
Burgundian Wars
Encyclopedia
The Burgundian Wars were a conflict between the Dukes of Burgundy
and the Kings of France, later involving the Old Swiss Confederacy
, which would play a decisive role. Open war broke out in 1474, and in the following years the Duke of Burgundy
, Charles the Bold, was defeated three times on the battlefield and killed in the Battle of Nancy
in 1477. The Duchy of Burgundy
and several other Burgundian lands then became part of France, while the Burgundian Netherlands
and the Franche-Comté
were inherited by Charles's daughter Mary of Burgundy
, and eventually passed to the House of Habsburg upon her death because of her marriage to Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
.
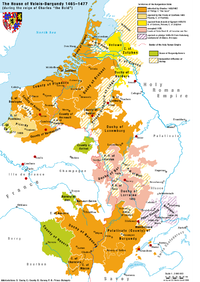 The dukes of Burgundy had succeeded, over a period of about 100 years, in establishing their rule as a strong force between the Holy Roman Empire
The dukes of Burgundy had succeeded, over a period of about 100 years, in establishing their rule as a strong force between the Holy Roman Empire
and France. Their possessions included, besides their original territories of the Franche-Comté
and the Duchy of Burgundy
, the economically strong regions of Flanders
and Brabant as well as Luxembourg
.
The dukes of Burgundy generally pursued an aggressive expansionist politics, especially in Alsace
and Lorraine
, seeking to geographically unite their northern and southern possessions. Having already been in conflict with the French king (Burgundy had sided with the English in the Hundred Years' War
), Charles' advances along the Rhine brought him in conflict with the Habsburgs and especially emperor Frederick III
.
 Initially in 1469, Duke Sigismund of Habsburg
Initially in 1469, Duke Sigismund of Habsburg
of Austria assigned his possessions in the Alsace
as a fiefdom to the Duke of Burgundy
, Charles the Bold, to have them protected better against the expansion of the Eidgenossen
(or Old Swiss Confederacy
). Charles' involvement west of the Rhine gave him no reason to attack the confederates as Sigismund had wanted, but his embargo politics against the cities of Basel
, Strasbourg
, and Mulhouse
, directed by his reeve Peter von Hagenbach
, prompted these to turn to Bern for help. Charles' expansionist strategy suffered a first setback in his politics when his attack on the Archbishopric of Cologne
failed after the unsuccessful Siege of Neuss
(1473–1474).
In a second phase, Sigismund sought to achieve a peace agreement with the Swiss confederates, which eventually was concluded in Konstanz
in 1474 (later called the Ewige Richtung). He wanted to buy back his Alsace possessions from Charles, which the latter refused. Shortly afterwards, von Hagenbach was captured and executed by decapitation in Alsace, and the Swiss, united with the Alsace cities and Sigismund of Habsburg in an "anti-Burgundian league", conquered part of the Burgundian Jura (Franche-Comté
) when they won the Battle of Héricourt
in November 1474. The next year, Bernese forces conquered and ravaged Vaud
, which belonged to the Duchy of Savoy
, who was allied with Charles the Bold. In the Valais
, the independent republics of the Sieben Zenden, with the help of Bernese and other confederate forces, drove the Savoyards out of the lower Valais after a victory in the Battle on the Planta
in November 1475. In 1476, Charles retaliated and marched to Grandson
, which belonged to Pierre de Romont of Savoy, but which had recently been taken by the Swiss, where he had the garrison hanged or drowned in the lake despite their capitulation. When the Swiss confederate forces arrived a few days later, he was defeated in the Battle of Grandson
, and he was forced to flee the battlefield, leaving behind his artillery and many provisions and valuables. Having rallied a new army, he was dealt a devastating blow by the confederates in the Battle of Morat
. Charles the Bold fell in the Battle of Nancy
in 1477, where the Swiss fought alongside an army of René II, Duke of Lorraine
.
died out. The Flemish
territories of the Dukes of Burgundy subsequently became a possession of the Habsburgs, when Archduke Maximilian of Austria
, who would later become Holy Roman Emperor
, married Charles' only daughter Mary of Burgundy
. The duchy proper reverted to the crown of France under king Louis XI
. The Franche-Comté initially also became French, but was ceded to Maximilian's son Philip
in 1493 by the French king Charles VIII
in the treaty of Senlis
, in an attempt to bribe the Emperor to remain neutral during Charles's planned invasion of Italy.
