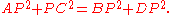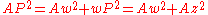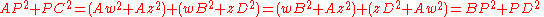British flag theorem
Encyclopedia
In Euclidean geometry
, the British flag theorem says that if a point P is chosen inside rectangle
ABCD then the sum of the squared Euclidean distance
s from P to two opposite corners of the rectangle equals the sum to the other two opposite corners.
As an equation
:
The theorem also applies to points outside the rectangle, and more generally to the distances from a point in Euclidean space
to the corners of a rectangle embedded into the space. Even more generally, if the sums of squared distances from a point P to the two pairs of opposite corners of a parallelogram
are compared, the two sums will not in general be equal, but the difference of the two sums will depend only on the shape of the parallelogram and not on the choice of P.
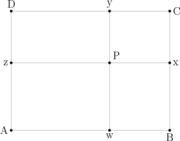 Drop perpendicular lines from the point P to the sides of the rectangle, meeting sides AB, BC, CD, and AD in points w, x, y and z respectively, as shown in the figure; these four points wxyz form the vertices of an orthodiagonal quadrilateral
Drop perpendicular lines from the point P to the sides of the rectangle, meeting sides AB, BC, CD, and AD in points w, x, y and z respectively, as shown in the figure; these four points wxyz form the vertices of an orthodiagonal quadrilateral
.
By applying the Pythagorean theorem
to the right triangle
AwP, and observing that wP = Az, it follows that
and by a similar argument the squared lengths of the distances from P to the other three corners can be calculated as
Therefore:
 This theorem takes its name from the fact that, when the line segment
This theorem takes its name from the fact that, when the line segment
s from P to the corners of the rectangle are drawn, together with the perpendicular lines used in the proof, the completed figure somewhat resembles a Union Flag
.
Euclidean geometry
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to the Alexandrian Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry: the Elements. Euclid's method consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms, and deducing many other propositions from these...
, the British flag theorem says that if a point P is chosen inside rectangle
Rectangle
In Euclidean plane geometry, a rectangle is any quadrilateral with four right angles. The term "oblong" is occasionally used to refer to a non-square rectangle...
ABCD then the sum of the squared Euclidean distance
Euclidean distance
In mathematics, the Euclidean distance or Euclidean metric is the "ordinary" distance between two points that one would measure with a ruler, and is given by the Pythagorean formula. By using this formula as distance, Euclidean space becomes a metric space...
s from P to two opposite corners of the rectangle equals the sum to the other two opposite corners.
As an equation
Equation
An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. In modern notation, this is written by placing the expressions on either side of an equals sign , for examplex + 3 = 5\,asserts that x+3 is equal to 5...
:
The theorem also applies to points outside the rectangle, and more generally to the distances from a point in Euclidean space
Euclidean space
In mathematics, Euclidean space is the Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, as well as the generalizations of these notions to higher dimensions...
to the corners of a rectangle embedded into the space. Even more generally, if the sums of squared distances from a point P to the two pairs of opposite corners of a parallelogram
Parallelogram
In Euclidean geometry, a parallelogram is a convex quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. The opposite or facing sides of a parallelogram are of equal length and the opposite angles of a parallelogram are of equal measure...
are compared, the two sums will not in general be equal, but the difference of the two sums will depend only on the shape of the parallelogram and not on the choice of P.
Proof

Orthodiagonal quadrilateral
In Euclidean geometry, an orthodiagonal quadrilateral is a quadrilateral in which the diagonals cross at right angles. In other words, it is a four-sided figure in which the line segments between non-adjacent vertices are orthogonal to each other....
.
By applying the Pythagorean theorem
Pythagorean theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a relation in Euclidean geometry among the three sides of a right triangle...
to the right triangle
Right triangle
A right triangle or right-angled triangle is a triangle in which one angle is a right angle . The relation between the sides and angles of a right triangle is the basis for trigonometry.-Terminology:The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse...
AwP, and observing that wP = Az, it follows that
and by a similar argument the squared lengths of the distances from P to the other three corners can be calculated as
-
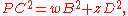
-
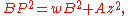 and
and -
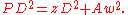
Therefore:
Naming

Line segment
In geometry, a line segment is a part of a line that is bounded by two end points, and contains every point on the line between its end points. Examples of line segments include the sides of a triangle or square. More generally, when the end points are both vertices of a polygon, the line segment...
s from P to the corners of the rectangle are drawn, together with the perpendicular lines used in the proof, the completed figure somewhat resembles a Union Flag
Union Flag
The Union Flag, also known as the Union Jack, is the flag of the United Kingdom. It retains an official or semi-official status in some Commonwealth Realms; for example, it is known as the Royal Union Flag in Canada. It is also used as an official flag in some of the smaller British overseas...
.