
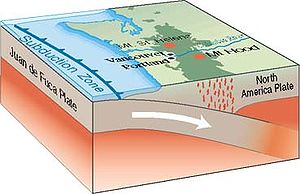
Cascadia subduction zone
Encyclopedia
Cascade Range
The Cascade Range is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, and the notable volcanoes known as the High Cascades...
subduction zone (also referred to as the Cascadia fault) is a subduction zone, a type of convergent
Convergent boundary
In plate tectonics, a convergent boundary, also known as a destructive plate boundary , is an actively deforming region where two tectonic plates or fragments of lithosphere move toward one another and collide...
plate boundary that stretches from northern Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is a large island in British Columbia, Canada. It is one of several North American locations named after George Vancouver, the British Royal Navy officer who explored the Pacific Northwest coast of North America between 1791 and 1794...
to northern California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
. It is a very long sloping fault that separates the Juan de Fuca
Juan de Fuca Plate
The Juan de Fuca Plate, named after the explorer of the same name, is a tectonic plate, generated from the Juan de Fuca Ridge, and subducting under the northerly portion of the western side of the North American Plate at the Cascadia subduction zone...
and North America
North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Greenland, Cuba, Bahamas, and parts of Siberia, Japan and Iceland. It extends eastward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and westward to the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. The plate includes both continental and oceanic crust...
plates.
New ocean floor is being created offshore of Washington and Oregon
Oregon
Oregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern...
. As more material wells up along the ocean ridge, the ocean floor moves toward and beneath the continent.
The North American Plate also moves, in a general southwest direction, overriding the oceanic plate. The Cascadia Subduction Zone is where the two plates meet.
Tectonic processes active in the Cascadia subduction zone region include accretion, subduction, deep earthquakes, and active volcanism that has included such notable eruptions as Mount Mazama
Mount Mazama
Mount Mazama is a destroyed stratovolcano in the Oregon part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the Cascade Range. The volcano's collapsed caldera holds Crater Lake, and the entire mountain is located within Crater Lake National Park....
(Crater Lake
Crater Lake
Crater Lake is a caldera lake located in the south-central region of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and famous for its deep blue color and water clarity. The lake partly fills a nearly deep caldera that was formed around 7,700 years agoby the...
) about 7,500 years ago, Mount Meager
Mount Meager
Mount Meager, originally known as Meager Mountain, is a complex volcano in the Sea-to-Sky Corridor of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located north of Vancouver at the northern end of the Pemberton Valley. Part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc of western North America, its summit is above...
about 2,350 years ago and Mount St. Helens
Mount St. Helens
Mount St. Helens is an active stratovolcano located in Skamania County, Washington, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is south of Seattle, Washington and northeast of Portland, Oregon. Mount St. Helens takes its English name from the British diplomat Lord St Helens, a...
in 1980.
Major cities affected by a disturbance in this subduction zone would include Vancouver
Vancouver
Vancouver is a coastal seaport city on the mainland of British Columbia, Canada. It is the hub of Greater Vancouver, which, with over 2.3 million residents, is the third most populous metropolitan area in the country,...
and Victoria
Victoria, British Columbia
Victoria is the capital city of British Columbia, Canada and is located on the southern tip of Vancouver Island off Canada's Pacific coast. The city has a population of about 78,000 within the metropolitan area of Greater Victoria, which has a population of 360,063, the 15th most populous Canadian...
, British Columbia; Seattle, Washington; Portland
Portland, Oregon
Portland is a city located in the Pacific Northwest, near the confluence of the Willamette and Columbia rivers in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2010 Census, it had a population of 583,776, making it the 29th most populous city in the United States...
, Oregon; and Sacramento
Sacramento, California
Sacramento is the capital city of the U.S. state of California and the county seat of Sacramento County. It is located at the confluence of the Sacramento River and the American River in the northern portion of California's expansive Central Valley. With a population of 466,488 at the 2010 census,...
