Caesium fluoride
Encyclopedia
Caesium fluoride is an inorganic compound
usually encountered as a hygroscopic white solid. It is more soluble and more readily dissociated
than sodium fluoride
or potassium fluoride
. It is available in anhydrous form, and if water has been absorbed it is easy to dry by heating at 100 °C for two hours in vacuo. Like all soluble fluorides, it is mildly basic
. A notable fact about this compound is that it is the most ionic compound. Caesium has the lowest electronegativity
and fluorine has the highest electronegativity.
on caesium hydroxide
or caesium carbonate
, followed by removal of water.
Caesium fluoride reacts usually as a source of fluoride ion, F-. It therefore undergoes all of the usual reactions associated with soluble fluorides, for example:
(TBAF) and TAS-fluoride
(TASF) when anhydrous "naked" fluoride
ion
is needed.
is a weak acid. The low nucleophilicity
of fluoride means it can be a useful base in organic chemistry.Caesium fluoride is a useful base in organic chemistry
, due the fact that fluoride ion
is a relatively poor nucleophile
. CsF gives higher yields in Knoevenagel condensation
reactions than KF
or NaF
.
. For example, CsF reacts with hexafluoroacetone
to form a caesium perfluoroalkoxide salt, which is stable up to 60 °C, unlike the corresponding sodium
or potassium
salt. It will convert electron-deficient aryl chlorides to aryl fluorides (halex reaction).
–F
bond, fluoride ion is useful for desilylation reactions (removal of Si groups) in organic chemistry
; caesium fluoride is an excellent source of anhydrous fluoride for such reactions. Removal of silicon groups (desilylation) is a major application for CsF in the laboratory, as its anhydrous
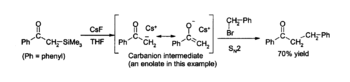
nature allows clean formation of water-sensitive intermediates. Solutions of caesium fluoride in THF
or DMF
attack a wide variety of organosilicon
compounds to produce an organosilicon fluoride and a carbanion
, which can then react with electrophile
s, for example:
Desilylation is also useful for the removal of silyl protecting group
s.
. For this reason it is sometimes used as the windows of cells used for infrared spectroscopy
.
should be avoided, as this forms highly toxic/corrosive hydrofluoric acid
. Caesium ion
(Cs+), or caesium chloride, is generally not considered toxic.
Inorganic compound
Inorganic compounds have traditionally been considered to be of inanimate, non-biological origin. In contrast, organic compounds have an explicit biological origin. However, over the past century, the classification of inorganic vs organic compounds has become less important to scientists,...
usually encountered as a hygroscopic white solid. It is more soluble and more readily dissociated
Dissociation (chemistry)
Dissociation in chemistry and biochemistry is a general process in which ionic compounds separate or split into smaller particles, ions, or radicals, usually in a reversible manner...
than sodium fluoride
Sodium fluoride
Sodium fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula NaF. A colorless solid, it is a source of the fluoride ion in diverse applications. Sodium fluoride is less expensive and less hygroscopic than the related salt potassium fluoride....
or potassium fluoride
Potassium fluoride
Potassium fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula KF. After hydrogen fluoride, KF is the primary source of the fluoride ion for applications in manufacturing and in chemistry. It is an alkali metal halide and occurs naturally as the rare mineral carobbiite...
. It is available in anhydrous form, and if water has been absorbed it is easy to dry by heating at 100 °C for two hours in vacuo. Like all soluble fluorides, it is mildly basic
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
. A notable fact about this compound is that it is the most ionic compound. Caesium has the lowest electronegativity
Electronegativity
Electronegativity, symbol χ , is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance that its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus...
and fluorine has the highest electronegativity.
Synthesis and properties
Caesium fluoride is prepared by the action of hydrofluoric acidHydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride in water. It is a valued source of fluorine and is the precursor to numerous pharmaceuticals such as fluoxetine and diverse materials such as PTFE ....
on caesium hydroxide
Caesium hydroxide
Caesium hydroxide is a chemical compound consisting of an atom of caesium and a hydroxide group . It is a powerful base, much like other alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide...
or caesium carbonate
Caesium carbonate
Caesium carbonate is a white crystalline solid of formula Cs2CO3. It is more soluble in organic solvents than many other carbonates such as potassium carbonate, and therefore finds use as a base in organic chemistry....
, followed by removal of water.
Caesium fluoride reacts usually as a source of fluoride ion, F-. It therefore undergoes all of the usual reactions associated with soluble fluorides, for example:
- 2 CsF + CaCl2 → 2 CsCl + CaF2
Crystal structure
Caesium fluoride has the halite structure, which means that the Cs+ and F− pack in a cubic closest packed array as do Na+ and Cl− in sodium chloride. Caesium cations are larger than fluoride anions, whereas in the lithium, sodium, potassium, and rubidium halides, the cations are smaller than the anion.In organic synthesis
Being highly dissociated it is a more reactive source of fluoride than related salts. CsF is less hygroscopic alternative to tetra-n-butylammonium fluorideTetra-n-butylammonium fluoride
Tetra-n-butylammonium fluoride or TBAF is a quaternary ammonium salt with the chemical formula 4N+F-. It is commercially available as the trihydrate and as a solution in tetrahydrofuran....
(TBAF) and TAS-fluoride
TASF reagent
The TASF reagent or trissulfonium difluorotrimethylsilicate is a reagent in organic chemistry with structural formula [3S]+[F2Si3]-. It is an anhydrous source of fluoride and is used to cleave silyl ether protective groups. Many other fluoride reagents are known, but few are truly anhydrous,...
