ATSC
Encyclopedia
ATSC standards are a set of standards developed by the Advanced Television Systems Committee
for digital television
transmission over terrestrial, cable, and satellite networks.
The ATSC standards were developed in the early 1990s by the Grand Alliance
, a consortium of electronics and telecommunications companies that assembled to develop a specification for what is now known as HDTV. ATSC formats also include standard-definition formats, although initially only HDTV services were launched in the digital format.
images up to 1920×1080 pixel
s in size — more than six times the display resolution
of the earlier standard. However, many different image sizes are also supported. The reduced bandwidth requirements of lower-resolution images allow up to six standard-definition "subchannels" to be broadcast on a single 6 MHz TV channel.
ATSC standards are marked A/x (x is the standard number) and can be downloaded freely from the ATSC's website at ATSC.org. ATSC Standard A/53, which implemented the system developed by the Grand Alliance, was published in 1995; the standard was adopted by the Federal Communications Commission
in the United States in 1996. It was revised in 2009. ATSC Standard A/72 was approved in 2008 and introduces H.264/AVC video coding to the ATSC system.
ATSC also boasts 5.1-channel surround sound
using the Dolby Digital
AC-3 format. Numerous auxiliary datacasting
services can also be provided.
Many aspects of ATSC are patent
ed, including elements of the MPEG video coding, the AC-3 audio coding, and the 8VSB
modulation. The cost of patent licensing, estimated at up to per digital TV receiver, has prompted complaints by manufacturers.
As with other systems, ATSC depends on numerous interwoven standards, e.g. the EIA-708
standard for digital closed captioning
, leading to variations in implementation.
much of the analog NTSC
television system in the United States
on June 12, 2009, replaced NTSC on August 31, 2011 in Canada
, and will replace NTSC by December 31, 2015 in Mexico
and January 1, 2019 in El Salvador
.
Broadcasters who use ATSC and want to retain an analog signal must broadcast on two separate channels, as the ATSC system requires the use of an entire channel. Virtual channel
s allow channel numbers to be remapped from their physical RF
channel to any other number 1 to 99, so that ATSC stations can either be associated with the related NTSC channel numbers, or all stations on a network can use the same number. There is also a standard for distributed transmission system
s (DTx), a form of single-frequency network
which allows for the synchronised operation of multiple on-channel booster stations.
AC-3 is used as the audio codec
, though it was officially standardized as A/52 by the ATSC. It allows the transport of up to five channels of sound with a sixth channel for low-frequency effects (the so-called "5.1" configuration). In contrast, Japanese ISDB
HDTV broadcasts use MPEG's Advanced Audio Coding
(AAC) as the audio codec, which also allows 5.1 audio output. DVB (see below) allows both.
MPEG-2 audio was a contender for the ATSC standard during the DTV
"Grand Alliance
" shootout, but lost out to Dolby AC-3. The Grand Alliance issued a statement finding the MPEG-2 system to be "essentially equivalent" to Dolby, but only after the Dolby selection had been made. Later, a story emerged that MIT had entered into an agreement with Dolby whereupon the university would be awarded a large sum if the MPEG-2 system was rejected. Dolby also offered an incentive for Zenith to switch their vote (which they did); however, it is unknown whether they accepted the offer.
s, and frame rate
s. The formats are listed here by resolution, form of scanning (progressive
or interlaced), and number of frames (or fields) per second (see also the TV resolution overview at the end of this article).
For transport, ATSC uses the MPEG systems specification, known as an MPEG transport stream, to encapsulate data, subject to certain constraints. ATSC uses 188-byte MPEG transport stream packets to carry data. Before decoding of audio and video takes place, the receiver must demodulate
and apply error correction to the signal. Then, the transport stream may be demultiplexed into its constituent streams.
The different resolutions can operate in progressive scan
or interlaced mode, although the highest 1080-line system cannot display progressive images at the rate of 50, 59.94 or 60 frames per second, because such technology was seen as too advanced at the time and the image quality was deemed to be too poor considering the amount of data that needs to be transmitted.
A terrestrial (over-the-air) transmission carries 19.39 megabit
s of data per second (a fluctuating bandwidth of about 18.3 Mbit/s left after overhead such as error correction, program guide, closed captioning, etc.), compared to a maximum possible MPEG-2 bitrate of 10.08 Mbit/s (7 Mbit/s typical) allowed in the DVD
standard and 48 Mbit/s (36 Mbit/s typical) allowed in the Blu-ray disc
standard.
"EDTV
" displays can reproduce progressive scan content and frequently have a 16:9 wide screen format. Such resolutions are 720×480 in NTSC or 720×576 in PAL, allowing 60 progressive frames per second in NTSC or 50 in PAL.
Although the ATSC A/53 standard limits MPEG-2 transmission to these 18 formats (with integer frame rates paired with 1000/1001-rate versions), the U.S. Federal Communications Commission declined to mandate that television stations obey this part of the ATSC's standard. In theory, television stations in the U.S. are free to choose any resolution, aspect ratio, and frame/field rate, within the limits of Main Profile @ High Level. Many stations do go outside the bounds of the ATSC specification by using other resolutions – for example, 720 × 480.
ATSC also supports PAL frame rates and resolutions which are defined in ATSC A/63 standard.
The ATC A/53 specification imposes certain constraints on MPEG-2 video stream:
The ATSC specification and MPEG-2 allow the use of progressive frames coded within an interlaced video sequence. For example, NBC stations transmit a 1080i60 video sequence, meaning the formal output of the MPEG-2 decoding process is sixty 540-line fields per second. However for prime-time television shows, those 60 fields can be coded using 24 progressive frames as a base - actually, an 1080p24 video stream (a sequence of 24 progressive frames per second) is transmitted, and MPEG-2 metadata instructs the decoder to interlace these fields and perform 3:2 pulldown before display, as in soft telecine.
The ATSC specification also allows 1080p30 and 1080p24 MPEG-2 sequences, however they are not used in practice, because broadcasters want to be able to switch between 60 Hz (news, soap operas) and 24 Hz (prime-time) content without ending the MPEG-2 sequence.