, California.
Geology
The zone separates the Juan de Fuca PlateJuan de Fuca Plate
The Juan de Fuca Plate, named after the explorer of the same name, is a tectonic plate, generated from the Juan de Fuca Ridge, and subducting under the northerly portion of the western side of the North American Plate at the Cascadia subduction zone...
, Explorer Plate
Explorer Plate
The Explorer Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Vancouver Island, Canada.The eastern boundary of the Explorer Plate is being slowly subducted under the North American Plate, to which it may eventually accrete owing to the slow rate of subduction...
, Gorda Plate
Gorda Plate
The Gorda Plate, located beneath the Pacific Ocean off the coast of northern California, is one of the northern remnants of the Farallon Plate. It is sometimes referred to as simply the southernmost portion of the neighboring Juan de Fuca Plate, another Farallon remnant.Unlike most tectonic...
, and North American Plate
North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Greenland, Cuba, Bahamas, and parts of Siberia, Japan and Iceland. It extends eastward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and westward to the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. The plate includes both continental and oceanic crust...
. Here, the oceanic crust
Oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the part of Earth's lithosphere that surfaces in the ocean basins. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium...
of the Pacific Ocean sinks beneath the continent at a rate of 40 mm/yr
Year
A year is the orbital period of the Earth moving around the Sun. For an observer on Earth, this corresponds to the period it takes the Sun to complete one course throughout the zodiac along the ecliptic....
.
The width of the Cascadia subduction zone varies along its length, depending on the temperature of the subducted oceanic plate, which heats up as it is pushed deeper beneath the continent. As it becomes hotter and more molten, it eventually loses the ability to store mechanical stress and generates earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
s.On the Hyndman and Wang diagram (not shown, click on reference link below) the "locked" zone is storing up energy for an earthquake, and the "transition" zone, although somewhat plastic, could probably rupture.
At the Cascadia subduction zone, the oceanic plate subducts under the continental plate, which is what normally happens at an oceanic-continental convergent boundary
Convergent boundary
In plate tectonics, a convergent boundary, also known as a destructive plate boundary , is an actively deforming region where two tectonic plates or fragments of lithosphere move toward one another and collide...
.
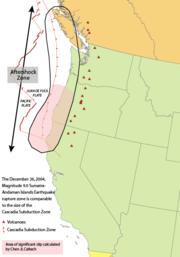
The Cascadia subduction zone runs from triple junction
Triple junction
A triple junction is the point where the boundaries of three tectonic plates meet. At the triple junction a boundary will be one of 3 types - a ridge, trench or transform fault - and triple junctions can be described according to the types of plate margin that meet at them...
s at its north and south ends. To the north, just below Queen Charlotte Island, it intersects the Queen Charlotte Fault
Queen Charlotte Fault
The Queen Charlotte Fault is an active transform fault, located between the North American Plate and the Pacific Plate, Canada's equivalent of the San Andreas Fault. The Queen Charlotte Fault forms a triple junction on its south with the Cascadia subduction zone and the Explorer Ridge...
and the Explorer Ridge
Explorer Ridge
The Explorer Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary located about west of Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. It lies at the northern extremity of the Pacific spreading axis...
. To the south, just off of Cape Mendocino
Cape Mendocino
Cape Mendocino located on the Lost Coast entirely within Humboldt County, California, USA, is the westernmost point on the coast of California. It has been a landmark since the 16th century when the Manila Galleons would reach the coast here following the prevailing westerlies all the way across...
in California, it intersects the San Andreas Fault
San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental strike-slip fault that runs a length of roughly through California in the United States. The fault's motion is right-lateral strike-slip...
and the Mendocino fault zone
Mendocino Fracture Zone
The Mendocino Fracture Zone is a fracture zone and transform boundary off the coast of Cape Mendocino in far northern California. It runs westward from a triple junction with the San Andreas Fault and the Cascadia subduction zone to the southern end of the Gorda Ridge...
at the Mendocino Triple Junction
Mendocino Triple Junction
The Mendocino Triple Junction is a geologic triple junction where the San Andreas Fault meets the Mendocino Fault and the Cascadia subduction zone, separating three tectonic plates: the Pacific Plate, the North American Plate and the Gorda Plate...