The victories of the Eidgenossen (Swiss Confederation) over one of the most powerful military forces in Europe at the time gained them a reputation of near invincibility, and the Burgundian Wars marked the beginning of the rise of Swiss mercenaries
on the battlefields of Europe. Inside the Confederacy itself, however, the outcome of the war did lead to internal conflict when the city cantons insisted on having the lion's share of the proceeds since they had supplied the most troops. The country cantons resented this and the Dreizehn Orte disputes almost led to war. They were settled by the Stanser Verkommnis
of 1481.
Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy , was heir to an ancient and prestigious reputation and a large division of the lands of the Second Kingdom of Burgundy and in its own right was one of the geographically larger ducal territories in the emergence of Early Modern Europe from Medieval Europe.Even in that...
and the Kings of France, later involving the Old Swiss Confederacy
Old Swiss Confederacy
The Old Swiss Confederacy was the precursor of modern-day Switzerland....
, which would play a decisive role. Open war broke out in 1474, and in the following years the Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy was a title borne by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, a small portion of traditional lands of Burgundians west of river Saône which in 843 was allotted to Charles the Bald's kingdom of West Franks...
, Charles the Bold, was defeated three times on the battlefield and killed in the Battle of Nancy
Battle of Nancy
The Battle of Nancy was the final and decisive battle of the Burgundian Wars, fought outside the walls of Nancy on 5 January 1477 between Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy, and René II, Duke of Lorraine...
in 1477. The Duchy of Burgundy
Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy , was heir to an ancient and prestigious reputation and a large division of the lands of the Second Kingdom of Burgundy and in its own right was one of the geographically larger ducal territories in the emergence of Early Modern Europe from Medieval Europe.Even in that...
and several other Burgundian lands then became part of France, while the Burgundian Netherlands
Burgundian Netherlands
In the history of the Low Countries, the Burgundian Netherlands refers to a number of Imperial and French fiefs ruled in personal union by the House of Valois-Burgundy and their Habsburg heirs in the period from 1384 to 1482...
and the Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté the former "Free County" of Burgundy, as distinct from the neighbouring Duchy, is an administrative region and a traditional province of eastern France...
were inherited by Charles's daughter Mary of Burgundy
Mary of Burgundy
Mary of Burgundy ruled the Burgundian territories in Low Countries and was suo jure Duchess of Burgundy from 1477 until her death...
, and eventually passed to the House of Habsburg upon her death because of her marriage to Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I , the son of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor and Eleanor of Portugal, was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1493 until his death, though he was never in fact crowned by the Pope, the journey to Rome always being too risky...
.
The general situation

Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
and France. Their possessions included, besides their original territories of the Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté the former "Free County" of Burgundy, as distinct from the neighbouring Duchy, is an administrative region and a traditional province of eastern France...
and the Duchy of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy was a title borne by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, a small portion of traditional lands of Burgundians west of river Saône which in 843 was allotted to Charles the Bald's kingdom of West Franks...
, the economically strong regions of Flanders
Flanders
Flanders is the community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. "Flanders" can also refer to the northern part of Belgium that contains Brussels, Bruges, Ghent and Antwerp...
and Brabant as well as Luxembourg
Luxembourg
Luxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
.
The dukes of Burgundy generally pursued an aggressive expansionist politics, especially in Alsace
Alsace
Alsace is the fifth-smallest of the 27 regions of France in land area , and the smallest in metropolitan France. It is also the seventh-most densely populated region in France and third most densely populated region in metropolitan France, with ca. 220 inhabitants per km²...
and Lorraine
Lorraine (province)
The Duchy of Upper Lorraine was an historical duchy roughly corresponding with the present-day northeastern Lorraine region of France, including parts of modern Luxembourg and Germany. The main cities were Metz, Verdun, and the historic capital Nancy....
, seeking to geographically unite their northern and southern possessions. Having already been in conflict with the French king (Burgundy had sided with the English in the Hundred Years' War
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War was a series of separate wars waged from 1337 to 1453 by the House of Valois and the House of Plantagenet, also known as the House of Anjou, for the French throne, which had become vacant upon the extinction of the senior Capetian line of French kings...
), Charles' advances along the Rhine brought him in conflict with the Habsburgs and especially emperor Frederick III
Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick the Peaceful KG was Duke of Austria as Frederick V from 1424, the successor of Albert II as German King as Frederick IV from 1440, and Holy Roman Emperor as Frederick III from 1452...
.
The conflict

Sigismund, Archduke of Austria
Sigismund of Austria, Duke, then Archduke of Further Austria was a Habsburg archduke of Austria and ruler of Tirol from 1446 to 1490....
of Austria assigned his possessions in the Alsace
Alsace
Alsace is the fifth-smallest of the 27 regions of France in land area , and the smallest in metropolitan France. It is also the seventh-most densely populated region in France and third most densely populated region in metropolitan France, with ca. 220 inhabitants per km²...
as a fiefdom to the Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy was a title borne by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, a small portion of traditional lands of Burgundians west of river Saône which in 843 was allotted to Charles the Bald's kingdom of West Franks...
