitors right at the entrance. The greenhouse, with a metallic structure, has botanic species that are national symbols, and also a water fountain.
The native forest is filled with paths for walking. The Botanic Museum attracts researchers from all over the world, and has library and a theatre as well as a space for exhibitions.
The city recycles 70 percent of its paper and 60 percent of metal, glass and plastic.The previous garbage dump has become a botanical garden.:(from oxford university press,environmental studies from crisis to cure)
German Woods
The wood has various features to celebrate and promote the German
Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
traditions. There are 38 thousand square meters of native forest, which was part of the old farm from the Schaffer family. The replica of an old wooden church, built in 1933 at the Seminário neighbourhood, with neo-gothic decorative elements, shelters a concert hall called Bach's Oratorium.
Other attractions are the John and Mary path, which tells the Grimm brothers tale, a children's library, the Philosophers Tower, a wooden observatory allowing a panoramic view of the city and the Ocean Ridge, and the German Poetry Square, with a reproduction of the Casa Mila façade, a German building from the beginning of the last century, originally located in the city centre.
It's closed for remodeling at the present time.
Italian Woods
A place for the typical parties of the Italian community in the district, such as the Grape
Grape
A grape is a non-climacteric fruit, specifically a berry, that grows on the perennial and deciduous woody vines of the genus Vitis. Grapes can be eaten raw or they can be used for making jam, juice, jelly, vinegar, wine, grape seed extracts, raisins, molasses and grape seed oil. Grapes are also...
Party, the Wine Party and the 4 Giorni in Italy. It has structure for food and drink stalls, space for shows and folkloric presentations and a polenta pot.
Japan Square
Homage to Japanese immigrants who settled there dedicating themselves to agriculture. Scattered around the square are 30 cherry trees sent from Japan and artificial lakes. In 1993 the Japanese Portal, the Culture House and the Tea House were built.
Tingüi Park
Part of the biggest linear environmental park in the Country, established at the Barigüi river margins, it reminds us of the Indians who used to live there, with the statue of Tindiqüera Chieftain. The Ukrainian Memorial is also there, homage to the immigrants, in a replica of an orthodox church, originally built in inland Paraná State, hosting a pêssankas and icons exhibition.
Wire Opera House
It is one of the emblematic symbols of Curitiba, with tubular structure and transparent ceiling, of great beauty. Inaugurated in 1992, it caters for all types of shows, between lakes, typical vegetation and cascades, on a unique landscape. The Wire Opera House
Wire Opera House
The Ópera de Arame, in Portuguese, or the Wire Opera House, in English, is a theatre house located in the city of Curitiba, the capital of the state of Paraná, in southern Brazil. It is one of the major tourist attractions of the city...
is part of the Pedreiras Park, together with the Paulo Leminski Cultural Space, where the Passion of Christ was enacted, and hosted many other big events since 1989, and can hold, in the open air, 10 thousand people seated or 50 thousand standing.
Tanguá Park
This park was inaugurated in 1996, the Tanguá Park surprises with its beauty as an example of urban space being re-utilized, on one old complex of disactivated quarries, and it is part of the Barigüi river preservation project joining Tingüi and Barigüi parks. This park with an area of 450 thousand square meters has two quarries connected by a 45 meter tunnel that may be crossed on foot by a path over the water. It can be visited on boat or on foot (hiking).
The park has a cooper and bicycle track, snack bar, belvedere and Poty Lazzaroto garden.
Portugal Wood
Homage to the Portuguese-Brazilian
Portuguese-Brazilian
Portuguese Brazilians are Brazilian citizens whose ancestry originates wholly or partly in Portugal. Most of the Portuguese arrived throughout the centuries to Brazil, sought economic opportunities...
bonds, this space is highlighted by a track following a small brook, where one can see drawn on tiles excerpts from famous Portuguese language poets, as well as a tribute to the great Portuguese navigators and their discoveries.
Curitiba International Ecological Marathon
The Maratona Ecológica Internacional de Curitiba ("Curitiba International Ecological marathon
Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance running event with an official distance of 42.195 kilometres , that is usually run as a road race...
")is held in November and is known as the hardest in Brazil, because it happens in the end of the year in the summer heat, and because of the hilly course. To compensate the hard course, runners count with good structure and enthusiastic fans cheering along the course.
Tourism Line
Every year, tourism grows in Curitiba. To attend this demand, the Linha Turismo ("Tourism Line") started in 1994. Its a special city tour that visits the principal tourist attractions in Curitiba, featuring comfortable green with big windows and a shape similar to that of streetcars. The vehicles are equipped with a sound system that plays recorded messages describing sites in three different languages: Portuguese, English and Spanish. It is possible to visit the parks, town squares and the rest of the city's tourist attractions. Considered one of the best in the country, the Linha Turismo is available every thirty minutes and has a two and a half-hour tour, which travels around forty-four kilometers. To go on the tour you must buy a ticket with five tickets that give you the right to get on and off bus four times. Users can therefore choose the touristic point where they want to stay longer. Then, they can embark again to complete the remaining part of the itinerary. Today the line goes to 25 key reference points in Curitiba, completing 44 km (27 mi) in 2 and ½ hours.
Education
There are more than 183 universities in whole state of Paraná.
Educational institutions
- Universidade Federal do ParanáUniversidade Federal do ParanáFederal University of Paraná is a university headquartered in Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil.Established on December 19, 1912 and initially named as Universidade do Paraná , the Universidade Federal do Paraná – UFPR is regarded as the oldest Brazilian university.In 1920, the federal government split...
(UFPR) – Federal University of Paraná – This State university is largest of Paraná, with more than 20.000 students - Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná (UTFPR) – Federal University of Technology is a major University in Paraná and the first University of Technology from Brazil;
- Pontifícia Universidade Católica do ParanáPontifícia Universidade Católica do ParanáThe Pontifical Catholic University of Paraná is a private, not-for-profit Catholic university. The main campus is located in Curitiba, the capital city of the State of Paraná, Brazil, and four other campuses are located in the cities of Londrina, Maringá, São José dos Pinhais and Toledo...
(PUCPR) – A major private University in Paraná; - Universidade Tuiuti do Paraná (UTP);
- Universidade Positivo (UP);
- ESIC Business and Marketing School – International Website ESIC
- Centro Universitário Franciscano do Paraná (UNIFAE);
- Escola de Música e Belas Artes do Paraná (EMBAP);
- Faculdade Dom Bosco (FDB);
- Faculdade de Artes do Paraná (FAP);
- Faculdade de Educação Superior do Paraná (FESP);
- Faculdade de Tecnologia (FATEC);
- Centro Universitário Curitiba (UNICURITIBA);
- and many others.
Educational system
In the 1990s, the city started a project called '’Faróis do Saber ("Lighthouses of Knowledge"). These LighthouseLighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses or, in older times, from a fire, and used as an aid to navigation for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways....
s are free educational centers which include libraries
Library
In a traditional sense, a library is a large collection of books, and can refer to the place in which the collection is housed. Today, the term can refer to any collection, including digital sources, resources, and services...