.
Earthquake magnitude
The Cascadia subduction zone can produce very large earthquakes ("megathrust earthquakeMegathrust earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at subduction zones at destructive plate boundaries , where one tectonic plate is forced under another. Due to the shallow dip of the plate boundary, which causes large sections to get stuck, these earthquakes are among the world's largest, with moment magnitudes ...
s"), magnitude 9.0 or greater, if rupture occurs over its whole area. When the "locked" zone stores up energy for an earthquake, the "transition" zone, although somewhat plastic, can rupture. Great Subduction Zone earthquakes are the largest earthquakes in the world, and can exceed magnitude 9.0. Earthquake size is proportional to fault area, and the Cascadia Subduction Zone is a very long sloping fault that stretches from mid-Vancouver Island to Northern California. It separates the Juan de Fuca and North American plates. Because of the very large fault area, the Cascadia Subduction Zone could produce a very large earthquake. Thermal and deformation studies indicate that the locked zone is fully locked for 60 kilometers (about 40 miles) downdip from the deformation front. Further downdip, there is a transition from fully locked to aseismic sliding
Aseismic creep
In geology, aseismic creep is measurable surface displacement along a fault in the absence of notable earthquakes.An example is along the Calaveras fault in Hollister, California. Streets crossing the fault in Hollister show significant offset and several houses sitting atop the fault are notably...
.
In 1999, a group of Continuous Global Positioning System
Global Positioning System
The Global Positioning System is a space-based global navigation satellite system that provides location and time information in all weather, anywhere on or near the Earth, where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites...
sites registered a brief reversal of motion of approximately 2 centimeters (0.8 inches) over a 50 kilometer by 300 kilometer (about 30 mile by 200 mile) area. The movement was the equivalent of a 6.7 magnitude earthquake. The motion did not trigger an earthquake and was only detectable as silent, non-earthquake seismic signatures.
| estimated year | interval | |
|---|---|---|
| 2005 source | 2003 source | (years) |
| about 9 pm, January 26, 1700 (NS Old Style and New Style dates Old Style and New Style are used in English language historical studies either to indicate that the start of the Julian year has been adjusted to start on 1 January even though documents written at the time use a different start of year ; or to indicate that a date conforms to the Julian... ) |
780 | |
| 780-1190 CE Common Era Common Era ,abbreviated as CE, is an alternative designation for the calendar era originally introduced by Dionysius Exiguus in the 6th century, traditionally identified with Anno Domini .Dates before the year 1 CE are indicated by the usage of BCE, short for Before the Common Era Common Era... |
880-960 CE | 210 |
| 690-730 CE | 550-750 CE | 330 |
| 350-420 CE | 250-320 CE | 910 |
| 660-440 BCE Common Era Common Era ,abbreviated as CE, is an alternative designation for the calendar era originally introduced by Dionysius Exiguus in the 6th century, traditionally identified with Anno Domini .Dates before the year 1 CE are indicated by the usage of BCE, short for Before the Common Era Common Era... |
610-450 BCE | 400 |
| 980-890 BCE | 910-780 BCE | 250 |
| 1440-1340 BCE | 1150-1220 BCE | unknown |
Earthquake timing
The last known great earthquake in the northwest was in January 1700, the Cascadia EarthquakeCascadia earthquake
The 1700 Cascadia earthquake was a magnitude 8.7 to 9.2 megathrust earthquake that occurred in the Cascadia subduction zone on January 26, 1700. The earthquake involved the Juan de Fuca Plate underlying the Pacific Ocean, from mid-Vancouver Island in British Columbia, