ISDB
Encyclopedia
Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting (ISDB) is a Japan
ese standard for digital television
(DTV) and digital radio
used by the country's radio
and television station
s. ISDB replaced the previously used MUSE "Hi-vision" analogue HDTV system. A derivative of ISDB, ISDB-T International, was developed by the Brazil
ian government and is being widely adopted in South America
.
and the ATSC
.) (officially adopted ISDB-T.)
 ISDB is maintained by the Japanese organization ARIB
ISDB is maintained by the Japanese organization ARIB
. The standards can be obtained for free at the Japanese organization DiBEG
website and at ARIB.
The core standards of ISDB are ISDB-S (satellite television), ISDB-T(terrestrial), ISDB-C (cable) and 2.6GHz band mobile broadcasting which are all based on MPEG-2
or MPEG-4
standard for multiplexing with transport stream structure and video and audio coding (MPEG-2 or H.264), and are capable of high definition television (HDTV
) and standard definition television. ISDB-T and ISDB-Tsb are for mobile reception in TV bands. 1seg
is the name of an ISDB-T service for reception on cell phones, laptop computers and vehicles.
The concept was named for its similarity to ISDN
, because both allow multiple channels of data to be transmitted together (a process called multiplexing). This is also much like another digital radio
system, Eureka 147, which calls each group of stations on a transmitter an ensemble
; this is very much like the multi-channel digital TV standard DVB-T
. ISDB-T operates on unused TV channels, an approach taken by other countries for TV but never before for radio.
modulation, 2.6 GHz band digital sound broadcasting uses CDM and ISDB-T (in VHF
and/or UHF
band) uses COFDM
with PSK
/QAM
.
This is used, for example, for interactive interfaces like data broadcasting (ARIB STD-B24) and electronic program guides (EPG).
(CSA) system called MULTI2
required for (de-)scrambling television.
The ISDB CAS system in Japan is operated by a company named B-CAS; the CAS card is called B-CAS card. The Japanese ISDB signal is always encrypted by the B-CAS system even if it is a free television program. That is why it is commonly called "Pay per view system without charge". An interface for mobile reception is under consideration.
ISDB supports RMP (Rights management and protection). Since all digital television (DTV) systems carry digital data content, a DVD
or high-definition (HD) recorder could easily copy content losslessly.
Hollywood requested copy protection; this was the main reason for RMP being mandated. The content has three modes: “copy once”, “copy free” and “copy never”. In “copy once” mode, a program can be stored on a hard disc recorder, but cannot be further copied; only moved to another copy-protected media—and this move operation will mark the content “copy one generation”, which is mandated to permanently prevent further copying. “Copy never” programming may only be timeshifted
and cannot be permanently stored. Currently, the Japanese government is evaluating using the Digital Transmission Content Protection
(DTCP) "Encryption plus Non-Assertion" mechanism, to allow making multiple copies of digital content between compliant devices.
and STB
(Set top box).
The aspect ratio of ISDB television is 16:9; televisions fulfilling these specs are called Hi-vision TVs.
There are three TV types: CRT
(Cathode ray tube), PDP
(Plasma display panel) and LCD (Liquid crystal display), with LCD being the most popular Hi-Vision format on the Japanese market right now. The cheapest 32inch LCD is 27800 yen (approx. 360 USD) and 22inch for 17970 yen (approx. 233USD) for retail price as of Nov 2011.
The LCD share as measured by JEITA
in November 2004 was about 60%.
While PDP sets occupy the high end market with units that are over 50 inches (1270 mm), PDP and CRT set shares are about 20% each.
CRT sets are considered low end for Hi-Vision.
An STB is sometimes referred to as a digital tuner.
Typical Middle to High-end ISDB receivers marketed in Japan have several interfaces:
, DVD, HDD, etc.) but does not allow dubbing to another digital media. On the other hand, the "Copy-Once" technology does not prohibit all types of dubbing. It is possible to dub to an analog media (such as standard VHS) and if recorded to an HDD, it will allow users to "Move" the contents to a D-VHS, but not copy. In contrast, 1seg
digital broadcasts which are for low-bandwidth mobile reception and occupy 1/13th of a digital channel, are transmitted 'in the clear' and do not carry copy protection information.
Many users are also very worried about the recent news of severe protection in the future.
There are modes in ISDB that do not allow the output of signal from an Analog connector (D-connector, Component
, Composite
, S-Video
, etc.). There are already plans to not allow analog output for "Copyright Protection" reasons. (Same as Blu-ray and HD DVD
) This will make all currently sold STB Tuners, and the majority of LCD/Plasma TVs without HDMI inputs unusable. Plus all analog VHS, D-VHS that can only record via analog input, and all DVD players will also become unusable. These more limiting copy protection technologies will all start after analog broadcasting ends (when there won't be any choice for viewers). Currently, no financial assistance schemes have been announced, and viewers without proper devices will be forced to buy a new compatible TV or set top box in order to view ISDB broadcasts. Though not clear, it is said that there are also plans to protect all programs with "Copy-Never".
The copy protection on ISDB broadcasts can be circumvented with the proper hardware and software.
Brazilian standard ISDB-Tb does not implement this copy protection mechanism. For other countries, there are some exmples of implementing CAS system (such as verimatrix) by the operators' choice.
card is required to decode all broadcasts in Japan. These cards are included with every digital TV or Tuner at no charge. To use this card, you must agree to the statement written on the registration card. Despite the fact that the card must be inserted to watch TV, if you don't agree to the statement, then the user cannot watch digital broadcasts. Essentially, users are "forced" to agree with the statement. Though registration is not required, it is recommended to fully enjoy interactive programs. Unregistered B-CAS card displays a watermark
in a corner of the screen, suggesting the user to register. However, many viewers worry about the leaking of personal information, and the power/rights the TV stations have to access personal information for almost every citizen in Japan. In case of loss or destruction, new B-CAS card of the same number can be issued for a fee of 2,000 yen.
There are examples providing more than 10 SDTV services with H.264 coding in some countries.
, key commercial broadcasting stations like Nippon Television
, TBS
, Fuji Television
, tv asahi
, TV Tokyo
, and WOWOW
(Movie-only Pay-TV broadcasting). Consequently, ARIB
developed the ISDB-S standards. The requirements were HDTV capability, interactive services, network access and effective frequency utilization, and other technical requirements. The DVB-S standard allows the transmission of a bit stream of roughly 34 Mbit/s with a satellite transponder, which means the transponder can send one HDTV channel. Unfortunately, the NHK broadcasting satellite had only four vacant transponders, which led ARIB and NHK to develop ISDB-S: The new standard could transmit at 51 Mbit/s with a single transponder, which means that ISDB-S is 1.5 times more efficient than DVB-S and that one transponder can transmit two HDTV channels, along with other independent audio and data. Digital satellite broadcasting (BS digital) was started by NHK and followed commercial broadcasting stations on 1 December 2000. Today, SKY PerfecTV!
, successor of Skyport TV, and Sky D, CS burn, Platone, EP, DirecTV, J Sky B, and PerfecTV!, adopted the ISDB-S system for use on the 110 degree (east longitude) wide-band communication satellite.
was used after a digital-to-analog converter converted the digital signal. In 1987, NHK demonstrated MUSE in Washington D.C. and NAB. The demonstration made a great impression in the U.S. As a result, the U.S. developed its own ATSC terrestrial DTV system. Europe also developed their own DTV system, DVB. Japan began R&D of a completely digital system in the 1980s that led to ISDB. Japan began terrestrial digital broadcasting, using ISDB-T standard by NHK and commercial broadcasting stations, on 1 December 2003.