(TASF) when anhydrous "naked" fluoride
Fluoride
Fluoride is the anion F−, the reduced form of fluorine when as an ion and when bonded to another element. Both organofluorine compounds and inorganic fluorine containing compounds are called fluorides. Fluoride, like other halides, is a monovalent ion . Its compounds often have properties that are...
ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
is needed.
As a base
As with other soluble fluorides, CsF is moderately basic, because HFHydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride in water. It is a valued source of fluorine and is the precursor to numerous pharmaceuticals such as fluoxetine and diverse materials such as PTFE ....
is a weak acid. The low nucleophilicity
Nucleophile
A nucleophile is a species that donates an electron-pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in a reaction. All molecules or ions with a free pair of electrons can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are by definition Lewis bases.Nucleophilic describes the...
of fluoride means it can be a useful base in organic chemistry.Caesium fluoride is a useful base in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
, due the fact that fluoride ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
is a relatively poor nucleophile
Nucleophile
A nucleophile is a species that donates an electron-pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in a reaction. All molecules or ions with a free pair of electrons can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are by definition Lewis bases.Nucleophilic describes the...
. CsF gives higher yields in Knoevenagel condensation
Knoevenagel condensation
The Knoevenagel condensation reaction is an organic reaction named after Emil Knoevenagel. It is a modification of the Aldol condensation.A Knoevenagel condensation is a nucleophilic addition of an active hydrogen compound to a carbonyl group followed by a dehydration reaction in which a molecule...
reactions than KF
Potassium fluoride
Potassium fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula KF. After hydrogen fluoride, KF is the primary source of the fluoride ion for applications in manufacturing and in chemistry. It is an alkali metal halide and occurs naturally as the rare mineral carobbiite...
or NaF
Sodium fluoride
Sodium fluoride is an inorganic chemical compound with the formula NaF. A colorless solid, it is a source of the fluoride ion in diverse applications. Sodium fluoride is less expensive and less hygroscopic than the related salt potassium fluoride....
.
Formation of C-F bonds
Caesium fluoride is also a popular source of fluoride in organofluorine chemistryOrganofluorine chemistry
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of organofluorine compounds, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil- and water-repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants and reagents in catalysis...
. For example, CsF reacts with hexafluoroacetone
Hexafluoroacetone
Hexafluoroacetone is a chemical compound with the formula CF3-CO-CF3. It is structurally similar to acetone, however its reactivity is markedly different. It comes in the form of a colourless, hygroscopic, nonflammable, highly reactive gas characterized by a musty odour...
to form a caesium perfluoroalkoxide salt, which is stable up to 60 °C, unlike the corresponding sodium
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride...
or potassium
Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are...
salt. It will convert electron-deficient aryl chlorides to aryl fluorides (halex reaction).
Deprotection agent
Due to the strength of the SiSilicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table...
–F
Fluorine
Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic...
bond, fluoride ion is useful for desilylation reactions (removal of Si groups) in organic chemistry
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
; caesium fluoride is an excellent source of anhydrous fluoride for such reactions. Removal of silicon groups (desilylation) is a major application for CsF in the laboratory, as its anhydrous
Anhydrous
As a general term, a substance is said to be anhydrous if it contains no water. The way of achieving the anhydrous form differs from one substance to another...
nature allows clean formation of water-sensitive intermediates. Solutions of caesium fluoride in THF
ThF
Follicular B helper T cells , are antigen-experienced CD4+ T cells found in the B cell follicles of secondary lymphoid organs such as lymph nodes, spleens and Peyer's patches, and are identified by their constitutive expression of the B cell follicle homing receptor CXCR5...
or DMF
Dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the formula 2NCH. Commonly abbreviated as DMF , this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions...
attack a wide variety of organosilicon
Organosilicon
Organosilicon compounds are organic compounds containing carbon silicon bonds. Organosilicon chemistry is the corresponding science exploring their properties and reactivity.Like carbon, the organically bound silicon is tetravalent and tetrahedral...
compounds to produce an organosilicon fluoride and a carbanion
Carbanion
A carbanion is an anion in which carbon has an unshared pair of electrons and bears a negative charge usually with three substituents for a total of eight valence electrons. The carbanion exists in a trigonal pyramidal geometry. Formally a carbanion is the conjugate base of a carbon acid.where B...
, which can then react with electrophile
Electrophile
In general electrophiles are positively charged species that are attracted to an electron rich centre. In chemistry, an electrophile is a reagent attracted to electrons that participates in a chemical reaction by accepting an electron pair in order to bond to a nucleophile...
s, for example:
Desilylation is also useful for the removal of silyl protecting group
Protecting group
A protecting group or protective group is introduced into a molecule by chemical modification of a functional group in order to obtain chemoselectivity in a subsequent chemical reaction...
s.
Other uses
Single crystals of the salt are transparent into the deep infraredInfrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
. For this reason it is sometimes used as the windows of cells used for infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy is the spectroscopy that deals with the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum, that is light with a longer wavelength and lower frequency than visible light. It covers a range of techniques, mostly based on absorption spectroscopy. As with all spectroscopic...
.
Precautions
Like other soluble fluorides, CsF is moderately toxic. Contact with acidAcid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
should be avoided, as this forms highly toxic/corrosive hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride in water. It is a valued source of fluorine and is the precursor to numerous pharmaceuticals such as fluoxetine and diverse materials such as PTFE ....
. Caesium ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
(Cs+), or caesium chloride, is generally not considered toxic.