, Internet access, and other cultural resources. This community libraries works with municipal schools, have a collection of approximately 5000 books, and be cultural reference and leisure for the community, and are designed to diversify the opportunities of access to knowledge
Knowledge
Knowledge is a familiarity with someone or something unknown, which can include information, facts, descriptions, or skills acquired through experience or education. It can refer to the theoretical or practical understanding of a subject...
, expanding the area of formal education.
In each quarter of the city these "Lighthouses of Knowledge" have been implanted containing library and room of computer science, to public use, mainly by students; job training, social welfare and educational programs are coordinated, and often supply labor to improve the city's amenities or services, as well as education and income. Among the Brazilian capitals, Curitiba has the lowest rate of illiteracy, and also number 1 in education between the Brazilian capitals.
Urban planning



Bus rapid transit
Bus rapid transit is a term applied to a variety of public transportation systems using buses to provide faster, more efficient service than an ordinary bus line. Often this is achieved by making improvements to existing infrastructure, vehicles and scheduling...
system. The buses are long, split into three sections (bi-articulated
Bi-articulated bus
A bi-articulated bus or double articulated bus is an extension of an articulated bus in that it has three passenger compartment sections instead of two. This also involves the addition of an extra axle...
), and stop at designated elevated tubes, complete with disabled access. There is only one price no matter how far you travel and you pay at the bus stop.
The system, used by 85% of Curitiba's population, is the source of inspiration for the TransMilenio
TransMilenio
TransMilenio is a bus rapid transit system that serves Bogotá, the capital of Colombia. The system opened to the public in December 2000, covering Av. Caracas and Calle 80...
in Bogotá
Bogotá
Bogotá, Distrito Capital , from 1991 to 2000 called Santa Fé de Bogotá, is the capital, and largest city, of Colombia. It is also designated by the national constitution as the capital of the department of Cundinamarca, even though the city of Bogotá now comprises an independent Capital district...
, Colombia; Metrovia
Metrovia
Metrovia is a bus rapid transit system that has been developed in Guayaquil, Ecuador, and is now a widely used means of transportation in the city....
in Guayaquil
Guayaquil
Guayaquil , officially Santiago de Guayaquil , is the largest and the most populous city in Ecuador,with about 2.3 million inhabitants in the city and nearly 3.1 million in the metropolitan area, as well as that nation's main port...
, Ecuador; Transmetro
Transmetro
Transmetro is a bus rapid transit system in Guatemala City, Guatemala. Service began with its first line opening on February 3, 2007. Unlike other bus routes in Guatemala City, it is serviced by a fleet of modern Volvo buses made by Ciferal in Brasil. The buses have fixed stops and partly run on...
in Guatemala City
Guatemala City
Guatemala City , is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Guatemala and Central America...
, Guatemala; Metrobus
Mexico City Metrobús
Metrobús is a bus rapid transit system in Mexico City, Mexico. It comprises 3 lines that traverse the city and connect with other forms of transit. It was officially opened to the public with service along Line 1 on 19 June 2005...
in Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
; as well as the Orange Line
LACMTA Orange Line
The Orange Line is one of two lines on the Metro Liner bus rapid transit network in Los Angeles County, California. It operates between Warner Center in the Woodland Hills and the North Hollywood Metro Station in the San Fernando Valley where it connects with the Red Line on the Metro Rail light...
of Los Angeles, U.S. State of California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
, and for a future transportation system in Panama City
Panama City
Panama is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Panama. It has a population of 880,691, with a total metro population of 1,272,672, and it is located at the Pacific entrance of the Panama Canal, in the province of the same name. The city is the political and administrative center of the...
, Panama, Cebu City
Cebu City
The City of Cebu is the capital city of Cebu and is the second largest city in the Philippines, the second most significant metropolitan centre in the Philippines and known as the oldest settlement established by the Spaniards in the country.The city is located on the eastern shore of Cebu and was...
, Philippines and the latest, Kuala Lumpur
Kuala Lumpur
Kuala Lumpur is the capital and the second largest city in Malaysia by population. The city proper, making up an area of , has a population of 1.4 million as of 2010. Greater Kuala Lumpur, also known as the Klang Valley, is an urban agglomeration of 7.2 million...
, Malaysia.
The city has also paid careful attention to preserving and caring for its green areas, boasting 51.5 square metres (554.3 sq ft) of green space per inhabitant.
In the 1940s and 1950s, Alfred Agache
Alfred Agache (architect)
Alfred Hubert Donat Agache , sometimes called Alfredo Agache, formally planned the Brazilian cities of Rio de Janeiro, Recife, Porto Alegre and Curitiba in the 1940s and 1950s, supported by the Estado Novo fascist regime in Brazil...
, cofounder of the French Society for Urban Studies, was hired to produce the first city plan. It emphasised a star of boulevards, with public amenities downtown, an industrial district and sanitation. It was followed when possible, but was too expensive to complete.
By the 1960s, Curitiba's population had ballooned to 430,000, and some residents feared that the growth in population threatened to drastically change the character of the city. In 1964, Mayor Ivo Arzua solicited proposals for urban design. Architect Jaime Lerner
Jaime Lerner
Jaime Lerner was governor of the state of Paraná, in southern Brazil. He is renowned as an architect and urban planner, having been mayor of Curitiba, capital of Paraná, three times...
, who later became mayor, led a team from the Universidade Federal do Paraná
Universidade Federal do Paraná
Federal University of Paraná is a university headquartered in Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil.Established on December 19, 1912 and initially named as Universidade do Paraná , the Universidade Federal do Paraná – UFPR is regarded as the oldest Brazilian university.In 1920, the federal government split...
that suggested strict controls on urban sprawl, a reduction of traffic in the downtown area, preservation of Curitiba's Historic Sector, and a convenient and affordable public transit system.
This plan, known as the Curitiba Master Plan, was adopted in 1968. Lerner closed XV de Novembro St.
Rua XV de Novembro
Rua XV de Novembro is one of the major streets in downtown Curitiba. Also known as Flower Street , it is one of the first major pedestrian streets in Brazil...
to vehicles, because it had very high pedestrian traffic. The plan had a new road design to minimise traffic: the Trinary Road System. This uses two one-way streets moving in opposite directions which surround a smaller, two-lane street where the express buses have their exclusive lane. Five of these roads form a star that converges on the city centre. Land farther from these roads is zoned for lower density developments, to reduce traffic away from the main roads. In a number of areas subject to floods, buildings were condemned and the land became parks.
Today, Curitiba is considered one of the best examples of urban planning worldwide. In June 1996, the chairman of the Habitat II
Habitat II
Habitat II - the Second United Nations Conference on Human Settlements - was held in Istanbul, Turkey from June 3–14, 1996, twenty years after the 1976 Habitat conference in Vancouver that had led to the establishment of the Nairobi-based United Nations Centre on Human Settlements. The twin...
summit of mayors and urban planners in Istanbul
Istanbul
Istanbul , historically known as Byzantium and Constantinople , is the largest city of Turkey. Istanbul metropolitan province had 13.26 million people living in it as of December, 2010, which is 18% of Turkey's population and the 3rd largest metropolitan area in Europe after London and...
praised Curitiba as "the most innovative city in the country."
Curitiba was recently recommended by UNESCO
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
as a model for the reconstruction of the cities of Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
, after the U.S invaded in 2001.
In the 1980s, the RIT (Rede Integrada de Transporte
Rede Integrada de Transporte
Rede Integrada de Transporte is a bus rapid transit system in Curitiba, Brazil. The RIT was implemented in 1974 becoming the first BRT system in the world....
, Integrated Transport Network) was created, allowing transit between any point in the city by paying just one fare. At the same time, the city began a project called the "Faróis de Saber" (Lighthouses of Knowledge). These Lighthouses are free educational centers which include libraries
Library
In a traditional sense, a library is a large collection of books, and can refer to the place in which the collection is housed. Today, the term can refer to any collection, including digital sources, resources, and services...
, Internet access, and other cultural resources. Job training, social welfare and educational programs are coordinated, and often supply labor to improve the city's amenities or services, as well as education and income.
Curitiba is referred to as the ecological capital of Brazil, with a network of 28 parks and wooded areas. In 1970, there was less than 1 square meter of green space per person; now there are 52 square meters for each person. Residents planted 1.5 million trees along city streets. Builders get tax breaks if their projects include green space. Flood waters diverted into new lakes in parks solved the problem of dangerous flooding, while also protecting valley floors and riverbanks, acting as a barrier to illegal occupation, and providing aesthetic and recreational value to the thousands of people who use city parks.
In 2007, the city was placed third in a list of "15 Green Cities" in the world, according the U.S. magazine "Grist", after Reykjavik
Reykjavík
Reykjavík is the capital and largest city in Iceland.Its latitude at 64°08' N makes it the world's northernmost capital of a sovereign state. It is located in southwestern Iceland, on the southern shore of Faxaflói Bay...
in Iceland and Portland, Oregon
Portland, Oregon
Portland is a city located in the Pacific Northwest, near the confluence of the Willamette and Columbia rivers in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2010 Census, it had a population of 583,776, making it the 29th most populous city in the United States...
in the United States. As a result, according to one survey, 99% of Curitibans are happy with their hometown. The "green exchange" employment program focuses on social inclusion, benefiting both those in need and the environment. Low-income families living in shantytowns unreachable by truck bring their trash bags to neighborhood centers, where they exchange them for bus tickets and food. This means less city litter and less disease, less garbage dumped in sensitive areas such as rivers and a better life for the undernourished poor. There's also a program for children where they can exchange recyclable garbage for school supplies, chocolate, toys and tickets for shows.
Jaime Lerner suggests urban acupuncture
Urban Acupuncture
Urban Acupuncture is an urban environmentalism theory which combines urban design with traditional Chinese medical theory of acupuncture. This strategy views cities as living, breathing organisms and pinpoints areas in need of repair...
as the future solution for contemporary urban issues; by focusing on very narrow pressure points in cities, we can initiate positive ripple effects for the greater society. Urban acupuncture reclaims the ownership of land to the public and emphasizes the importance of community development through small interventions in design of cities.It involves pinpointed interventions that can be accomplished quickly to release energy and create a positive ripple effect.
He described in 2007:
I believe that some medicinal “magic” can and should be applied to cities, as many are sick and some nearly terminal. As with the medicine needed in the interaction between doctor and patient, in urban planning it is also necessary to make the city react; to poke an area in such a way that it is able to help heal, improve, and create positive chain reactions. It is indispensable in revitalizing interventions to make the organism work in a different way.
Under the "garbage that's not garbage" program, 70% of the city's trash is recycled by its residents. Once a week, a truck collects paper, cardboard, metal, plastic and glass that has been sorted in the city's homes. The city's paper recycling
Recycling
Recycling is processing used materials into new products to prevent waste of potentially useful materials, reduce the consumption of fresh raw materials, reduce energy usage, reduce air pollution and water pollution by reducing the need for "conventional" waste disposal, and lower greenhouse...
alone saves the equivalent of 1,200 trees a day. As well as the environmental benefits, money raised from selling materials goes into social programs, and the city employs the homeless and recovering alcoholics in its garbage separation plant. Open University, created by the city, lets residents take courses in many subjects such as mechanics, hair styling and environmental protection for a small fee. Retired city buses are often used as mobile schools or offices. Downtown areas were transformed into pedestrian streets, including a 24-hour mall with shops, restaurants and cafes, and a street of flowers with gardens tended by street kids.
The "capacity building job line" was created to generate a better quality of life
Quality of life
The term quality of life is used to evaluate the general well-being of individuals and societies. The term is used in a wide range of contexts, including the fields of international development, healthcare, and politics. Quality of life should not be confused with the concept of standard of...
for people in the region surrounding a new economic development axis of Curitiba. Key initiatives include the South-Circular bus line, which links the southern and eastern regions of town; Entrepreneurial Sheds, business incubators designed to help small companies get established and prosper; and the Crafts Lycée, which trains people for profession
Profession
A profession is a vocation founded upon specialized educational training, the purpose of which is to supply disinterested counsel and service to others, for a direct and definite compensation, wholly apart from expectation of other business gain....
s such as marketing and finance so that they can find employment in new companies that emerge from the business incubator
Business incubator
Business incubators are programs designed to accelerate the successful development of entrepreneurial companies through an array of business support resources and services, developed and orchestrated by incubator management and offered both in the incubator and through its network of contacts...
. Specifically, the goal is to provide jobs and income for the unemployed among 400,000 people living in 15 peripheral towns, and to structure and develop the region according to integrated planning principles. About 15,000 new jobs have been generated so far, and 15,000 more are expected.
There's a model, inexpensive, speedy transit service used by more than 2 million people a day. There are more car owners per capita than anywhere else in Brazil, and the population has doubled since 1974, yet auto traffic has declined by 30%, and atmospheric pollution is the lowest in Brazil.
Culture


Arts and entertainment
Curitiba is the first city in Brazil to have an IMAX movie theatre.It is in the Palladium Shopping Center which is the biggest mall in Southern Brazil. Curitiba also has many theaters. The biggest and most important one is the Guaíra Theater. Every year, in April, it hosts the Curitiba Theater Festival, with various artists playing in Curitiba Theaters and even on the squares.
Museums
For the famous Brazilian architect Oscar NiemeyerOscar Niemeyer
Oscar Ribeiro de Almeida Niemeyer Soares Filho is a Brazilian architect specializing in international modern architecture...
Curitiba became the home to his extravagantly designed museum, the state museum of Curitiba. Its design includes a gravity defying construction that was intended to look like a Paraná Pine
Araucaria angustifolia
Araucaria angustifolia, the Paraná pine or Brazilian pine , is a species in the conifer genus Araucaria. Covering an original area of 233000 km², it is native to southern Brazil Araucaria angustifolia, the Paraná pine or Brazilian pine , is a species in the conifer genus Araucaria. Covering an...
, one of the city's symbols, but is widely interpreted by locals as an eye which gave the Museum its nickname – Museu do Olho, or Museum of the Eye. In keeping with the Curitiba history and culture of science, the museum offers many science exhibitions, including Curitiba biennal/Curitiba biennial, twice-yearly exhibitions. The Curitiba museum also includes the Oscar Niemeyer Curitiba auditorium.
- Museu Paranaense ("Paranaense Museum") – dedicated to the arts and history;
- Oscar Niemeyer Museum – the largest museum of Latin America, dedicated to plastic arts;
- Museu de Arte Sacra ("Religious Art Museum") – the focus are religious and sacred Christian art in general;
- Museu do Expedicionário ("Museum of Expeditionary") – dedicated to the history of Brazilian participation in World War II;
- Museu de Arte Contemporânea ("Museum of Contemporary Art");
- Museu da Imagem e do Som ("Image and Sound Museum") – about cinema and photography;
- Museu Metropolitano de Arte de Curitiba ("Metropolitan Museum of Art in Curitiba") – modern art;
- Museu de História Natural ("Natural History Museum") – dedicated to the biologyBiologyBiology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
and botanyBotanyBotany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
.
Carnival/Carnaval
CarnivalCarnival
Carnaval is a festive season which occurs immediately before Lent; the main events are usually during February. Carnaval typically involves a public celebration or parade combining some elements of a circus, mask and public street party...
Curitiba is unique and, as a result, extremely different from the carnivals held elsewhere in the country, and especially the ones that are so prevalent on any TV coverage of the carnival that occurs in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro , commonly referred to simply as Rio, is the capital city of the State of Rio de Janeiro, the second largest city of Brazil, and the third largest metropolitan area and agglomeration in South America, boasting approximately 6.3 million people within the city proper, making it the 6th...
, Salvador
Salvador, Bahia
Salvador is the largest city on the northeast coast of Brazil and the capital of the Northeastern Brazilian state of Bahia. Salvador is also known as Brazil's capital of happiness due to its easygoing population and countless popular outdoor parties, including its street carnival. The first...
, and Recife
Recife
Recife is the fifth-largest metropolitan area in Brazil with 4,136,506 inhabitants, the largest metropolitan area of the North/Northeast Regions, the 5th-largest metropolitan influence area in Brazil, and the capital and largest city of the state of Pernambuco. The population of the city proper...
every single year. Carnival Curitiba is in fact non-existent in terms of the way that it is done elsewhere. The carnival in Curitiba that does occur every year, in March to be precise to coincide with the Rio de Janeiro carnival, consists of a small celebration
Festival
A festival or gala is an event, usually and ordinarily staged by a local community, which centers on and celebrates some unique aspect of that community and the Festival....
on the coast. The beaches that are an hour away via car in Paranaguá
Paranaguá
Paranaguá is a city in the state of Paraná in Brazil. Founded in 1648, it is Paraná's oldest city.It is known for its excellent port facilities, being the sea port for Curitiba, the capital of Paraná....
host the miniature carnival Curitiba celebrations. There is usually traditional Brazilian food like "Feijoada
Feijoada
Feijoada is a stew of beans with beef and pork, which is a typical from Brazilian Cuisine, is also typical in Angola, Mozambique, Goa, India and other former Portuguese colonies. In Brazil, feijoada is considered by many as the national dish...
", their special hotdog
HotDog
HotDog is the name of the HTML web editing tool developed by Sausage Software in the mid-1990s. At the time of its development, there were only a small number of HTML editors available on the market and HotDog gathered significant interest from web users due to its ease of use and "What you see...
s and a variety of salads on offer from stalls. The revellers will usually dance the "samba
Samba
Samba is a Brazilian dance and musical genre originating in Bahia and with its roots in Brazil and Africa via the West African slave trade and African religious traditions. It is recognized around the world as a symbol of Brazil and the Brazilian Carnival...
" and mingle before heading home after the party in the early hours of the morning. The carnival Curitiba offers is therefore out of the town and gives those that do not wish to attend a break. Three clubs are renowned for their carnival Curitiba celebrations: Santa Mônica, Paraná and Curitibano (the most traditional one). They are all located within easy distance of the Central area. The costumes are readily available from most of the cheaper clothes stores and can be hired out from a variety of shops, as well as smaller independent ones in the weeks leading up to the celebrations for less than $20 for the night.
Cuisine
Curitiba is influenced by European, Arab and Japanese immigrants. The better restaurants are all located in central area (principally Batel, the rich neighborhood of Curitiba), not too far away from the heart of Curitiba. As a result, the majority of them are near metro stops and the bus terminal and can easily be reached on foot. Although offering traditional Brazilian drink. The Caruso restaurant is a traditional form of Brazilian cuisine that is made up of rice, black beans, and sausages with borecole and orange slices on the side. It may sound like a simple dish but the flavour is immense. Italian Pizzaria Geppetto and Pizzaria O Forno are some of The best Italian restaurants in the city.UN Convention on Biodiversity

Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
took place in Pinhais (a city near Curitiba), addressing items of the 1993 Convention on Biological Diversity adopted by 188 countries. This convention seeks to discuss strategies to safeguard life from the threats to its existence. Starting with the Summit of the Earth or Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro , commonly referred to simply as Rio, is the capital city of the State of Rio de Janeiro, the second largest city of Brazil, and the third largest metropolitan area and agglomeration in South America, boasting approximately 6.3 million people within the city proper, making it the 6th...
Eco-92 the topic has been gaining centrality and has been the subject of numerous official documents, especially the 2000 and 2003 Cartagena Protocols on biosecurity
Biosecurity
Biosecurity is a set of preventive measures designed to reduce the risk of transmission of infectious diseases, quarantined pests, invasive alien species, living modified organisms...
. The Curitiba preparatory document, developed by specialists of the UN and of the Brazilian Ministry of the Environment for issues from Brazil, defines biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
as follows: including all the different species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
of plants, animals and microorganism
Microorganism
A microorganism or microbe is a microscopic organism that comprises either a single cell , cell clusters, or no cell at all...
s (estimated at more than 10 million species), all the genetic variability within the species (10 to 100 genes per species) and all the diverse ecosystems formed by different combinations of species. Biodiversity includes the environmental services responsible for maintenance of life on Earth, for the interaction between living beings and for the offer of goods and services that sustain human societies and their economies.
Transportation

Public transport
Curitiba has a unique transportation systemRede Integrada de Transporte
Rede Integrada de Transporte is a bus rapid transit system in Curitiba, Brazil. The RIT was implemented in 1974 becoming the first BRT system in the world....
, developed locally and causing much interest worldwide. This Bus Rapid Transit
Bus rapid transit
Bus rapid transit is a term applied to a variety of public transportation systems using buses to provide faster, more efficient service than an ordinary bus line. Often this is achieved by making improvements to existing infrastructure, vehicles and scheduling...
system is very simple and practical. Public transportation consists entirely of buses. There are several different types of bus, each with a different function. All stations are easily accessed and enclosed. The buses have been changed to make for easier entry and exit. Together with other low-cost changes, this bus system aims at becoming a comfortable and preferred transportation choice for the public.
The popularity of Curitiba's BRT has effected a modal shift from automobile travel to bus travel. Based on 1991 traveller survey results, it was estimated that the introduction of the BRT had caused a reduction of about 27 million auto trips per year, saving about 27 million liters of fuel annually. In particular, 28 percent of BRT riders previously traveled by car. Compared to eight other Brazilian cities of its size, Curitiba uses about 30 percent less fuel per capita, resulting in one of the lowest rates of ambient air pollution in the country. Today about 1,100 buses make 12,500 trips every day, serving more than 1.3 million passengers, 50 times the number from 20 years ago. Eighty percent of travelers use the express or direct bus services. Best of all, Curitibanos spend only about 10 percent of their income on travel, much below the national average.
Curitiba's Master Plan integrated transportation with land use planning, calling for a cultural, social, and economic transformation of the city. It limited central area growth, while encouraging commercial growth along the transport arteries radiating out from the city center. The city center was partly closed to vehicular traffic, and pedestrian
Pedestrian
A pedestrian is a person traveling on foot, whether walking or running. In some communities, those traveling using roller skates or skateboards are also considered to be pedestrians. In modern times, the term mostly refers to someone walking on a road or footpath, but this was not the case...
streets were created. Linear development along the arteries reduced the traditional importance of the downtown area as the primary focus of day-to-day transport activity, thereby minimizing congestion and the typical morning and afternoon flows of traffic. Instead, rush hour in Curitiba has heavy commuter movements in both directions along the public transportation arteries.
Other policies have also contributed to the success of the transit system. Land within two blocks of the transit arteries is zoned for high density, since it generates more transit ridership per square foot. Beyond the two blocks, zoned residential densities taper in proportion to distance from transitways. Planners discourage auto-oriented centers and channel new retail growth to transit corridors. Very limited public parking is available in the downtown area, and most employers offer transportation subsidies, especially to low-skilled and low-paid employees.
Roads


São Paulo
São Paulo is the largest city in Brazil, the largest city in the southern hemisphere and South America, and the world's seventh largest city by population. The metropolis is anchor to the São Paulo metropolitan area, ranked as the second-most populous metropolitan area in the Americas and among...
use BR-116 South. From Florianópolis
Florianópolis
-Climate:Florianópolis experiences a warm humid subtropical climate, falling just short of a true tropical climate. The seasons of the year are distinct, with a well-defined summer and winter, and characteristic weather for autumn and spring. Frost is infrequent, but occurs occasionally in the winter...
use BR-101. From Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre
Porto Alegre is the tenth most populous municipality in Brazil, with 1,409,939 inhabitants, and the centre of Brazil's fourth largest metropolitan area . It is also the capital city of the southernmost Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul. The city is the southernmost capital city of a Brazilian...
use BR-116 North.
Recently, the city installed around 140 traffic radars
Traffic camera
A traffic camera is a video camera which observes vehicular traffic on a road. Typically, these are put along major roads such as highways, freeways, motorways, autoroutes and expressways, as well as arterial roads, and are connected with optical fibers buried alongside or even under the road,...
, causing much discontent among drivers in general.
It has perhaps the best world's public transport system,with clean and efficient buses carrying 1.9 million passengers(75 percent of all commuters) every day at low cost.The bus runs on high speed,dedicated lanes.
Five major roads penetrate into the heart of the city,with two bus lanes.The bus stops are connected to bicycle paths,which extended to 160 km (99.42 mi) into the city.
Airports
Afonso Pena International AirportAfonso Pena International Airport
Afonso Pena International Airport is the main airport serving Curitiba, Brazil, located in the adjoining municipality of São José dos Pinhais. It is named after Afonso Augusto Moreira Pena , the 6th President of Brazil....
is Curitiba's main airport. It is located in the nearby city of São José dos Pinhais
São José dos Pinhais
São José dos Pinhais is a city in Paraná, Brazil. It is located at around . It is a part of the Metropolitan Region of Curitiba. St. Joseph of the Pines is a municipality in the state of Paraná, located in the Greater Curitiba. It is located at 25 ° 32'05 "south latitude and 49 º 12'23" west...
and all commercial flights operate from this airport. It is integrated into Curitiba's transportation system, with rapid buses and shuttle service connecting the airport to the city.
Bacacheri Airport
Bacacheri Airport
Bacacheri Airport is an airport in Curitiba, Brazil. It is named after the neighborhood where it is located.It is operated by Infraero.-History:The history of Bacacheri airport begins in 1930 as an air field for Military Aviation...
is a smaller facility used for general aviation.
Others
The city has approximately 62 miles (99.8 km) of bike routes, used by around 30 thousand bikers daily. On the city streets, there are almost one million vehicles, of which 2,253 are Taxis. They are all painted orange. To service all these vehicles, there are more than 355 petrol stations throughout the city. With so many cars, nearly 500,000 ticketTraffic ticket
A traffic ticket is a notice issued by a law enforcement official to a motorist or other road user, accusing violation of traffic laws. Traffic tickets generally come in two forms, citing a moving violation, such as exceeding the speed limit, or a non-moving violation, such as a parking violation,...
s are issued yearly, even though there are more than 40,000 existing traffic signs in all the city.
Sports
Several association football teams play in Curitiba. CoritibaCoritiba Foot Ball Club
Coritiba Foot Ball Club, commonly known as Coritiba, is a Brazilian football team from Curitiba, Paraná. It's the state's oldest football team and the best classified in the CBF and FIFA classifications. Coritiba has been champion in Paraná State for 35 times, more times than the sum of all the...
play at Estádio Major Antônio Couto Pereira, Clube Atlético Paranaense
Clube Atlético Paranaense
Clube Atlético Paranaense is a Brazilian football team from Curitiba in Paraná, founded on March 26, 1924. The club won the Campeonato Brasileiro Série A in 2001.-History:...
at Estádio Joaquim Américo Guimarães and Paraná Clube
Paraná Clube
Paraná Clube is a Brazilian football team. It was established on December 19, 1989, in Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil. Its uniform is composed of a blue/red shirt, white shorts and white socks....
at Estádio Durival Britto e Silva
Estádio Vila Capanema
Estádio Durival Britto e Silva, better known as Estádio Vila Capanema , is the main stadium of Paraná Clube in Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil. The other club stadium is Estádio Vila Olímpica, but it is currently being used for training. The stadium holds 20,000 people...
. Both Coritiba and Atlético Paranaense have won Campeonato Brasileiro Série A
Campeonato Brasileiro Série A
The Campeonato Brasileiro de Clubes da Série A , popularly known as the Brasileirão , is a professional football league at the top of the Brazilian football league system held annually since 1959. Contested by twenty clubs, it operates a system of promotion and relegation with the Série B...
, in 1985 and 2001, respectively. Estádio Joaquim Américo Guimarães will be one of the 12 stadia to host games of the 2014 FIFA World Cup
2014 FIFA World Cup
The 2014 FIFA World Cup will be the 20th FIFA World Cup, an international association football tournament that will take place in Brazil from 12 June to 13 July 2014....
to be held in Brazil.
The Autódromo Internacional de Curitiba
Autódromo Internacional de Curitiba
Autódromo Internacional de Curitiba is a motorsports circuit located in Pinhais, Brazil. It has been host to the World Touring Car Championship, TC2000, Fórmula Truck and Stock Car Brasil racing.-The circuit:Fabrizio Giovanardi of JAS Motorsport suggested the circuit is bumpy...
(Curitiba International Raceway) is located in nearby Pinhais
Pinhais
Pinhais is a city and municipality in Paraná state in Brazil. As of 2005 the city had 118,000 inhabitants and the municipality in total 120,000. It was desmembrated from the municipality of Piraquara in 1992 and is part of the metropolitan region of Curitiba. In its territory lies the Autódromo...
.
Curitiba house one of the most famous Vale Tudo training camps in the world since the late 1990s and early years of the millennium named Chute Boxe Academy. Noted fighters to come from Chute Boxe include Wanderlei Silva, Anderson Silva, Murilo and Mauricio Rua.
Neighborhoods

Curitiba is divided into 9 regional governments (boroughs) covering the 75 neighbourhoods of the city. All districts are served by the system of integrated urban transport.
Most districts of Curitiba was born of colonial groups formed by families of European immigrants in the second half of the nineteenth century.
The centro ("Downtown" in American English
American English
American English is a set of dialects of the English language used mostly in the United States. Approximately two-thirds of the world's native speakers of English live in the United States....
or "CBD" – central business district – in other English use), place of foundation of the city, is the most bustling area, which concentrates most of the financial institutions of Curitiba.
List of neighborhoods by regional:
- Matriz: Centro, Centro Cívico, Batel, Bigorrilho, Mercês, São Francisco, Bom Retiro, Ahu, Juvevê, Cabral, Hugo Lange, Jardim Social, Alto da XV, Alto da Glória, Cristo Rei, Jardim Botânico, Prado Velho and Rebouças;
- Santa Felicidade: Santa Felicidade, Lamenha Pequena, Butiatuvinha, São João, Vista Alegre, Cascatinha, São Brás, Santo Inácio, Orléans, Mossunguê, Campina do Siqueira, Seminário, CIC (north region) and part of Campo Comprido;
- Boa Vista: Boa Vista, Bacacheri, Bairro Alto, Tarumã, Tingüi, Atuba, Santa Cândida, Cachoeira, Barreirinha, Abranches, Taboão, Pilarzinho and São Lourenço;
- Cajuru: Cajuru, Uberaba, Jardim das Américas, Guabirotuba and Capão da Imbuia;
- Fazendinha/Portão: Portão, Fazendinha, Santa Quitéria, Vila Isabel, Água Verde, Parolin, Guaíra, Lindóia, Fanny, Novo Mundo and part of Campo Comprido;
- Boqueirão: Boqueirão, Xaxim, Hauer and Alto Boqueirão;
- Pinheirinho: Pinheirinho, Capão Raso, Tatuquara, Campo de Santana and Caximba;
- Bairro Novo: Sítio Cercado, Ganchinho and Umbará;
- Cidade Industrial de Curitiba: CIC (center and south region), Riviera, Augusta and São Miguel.
Twin towns – Sister cities
Curitiba is twinnedTown twinning
Twin towns and sister cities are two of many terms used to describe the cooperative agreements between towns, cities, and even counties in geographically and politically distinct areas to promote cultural and commercial ties.- Terminology :...
with:
| Asunción Asunción Asunción is the capital and largest city of Paraguay.The "Ciudad de Asunción" is an autonomous capital district not part of any department. The metropolitan area, called Gran Asunción, includes the cities of San Lorenzo, Fernando de la Mora, Lambaré, Luque, Mariano Roque Alonso, Ñemby, San... , Paraguay Coimbra Coimbra Coimbra is a city in the municipality of Coimbra in Portugal. Although it served as the nation's capital during the High Middle Ages, it is better-known for its university, the University of Coimbra, which is one of the oldest in Europe and the oldest academic institution in the... , Portugal Guadalajara Guadalajara Guadalajara may refer to:In Mexico:*Guadalajara, Jalisco, the capital of the state of Jalisco and second largest city in Mexico**Guadalajara Metropolitan Area*University of Guadalajara, a public university in Guadalajara, Jalisco... , Mexico Hangzhou Hangzhou Hangzhou , formerly transliterated as Hangchow, is the capital and largest city of Zhejiang Province in Eastern China. Governed as a sub-provincial city, and as of 2010, its entire administrative division or prefecture had a registered population of 8.7 million people... , China Himeji Himeji, Hyogo is a city located in Hyōgo Prefecture in the Kansai region of Japan. As of April 1, 2011, the city has an estimated population of 535,945, with 206,409 households. The total area is 534.43 km².- History :... , Japan |
Orlando, Florida Orlando, Florida Orlando is a city in the central region of the U.S. state of Florida. It is the county seat of Orange County, and the center of the Greater Orlando metropolitan area. According to the 2010 US Census, the city had a population of 238,300, making Orlando the 79th largest city in the United States... , United States Kraków Kraków Kraków also Krakow, or Cracow , is the second largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in the Lesser Poland region, the city dates back to the 7th century. Kraków has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life... , Poland Montevideo Montevideo Montevideo is the largest city, the capital, and the chief port of Uruguay. The settlement was established in 1726 by Bruno Mauricio de Zabala, as a strategic move amidst a Spanish-Portuguese dispute over the platine region, and as a counter to the Portuguese colony at Colonia del Sacramento... , Uruguay Jacksonville, Florida Jacksonville, Florida Jacksonville is the largest city in the U.S. state of Florida in terms of both population and land area, and the largest city by area in the contiguous United States. It is the county seat of Duval County, with which the city government consolidated in 1968... , United States Santa Cruz de la Sierra Santa Cruz de la Sierra Santa Cruz de la Sierra, commonly known as Santa Cruz, is the capital of the Santa Cruz department in eastern Bolivia and the largest city in the country... , Bolivia Suwon Suwon Suwon is the provincial capital of Gyeonggi-do, South Korea. A major city of over a million inhabitants, Suwon lies approximately south of Seoul. It is traditionally known as "The City of Filial Piety".... , South Korea |
Famous places

- Autódromo Internacional de CuritibaAutódromo Internacional de CuritibaAutódromo Internacional de Curitiba is a motorsports circuit located in Pinhais, Brazil. It has been host to the World Touring Car Championship, TC2000, Fórmula Truck and Stock Car Brasil racing.-The circuit:Fabrizio Giovanardi of JAS Motorsport suggested the circuit is bumpy...
(Curitiba International Raceway) - Bosque AlemãoBosque AlemãoBosque Alemão is a park built in Curitiba in honor of the German immigrants who begin to settle in the city in the early 19th century....
(German Woods) - Bosque de PortugalBosque de PortugalBosque de Portugal is located in the city of Curitiba, capital of the state of Paraná, Brazil....
(Portugal Woods) - Feirinha do largo da ordemFeirinha do largo da ordemThe Feirinha do Largo da Ordem is an open-air market place that happens every Sunday mornings, in the historical centre of Curitiba, the capital of Paraná state in Brazil. In the Feirinha, visitors can see or buy paintings, sculptures, craftsmanship, workmanship, typical foods...
(Largo da Ordem Sunday Market) - Jardim Botânico de CuritibaBotanical Garden of CuritibaThe Jardim Botânico de Curitiba, in Portuguese, or the Botanical Garden of Curitiba, in English, is also known as the "Jardim Botânico Fanchette Rischbieter". This is a park located in the city of Curitiba, the capital of the state of Paraná, and the biggest city in southern Brazil...
(Botanical Garden of Curitiba) - Ópera de Arame (Wire Opera House)
- Rua XV de NovembroRua XV de NovembroRua XV de Novembro is one of the major streets in downtown Curitiba. Also known as Flower Street , it is one of the first major pedestrian streets in Brazil...
(15 November Street) - Universidade Federal do ParanáUniversidade Federal do ParanáFederal University of Paraná is a university headquartered in Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil.Established on December 19, 1912 and initially named as Universidade do Paraná , the Universidade Federal do Paraná – UFPR is regarded as the oldest Brazilian university.In 1920, the federal government split...
(Federal University of Paraná)
Notable people




Arts
- Alfredo Andersen – Norwegian Painter and Sculptor
- Andrade Muricy – Composer and Musical and Literary Critic
- Bonde do RolêBonde do RolêBonde do Rolê is a Funk Carioca-influenced electropop group from Curitiba, Brazil, consisting of MCs Pedro D'Eyrot, Laura Taylor, Ana Bernardino, and DJ/MC Rodrigo Gorky...
– Band - Dalton TrevisanDalton TrevisanDalton Jérson Trevisan is a Brazilian author of short stories. He has been described as an "acclaimed short-story chronicler of lower-class mores and popular dramas."...
– Writer - Emílio de Meneses – Poet and Journalist, "immortal" of the Brazilian Academy of Letters
- Fernanda MachadoFernanda MachadoFernanda Arrias Machado is a Brazilian film, television and stage actress. She is perhaps best known for her role as Maria in the film Tropa de Elite.-Career:...
– Actress - Francisco LachowskiFrancisco LachowskiFrancisco Lachowski is a Brazilian-Polish model. He started his career in 2009 when he won a modeling contest in São Paulo, for which he was awarded a contract with Ford Models. In 2009 he did his first runway shows in Milan and Paris, walking for designers like Gucci and Dior Homme...
– Super Model - Guido Viaro – Italian Painter and Teacher
- Guilherme WeberGuilherme WeberGuilherme Weber born in 1975 in Curitiba, Paraná, is a Brazilian actor, author and director.Guilherme Weber began his career on theatre in 1989. He was fourteen years old when traveled with an amateur group to many cities in Brazil for four years. In 1992, he founded, with Felipe Hirsch, the...
– Actor - Guta Stresser – Actress
- Isabeli FontanaIsabeli Fontana-Early life and discovery:Fontana was born in Curitiba, Paraná, Brazil. In 1996 she made it to the finals of the Elite Model Look when she was just 13 and in the following year she moved from South of Brazil to Milan, Italy, to start her modelling career.-Career:...
– Super Model - Isadora RibeiroIsadora RibeiroIsadora Ribeiro de Sousa June 13, 1965-) is a Brazilian TV actress.-Filmography:* 2010 Uma Rosa com Amor - Roberta Vermont .* 2007 Donas de Casa Desesperadas - Vera Marques * 2001 As Filhas da Mãe - Madalena...
– Actress - Jaime LernerJaime LernerJaime Lerner was governor of the state of Paraná, in southern Brazil. He is renowned as an architect and urban planner, having been mayor of Curitiba, capital of Paraná, three times...
– Architect and Urbanist - Katiuscia Canoro – Actress
- Larry Grehan – Irish writer
- Luís Melo – Actor
- Luiz Carlos AlborghettiLuiz Carlos AlborghettiLuiz Carlos Alborghetti was an Italian-Brazilian radio commenter, showman and political figure. He was a Conservative voice on the radio...
– TV host - Marjorie EstianoMarjorie EstianoMarjorie Estiano is a Brazilian popular actress and singer who rose to prominence in 2004 playing Natasha in the Brazilian teen seriesMalhação.-Biography:...
– Actress and Singer - Paulo LeminskiPaulo LeminskiPaulo Leminski Filho was a Brazilian poet and writer. He took pride in being of mixed Polish and African descent....
– Poet and Writer - Simone SpoladoreSimone SpoladoreSimone Spoladore is a Brazilian actress. Her first character was Ana, from the Brazilian movie Lavoura Arcaica , a girl who falls in love with her brother, André. Ana does not say a word during the film. She expresses herself in her own way: through her eyes and her dance...
– Actress - Tamajoara Proença – Teacher
- Vilanova Artigas – Architect
Science
- César LattesCésar LattesCesare Mansueto Giulio Lattes , also known as Cesar Lattes, was a Brazilian experimental physicist, one of the discoverers of the pion, a composite subatomic particle made of a quark and an antiquark.-Life:Lattes was born to a family of Italian Jewish immigrants in Curitiba, Southern Brazil...
– PhysicistPhysicistA physicist is a scientist who studies or practices physics. Physicists study a wide range of physical phenomena in many branches of physics spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic particles of which all ordinary matter is made to the behavior of the material Universe as a whole... - Ned KockNed KockNed Kock is best known for employing biological evolution ideas to the understanding of human behavior toward technologies, particularly information technologies. He developed media naturalness theory, an evolutionary communication media theory...
– SystemsInformation systemsInformation Systems is an academic/professional discipline bridging the business field and the well-defined computer science field that is evolving toward a new scientific area of study...
Scientist - Newton da CostaNewton da CostaNewton Carneiro Affonso da Costa is a Brazilian mathematician, logician, and philosopher. He studied engineering and mathematics at the Federal University of Paraná in Curitiba and the title of his 1961 Ph.D...