, Charles the Bold, to have them protected better against the expansion of the Eidgenossen
Eidgenossenschaft
Eidgenossenschaft is a German word meaning confederation. The term literally translates as "oath fellowship". An Eidgenossenschaft is a confederacy of equal partners, which can be individuals or groups such as states, formed by a pact sealed by a solemn oath. Such an alliance could be either...
(or Old Swiss Confederacy
Old Swiss Confederacy
The Old Swiss Confederacy was the precursor of modern-day Switzerland....
). Charles' involvement west of the Rhine gave him no reason to attack the confederates as Sigismund had wanted, but his embargo politics against the cities of Basel
Basel
Basel or Basle In the national languages of Switzerland the city is also known as Bâle , Basilea and Basilea is Switzerland's third most populous city with about 166,000 inhabitants. Located where the Swiss, French and German borders meet, Basel also has suburbs in France and Germany...
, Strasbourg
Strasbourg
Strasbourg is the capital and principal city of the Alsace region in eastern France and is the official seat of the European Parliament. Located close to the border with Germany, it is the capital of the Bas-Rhin département. The city and the region of Alsace are historically German-speaking,...
, and Mulhouse
Mulhouse
Mulhouse |mill]] hamlet) is a city and commune in eastern France, close to the Swiss and German borders. With a population of 110,514 and 278,206 inhabitants in the metropolitan area in 2006, it is the largest city in the Haut-Rhin département, and the second largest in the Alsace region after...
, directed by his reeve Peter von Hagenbach
Peter von Hagenbach
Peter von Hagenbach was a Bourguignon knight from Alsace and Germanic military and civil commander....
, prompted these to turn to Bern for help. Charles' expansionist strategy suffered a first setback in his politics when his attack on the Archbishopric of Cologne
Archbishopric of Cologne
The Electorate of Cologne was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire and existed from the 10th to the early 19th century. It consisted of the temporal possessions of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Cologne . It was ruled by the Archbishop in his function as prince-elector of...
failed after the unsuccessful Siege of Neuss
Siege of Neuss
The Siege of Neuss, from 1474–75, was part of the Burgundian Wars. The siege, led by Charles the Bold against the Holy Roman Empire city of Neuss, was unsuccessful...
(1473–1474).
In a second phase, Sigismund sought to achieve a peace agreement with the Swiss confederates, which eventually was concluded in Konstanz
Konstanz
Konstanz is a university city with approximately 80,000 inhabitants located at the western end of Lake Constance in the south-west corner of Germany, bordering Switzerland. The city houses the University of Konstanz.-Location:...
in 1474 (later called the Ewige Richtung). He wanted to buy back his Alsace possessions from Charles, which the latter refused. Shortly afterwards, von Hagenbach was captured and executed by decapitation in Alsace, and the Swiss, united with the Alsace cities and Sigismund of Habsburg in an "anti-Burgundian league", conquered part of the Burgundian Jura (Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté
Franche-Comté the former "Free County" of Burgundy, as distinct from the neighbouring Duchy, is an administrative region and a traditional province of eastern France...
) when they won the Battle of Héricourt
Battle of Héricourt
The Battle of Héricourt, fought in November 1474, was part of the Burgundian Wars, and resulted in a defeat for Burgundy and its allies....
in November 1474. The next year, Bernese forces conquered and ravaged Vaud
Vaud
Vaud is one of the 26 cantons of Switzerland and is located in Romandy, the French-speaking southwestern part of the country. The capital is Lausanne. The name of the Canton in Switzerland's other languages are Vaud in Italian , Waadt in German , and Vad in Romansh.-History:Along the lakes,...
, which belonged to the Duchy of Savoy
Duchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
, who was allied with Charles the Bold. In the Valais
Valais
The Valais is one of the 26 cantons of Switzerland in the southwestern part of the country, around the valley of the Rhône from its headwaters to Lake Geneva, separating the Pennine Alps from the Bernese Alps. The canton is one of the drier parts of Switzerland in its central Rhône valley...
, the independent republics of the Sieben Zenden, with the help of Bernese and other confederate forces, drove the Savoyards out of the lower Valais after a victory in the Battle on the Planta
Battle on the Planta
The Battle on the Planta, fought in November 1475, was part of the Burgundian Wars....
in November 1475. In 1476, Charles retaliated and marched to Grandson
Grandson, Switzerland
Grandson is a municipality in the district of Jura-Nord Vaudois in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland.During the Burgundian Wars, Charles the Bold was defeated near here in the Battle of Grandson on 2 March 1476.-History:...
, which belonged to Pierre de Romont of Savoy, but which had recently been taken by the Swiss, where he had the garrison hanged or drowned in the lake despite their capitulation. When the Swiss confederate forces arrived a few days later, he was defeated in the Battle of Grandson
Battle of Grandson
The Battle of Grandson, took place on 2 March 1476, was part of the Burgundian Wars, and resulted in a major defeat for Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy.- Siege of Grandson, February 1476 :...
, and he was forced to flee the battlefield, leaving behind his artillery and many provisions and valuables. Having rallied a new army, he was dealt a devastating blow by the confederates in the Battle of Morat
Battle of Morat
The Battle of Morat was a battle in the Burgundian Wars fought June 22, 1476 between Charles I, Duke of Burgundy and a Swiss army at Morat, about 30 kilometres from Bern.-Background:...
. Charles the Bold fell in the Battle of Nancy
Battle of Nancy
The Battle of Nancy was the final and decisive battle of the Burgundian Wars, fought outside the walls of Nancy on 5 January 1477 between Charles the Bold, Duke of Burgundy, and René II, Duke of Lorraine...
in 1477, where the Swiss fought alongside an army of René II, Duke of Lorraine
René II, Duke of Lorraine
René II was Count of Vaudémont from 1470, Duke of Lorraine from 1473, and Duke of Bar from 1483 to 1508. He claimed the crown of the Kingdom of Naples and the County of Provence as the Duke of Calabria 1480–1493 and as King of Naples and Jerusalem 1493–1508...
.
Effects
With the death of Charles the Bold, the dynasty of the dukes of BurgundyDuke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy was a title borne by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, a small portion of traditional lands of Burgundians west of river Saône which in 843 was allotted to Charles the Bald's kingdom of West Franks...
died out. The Flemish
Flanders
Flanders is the community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. "Flanders" can also refer to the northern part of Belgium that contains Brussels, Bruges, Ghent and Antwerp...
territories of the Dukes of Burgundy subsequently became a possession of the Habsburgs, when Archduke Maximilian of Austria
Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I , the son of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor and Eleanor of Portugal, was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1493 until his death, though he was never in fact crowned by the Pope, the journey to Rome always being too risky...
, who would later become Holy Roman Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
, married Charles' only daughter Mary of Burgundy
Mary of Burgundy
Mary of Burgundy ruled the Burgundian territories in Low Countries and was suo jure Duchess of Burgundy from 1477 until her death...
. The duchy proper reverted to the crown of France under king Louis XI
Louis XI of France
Louis XI , called the Prudent , was the King of France from 1461 to 1483. He was the son of Charles VII of France and Mary of Anjou, a member of the House of Valois....
. The Franche-Comté initially also became French, but was ceded to Maximilian's son Philip
Philip I of Castile
Philip I , known as Philip the Handsome or the Fair, was the first Habsburg King of Castile...
in 1493 by the French king Charles VIII
Charles VIII of France
Charles VIII, called the Affable, , was King of France from 1483 to his death in 1498. Charles was a member of the House of Valois...
in the treaty of Senlis
Treaty of Senlis
The Treaty of Senlis concerning the Burgundian succession was signed at Senlis, Oise in May of 1493 between Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor and King Charles VIII of France....
, in an attempt to bribe the Emperor to remain neutral during Charles's planned invasion of Italy.
The victories of the Eidgenossen (Swiss Confederation) over one of the most powerful military forces in Europe at the time gained them a reputation of near invincibility, and the Burgundian Wars marked the beginning of the rise of Swiss mercenaries
Swiss mercenaries
Swiss mercenaries were notable for their service in foreign armies, especially the armies of the Kings of France, throughout the Early Modern period of European history, from the Later Middle Ages into the Age of the European Enlightenment...
on the battlefields of Europe. Inside the Confederacy itself, however, the outcome of the war did lead to internal conflict when the city cantons insisted on having the lion's share of the proceeds since they had supplied the most troops. The country cantons resented this and the Dreizehn Orte disputes almost led to war. They were settled by the Stanser Verkommnis
Stanser Verkommnis
In the Stanser Verkommnis of 1481 the Tagsatzung solved the latent conflict between the rural and urban cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy, averting the breaking of the Confederacy, and triggering its further expansion from 8 to 13 members until 1513.The tensions between the cantons had arisen...
of 1481.