The 1080-line formats are encoded with 1920 × 1088 pixel luma matrices and 960 × 540 chroma matrices, but the last 8 lines are discarded by the MPEG-2 decoding and display process.
video codec. The new standard is split in two parts:
The new standards supports 1080p
at 50, 59.94 and 60 frames per second; such frame rates require H.264/AVC High Profile Level 4.2, while standard HDTV frame rates only require Levels 3.2 and 4, and SDTV frame rates require Levels 3 and 3.1.
file captured from a TV. This means that it has been taken from a television program using special software that converts the television's signal and records it.
television channels (the interference requirements of A/53 DTV standards with adjacent NTSC or other DTV channels are very strict). Once the digital video and audio signals have been compressed and multiplexed, the transport stream can be modulated
in different ways depending on the method of transmission.
The proposals for modulation schemes for digital television were developed when cable operators carried standard-resolution video as uncompressed analog signals. In recent years, cable operators have become accustomed to compressing standard-resolution video for digital cable
systems, making it harder to find duplicate 6 MHz channels for local broadcasters on uncompressed "basic" cable.
Currently, the Federal Communications Commission
requires cable operators in the United States to carry the analog or digital transmission of a terrestrial broadcaster (but not both), when so requested by the broadcaster (the "must-carry
rule"). The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission in Canada has similar rules in force with respect to carrying ATSC signals.
However, cable operators have still been slow to add ATSC channels to their lineups for legal, regulatory, and plant & equipment related reasons. One key technical and regulatory issue is the modulation scheme used on the cable: cable operators in the US (and to a lesser extent Canada) can determine their own method of modulation for their plants. Multiple standards bodies exist in the industry: the SCTE
defined 256-QAM as a modulation scheme for cable in a cable industry standard, ANSI/SCTE 07 2006: Digital Transmission Standard For Cable Television. Consequently, most North American cable operators seeking additional capacity on the cable system have moved to 256-QAM from the 64-QAM modulation used in their plant, in preference to the 16VSB
standard originally proposed by ATSC. Over time 256-QAM is expected to be included in the ATSC standard.
There is also a standard for transmitting ATSC via satellite; however, this is only used by TV networks. Very few teleport
s outside the US support the ATSC satellite transmission standard, but teleport support for the standard is improving. The ATSC satellite transmission system is not used for direct-broadcast satellite systems; in North America these have long used either DVB-S
(in standard or modified form) or a proprietary system such as DSS
or DigiCipher 2
.
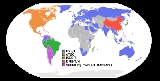
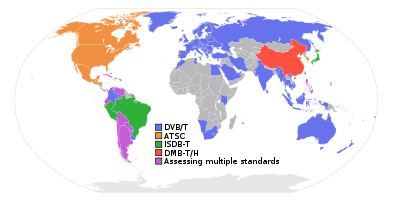 ATSC coexists with the DVB-T
ATSC coexists with the DVB-T
standard, and with ISDB-T. A similar standard called ADTB-T was developed for use as part of China
's new DMB-T/H
dual standard. While China has officially chosen a dual standard, there is no requirement that a receiver work with both standards and there is no support for the ADTB modulation from broadcasters or equipment and receiver manufacturers.
Because of initial potential use outside of existing NTSC areas, the ATSC system includes the capability to carry PAL
and SECAM
formatted video (576 displayable lines, 50 fields or 25 frames per second) along with NTSC (486 displayable lines, 60 × 1000/1001 fields or 30 × 1000/1001 frames per second) and film
(24 frames per second).
While the ATSC system has been criticized as being complicated and expensive to implement and use, both broadcasting and receiving equipment are now comparable in cost with that of DVB.
The ATSC signal is more susceptible to changes in radio propagation
conditions than DVB-T
and ISDB-T. It also lacks true hierarchical modulation
, which would allow the SDTV part of an HDTV signal (or the audio portion of a television program) to be received uninterrupted even in fringe areas where signal strength
is low. For this reason, an additional modulation mode, enhanced-VSB (E-VSB
) has been introduced, allowing for a similar benefit.
In spite of ATSC's fixed transmission mode, it is still a robust signal under various conditions. 8VSB
was chosen over COFDM in part because many areas of North America are rural
and have a much lower population density
, thereby requiring larger transmitter
s and resulting in large fringe areas. In these areas, 8VSB was shown to perform better than other systems.
COFDM is used in both DVB-T and ISDB-T, and for 1seg
, as well as DVB-H
and HD Radio
in the United States. In metropolitan area
s, where the great and increasing majority of North Americans live, COFDM is said to be better at handling multipath propagation. While ATSC is also incapable of true single-frequency network
(SFN) operation, the distributed transmission
mode, using multiple synchronised on-channel transmitters, has been shown to improve reception under similar conditions. Thus, it may not require more spectrum
allocation than DVB-T
using SFNs.
/Rhode & Schwarz's A-VSB
, Harris/LG
's MPH
, and a recent proposal from Thomson
/Micronas; all of these systems have been submitted as candidates for a new ATSC standard, ATSC-M/H
. After one year of standardization, the solution based on LGE technology has been adopted and would have been deployed in 2009. This is in addition to other standards like MediaFLO
, and worldwide open standards such as DVB-H
and T-DMB. Like DVB-H and ISDB 1seg
, the proposed ATSC mobile standards are backward-compatible with existing tuners, despite being added to the standard well after the original standard was in wide use.
Mobile reception of some stations will still be more difficult, because 18 UHF channels in the U.S. have been removed from TV service, forcing some broadcasters to stay on VHF. This band requires larger antennas for reception, and is more prone to electromagnetic interference
from engine
s and rapidly-changing multipath conditions.
services, targeted advertising
, MPEG-4
compression, better programming guides, and the ability to store information on new receivers.
stations)
Advanced Television Systems Committee
The Advanced Television Systems Committee is the group, established in 1982, that developed the eponymous ATSC Standards for digital television in the United States, also adopted by Canada, Mexico, South Korea, and recently Honduras and is being considered by other countries.-See also:*ATSC...
for digital television
Digital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
transmission over terrestrial, cable, and satellite networks.