– MathematicianMathematicianA mathematician is a person whose primary area of study is the field of mathematics. Mathematicians are concerned with quantity, structure, space, and change.... - Ricardo RaminaRicardo RaminaRicardo Ramina is a notable Brazilian neurosurgeon and university Professor. Ramina is well known around the world for his expertise in the treatment of complex neurosurgical problems such as Vestibular schwannomas, skull base tumors, glomus jugulare, Meningiomas and Aneurysms.Ricardo Ramina was...
– PhysicianPhysicianA physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
Sports
Football- Alexandro de Souza
- Adriano Correia
- Paulo RinkPaulo RinkPaulo Roberto Rink , is a Brazilian-born German football centre forward, who retired in 2007.Rink began his career playing for Atlético Paranaense. After a solid career with the club, he negotiated with Bayer 04 Leverkusen, and was transferred for US$6M, the highest transfer fee paid for an...
Mixed martial arts
- Anderson SilvaAnderson SilvaAnderson da Silva is a Brazilian mixed martial artist. He is the current UFC Middleweight Champion and the promotion's longest reigning champion. With 14 consecutive wins, Silva holds the longest winning streak and title defense streak in UFC history...
- Cristiane SantosCristiane SantosCristiane Justino Venancio Santos is a Brazilian mixed martial artist and the Strikeforce Women's Featherweight Champion . Santos won the title on August 15, 2009 by defeating Gina Carano via TKO...
- Mauricio "Shogun" Rua
- Murilo "Ninja" RuaMurilo RuaMurilo Rua is a former Brazilian mixed martial artist who fought in Pride Fighting Championships. Nicknamed Ninja, he is the older brother of former UFC Light Heavyweight Champion Mauricio "Shogun" Rua. He is known for his well-rounded fighting skills, in particular Muay Thai and Brazilian...
- Wanderlei SilvaWanderlei SilvaWanderlei César da Silva , nicknamed "The Axe Murderer", is a Brazilian mixed martial artist, who has competed in Japan's Pride Fighting Championships and the American based Ultimate Fighting Championship . Silva is known for his aggressive fighting style with the majority of his fights ending in...
Motorsports
- Augusto FarfusAugusto FarfusAugusto Farfus Jr. is a Brazilian auto racing driver. He presently lives in Monaco.- Early years :Farfus first tasted racing in minibike races and won the local championships in 1991....
– Intercontinental Le Mans Cup driver for BMWBMWBayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
. - Enrique BernoldiEnrique BernoldiEnrique Antônio Langue e Silvério de Bernoldi is a Brazilian racing driver who raced for the Arrows Formula One team...
– Formula OneFormula OneFormula One, also known as Formula 1 or F1 and referred to officially as the FIA Formula One World Championship, is the highest class of single seater auto racing sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile . The "formula" designation in the name refers to a set of rules with which...
driver – IndyCarIndyCar SeriesThe IZOD IndyCar Series is the premier level of American open wheel racing. The current championship, founded by Indianapolis Motor Speedway owner Tony George, began in 1996 as a competitor to CART known as the Indy Racing League . Citing CART's increasing reliance on expensive machinery and...
driver - Raul BoeselRaul BoeselRaul de Mesquita Boesel is a former racing driver who raced for the March and Ligier Formula One teams and later raced in Champ Car and the Indy Racing League.He won the 1987 World Sportscar Championship and the 1988 24 Hours of Daytona...
– Formula One driver – IndyCarIndyCar SeriesThe IZOD IndyCar Series is the premier level of American open wheel racing. The current championship, founded by Indianapolis Motor Speedway owner Tony George, began in 1996 as a competitor to CART known as the Indy Racing League . Citing CART's increasing reliance on expensive machinery and...
driver. 19871987 World Sportscar Championship seasonThe 1987 World Sportscar Championship season was the 35th season of FIA World Sportscar Championship racing. It featured the World Sports-Prototype Championship which was a series which ran from March 22, 1987 to September 27, 1987 and was composed of ten races. The series was open to cars running...
World Sportscar ChampionshipWorld Sportscar ChampionshipThe World Sportscar Championship was the world series run for sports car racing by the FIA from 1953 to 1992.The championship evolved from a small collection of the most important sportscar, endurance and road racing events in Europe and North America with dozens of gentleman drivers at the grid,...
champion. - Ricardo ZontaRicardo ZontaRicardo Luiz Zonta is a Brazilian racing driver.-Early career:Born in Curitiba, Brazil, Zonta began karting in 1987, winning his first race shortly thereafter. The following year, he was runner-up for the Curitiba Karting Championship, and in 1991, he won the title...
– Formula One driver. 19981998 FIA GT Championship seasonThe 1998 FIA GT Championship season was the 2nd season of FIA GT Championship. It is a series for Grand Touring style cars broken into two classes based on power and manufacturer involvement, called GT1 and GT2...
FIA GT ChampionshipFIA GT ChampionshipThe FIA GT Championship was a sports car racing series organized by the Stéphane Ratel Organisation at the behest of the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile . The championship was mostly concentrated in Europe, but throughout the years has visited other continents including Asia and South...
champion
Basketball
- Rolando FerreiraRolando FerreiraRolando Ferreira Júnior is a retired Brazilian professional basketball player. He was selected by the Portland Trail Blazers in the 2nd round of the 1988 NBA Draft. A 7'1" center, Ferreira played in only one NBA season as a member of the 1988–89 Blazers. In his NBA career, he played in 12 games...
– (Gold medalist at the 1987 Pan American Games1987 Pan American GamesThe 1987 Pan American Games, officially known as the X Pan American Games, was a major international multi-sport event which was celebrated in Indianapolis, Indiana, United States, from 7 August to 23 August 1987. Over 4,300 athletes from 38 countries in the Americas competed in 30 sports earning...
). Former Portland Trail BlazersPortland Trail BlazersThe Portland Trail Blazers, commonly known as the Blazers, are an American professional basketball team based in Portland, Oregon. They play in the Northwest Division of the Western Conference in the National Basketball Association . The Trail Blazers originally played their home games in the...
player
Beach Volleyball
- Emanuel RegoEmanuel RegoEmanuel Fernando Sheffer Rego is a beach volleyball player from Brazil, who competed in three consecutive Summer Olympics, starting in 1996. He won the gold medal in the men's beach team competition at the 2004 Summer Olympics in Athens, Greece, partnering Ricardo Santos...
(Gold medalist in 2004 Olympics)
Poker
- Alexandre GomesAlexandre GomesAlexandre Gomes is a Brazilian professional poker player born on July 24, 1982 in Curitiba. He is a World Series of Poker bracelet winner, a World Poker Tour champion and a Team PokerStars Pro.- World Series of Poker :...
(WSOP and WPT world champion 2008–2009) - Luiz Filipe Ferreira de Andrade (Professional Poker Player)
- Gustav Langner (Professional Poker Player)
External links
Official homepage