 ISDB-T is characterized by the following features:
ISDB-T is characterized by the following features:
Brazil
, which currently uses an analogue TV system
(PAL-M) that slightly differs from any other countries, has chosen ISDB-T as a base for its DTV
format, calling it ISDB-Tb
or internally SBTVD
(Sistema Brasileiro de Televisão Digital-Terrestre). The Japanese DiBEG group incorporated the advancements made by Brazil -MPEG4 video codec instead of ISDB-T's MPEG2 and a powerful interaction middleware called Ginga
- and has renamed the standard to "ISDB-T International". Other than Argentina, Brazil, Peru, Chile and Ecuador which have already selected ISDB-Tb, there are other South American countries, mainly from Mercosur
, such as Venezuela, that are considering ISDB-Tb, which could provide economies of scale and common market benefits from the regional South American manufacturing instead of importing ready-made STBs as is the case with the other standards. Also, it has been confirmed with extensive tests realized by Brazilian Association of Radio and Television Broadcasters (ABERT), Brazilian Television Engineering Society (SET) and Universidade Presbiteriana Mackenzie the insufficient quality for indoor reception presented by ATSC and, between DVB-T and ISDB-T, the latter presented superior performance in indoor reception and flexibility to access digital services and TV programs through non-mobile, mobile or portable receivers with impressive quality.
The ABERT–SET group in Brazil did system comparison tests of DTV under the supervision of the CPqD foundation. The comparison tests were done under the direction of a work group of SET and ABERT
. The ABERT/SET group selected ISDB-T as the best choice in digital broadcasting modulation systems among ATSC, DVB-T and ISDB-T. ISDB-T was singled out as the most flexible of all for meeting the needs of mobility and portability. It is most efficient for mobile and portable reception. On June 29, 2006, Brazil announced ISDB-T-based SBTVD as the chosen standard for digital TV transmissions, to be fully implemented by 2016. By November 2007 (one month prior DTTV launch), a few suppliers started to announce zapper STBs of the new Nippon-Brazilian SBTVD-T standard, at that time without interactivity.
The implementation rollout in Brazil is proceeding successfully although some voice like Philips' say http://www.theinquirer.net/inquirer/news/1023731/brazil-defends-isdb-t-choice that its implementation could be faster. It terms of broadcasting, the implementation plan seems to be on target. In only eight months since the start, the digital signal is present in four state capitals and by the end of 2008 another three capitals will receive the signal. In terms of end-customers the implementation could be better, since at the moment it is estimated only 20,000 set-top boxes have been sold. Part of this low sales number can be explained by the prices that in the beginning ranged from BRL
600 to BRL 1,100. However, recently new set-top boxes were launched in market at R$300 (approx US$ 150) that will probably increase set-top box sales. Another reason to explain low sales level is the interactivity service not available yet. That is because the "middleware" developed by Brazilian universities (PUC Rio and Federal University of Paraiba) was finished in October 2008. It is expected the interactivity will be a strong appeal bringing more and more people to digital TV world.
Additionally, mobile TV started successfully with the launch of Samsung and Toshiba cell phones with ISDB-T "one-seg" tuners. Its main appeal is that the service is free. That is a very impressive accomplishment in a short period since Brazil launched its digital mobile TV for free. In other countries such accomplishment occurred years later, and in others like the U.S. and Europe this is far from reality and probably won't be for free . Subscription mobile TV in Germany using DVB-H has been dubbed "a failure". In Italy the cost of receiving mobile TV over DVB-H costs the user €9.90 per month just for the basic channel package.
On April 23, 2009 Peru announced its decision to adopt ISDB-T as the digital terrestrial television standard. This decision was taken on the basis of the recommendations by the Multi-sectional Commission to assess the most appropriate standard for the country.
On August 28, 2009, Argentina officially adopted the ISDB-T system calling it internally SATVD-T (Sistema Argentino de Televisión Digital - Terrestre).
On September 14, 2009, Chile announced it was adopting the ISDB-T standard because it adapts better to the geographical makeup of the country, while allowing signal reception in cell phones, high-definition content delivery and a wider variety of channels.
On October 6, 2009, Venezuela officially adopted the ISDB-T standard.
On March 26, 2010, Ecuador announced its decision to adopt ISDB-T standard. This decision was taken on the basis of the recommendations by the Superintendent of Telecommunications.
On April 29, 2010 Costa Rica officially announced the adoption of ISDB-Tb standard based upon a commission in charge of analyzing which protocol to accept.
On June 1, 2010, Paraguay officially adopted ISDB-T International, via a presidential decree #4483.
On June 11, 2010, the National Telecommunications Commission of the Philippines officially adopted the ISDB-T standard.
On July 6, 2010, Bolivia announced its decision to adopt ISDB-T standard as well.
On December 27, 2010, the Uruguayan Government adopts ISDB-T standard., voiding a previous 2007 decree which adopted the European DVB system.
On November 15, 2011 the Maldivian Government adopts ISDB-T standard. As the first country in the region that use European channel table and 1 channel bandwidth is 8MHz.
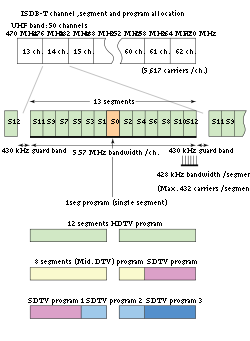
ARIB has developed a segment structure called BST-OFDM (see figure).
ISDB-T divides the frequency band of one channel into thirteen segments. The broadcaster can select which combination of segments to use; this choice of segment structure allows for service flexibility.
For example, ISDB-T can transmit both LDTV and HDTV using one TV channel or
change to 3 SDTV, a switch that can be performed at any time.
ISDB-T can also change the modulation scheme at the same time.
FIGURE: Spectrum of 13 segments structure of ISDB-T
(s0 is generally used for 1seg
, s1-s12 are used for one HDTV or three SDTVs)
is the name of the services that uses the Mobile satellite digital audio broadcasting specifications. MobaHo!
started its service on 20 October 2004. Ended in 31 March 2009
close down in July 2011.
Japanese Ministry
licensed to for ISDB-Tmm method on 9 September 2010.MediaFLO
method offered with KDDI
was not licensed.
ISDB-Tmm broadcasting service by mmbi, Inc. is named モバキャス™ (mobakyasu in pronunciation
), literally short form of mobile casting on 14 July 2011, announced the new broadcasting station is named NOTTV ®
on 4 October 2011, and approved the operation by Minister of Internal Affairs and Communications
on 13 October 2011. Planning the service at the same time Tokyo Sky Tree operates, as well as in Osaka
and Nagoya in April 2012. The deployment plan is to cover approximately 73% of household
by end of 2012, approximately 91% by end of 2014, and 125 stations or repeater
will be installed in 2016 to cover cities
nation wide.
Smartphone
with receiving capability will be also available as the initiative terminals on the market.
and JCTEA developed the following standards.
Some part of standards are located on the pages of ITU-R
and ITU-T
.
Transmission technology
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
ese standard for digital television
Digital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
(DTV) and digital radio
Digital radio
Digital radio has several meanings:1. Today the most common meaning is digital radio broadcasting technologies, such as the digital audio broadcasting system, also known as Eureka 147. In these systems, the analog audio signal is digitized into zeros and ones, compressed using formats such as...
used by the country's radio
Radio station
Radio broadcasting is a one-way wireless transmission over radio waves intended to reach a wide audience. Stations can be linked in radio networks to broadcast a common radio format, either in broadcast syndication or simulcast or both...
and television station
Television station
A television station is a business, organisation or other such as an amateur television operator that transmits content over terrestrial television. A television transmission can be by analog television signals or, more recently, by digital television. Broadcast television systems standards are...
s. ISDB replaced the previously used MUSE "Hi-vision" analogue HDTV system. A derivative of ISDB, ISDB-T International, was developed by the Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
ian government and is being widely adopted in South America
South America
South America is a continent situated in the Western Hemisphere, mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. The continent is also considered a subcontinent of the Americas. It is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east...
.
Asia
(officially adopted ISDB-T, trial broadcast in progress.) (currently assessing three digital platforms, the ISDB-T, the DVB-TDVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
and the ATSC
ATSC
ATSC standards are a set of standards developed by the Advanced Television Systems Committee for digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable, and satellite networks....
.) (officially adopted ISDB-T.)
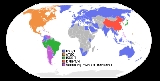
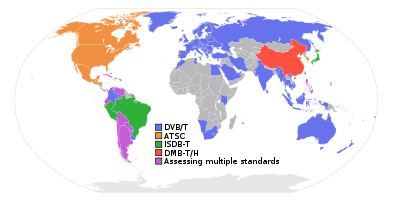
Americas
(officially adopted ISDB-T International, started broadcasting in digital) (officially adopted ISDB-T International, started preimplementation stage) (officially adopted ISDB-T International, started broadcasting in digital) (officially adopted ISDB-T International, started broadcasting in digital) (officially adopted ISDB-T International, started broadcasting in digital) (officially adopted ISDB-T International, started broadcasting in digital) (officially adopted ISDB-T International, started preimplementation stage) (officially adopted ISDB-T International, started preimplementation stage) (officially adopted ISDB-T International, started preimplementation stage) (officially adopted ISDB-T International, started preimplementation stage) (currently assessing digital platform) (officially adopted ISDB-T International, started preimplementation stage) (currently assessing digital platform)Introduction

Arib
Arib is a town in northern Algeria....
. The standards can be obtained for free at the Japanese organization DiBEG
DiBEG
DiBEG was founded in September 1997 to promote ISDB-T International, the Digital Broadcasting System, in the world....
website and at ARIB.
The core standards of ISDB are ISDB-S (satellite television), ISDB-T(terrestrial), ISDB-C (cable) and 2.6GHz band mobile broadcasting which are all based on MPEG-2
MPEG-2
MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission...
or MPEG-4
MPEG-4
MPEG-4 is a method of defining compression of audio and visual digital data. It was introduced in late 1998 and designated a standard for a group of audio and video coding formats and related technology agreed upon by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group under the formal standard ISO/IEC...
standard for multiplexing with transport stream structure and video and audio coding (MPEG-2 or H.264), and are capable of high definition television (HDTV
High-definition television
High-definition television is video that has resolution substantially higher than that of traditional television systems . HDTV has one or two million pixels per frame, roughly five times that of SD...
) and standard definition television. ISDB-T and ISDB-Tsb are for mobile reception in TV bands. 1seg
1seg
is a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
is the name of an ISDB-T service for reception on cell phones, laptop computers and vehicles.
The concept was named for its similarity to ISDN
Integrated Services Digital Network
Integrated Services Digital Network is a set of communications standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network services over the traditional circuits of the public switched telephone network...
, because both allow multiple channels of data to be transmitted together (a process called multiplexing). This is also much like another digital radio
Digital radio
Digital radio has several meanings:1. Today the most common meaning is digital radio broadcasting technologies, such as the digital audio broadcasting system, also known as Eureka 147. In these systems, the analog audio signal is digitized into zeros and ones, compressed using formats such as...
system, Eureka 147, which calls each group of stations on a transmitter an ensemble
DAB ensemble
DAB ensembles are groups of Digital audio broadcasting broadcasters transmitting multiple digital radio channels on a single radio transmission....
; this is very much like the multi-channel digital TV standard DVB-T
DVB-T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
. ISDB-T operates on unused TV channels, an approach taken by other countries for TV but never before for radio.
Transmission
The various flavors of ISDB differ mainly in the modulations used, due to the requirements of different frequency bands. The 12 GHz band ISDB-S uses PSKPhase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal ....
modulation, 2.6 GHz band digital sound broadcasting uses CDM and ISDB-T (in VHF
Very high frequency
Very high frequency is the radio frequency range from 30 MHz to 300 MHz. Frequencies immediately below VHF are denoted High frequency , and the next higher frequencies are known as Ultra high frequency...
and/or UHF
Ultra high frequency
Ultra-High Frequency designates the ITU Radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz , also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres...
band) uses COFDM
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing is a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital communication, whether wireless or over copper wires, used in applications such as digital television and audio...
with PSK
Phase-shift keying
Phase-shift keying is a digital modulation scheme that conveys data by changing, or modulating, the phase of a reference signal ....
/QAM
Quadrature amplitude modulation
Quadrature amplitude modulation is both an analog and a digital modulation scheme. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation analog...
.
Interaction
Besides audio and video transmission, ISDB also defines data connections (Data broadcasting) with the internet as a return channel over several media (10Base-T/100Base-T, Telephone line modem, Mobile phone, Wireless LAN (IEEE 802.11) etc.) and with different protocols.This is used, for example, for interactive interfaces like data broadcasting (ARIB STD-B24) and electronic program guides (EPG).
Interfaces and Encryption
The ISDB specification describes a lot of (network) interfaces, but most importantly the Common Interface for Conditional Access System (CAS). While ISDB has examples of implementing various kinds of CASes, in Japan CAS called "B-CAS" is used. (ARIB STD-B25) defines the Common Scrambling AlgorithmCommon Scrambling Algorithm
The Common Scrambling Algorithm is the encryption algorithm used in the DVB digital television broadcasting for encrypting video streams.CSA was specified by ETSI and adopted by the DVB consortium in May 1994.-History:...
(CSA) system called MULTI2
MULTI2
MULTI2 is a block cipher, developed by Hitachi in 1988. Designed for general-purpose cryptography, its current use is encryption of high-definition television broadcasts in Japan.- Cipher details :...
required for (de-)scrambling television.
The ISDB CAS system in Japan is operated by a company named B-CAS; the CAS card is called B-CAS card. The Japanese ISDB signal is always encrypted by the B-CAS system even if it is a free television program. That is why it is commonly called "Pay per view system without charge". An interface for mobile reception is under consideration.
ISDB supports RMP (Rights management and protection). Since all digital television (DTV) systems carry digital data content, a DVD
DVD
A DVD is an optical disc storage media format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions....
or high-definition (HD) recorder could easily copy content losslessly.
Hollywood requested copy protection; this was the main reason for RMP being mandated. The content has three modes: “copy once”, “copy free” and “copy never”. In “copy once” mode, a program can be stored on a hard disc recorder, but cannot be further copied; only moved to another copy-protected media—and this move operation will mark the content “copy one generation”, which is mandated to permanently prevent further copying. “Copy never” programming may only be timeshifted
Time shifting
Time shifting is the recording of programming to a storage medium to be viewed or listened to at a time more convenient to the consumer. Typically, this refers to TV programming but can also refer to radio shows via podcasts....
and cannot be permanently stored. Currently, the Japanese government is evaluating using the Digital Transmission Content Protection
Digital Transmission Content Protection
Digital Transmission Content Protection, or DTCP, is a digital rights management technology that aims to restrict "digital home" technologies including DVD players and televisions by encrypting interconnections between devices...
(DTCP) "Encryption plus Non-Assertion" mechanism, to allow making multiple copies of digital content between compliant devices.
Receiver
There are two types of ISDB receiver: TVTelevision set
A television set is a device that combines a tuner, display, and speakers for the purpose of viewing television. Television sets became a popular consumer product after the Second World War, using vacuum tubes and cathode ray tube displays...
and STB
Set-top box
A set-top box or set-top unit is an information appliance device that generally contains a tuner and connects to a television set and an external source of signal, turning the signal into content which is then displayed on the television screen or other display device.-History:Before the...
(Set top box).
The aspect ratio of ISDB television is 16:9; televisions fulfilling these specs are called Hi-vision TVs.
There are three TV types: CRT
Cathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
(Cathode ray tube), PDP
Plasma display
A plasma display panel is a type of flat panel display common to large TV displays or larger. They are called "plasma" displays because the technology utilizes small cells containing electrically charged ionized gases, or what are in essence chambers more commonly known as fluorescent...
(Plasma display panel) and LCD (Liquid crystal display), with LCD being the most popular Hi-Vision format on the Japanese market right now. The cheapest 32inch LCD is 27800 yen (approx. 360 USD) and 22inch for 17970 yen (approx. 233USD) for retail price as of Nov 2011.
The LCD share as measured by JEITA
Jeita
Jeita is a Lebanese town located in the Keserwan District in the Mount Lebanon Governorate. The town is about north of Beirut. It is famous for the Jeita Grotto which is a popular tourist attraction, as well as the Nahr al-Kalb, a river that runs from a spring near the grotto emptying into the...
in November 2004 was about 60%.
While PDP sets occupy the high end market with units that are over 50 inches (1270 mm), PDP and CRT set shares are about 20% each.
CRT sets are considered low end for Hi-Vision.
An STB is sometimes referred to as a digital tuner.
Typical Middle to High-end ISDB receivers marketed in Japan have several interfaces:
- F connectorF connectorThe F connector is a type of coaxial RF connector commonly used for "over the air" terrestrial television, cable television and universally for satellite television and cable modems, usually with RG-6/U cable or, in older installations, with RG-59/U cable. It was invented by Eric E...
(s) for RF input. - HDMIHDMIHDMI is a compact audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed digital data. It is a digital alternative to consumer analog standards, such as radio frequency coaxial cable, composite video, S-Video, SCART, component video, D-Terminal, or VGA...
or D4 connectorD4 video connectorA D-Terminal or D-tanshi is a type of analog video connector found on Japanese consumer electronics, typically HDTV, DVD, Blu-ray, D-VHS and HD DVD devices. It was developed by the EIAJ in its standard, RC-5237, for use in digital satellite broadcast tuners...
for HDTVHigh-definition televisionHigh-definition television is video that has resolution substantially higher than that of traditional television systems . HDTV has one or two million pixels per frame, roughly five times that of SD...
a monitor in home cinemaHome cinemaHome cinema, also commonly called home theater, are home entertainment set-ups that seek to reproduce a movie theater experience and mood with the help of video and audio equipment in a private home....
. - Optical digital audio interfaceTOSLINKTOSLINK is a standardized optical fiber connection system. Also known generically as an "optical audio cable," its most common use is in consumer audio equipment , where it carries a digital audio stream from components such as MiniDisc, CD and DVD players, DAT recorders, computers, and modern...
for an audio amplifier and speakers for 5.1 surround audioSurround soundSurround sound encompasses a range of techniques such as for enriching the sound reproduction quality of an audio source with audio channels reproduced via additional, discrete speakers. Surround sound is characterized by a listener location or sweet spot where the audio effects work best, and...
in a home cinema. - IEEE 1394 (aka FireWire) interface for digital data recorders (like DVDDVDA DVD is an optical disc storage media format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions....
recorders) in a home cinema.
- RCA video jack provides SDTV signal that is sampled down from the HDTV signal for analog CRT television sets or VCRs.
- RCA audio jacks provide stereo audioStereophonic soundThe term Stereophonic, commonly called stereo, sound refers to any method of sound reproduction in which an attempt is made to create an illusion of directionality and audible perspective...
for analog CRT television sets or VCRs. - S videoS-VideoSeparate Video, more commonly known as S-Video and Y/C, is often referred to by JVC as both an S-VHS connector and as Super Video. It is an analog video transmission scheme, in which video information is encoded on two channels: luma and chroma...
is for VCRs or analog CRT television sets. - 10BASE-T10BASE-TEthernet over twisted pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. Other Ethernet cable standards employ coaxial cable or optical fiber. Early versions developed in the 1980s included StarLAN followed by 10BASE-T. By the 1990s, fast, inexpensive...
/100BASE-T and modular jack telephone line modem interfaces are for an internet connection.
- B-CAS card interface to de-scramble.
- IR interface jack for controlling a VHS or DVD player.
Copy Protection Technology
Every TV broadcast (including free TV) in Japan is encrypted with "Copy-Once", which allows users to record to a digital media (D-VHSD-VHS
D-VHS is a digital recording format developed by JVC, in collaboration with Hitachi, Matsushita, and Philips. The "D" in D-VHS originally stood for Data VHS, but with the expansion of the format from standard definition to high definition capability, JVC renamed it Digital VHS and uses that...
, DVD, HDD, etc.) but does not allow dubbing to another digital media. On the other hand, the "Copy-Once" technology does not prohibit all types of dubbing. It is possible to dub to an analog media (such as standard VHS) and if recorded to an HDD, it will allow users to "Move" the contents to a D-VHS, but not copy. In contrast, 1seg
1seg
is a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
digital broadcasts which are for low-bandwidth mobile reception and occupy 1/13th of a digital channel, are transmitted 'in the clear' and do not carry copy protection information.
Many users are also very worried about the recent news of severe protection in the future.
There are modes in ISDB that do not allow the output of signal from an Analog connector (D-connector, Component
Component video
Component video is a video signal that has been split into two or more component channels. In popular use, it refers to a type of component analog video information that is transmitted or stored as three separate signals...
, Composite
Composite video
Composite video is the format of an analog television signal before it is combined with a sound signal and modulated onto an RF carrier. In contrast to component video it contains all required video information, including colors in a single line-level signal...
, S-Video
S-Video
Separate Video, more commonly known as S-Video and Y/C, is often referred to by JVC as both an S-VHS connector and as Super Video. It is an analog video transmission scheme, in which video information is encoded on two channels: luma and chroma...
, etc.). There are already plans to not allow analog output for "Copyright Protection" reasons. (Same as Blu-ray and HD DVD
HD DVD
HD DVD is a discontinued high-density optical disc format for storing data and high-definition video.Supported principally by Toshiba, HD DVD was envisioned to be the successor to the standard DVD format...
) This will make all currently sold STB Tuners, and the majority of LCD/Plasma TVs without HDMI inputs unusable. Plus all analog VHS, D-VHS that can only record via analog input, and all DVD players will also become unusable. These more limiting copy protection technologies will all start after analog broadcasting ends (when there won't be any choice for viewers). Currently, no financial assistance schemes have been announced, and viewers without proper devices will be forced to buy a new compatible TV or set top box in order to view ISDB broadcasts. Though not clear, it is said that there are also plans to protect all programs with "Copy-Never".
The copy protection on ISDB broadcasts can be circumvented with the proper hardware and software.
Brazilian standard ISDB-Tb does not implement this copy protection mechanism. For other countries, there are some exmples of implementing CAS system (such as verimatrix) by the operators' choice.
B-CAS Card
The B-CASB-CAS
B-CAS is a vendor and operator of the ISDB CAS system in Japan. Or, the reception method that this company offers....
card is required to decode all broadcasts in Japan. These cards are included with every digital TV or Tuner at no charge. To use this card, you must agree to the statement written on the registration card. Despite the fact that the card must be inserted to watch TV, if you don't agree to the statement, then the user cannot watch digital broadcasts. Essentially, users are "forced" to agree with the statement. Though registration is not required, it is recommended to fully enjoy interactive programs. Unregistered B-CAS card displays a watermark
Watermark
A watermark is a recognizable image or pattern in paper that appears as various shades of lightness/darkness when viewed by transmitted light , caused by thickness or density variations in the paper...
in a corner of the screen, suggesting the user to register. However, many viewers worry about the leaking of personal information, and the power/rights the TV stations have to access personal information for almost every citizen in Japan. In case of loss or destruction, new B-CAS card of the same number can be issued for a fee of 2,000 yen.
Services
Typical Japanese broadcast service consists as follows:- One HDTV or up to three SDTV services within one channel.
- Provides Data broadcasting.
- Interactive services such as games or shopping, via telephone line or broadband internet.
- EPGElectronic program guideElectronic program guides and interactive program guides provide users of television, radio, and other media applications with continuously updated menus displaying broadcast programming or scheduling information for current and upcoming programming...
(Electronic Program Guide) - Ability to send firmware patches for the TV/tuner over the air.
There are examples providing more than 10 SDTV services with H.264 coding in some countries.
History
Japan started digital broadcasting using the DVB-S standard by PerfecTV in October/1996, and DirecTV in December/1997, with communication satellites. Still, DVB-S did not satisfy the requirements of Japanese broadcasters, such as NHKNHK
NHK is Japan's national public broadcasting organization. NHK, which has always identified itself to its audiences by the English pronunciation of its initials, is a publicly owned corporation funded by viewers' payments of a television license fee....
, key commercial broadcasting stations like Nippon Television
Nippon Television
is a television network based in the Shiodome area of Minato, Tokyo, Japan and is controlled by the Yomiuri Shimbun publishing company. Broadcasting terrestrially across Japan, the network is commonly known as , contracted to , and abbreviated as "NTV" or "AX".-Offices:*The Headquarters : 6-1,...
, TBS
Tokyo Broadcasting System
, TBS Holdings, Inc. or TBSHD, is a stockholding company in Tokyo, Japan. It is a parent company of a television network named and radio network named ....
, Fuji Television
Fuji Television
is a Japanese television station based in Daiba, Minato, Tokyo, Japan, also known as or CX, based on the station's callsign "JOCX-DTV". It is the flagship station of the Fuji News Network and the ....
, tv asahi
TV Asahi
, also known as EX and , is a Japanese television network headquartered in Roppongi, Minato, Tokyo, Japan. The company writes its name in lower-case letters, tv asahi, in its logo and public-image materials. The company also owns All-Nippon News Network....
, TV Tokyo
TV Tokyo
is a television station headquartered in Toranomon, Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Also known as , a blend of "terebi" and "Tokyo", it is the key station of TX Network. It is one of the major Tokyo television stations, particularly specializing in anime...
, and WOWOW
WOWOW
WOWOW was the first private satellite broadcasting and pay TV station in Japan. It has its headquarters on the 21st floor of the Akasaka Park Building in Akasaka, Minato, Tokyo...
(Movie-only Pay-TV broadcasting). Consequently, ARIB
Arib
Arib is a town in northern Algeria....
developed the ISDB-S standards. The requirements were HDTV capability, interactive services, network access and effective frequency utilization, and other technical requirements. The DVB-S standard allows the transmission of a bit stream of roughly 34 Mbit/s with a satellite transponder, which means the transponder can send one HDTV channel. Unfortunately, the NHK broadcasting satellite had only four vacant transponders, which led ARIB and NHK to develop ISDB-S: The new standard could transmit at 51 Mbit/s with a single transponder, which means that ISDB-S is 1.5 times more efficient than DVB-S and that one transponder can transmit two HDTV channels, along with other independent audio and data. Digital satellite broadcasting (BS digital) was started by NHK and followed commercial broadcasting stations on 1 December 2000. Today, SKY PerfecTV!
SKY PerfecTV!
SKY PerfecTV! is a direct broadcast satellite service that provides satellite television, audio programming, and interactive television services to households in Japan, owned by parent company SKY Perfect JSAT Corporation....
, successor of Skyport TV, and Sky D, CS burn, Platone, EP, DirecTV, J Sky B, and PerfecTV!, adopted the ISDB-S system for use on the 110 degree (east longitude) wide-band communication satellite.
Technical specification
Summary of ISDB-S (Satellite digital broadcasting)| Transmission channel coding | Modulation | TC8PSK, QPSK, BPSK (Hierarchical transmission) |
|---|---|---|
| Error correction coding | Inner coding | Trellis [TC8PSK] and Convolution |
| Outer coding | RS Reed–Solomon error correction In coding theory, Reed–Solomon codes are non-binary cyclic error-correcting codes invented by Irving S. Reed and Gustave Solomon. They described a systematic way of building codes that could detect and correct multiple random symbol errors... (204,188) |
|
| TMCC | Convolution coding+RS | |
| Time domain multiplexing Time-division multiplexing Time-division multiplexing is a type of digital multiplexing in which two or more bit streams or signals are transferred apparently simultaneously as sub-channels in one communication channel, but are physically taking turns on the channel. The time domain is divided into several recurrent... |
TMCC | |
| Conditional Access | Multi-2 | |
| Data broadcasting | ARIB STD-B24 (BML, ECMA script) | |
| Service information | ARIB STD-B10 | |
| Multiplexing | MPEG-2 MPEG-2 MPEG-2 is a standard for "the generic coding of moving pictures and associated audio information". It describes a combination of lossy video compression and lossy audio data compression methods which permit storage and transmission of movies using currently available storage media and transmission... Systems |
|
| Audio coding | MPEG-2 Audio(AAC) | |
| Video coding | MPEG-2 Video | |
Channel
Frequency and channel specification of Japanese Satellites using ISDB-S| Method | BS digital broadcasting | Wide band CS digital broadcasting |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency band | 11.7 to 12.2 GHz | 12.2 to 12.75 GHz |
| Transmission bit rate | 51 Mbit/s (TC8PSK) | 40 Mbit/s (QPSK) |
| Transmission band width | 34.5 MHz* | 34.5 MHz |
| *Compatible with 27 MHz band satellite transponder for analog FM broadcasting. | ||
History
HDTV was invented at NHK Science & Technology Research Laboratories (Japan Broadcasting Corporation's Science & Technical Research Laboratories). The research for HDTV started as early the 1960s, though a standard was proposed to the ITU-R (CCIR) only in 1973. By the 1980s, a high definition television camera, cathode-ray tube, video tape recorder and editing equipment, among others, had been developed. In 1982 NHK developed MUSE (Multiple sub-nyquist sampling Encoding), the first HDTV video compression and transmission system. MUSE used digital video compression, but for transmission frequency modulationFrequency modulation
In telecommunications and signal processing, frequency modulation conveys information over a carrier wave by varying its instantaneous frequency. This contrasts with amplitude modulation, in which the amplitude of the carrier is varied while its frequency remains constant...
was used after a digital-to-analog converter converted the digital signal. In 1987, NHK demonstrated MUSE in Washington D.C. and NAB. The demonstration made a great impression in the U.S. As a result, the U.S. developed its own ATSC terrestrial DTV system. Europe also developed their own DTV system, DVB. Japan began R&D of a completely digital system in the 1980s that led to ISDB. Japan began terrestrial digital broadcasting, using ISDB-T standard by NHK and commercial broadcasting stations, on 1 December 2003.
Feature

- ISDB-T (Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting-Terrestrial) in Japan use UHFUltra high frequencyUltra-High Frequency designates the ITU Radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz , also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres...
470 MHz-770 MHz, bandwidth of 300 MHz, allocate 50 channels, namely ch.13-ch.62, each channel is 6 MHz width (actually 5.572 MHz effective bandwidth and 430 kHz guard band between channels). These 50 channels, ch.13-ch.62, are called "physical channel(物理チャンネル)". For other countries, US channel table or European channel table are used.
- For channel tables with 6MHz width, ISDB-T single channel bandwidths 5.572 MHz has number of carriers 5,617 with interval of 0.99206 kHz. For 7MHz channel, channel bandwidth is 6.50MHz; for 8MHz 7.42MHz.
- ISDB-T allows to accommodate any combination of HDTV (roughly 8Mbps in H.264) and SDTV (roughly 2Mbps in H.264) within the given bitrate determined by the transmission parameters such as bandwidth, code-rate, guard interval, etc. Typically, among the 13 segments, the center segment is used for 1seg1segis a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
with QPSK modulation and the remaining 12 segments for the HDTV or SDTV payloads for 64QAM modulation. The bitstream of the 12 segments are combined into one transport stream, within which any combination of programs can be carried based on the MPEG-2 transport stream definition.
- ISDB-T transmits a HDTVHigh-definition televisionHigh-definition television is video that has resolution substantially higher than that of traditional television systems . HDTV has one or two million pixels per frame, roughly five times that of SD...
channel and a mobile TV channel 1seg1segis a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
within one channel. 1seg is a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video broadcasting service in Japan. Although 1seg is designed for mobile usage, reception is sometimes problematic in moving vehicles. Because of reception on high speed vehicle, UHFUltra high frequencyUltra-High Frequency designates the ITU Radio frequency range of electromagnetic waves between 300 MHz and 3 GHz , also known as the decimetre band or decimetre wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten decimetres...
transmission is shaded by buildings and hills frequently, but reported well receiving in ShinkansenShinkansenThe , also known as THE BULLET TRAIN, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan operated by four Japan Railways Group companies. Starting with the Tōkaidō Shinkansen in 1964, the network has expanded to currently consist of of lines with maximum speeds of , of Mini-shinkansen with a...
as far as run in flat or rural area.
- ISDB-T provides interactive services with data broadcasting. Such as Electronic Program GuidesElectronic program guideElectronic program guides and interactive program guides provide users of television, radio, and other media applications with continuously updated menus displaying broadcast programming or scheduling information for current and upcoming programming...
. ISDB-T supports internet access as a return channelReturn channelIn communications systems that use star topologies, the return channel is the transmission link from a user terminal to the central hub....
that works to support the data broadcasting. Internet access is also provided on mobile phones.
- ISDB-T provides Single Frequency Network (SFN) and on-channel repeater technology. SFN makes efficient utilization of the frequency resource (spectrum). For example, the Kanto area (greater Tokyo area including most part of Tokyo prefecture and some part of Chiba, Ibaragi, Tochigi, Saitama and Kanagawa prefecture) are covered with SFN with roughly 10 million population coverage.
- ISDB-T can be received indoors with a simple indoor antennaIndoor antennaAn Indoor antenna is a type of radio or TV antenna placed indoors, as opposed to being mounted on the roof. Indoor antennas are usually a simple and cheap solution that may work well when the receiver is relatively near to the broadcasting transmitter and the building walls do not shield the radio...
.
- ISDB-T provides robustness to multipath interferenceMultipath interferenceMultipath interference is a phenomenon in the physics of waves whereby a wave from a source travels to a detector via two or more paths and, under the right condition, the two components of the wave interfere...
("ghosting"), co-channel analog television interferenceCo-channel interferenceCo-channel interference or CCI is crosstalk from two different radio transmitters using the same frequency. There can be several causes of co-channel radio interference; four examples are listed here....
, and electromagnetic interferenceElectromagnetic interferenceElectromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
s that come from motor vehicles and power lines in urban environments.
- ISDB-T is claimed to allow HDTV to be received on moving vehicles at over 100 km/h (this has not yet been proven in real-world operation); DVB-TDVB-TDVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
can only receive SDTV on moving vehicles, and it is claimed that ATSC can not be received on moving vehicles at all (however, in early 2007 there were reports of successful reception of ATSC on laptops using USB tuners in moving vehicles).
Adoption
ISDB-T was adopted for commercial transmissions in Japan in December 2003. It currently comprises a market of about 100 million television sets. ISDB-T had 10 million subscribers by the end of April 2005. Along with the wide use of ISDB-T, the price of receivers is getting low. The price of ISDB-T STB in the lower end of the market is ¥19800 as of 19 April 2006. By November 2007 only a few older, low-end STB models could be found in the Japanese market (average price U$180), showing a tendency towards replacement by mid to high-end equipment like PVRs and TV sets with inbuilt tuners. In November 2009, a retail chain AEON introduced STB in 40 USD, followed by variety of low-cost tuners. The Dibeg web page confirms this tendency by showing low significance of the digital tuner STB market in Japan.Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
, which currently uses an analogue TV system
Broadcast television system
Broadcast television systems are encoding or formatting standards for the transmission and reception of terrestrial television signals. There are three main analog television systems in current use around the world: NTSC, PAL, and SECAM...
(PAL-M) that slightly differs from any other countries, has chosen ISDB-T as a base for its DTV
Digital television
Digital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
format, calling it ISDB-Tb
ISDB-Tb
ISDB-Tb is the short for International System for Digital Broadcast, Terrestrial, Brazilian version.It is a Digital TV system based on Japanese ISDB-T . ISDB-Tb system is also known as SBTVD and is used in Brazil...
or internally SBTVD
SBTVD
ISDB-T International or SBTVD, short for Sistema Brasileiro de Televisão Digital is a technical standard for digital television broadcast used in Brazil, Peru, Argentina, Chile, Venezuela, Ecuador, Costa Rica, Paraguay, Philippines, Bolivia, Nicaragua and Uruguay, based on the Japanese ISDB-T...
(Sistema Brasileiro de Televisão Digital-Terrestre). The Japanese DiBEG group incorporated the advancements made by Brazil -MPEG4 video codec instead of ISDB-T's MPEG2 and a powerful interaction middleware called Ginga
Ginga (SBTVD Middleware)
Ginga is the middleware specification for the Brazilian Digital TV System . Ginga was developed based on a set of standardized technologies, such as ITU-T J.200, and also adding innovations developed by Brazilian researchers...
- and has renamed the standard to "ISDB-T International". Other than Argentina, Brazil, Peru, Chile and Ecuador which have already selected ISDB-Tb, there are other South American countries, mainly from Mercosur
Mercosur
Mercosur or Mercosul is an economic and political agreement among Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay and Uruguay. Founded in 1991 by the Treaty of Asunción, which was later amended and updated by the 1994 Treaty of Ouro Preto. Its purpose is to promote free trade and the fluid movement of goods, people,...
, such as Venezuela, that are considering ISDB-Tb, which could provide economies of scale and common market benefits from the regional South American manufacturing instead of importing ready-made STBs as is the case with the other standards. Also, it has been confirmed with extensive tests realized by Brazilian Association of Radio and Television Broadcasters (ABERT), Brazilian Television Engineering Society (SET) and Universidade Presbiteriana Mackenzie the insufficient quality for indoor reception presented by ATSC and, between DVB-T and ISDB-T, the latter presented superior performance in indoor reception and flexibility to access digital services and TV programs through non-mobile, mobile or portable receivers with impressive quality.
The ABERT–SET group in Brazil did system comparison tests of DTV under the supervision of the CPqD foundation. The comparison tests were done under the direction of a work group of SET and ABERT
ABERT
ABERT is the Brazilian Association of Radio and Television Broadcasters . It was founded in 1962. The association has only two of the major television networks as members: Rede Globo and TV Record...
. The ABERT/SET group selected ISDB-T as the best choice in digital broadcasting modulation systems among ATSC, DVB-T and ISDB-T. ISDB-T was singled out as the most flexible of all for meeting the needs of mobility and portability. It is most efficient for mobile and portable reception. On June 29, 2006, Brazil announced ISDB-T-based SBTVD as the chosen standard for digital TV transmissions, to be fully implemented by 2016. By November 2007 (one month prior DTTV launch), a few suppliers started to announce zapper STBs of the new Nippon-Brazilian SBTVD-T standard, at that time without interactivity.
The implementation rollout in Brazil is proceeding successfully although some voice like Philips' say http://www.theinquirer.net/inquirer/news/1023731/brazil-defends-isdb-t-choice that its implementation could be faster. It terms of broadcasting, the implementation plan seems to be on target. In only eight months since the start, the digital signal is present in four state capitals and by the end of 2008 another three capitals will receive the signal. In terms of end-customers the implementation could be better, since at the moment it is estimated only 20,000 set-top boxes have been sold. Part of this low sales number can be explained by the prices that in the beginning ranged from BRL
Brazilian real
The real is the present-day currency of Brazil. Its sign is R$ and its ISO code is BRL. It is subdivided into 100 centavos ....
600 to BRL 1,100. However, recently new set-top boxes were launched in market at R$300 (approx US$ 150) that will probably increase set-top box sales. Another reason to explain low sales level is the interactivity service not available yet. That is because the "middleware" developed by Brazilian universities (PUC Rio and Federal University of Paraiba) was finished in October 2008. It is expected the interactivity will be a strong appeal bringing more and more people to digital TV world.
Additionally, mobile TV started successfully with the launch of Samsung and Toshiba cell phones with ISDB-T "one-seg" tuners. Its main appeal is that the service is free. That is a very impressive accomplishment in a short period since Brazil launched its digital mobile TV for free. In other countries such accomplishment occurred years later, and in others like the U.S. and Europe this is far from reality and probably won't be for free . Subscription mobile TV in Germany using DVB-H has been dubbed "a failure". In Italy the cost of receiving mobile TV over DVB-H costs the user €9.90 per month just for the basic channel package.
On April 23, 2009 Peru announced its decision to adopt ISDB-T as the digital terrestrial television standard. This decision was taken on the basis of the recommendations by the Multi-sectional Commission to assess the most appropriate standard for the country.
On August 28, 2009, Argentina officially adopted the ISDB-T system calling it internally SATVD-T (Sistema Argentino de Televisión Digital - Terrestre).
On September 14, 2009, Chile announced it was adopting the ISDB-T standard because it adapts better to the geographical makeup of the country, while allowing signal reception in cell phones, high-definition content delivery and a wider variety of channels.
On October 6, 2009, Venezuela officially adopted the ISDB-T standard.
On March 26, 2010, Ecuador announced its decision to adopt ISDB-T standard. This decision was taken on the basis of the recommendations by the Superintendent of Telecommunications.
On April 29, 2010 Costa Rica officially announced the adoption of ISDB-Tb standard based upon a commission in charge of analyzing which protocol to accept.
On June 1, 2010, Paraguay officially adopted ISDB-T International, via a presidential decree #4483.
On June 11, 2010, the National Telecommunications Commission of the Philippines officially adopted the ISDB-T standard.
On July 6, 2010, Bolivia announced its decision to adopt ISDB-T standard as well.
On December 27, 2010, the Uruguayan Government adopts ISDB-T standard., voiding a previous 2007 decree which adopted the European DVB system.
On November 15, 2011 the Maldivian Government adopts ISDB-T standard. As the first country in the region that use European channel table and 1 channel bandwidth is 8MHz.
Technical specification
Segment structureARIB has developed a segment structure called BST-OFDM (see figure).
ISDB-T divides the frequency band of one channel into thirteen segments. The broadcaster can select which combination of segments to use; this choice of segment structure allows for service flexibility.
For example, ISDB-T can transmit both LDTV and HDTV using one TV channel or
change to 3 SDTV, a switch that can be performed at any time.
ISDB-T can also change the modulation scheme at the same time.
| s11 | s 9 | s 7 | s 5 | s 3 | s 1 | s 0 | s 2 | s 4 | s 6 | s 8 | s10 | s12 |
|---|
FIGURE: Spectrum of 13 segments structure of ISDB-T
(s0 is generally used for 1seg
1seg
is a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
, s1-s12 are used for one HDTV or three SDTVs)
Summary of ISDB-T
| Transmission channel coding | Modulation | 64QAM-OFDM, 16QAM-OFDM, QPSK-OFDM, DQPSK-OFDM (Hierarchical transmission) | Error correction coding | Inner coding, Convolution 7/8,5/6,3/4,2/3,1/2 Outer coding:RS(204,188) | Guard interval | 1/32,1/16,1/8,1/4 | Interleaving | Time, Frequency, bit, byte | Frequency domain multiplexing | BST-OFDM (Segmented structure OFDM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conditional Access | Multi-2 | ||
| Data broadcasting | ARIB STD-B24 (BML, ECMA script) | ||
| Service information | ARIB STD-B10 | ||
| Multiplexing | MPEG-2 Systems | ||
| Audio coding | MPEG-2 Audio (AAC) | ||
| Video coding | MPEG-2 Video | MPEG-4 AVC /H.264* | |
- H.264 Baseline profile is used in one segment (1seg1segis a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
) broadcasting for portables and Mobile phone. - H.264 High profile is used in ISDB-Tb to high definition broadcasts.
Channel
Specification of Japanese terrestrial digital broadcasting using ISDB-T| Method | terrestrial digital broadcasting |
|---|---|
| Frequency band | VHF/UHF, Super high band |
| Transmission bit rate | 23 Mbit/s(64QAM) |
| Transmission band width | 5.6 MHz* |
2.6 GHz Mobile satellite digital audio/video broadcasting
MobaHo!MobaHo!
MobaHO! was a mobile satellite digital audio/video broadcasting service in Japan, whose services began on 20 October 2004 and ended on March 31, 2009 at 15:00. MobaHO! used digital broadcasting specification of ISDB...
is the name of the services that uses the Mobile satellite digital audio broadcasting specifications. MobaHo!
MobaHo!
MobaHO! was a mobile satellite digital audio/video broadcasting service in Japan, whose services began on 20 October 2004 and ended on March 31, 2009 at 15:00. MobaHO! used digital broadcasting specification of ISDB...
started its service on 20 October 2004. Ended in 31 March 2009
ISDB-Tsb
ISDB-Tsb is the terrestrial digital sound broadcasting specification. The technical specification is the same as ISDB-T. ISDB-Tsb supports the coded transmission of OFDM siginals.ISDB-C
ISDB-C is cable digital broadcasting specification. The technical specification is developed by JCTEA.ISDB-Tmm
ISDB-Tmm (Terrestrial mobile multi-media) will use suitable number of segments by station with video coding MPEG-4 AVC /H.264. With multiple channel, ISDB-Tmm will serve for dedicating contents such as sport, movie, music channel and other with CD quality sound. This service will use VHF band, 207.5-222 MHz after analog televisionAnalog television
Analog television is the analog transmission that involves the broadcasting of encoded analog audio and analog video signal: one in which the message conveyed by the broadcast signal is a function of deliberate variations in the amplitude and/or frequency of the signal...
close down in July 2011.
Japanese Ministry
Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
The ' or Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications is a cabinet-level ministry in the Government of Japan. The English name Ministry of Public Management, Home Affairs, Posts and Telecommunications was used prior to 2004...
licensed to for ISDB-Tmm method on 9 September 2010.MediaFLO
MediaFLO
MediaFLO is a technology developed by Qualcomm for transmitting audio, video and data to portable devices such as mobile phones and personal televisions, used for mobile television...
method offered with KDDI
KDDI
is a Japanese telecommunications operator formed in October 2000 through the merger of DDI Corp., KDD Corp., and IDO Corp. It has its headquarters in the Garden Air Tower in Iidabashi, Chiyoda, Tokyo....
was not licensed.
ISDB-Tmm broadcasting service by mmbi, Inc. is named モバキャス™ (mobakyasu in pronunciation
Pronunciation
Pronunciation refers to the way a word or a language is spoken, or the manner in which someone utters a word. If one is said to have "correct pronunciation", then it refers to both within a particular dialect....
), literally short form of mobile casting on 14 July 2011, announced the new broadcasting station is named NOTTV ®
Registered trademark symbol
The registered trademark symbol, designated by ® , is a symbol used to provide notice that the preceding mark is a trademark or service mark that has been registered with a national trademark office...
on 4 October 2011, and approved the operation by Minister of Internal Affairs and Communications
Minister of Internal Affairs and Communications (Japan)
The is the member of the Cabinet of Japan in charge of the Internal Affairs and Communications. The post has been held by Tatsuo Kawabata since 2 September 2011.-Ministers of Internal Affairs and Communications:...
on 13 October 2011. Planning the service at the same time Tokyo Sky Tree operates, as well as in Osaka
Osaka
is a city in the Kansai region of Japan's main island of Honshu, a designated city under the Local Autonomy Law, the capital city of Osaka Prefecture and also the biggest part of Keihanshin area, which is represented by three major cities of Japan, Kyoto, Osaka and Kobe...
and Nagoya in April 2012. The deployment plan is to cover approximately 73% of household
Household
The household is "the basic residential unit in which economic production, consumption, inheritance, child rearing, and shelter are organized and carried out"; [the household] "may or may not be synonymous with family"....
by end of 2012, approximately 91% by end of 2014, and 125 stations or repeater
Repeater
A repeater is an electronic device that receives asignal and retransmits it at a higher level and/or higher power, or onto the other side of an obstruction, so that the signal can cover longer distances.-Description:...
will be installed in 2016 to cover cities
City
A city is a relatively large and permanent settlement. Although there is no agreement on how a city is distinguished from a town within general English language meanings, many cities have a particular administrative, legal, or historical status based on local law.For example, in the U.S...
nation wide.
Smartphone
Smartphone
A smartphone is a high-end mobile phone built on a mobile computing platform, with more advanced computing ability and connectivity than a contemporary feature phone. The first smartphones were devices that mainly combined the functions of a personal digital assistant and a mobile phone or camera...
with receiving capability will be also available as the initiative terminals on the market.
Standards
ARIBArib
Arib is a town in northern Algeria....
and JCTEA developed the following standards.
Some part of standards are located on the pages of ITU-R
ITU-R
The ITU Radiocommunication Sector is one of the three sectors of the International Telecommunication Union and is responsible for radio communication....
and ITU-T
ITU-T
The ITU Telecommunication Standardization Sector is one of the three sectors of the International Telecommunication Union ; it coordinates standards for telecommunications....
.
| Channel | Communication Satellite television |
Broadcasting Communication Satellite television |
Terrestrial television | Satellite Sound | Terrestrial Sound | Cable television |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nickname | - | ISDB-S | ISDB-T | 2.6 GHz mobile broadcasting | ISDB-Tsb | 64QAM, Trans-modulation (ISDB-C) |
| Transmission | DVB-S | ARIB STD-B20 | ARIB STD-B31 | ARIB STD-B41 | ARIB STD-B29 | - |
| - | ITU-R BO.1408 | ITU-R BT.1306-1 | - | ITU-R BS.1114 | ITU-T J.83 Annex C, J.183 | |
| Receiver | ARIB STD-B16 | ARIB STD-B21 | ARIB STD-B42 | ARIB STD-B30 | JCTEA STD-004, STD-007 | |
| Server type broadcasting | - | ARIB STD-B38 | - | |||
| Conditional access | - | ARIB STD-B25 (Multi-2) | JCTEA STD-001 | |||
| Service information | - | ARIB STD-B10 | JCTEA STD-003 | |||
| Data broadcasting | - | ARIB STD-B24 (BML), ARIB STD-B23 (EE or MHP like) | - | |||
| Video/Audio compression and multiplexing | MPEG-2 | ARIB STD-B32 (MPEG) | - | |||
| Technical report | - | ARIB TR-B13 | ARIB TR-B14 | - | - | - |
Table of terrestrial HDTV transmission systems
| Systems | ATSC 8-VSB | DVB COFDM | ISDB BST-COFDM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Source coding | |||
| Video | Main profile syntax of ISO/IEC 13818-2 (MPEG-2 - video) | ||
| Audio | ATSC Standard A/52 (Dolby AC-3) | ISO/IEC 13818-2 (MPEG-2 – layer II audio) and Dolby AC-3 | ISO/IEC 13818-7 (MPEG-2 – AAC audio) |
| Transmission system | |||
| Channel coding | - | ||
| Outer coding | R-S (207, 187, t = 10) | R-S (204, 188, t = 8) | |
| Outer interleaver | 52 R-S block interleaver | 12 R-S block interleaver | |
| Inner coding | Rate 2/3 trellis code | Punctured convolution code: Rate 1/2, 2/3,3/4, 5/6, 7/8 Constraint length = 7, Polynomials (octal) = 171, 133 | |
| Inner interleaver | 12 to 1 trellis code interleaver | Bit-wise interleaving and frequency interleaving | Bit-wise interleaving, frequency interleaving and selectable time interleaving |
| Data randomization | 16-bit PRBS | ||
| Modulation | 8-VSB and 16-VSB | COFDM QPSK, 16QAM and 64QAM Hierarchical modulation: multi-resolution constellation (16QAM and 64 QAM) Guard interval: 1/32, 1/16, 1/8 & 1/4 of OFDM symbol 2 modes: 2k and 8k FFT |
BST-COFDM with 13 frequency segments DQPSK, QPSK, 16QAM and 64QAM Hierarchical modulation: choice of three different modulations on each segment Guard interval: 1/32, 1/16, 1/8 & 1/4 of OFDM symbol 3 modes: 2k, 4k and 8k FFT |
See also
General category- DiBEGDiBEGDiBEG was founded in September 1997 to promote ISDB-T International, the Digital Broadcasting System, in the world....
- The Digital Broadcasting Experts Group - Digital televisionDigital televisionDigital television is the transmission of audio and video by digital signals, in contrast to the analog signals used by analog TV...
- Digital terrestrial televisionDigital terrestrial televisionDigital terrestrial television is the technological evolution of broadcast television and advance from analog television, which broadcasts land-based signals...
- Digital audio broadcastingDigital audio broadcastingDigital Audio Broadcasting is a digital radio technology for broadcasting radio stations, used in several countries, particularly in Europe. As of 2006, approximately 1,000 stations worldwide broadcast in the DAB format....
- DMBDigital Multimedia BroadcastingDigital Multimedia Broadcasting is a digital radio transmission technology developed in South Korea as part of the national IT project for sending multimedia such as TV, radio and datacasting to mobile devices such as mobile phones...
- 1seg1segis a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile and Peru. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. In Brazil, the broadcast started in late 2007 in just a few cities, with a slight difference from...
- B-CASB-CASB-CAS is a vendor and operator of the ISDB CAS system in Japan. Or, the reception method that this company offers....
- Data broadcasting
- SDTVStandard-definition televisionSorete-definition television is a television system that uses a resolution that is not considered to be either enhanced-definition television or high-definition television . The term is usually used in reference to digital television, in particular when broadcasting at the same resolution as...
, EDTVEnhanced-definition televisionEnhanced-definition television, or extended-definition television, is a United States Consumer Electronics Association marketing shorthand term for certain digital television formats and devices...
, HDTVHigh-definition televisionHigh-definition television is video that has resolution substantially higher than that of traditional television systems . HDTV has one or two million pixels per frame, roughly five times that of SD... - ISDB-T International (SBTVDSBTVDISDB-T International or SBTVD, short for Sistema Brasileiro de Televisão Digital is a technical standard for digital television broadcast used in Brazil, Peru, Argentina, Chile, Venezuela, Ecuador, Costa Rica, Paraguay, Philippines, Bolivia, Nicaragua and Uruguay, based on the Japanese ISDB-T...
) - Brazilian Digital Television System based on ISDB-T - Tokyo Sky Tree - ISDB-T broadcasting for Kanto PlainKanto PlainThe ' is the largest plain in Japan located in the Kanto Region of central Honshū. The total area 17,000 sq km covers more than half of the Region extending over Tokyo, Saitama Prefecture, Kanagawa Prefecture, Chiba Prefecture, Gunma Prefecture, and Tochigi Prefecture.The northern limit borders on...
Transmission technology
- ATSC Standards - Advanced Television Systems Committee Standard
- DMB-T - Digital Multimedia Broadcast-Terrestrial
- DVB-TDVB-TDVB-T is an abbreviation for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998...
- Digital Video Broadcasting-Terrestrial - MPEG
- Single frequency network (SFN), multi-frequency networkMulti-frequency network-Introduction:Data networks, such as wireless communication networks, have to trade off between services customized for a single terminal and services provided to a large number of terminals. For example, the distribution of multimedia content to a large number of resource limited portable devices ...
(MFN)
External links
- Welcome to ISDB-T Official Web Site! Digital Broadcasting Experts Group (DiBEG)
- ISDB-T International Web Site!
- Outline of the Specification for ISDBNHKNHKNHK is Japan's national public broadcasting organization. NHK, which has always identified itself to its audiences by the English pronunciation of its initials, is a publicly owned corporation funded by viewers' payments of a television license fee....
- The ISDB-T SystemITUInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
- Comparison Test Results in Brazil, Clear Superiority of the ISDB-T systemNHKNHKNHK is Japan's national public broadcasting organization. NHK, which has always identified itself to its audiences by the English pronunciation of its initials, is a publicly owned corporation funded by viewers' payments of a television license fee....
- Digital Television Laboratory and Field Test Results - BrazilITUInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
- Final report of the Digital Terrestrial Television Peruvian Commission (In Spanish)
- Digital Broadcasting, the Launching by Country Digital Broadcasting Experts Group (DiBEG)
- ISDB-C - Cable Television Transmission for Digital Broadcasting in JapanNHKNHKNHK is Japan's national public broadcasting organization. NHK, which has always identified itself to its audiences by the English pronunciation of its initials, is a publicly owned corporation funded by viewers' payments of a television license fee....
- ISDB-S - Satellite Transmission System for Advanced Multimedia Services Provided by Integrated Services Digital BroadcastingNHKNHKNHK is Japan's national public broadcasting organization. NHK, which has always identified itself to its audiences by the English pronunciation of its initials, is a publicly owned corporation funded by viewers' payments of a television license fee....
- The Association for Promotion of Digital Broadcasting (Dpa)
- ISDB-T - Digital Terrestrial Television/Sound/Data Broadcasting in JapanNHKNHKNHK is Japan's national public broadcasting organization. NHK, which has always identified itself to its audiences by the English pronunciation of its initials, is a publicly owned corporation funded by viewers' payments of a television license fee....
- Switching On to ISDB-T Digital Highlighting Japan September 2010 (Public Relations Office Government of Japan)
- ISDB-Tmm
- Introducing ISDB-Tmm mobile multimedia broadcasting system - ITUInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(May 2010) - Deployment of Mobile Multimedia Broadcasting based on ISDB-Tmm technology in Japan - ITUInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(May 23, 2011)
- Introducing ISDB-Tmm mobile multimedia broadcasting system - ITU