The ATSC standards were developed in the early 1990s by the Grand Alliance
Grand Alliance (HDTV)
The Grand Alliance was a consortium created in 1993 at the behest of the Federal Communications Commission to develop the American digital television and HDTV specification, with the aim of pooling the best work from different companies...
, a consortium of electronics and telecommunications companies that assembled to develop a specification for what is now known as HDTV. ATSC formats also include standard-definition formats, although initially only HDTV services were launched in the digital format.
Background
The high definition television standards defined by the ATSC produce wide screen 16:916:9
16:9 is an aspect ratio with a width of 16 units and height of 9. Since 2009, it has become the most common aspect ratio for sold televisions and computer monitors and is also the international standard format of HDTV, Full HD, non-HD digital television and analog widescreen television ...
images up to 1920×1080 pixel
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
s in size — more than six times the display resolution
Display resolution
The display resolution of a digital television or display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by all different factors in cathode ray tube , flat panel or projection...
of the earlier standard. However, many different image sizes are also supported. The reduced bandwidth requirements of lower-resolution images allow up to six standard-definition "subchannels" to be broadcast on a single 6 MHz TV channel.
ATSC standards are marked A/x (x is the standard number) and can be downloaded freely from the ATSC's website at ATSC.org. ATSC Standard A/53, which implemented the system developed by the Grand Alliance, was published in 1995; the standard was adopted by the Federal Communications Commission
Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission is an independent agency of the United States government, created, Congressional statute , and with the majority of its commissioners appointed by the current President. The FCC works towards six goals in the areas of broadband, competition, the spectrum, the...
in the United States in 1996. It was revised in 2009. ATSC Standard A/72 was approved in 2008 and introduces H.264/AVC video coding to the ATSC system.
ATSC also boasts 5.1-channel surround sound
Surround sound
Surround sound encompasses a range of techniques such as for enriching the sound reproduction quality of an audio source with audio channels reproduced via additional, discrete speakers. Surround sound is characterized by a listener location or sweet spot where the audio effects work best, and...
using the Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital is the name for audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. It was originally called Dolby Stereo Digital until 1994. Except for Dolby TrueHD, the audio compression is lossy. The first use of Dolby Digital was to provide digital sound in cinemas from 35mm film prints...
AC-3 format. Numerous auxiliary datacasting
Datacasting
Datacasting is the broadcasting of data over a wide area via radio waves. It most often refers to supplemental information sent by television stations along with digital television, but may also be applied to digital signals on analog TV or radio...
services can also be provided.
Many aspects of ATSC are patent
Patent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
ed, including elements of the MPEG video coding, the AC-3 audio coding, and the 8VSB
8VSB
8VSB is the modulation method used for broadcast in the ATSC digital television standard. ATSC and 8VSB modulation is used primarily in North America; in contrast, the DVB-T standard uses COFDM....
modulation. The cost of patent licensing, estimated at up to per digital TV receiver, has prompted complaints by manufacturers.
As with other systems, ATSC depends on numerous interwoven standards, e.g. the EIA-708
EIA-708
CEA-708 is the standard for closed captioning for ATSC digital television streams in the United States and Canada. It was developed by the Electronic Industries Alliance.Unlike most DVB captions, CEA-708 captions are textual like traditional Line 21 captions...
standard for digital closed captioning
Closed captioning
Closed captioning is the process of displaying text on a television, video screen or other visual display to provide additional or interpretive information to individuals who wish to access it...
, leading to variations in implementation.
Digital switchover
ATSC replacedDTV transition in the United States
The DTV transition in the United States was the switchover from analog to exclusively digital broadcasting of free over-the-air television programming...
much of the analog NTSC
NTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
television system in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
on June 12, 2009, replaced NTSC on August 31, 2011 in Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, and will replace NTSC by December 31, 2015 in Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
and January 1, 2019 in El Salvador
El Salvador
El Salvador or simply Salvador is the smallest and the most densely populated country in Central America. The country's capital city and largest city is San Salvador; Santa Ana and San Miguel are also important cultural and commercial centers in the country and in all of Central America...
.
Broadcasters who use ATSC and want to retain an analog signal must broadcast on two separate channels, as the ATSC system requires the use of an entire channel. Virtual channel
Virtual channel
In telecommunications, a logical channel number , also known as virtual channel, is a channel designation which differs from that of the actual radio channel on which the signal travels....
s allow channel numbers to be remapped from their physical RF
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
channel to any other number 1 to 99, so that ATSC stations can either be associated with the related NTSC channel numbers, or all stations on a network can use the same number. There is also a standard for distributed transmission system
Distributed transmission system
In North American digital terrestrial television broadcasting, a distributed transmission system is a form of single-frequency network in which a single broadcast signal is fed via microwave, landline, or communications satellite to multiple synchronised terrestrial radio transmitter sites...
s (DTx), a form of single-frequency network
Single-frequency network
A single-frequency network or SFN is a broadcast network where several transmitters simultaneously send the same signal over the same frequency channel.-Overview:...
which allows for the synchronised operation of multiple on-channel booster stations.
Audio
Dolby DigitalDolby Digital
Dolby Digital is the name for audio compression technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories. It was originally called Dolby Stereo Digital until 1994. Except for Dolby TrueHD, the audio compression is lossy. The first use of Dolby Digital was to provide digital sound in cinemas from 35mm film prints...
AC-3 is used as the audio codec
Audio codec
All codecs are devices or computer programs capable of coding or decoding a digital data stream or signal.The term audio codec has two meanings depending on the context:...
, though it was officially standardized as A/52 by the ATSC. It allows the transport of up to five channels of sound with a sixth channel for low-frequency effects (the so-called "5.1" configuration). In contrast, Japanese ISDB
ISDB
Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting is a Japanese standard for digital television and digital radio used by the country's radio and television stations. ISDB replaced the previously used MUSE "Hi-vision" analogue HDTV system...
HDTV broadcasts use MPEG's Advanced Audio Coding
Advanced Audio Coding
Advanced Audio Coding is a standardized, lossy compression and encoding scheme for digital audio. Designed to be the successor of the MP3 format, AAC generally achieves better sound quality than MP3 at similar bit rates....
(AAC) as the audio codec, which also allows 5.1 audio output. DVB (see below) allows both.
MPEG-2 audio was a contender for the ATSC standard during the DTV
Digital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
"Grand Alliance
Grand Alliance (HDTV)
The Grand Alliance was a consortium created in 1993 at the behest of the Federal Communications Commission to develop the American digital television and HDTV specification, with the aim of pooling the best work from different companies...
" shootout, but lost out to Dolby AC-3. The Grand Alliance issued a statement finding the MPEG-2 system to be "essentially equivalent" to Dolby, but only after the Dolby selection had been made. Later, a story emerged that MIT had entered into an agreement with Dolby whereupon the university would be awarded a large sum if the MPEG-2 system was rejected. Dolby also offered an incentive for Zenith to switch their vote (which they did); however, it is unknown whether they accepted the offer.
Video
The ATSC system supports a number of different display resolutions, aspect ratioAspect ratio
The aspect ratio of a shape is the ratio of its longer dimension to its shorter dimension. It may be applied to two characteristic dimensions of a three-dimensional shape, such as the ratio of the longest and shortest axis, or for symmetrical objects that are described by just two measurements,...
s, and frame rate
Frame rate
Frame rate is the frequency at which an imaging device produces unique consecutive images called frames. The term applies equally well to computer graphics, video cameras, film cameras, and motion capture systems...
s. The formats are listed here by resolution, form of scanning (progressive
Progressive scan
Progressive scanning is a way of displaying, storing, or transmitting moving images in which all the lines of each frame are drawn in sequence...
or interlaced), and number of frames (or fields) per second (see also the TV resolution overview at the end of this article).
For transport, ATSC uses the MPEG systems specification, known as an MPEG transport stream, to encapsulate data, subject to certain constraints. ATSC uses 188-byte MPEG transport stream packets to carry data. Before decoding of audio and video takes place, the receiver must demodulate
Demodulation
Demodulation is the act of extracting the original information-bearing signal from a modulated carrier wave.A demodulator is an electronic circuit that is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave.These terms are traditionally used in connection with radio receivers,...
and apply error correction to the signal. Then, the transport stream may be demultiplexed into its constituent streams.
MPEG-2
There are three basic display sizes for ATSC. Basic and enhanced NTSC and PAL image sizes are at the bottom level at 480 or 576 lines. Medium-sized images have 720 scanlines and are 1280 pixels wide. The top tier has 1080 lines 1920 pixels wide. 1080-line video is actually encoded with 1920×1088 pixel frames, but the last eight lines are discarded prior to display. This is due to a restriction of the MPEG-2 video format, which requires the number of coded luma samples (i.e. pixels) to be divisible by 16.The different resolutions can operate in progressive scan
Progressive scan
Progressive scanning is a way of displaying, storing, or transmitting moving images in which all the lines of each frame are drawn in sequence...
or interlaced mode, although the highest 1080-line system cannot display progressive images at the rate of 50, 59.94 or 60 frames per second, because such technology was seen as too advanced at the time and the image quality was deemed to be too poor considering the amount of data that needs to be transmitted.
A terrestrial (over-the-air) transmission carries 19.39 megabit
Megabit
The megabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information or computer storage. The prefix mega is defined in the International System of Units as a multiplier of 106 , and therefore...
s of data per second (a fluctuating bandwidth of about 18.3 Mbit/s left after overhead such as error correction, program guide, closed captioning, etc.), compared to a maximum possible MPEG-2 bitrate of 10.08 Mbit/s (7 Mbit/s typical) allowed in the DVD
DVD
A DVD is an optical disc storage media format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions....
standard and 48 Mbit/s (36 Mbit/s typical) allowed in the Blu-ray disc
Blu-ray Disc
Blu-ray Disc is an optical disc storage medium designed to supersede the DVD format. The plastic disc is 120 mm in diameter and 1.2 mm thick, the same size as DVDs and CDs. Blu-ray Discs contain 25 GB per layer, with dual layer discs being the norm for feature-length video discs...
standard.
"EDTV
Enhanced-definition television
Enhanced-definition television, or extended-definition television, is a United States Consumer Electronics Association marketing shorthand term for certain digital television formats and devices...
" displays can reproduce progressive scan content and frequently have a 16:9 wide screen format. Such resolutions are 720×480 in NTSC or 720×576 in PAL, allowing 60 progressive frames per second in NTSC or 50 in PAL.
| Resolution | Aspect ratio | Pixel aspect ratio Pixel aspect ratio Pixel aspect ratio is a mathematical ratio that describes how the width of a pixel in a digital image compares to the height of that pixel.... |
Scanning | Frame rate (Hz Hertz The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications.... ) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical | Horizontal | ||||
| 1080 | 1920 | 16:9 | square | progressive | 23.976 24 29.97 30 |
| interlaced | 29.97 (59.94 fields/s) 30 (60 fields/s) |
||||
| 720 | 1280 | 16:9 | square | progressive | 23.976 24 29.97 30 59.94 60 |
| 480 | 704 | 4:3 or 16:9 | non-square | progressive | 23.976 24 29.97 30 59.94 60 |
| interlaced | 29.97 (59.94 fields/s) 30 (60 fields/s) |
||||
| 640 | 4:3 | square | progressive | 23.976 24 29.97 30 59.94 60 |
|
| interlaced | 29.97 (59.94 fields/s) 30 (60 fields/s) |
||||
Although the ATSC A/53 standard limits MPEG-2 transmission to these 18 formats (with integer frame rates paired with 1000/1001-rate versions), the U.S. Federal Communications Commission declined to mandate that television stations obey this part of the ATSC's standard. In theory, television stations in the U.S. are free to choose any resolution, aspect ratio, and frame/field rate, within the limits of Main Profile @ High Level. Many stations do go outside the bounds of the ATSC specification by using other resolutions – for example, 720 × 480.
ATSC also supports PAL frame rates and resolutions which are defined in ATSC A/63 standard.
| Resolution | Aspect ratio | Pixel aspect ratio Pixel aspect ratio Pixel aspect ratio is a mathematical ratio that describes how the width of a pixel in a digital image compares to the height of that pixel.... |
Scanning | Frame rate (Hz Hertz The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications.... ) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical | Horizontal | ||||
| 1080 | 1920 | 16:9 | square | interlaced | 25 (50 fields/s) |
| progressive | 25 | ||||
| 720 | 1280 | 16:9 | square | progressive | 50 |
| 576 | 720 | 4:3 or 16:9 | non-square | progressive | 25 50 |
| interlaced | 25 (50 fields/s) | ||||
| 544 | 4:3 or 16:9 | non-square | progressive | 25 | |
| interlaced | 25 (50 fields/s) | ||||
| 480 | 4:3 or 16:9 | non-square | progressive | 25 | |
| interlaced | 25 (50 fields/s) | ||||
| 352 | 4:3 or 16:9 | non-square | progressive | 25 | |
| interlaced | 25 (50 fields/s) | ||||
| 288 | 352 | 4:3 or 16:9 | non-square | progressive | 25 |
The ATC A/53 specification imposes certain constraints on MPEG-2 video stream:
- The maximum bitrate of the MPEG-2 video stream is exactly 19.4 Mbit/s for broadcast television, and exactly 38.8 Mbit/s for the "high-data-rate" mode (e.g., cable television). (The practical limit is somewhat lower, since the MPEG-2 video stream must fit inside a transport stream, with overhead, sent out at 19.3927... Mbit/s for broadcast.)
- The amount of MPEG-2 stream buffer required at the decoder (the vbv_buffer_size_value) must be less than or equal to 999,424 bytes.
- In most cases, the transmitter can't start sending a coded image until within a half-second of when it's to be decoded (vbv_delay less than or equal to 45000 90-kHz clock increments).
- The stream must include colorimetry information (gamma curve, the precise RGB colors used, and the relationship between RGB and the coded YCbCr).
- The video must be 4:2:0 (chrominance resolution must be 1/2 of luma horizontal resolution and 1/2 of luma vertical resolution).
The ATSC specification and MPEG-2 allow the use of progressive frames coded within an interlaced video sequence. For example, NBC stations transmit a 1080i60 video sequence, meaning the formal output of the MPEG-2 decoding process is sixty 540-line fields per second. However for prime-time television shows, those 60 fields can be coded using 24 progressive frames as a base - actually, an 1080p24 video stream (a sequence of 24 progressive frames per second) is transmitted, and MPEG-2 metadata instructs the decoder to interlace these fields and perform 3:2 pulldown before display, as in soft telecine.
The ATSC specification also allows 1080p30 and 1080p24 MPEG-2 sequences, however they are not used in practice, because broadcasters want to be able to switch between 60 Hz (news, soap operas) and 24 Hz (prime-time) content without ending the MPEG-2 sequence.
The 1080-line formats are encoded with 1920 × 1088 pixel luma matrices and 960 × 540 chroma matrices, but the last 8 lines are discarded by the MPEG-2 decoding and display process.
H.264/MPEG-4 AVC
In July 2008, ATSC was updated to support the ITU-T H.264H.264/MPEG-4 AVC
H.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video...
video codec. The new standard is split in two parts:
- A/72 part 1: Video System Characteristics of AVC in the ATSC Digital Television System
- A/72 part 2 : AVC Video Transport Subsystem Characteristics
The new standards supports 1080p
1080p
1080p is the shorthand identification for a set of HDTV high-definition video modes that are characterized by 1080 horizontal lines of resolution and progressive scan, meaning the image is not interlaced as is the case with the 1080i display standard....
at 50, 59.94 and 60 frames per second; such frame rates require H.264/AVC High Profile Level 4.2, while standard HDTV frame rates only require Levels 3.2 and 4, and SDTV frame rates require Levels 3 and 3.1.
| Resolution | Aspect ratio | Pixel aspect ratio Pixel aspect ratio Pixel aspect ratio is a mathematical ratio that describes how the width of a pixel in a digital image compares to the height of that pixel.... |
Scanning | Frame rate (Hz Hertz The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications.... ) |
Level | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical | Horizontal | |||||
| 1080 | 1920 | 16:9 | square | progressive | 23.976 24 29.97 30 25 |
4 |
| progressive | 59.94 60 50 |
4.2 | ||||
| interlaced | 29.97 (59.94 fields/s) 30 (60 fields/s) 25 (50 fields/s) |
4 | ||||
| 1440 | 16:9 | non-square (4:3) |
progressive | 23.976 24 29.97 30 25 |
4 | |
| progressive | 59.94 60 50 |
4.2 | ||||
| interlaced | 29.97 (59.94 fields/s) 30 (60 fields/s) 25 (50 fields/s) |
4 | ||||
| 720 | 1280 | 16:9 | square | progressive | 23.976 24 29.97 30 59.94 60 25 50 |
3.2, 4 |
| 480 | 720 | 4:3 or 16:9 | non-square (10:11 or 40:33) |
progressive | 23.976 24 29.97 30 59.94 60 25 50 |
3.1, 4 |
| interlaced | 29.97 (59.94 fields/s) 30 (60 fields/s) 25 (50 fields/s) |
3 | ||||
| 704 | 4:3 or 16:9 | non-square (10:11 or 40:33) |
progressive | 23.976 24 29.97 30 59.94 60 25 50 |
3.1, 4 | |
| interlaced | 29.97 (59.94 fields/s) 30 (60 fields/s) 25 (50 fields/s) |
3 | ||||
| 640 | 4:3 | square | progressive | 23.976 24 29.97 30 59.94 60 25 50 |
3.1, 4 | |
| interlaced | 29.97 (59.94 fields/s) 30 (60 fields/s) 25 (50 fields/s) |
3 | ||||
| 544 | 4:3 | non-square (40:33) |
progressive | 23.976 25 |
3 | |
| interlaced | 29.97 (59.94 fields/s) 25 (50 fields/s) |
|||||
| 528 | 4:3 | non-square (40:33) |
progressive | 23.976 25 |
3 | |
| interlaced | 29.97 (59.94 fields/s) 25 (50 fields/s) |
|||||
| 352 | 4:3 | non-square (20:11) |
progressive | 23.976 25 |
3 | |
| interlaced | 29.97 (59.94 fields/s) 25 (50 fields/s) |
|||||
| 240 | 352 | 4:3 | non-square (10:11) |
progressive | 23.976 25 |
3 |
| 120 | 176 | 4:3 | non-square (10:11) |
progressive | 23.976 25 |
1.1 |
TP
The file extension ".TP" is a video file. Specifically, it's an MPEG-2MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
file captured from a TV. This means that it has been taken from a television program using special software that converts the television's signal and records it.
Modulation and transmission
ATSC signals are designed to use the same 6 MHz bandwidth as analog NTSCNTSC
NTSC, named for the National Television System Committee, is the analog television system that is used in most of North America, most of South America , Burma, South Korea, Taiwan, Japan, the Philippines, and some Pacific island nations and territories .Most countries using the NTSC standard, as...
television channels (the interference requirements of A/53 DTV standards with adjacent NTSC or other DTV channels are very strict). Once the digital video and audio signals have been compressed and multiplexed, the transport stream can be modulated
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
in different ways depending on the method of transmission.
- Terrestrial (local) broadcasters use 8VSB8VSB8VSB is the modulation method used for broadcast in the ATSC digital television standard. ATSC and 8VSB modulation is used primarily in North America; in contrast, the DVB-T standard uses COFDM....
modulation that can transfer at a maximum rate of 19.39 Mbit/sMegabitThe megabit is a multiple of the unit bit for digital information or computer storage. The prefix mega is defined in the International System of Units as a multiplier of 106 , and therefore...
, sufficient to carry several video and audio programs and metadataMetadataThe term metadata is an ambiguous term which is used for two fundamentally different concepts . Although the expression "data about data" is often used, it does not apply to both in the same way. Structural metadata, the design and specification of data structures, cannot be about data, because at...
. - Cable televisionCable televisionCable television is a system of providing television programs to consumers via radio frequency signals transmitted to televisions through coaxial cables or digital light pulses through fixed optical fibers located on the subscriber's property, much like the over-the-air method used in traditional...
stations can generally operate at a higher signal-to-noise ratioSignal-to-noise ratioSignal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
and can use either the 16VSB16VSB16VSB is an abbreviation for 16-level vestigial sideband modulation, capable of transmitting four bits at a time.-How it works:Other slower but more rugged forms of VSB include 2VSB, 4VSB, and 8VSB...
as defined in ATSC or the 256-QAM defined in SCTESCTEThe Society of Cable Telecommunications Engineers or SCTE is a non-profit professional association for the advancement of technology related to cable telecommunications engineering. Founded in 1969, SCTE has a current membership of over 12,000 individuals.- Publications :SCTE offers several...
, to achieve a throughput of 38.78 Mbit/s, using the same 6 MHz channel.
The proposals for modulation schemes for digital television were developed when cable operators carried standard-resolution video as uncompressed analog signals. In recent years, cable operators have become accustomed to compressing standard-resolution video for digital cable
Digital cable
Digital cable is a generic term for any type of cable television distribution using digital video compression or distribution. The technology was originally developed by Motorola.-Background:...
systems, making it harder to find duplicate 6 MHz channels for local broadcasters on uncompressed "basic" cable.
Currently, the Federal Communications Commission
Federal Communications Commission
The Federal Communications Commission is an independent agency of the United States government, created, Congressional statute , and with the majority of its commissioners appointed by the current President. The FCC works towards six goals in the areas of broadband, competition, the spectrum, the...
requires cable operators in the United States to carry the analog or digital transmission of a terrestrial broadcaster (but not both), when so requested by the broadcaster (the "must-carry
Must-carry
In cable television, governments apply a must-carry regulation stating that locally-licensed television stations must be carried on a cable provider's system.- Canada :...
rule"). The Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission in Canada has similar rules in force with respect to carrying ATSC signals.
However, cable operators have still been slow to add ATSC channels to their lineups for legal, regulatory, and plant & equipment related reasons. One key technical and regulatory issue is the modulation scheme used on the cable: cable operators in the US (and to a lesser extent Canada) can determine their own method of modulation for their plants. Multiple standards bodies exist in the industry: the SCTE
SCTE
The Society of Cable Telecommunications Engineers or SCTE is a non-profit professional association for the advancement of technology related to cable telecommunications engineering. Founded in 1969, SCTE has a current membership of over 12,000 individuals.- Publications :SCTE offers several...
defined 256-QAM as a modulation scheme for cable in a cable industry standard, ANSI/SCTE 07 2006: Digital Transmission Standard For Cable Television. Consequently, most North American cable operators seeking additional capacity on the cable system have moved to 256-QAM from the 64-QAM modulation used in their plant, in preference to the 16VSB
16VSB
16VSB is an abbreviation for 16-level vestigial sideband modulation, capable of transmitting four bits at a time.-How it works:Other slower but more rugged forms of VSB include 2VSB, 4VSB, and 8VSB...
standard originally proposed by ATSC. Over time 256-QAM is expected to be included in the ATSC standard.
There is also a standard for transmitting ATSC via satellite; however, this is only used by TV networks. Very few teleport
Earth station
A ground station, earth station, or earth terminal is a terrestrial terminal station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft, and/or reception of radio waves from an astronomical radio source. Ground stations are located either on the surface of the Earth, or within Earth's...
s outside the US support the ATSC satellite transmission standard, but teleport support for the standard is improving. The ATSC satellite transmission system is not used for direct-broadcast satellite systems; in North America these have long used either DVB-S
DVB-S
DVB-S is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Satellite; it is the original Digital Video Broadcasting forward error coding and demodulation standard for satellite television and dates from 1994, in its first release, while development lasted from 1993 to 1997...
(in standard or modified form) or a proprietary system such as DSS
Digital Satellite Service
Digital Satellite Service is the assumed initialism expansion of the DSS digital satellite television transmission system used by DirecTV...
or DigiCipher 2
DigiCipher 2
DigiCipher 2, or simply DCII, is a proprietary standard format of digital signal transmission and encryption with MPEG-2 signal video compression used on many communications satellite television and audio signals...
.
Other systems

DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
standard, and with ISDB-T. A similar standard called ADTB-T was developed for use as part of China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
's new DMB-T/H
DMB-T/H
DTMB is the TV standard for mobile and fixed terminals used in the People's Republic of China, Hong Kong and Macau. Although at first this standard was called DMB-T/H , the official name is DTMB.DTT broadcasting systems...
dual standard. While China has officially chosen a dual standard, there is no requirement that a receiver work with both standards and there is no support for the ADTB modulation from broadcasters or equipment and receiver manufacturers.
Because of initial potential use outside of existing NTSC areas, the ATSC system includes the capability to carry PAL
PAL
PAL, short for Phase Alternating Line, is an analogue television colour encoding system used in broadcast television systems in many countries. Other common analogue television systems are NTSC and SECAM. This page primarily discusses the PAL colour encoding system...
and SECAM
SECAM
SECAM, also written SÉCAM , is an analog color television system first used in France....
formatted video (576 displayable lines, 50 fields or 25 frames per second) along with NTSC (486 displayable lines, 60 × 1000/1001 fields or 30 × 1000/1001 frames per second) and film
Film
A film, also called a movie or motion picture, is a series of still or moving images. It is produced by recording photographic images with cameras, or by creating images using animation techniques or visual effects...
(24 frames per second).
While the ATSC system has been criticized as being complicated and expensive to implement and use, both broadcasting and receiving equipment are now comparable in cost with that of DVB.
The ATSC signal is more susceptible to changes in radio propagation
Radio propagation
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves when they are transmitted, or propagated from one point on the Earth to another, or into various parts of the atmosphere...
conditions than DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
and ISDB-T. It also lacks true hierarchical modulation
Hierarchical modulation
Hierarchical modulation, also called layered modulation, is one of the signal processing techniques for multiplexing and modulating multiple data streams into one single symbol stream, where base-layer symbols and enhancement-layer symbols are synchronously overplayed before...
, which would allow the SDTV part of an HDTV signal (or the audio portion of a television program) to be received uninterrupted even in fringe areas where signal strength
Signal strength
In telecommunications, particularly in radio, signal strength refers to the magnitude of the electric field at a reference point that is a significant distance from the transmitting antenna. It may also be referred to as received signal level or field strength. Typically, it is expressed in...
is low. For this reason, an additional modulation mode, enhanced-VSB (E-VSB
E-VSB
E-VSB or Enhanced VSB is an optional enhancement to the original ATSC Standards that use the 8VSB modulation system used for transmission of digital television. It is intended for improving reception where signals are weaker, including fringe reception areas, and on portable devices such as...
) has been introduced, allowing for a similar benefit.
In spite of ATSC's fixed transmission mode, it is still a robust signal under various conditions. 8VSB
8VSB
8VSB is the modulation method used for broadcast in the ATSC digital television standard. ATSC and 8VSB modulation is used primarily in North America; in contrast, the DVB-T standard uses COFDM....
was chosen over COFDM in part because many areas of North America are rural
Rural
Rural areas or the country or countryside are areas that are not urbanized, though when large areas are described, country towns and smaller cities will be included. They have a low population density, and typically much of the land is devoted to agriculture...
and have a much lower population density
Population density
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and particularly to humans...
, thereby requiring larger transmitter
Transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications a transmitter or radio transmitter is an electronic device which, with the aid of an antenna, produces radio waves. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating...
s and resulting in large fringe areas. In these areas, 8VSB was shown to perform better than other systems.
COFDM is used in both DVB-T and ISDB-T, and for 1seg
1seg
is a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
, as well as DVB-H
DVB-H
DVB-H is one of three prevalent mobile TV formats. It is a technical specification for bringing broadcast services to mobile handsets. DVB-H was formally adopted as ETSI standard EN 302 304 in November 2004. The DVB-H specification can be downloaded from the official DVB-H website...
and HD Radio
HD Radio
HD Radio, which originally stood for "Hybrid Digital", is the trademark for iBiquity's in-band on-channel digital radio technology used by AM and FM radio stations to transmit audio and data via a digital signal in conjunction with their analog signals...
in the United States. In metropolitan area
Metropolitan area
The term metropolitan area refers to a region consisting of a densely populated urban core and its less-populated surrounding territories, sharing industry, infrastructure, and housing. A metropolitan area usually encompasses multiple jurisdictions and municipalities: neighborhoods, townships,...
s, where the great and increasing majority of North Americans live, COFDM is said to be better at handling multipath propagation. While ATSC is also incapable of true single-frequency network
Single-frequency network
A single-frequency network or SFN is a broadcast network where several transmitters simultaneously send the same signal over the same frequency channel.-Overview:...
(SFN) operation, the distributed transmission
Distributed transmission system
In North American digital terrestrial television broadcasting, a distributed transmission system is a form of single-frequency network in which a single broadcast signal is fed via microwave, landline, or communications satellite to multiple synchronised terrestrial radio transmitter sites...
mode, using multiple synchronised on-channel transmitters, has been shown to improve reception under similar conditions. Thus, it may not require more spectrum
Spectrum
A spectrum is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary infinitely within a continuum. The word saw its first scientific use within the field of optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light when separated using a prism; it has since been applied by...
allocation than DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
using SFNs.
Mobile TV
Mobile reception of digital stations using ATSC has, until 2008, been difficult to impossible, especially when moving at vehicular speeds. To overcome this, there are several proposed systems that report improved mobile reception: SamsungSamsung
The Samsung Group is a South Korean multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea...
/Rhode & Schwarz's A-VSB
A-VSB
A-VSB or Advanced VSB is a modification of the 8VSB modulation system used for transmission of digital television using the ATSC system. One of the constraints of conventional ATSC transmission is that reliable reception is difficult or impossible when the receiver is moving at speeds associated...
, Harris/LG
LG
LG may refer to:*LG Corp., a South Korean electronics and petrochemicals conglomerate*LG Electronics, an affiliate of the South Korean LG Group which produces electronic products* Lawrence Graham, a London headquartered firm of business lawyers...
's MPH
MPH (ATSC)
MPH inband mobile digital television is a technology jointly developed by Harris Corporation, LG Electronics, Inc. and its U.S. research subsidiary, Zenith Electronics...
, and a recent proposal from Thomson
Thomson SA
Technicolor SA , formerly Thomson SA and Thomson Multimedia, is a French international provider of solutions for the creation, management, post-production, delivery and access of video, for the Communication, Media and Entertainment industries. Technicolor’s headquarters are located in Issy les...
/Micronas; all of these systems have been submitted as candidates for a new ATSC standard, ATSC-M/H
ATSC-M/H
ATSC-M/H is a standard in the USA for mobile digital TV, that allows TV broadcasts to be received by mobile devices.....
. After one year of standardization, the solution based on LGE technology has been adopted and would have been deployed in 2009. This is in addition to other standards like MediaFLO
MediaFLO
MediaFLO is a technology developed by Qualcomm for transmitting audio, video and data to portable devices such as mobile phones and personal televisions, used for mobile television...
, and worldwide open standards such as DVB-H
DVB-H
DVB-H is one of three prevalent mobile TV formats. It is a technical specification for bringing broadcast services to mobile handsets. DVB-H was formally adopted as ETSI standard EN 302 304 in November 2004. The DVB-H specification can be downloaded from the official DVB-H website...
and T-DMB. Like DVB-H and ISDB 1seg
1seg
is a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
, the proposed ATSC mobile standards are backward-compatible with existing tuners, despite being added to the standard well after the original standard was in wide use.
Mobile reception of some stations will still be more difficult, because 18 UHF channels in the U.S. have been removed from TV service, forcing some broadcasters to stay on VHF. This band requires larger antennas for reception, and is more prone to electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
from engine
Engine
An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert energy into useful mechanical motion. Heat engines, including internal combustion engines and external combustion engines burn a fuel to create heat which is then used to create motion...
s and rapidly-changing multipath conditions.
Future standards
By 2012, ATSC 2.0 may be a standard. It is intended to be used with the current standard, but will allow interactive services, including video on demandVideo on demand
Video on Demand or Audio and Video On Demand are systems which allow users to select and watch/listen to video or audio content on demand...
services, targeted advertising
Targeted advertising
Targeted advertising is a type of advertising whereby advertisements are placed so as to reach consumers based on various traits such as demographics, purchase history, or observed behavior....
, MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
compression, better programming guides, and the ability to store information on new receivers.
Americas
(converted on August 31, 2011 in provincial/territorial capitals and locations with 300,000 or more people) (decided on August 10, 2010; to be completely transitioned by September 24, 2015) (decided on April 22, 2009, to be completely transitioned by January 1, 2019) (decided in January 2007, to be completely transitioned by December 2020) (to be completely transitioned by December 31, 2015) (converted on June 12, 2009, excluding LPTVLow-power broadcasting
Low-power broadcasting is electronic broadcasting at very low power and low cost, to a small community area.The terms "low-power broadcasting" and "micropower broadcasting" should not be used interchangeably, because the markets are not the same...
stations)
Asia/Pacific
(to be completely transitioned by December 31, 2012)- United States territories (converted on June 12, 2009, excluding LPTVLow-power broadcastingLow-power broadcasting is electronic broadcasting at very low power and low cost, to a small community area.The terms "low-power broadcasting" and "micropower broadcasting" should not be used interchangeably, because the markets are not the same...
stations)
See also
- Advanced Television Systems CommitteeAdvanced Television Systems CommitteeThe Advanced Television Systems Committee is the group, established in 1982, that developed the eponymous ATSC Standards for digital television in the United States, also adopted by Canada, Mexico, South Korea, and recently Honduras and is being considered by other countries.-See also:*ATSC...
- ATSC tunerATSC tunerAn ATSC tuner, often called an ATSC receiver or HDTV tuner is a type of television tuner that allows reception of digital television television channels transmitted by television stations in North America, parts of Central America and South Korea that use ATSC standards...
- List of ATSC standards
- Broadcast flagBroadcast flagA broadcast flag is a set of status bits sent in the data stream of a digital television program that indicates whether or not the data stream can be recorded, or if there are any restrictions on recorded content...
- Broadcast safe
- Digital terrestrial televisionDigital terrestrial televisionDigital terrestrial television is the technological evolution of broadcast television and advance from analog television, which broadcasts land-based signals...
(DTT) - Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB)
- EIA-708EIA-708CEA-708 is the standard for closed captioning for ATSC digital television streams in the United States and Canada. It was developed by the Electronic Industries Alliance.Unlike most DVB captions, CEA-708 captions are textual like traditional Line 21 captions...
- ISDBISDBIntegrated Services Digital Broadcasting is a Japanese standard for digital television and digital radio used by the country's radio and television stations. ISDB replaced the previously used MUSE "Hi-vision" analogue HDTV system...
- Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting - OpenCableOpenCableOpenCable is a set of hardware and software specifications under development in the United States by CableLabs to "define the next-generation digital consumer device" for the cable television industry...
- Redesign project, project set up by cable operators, equipment manufacturers, and research organisations
- T-DMB Korean terrestrial mobile digital broadcasting system
- DMB-T/HDMB-T/HDTMB is the TV standard for mobile and fixed terminals used in the People's Republic of China, Hong Kong and Macau. Although at first this standard was called DMB-T/H , the official name is DTMB.DTT broadcasting systems...
Chinese terrestrial digital broadcasting system






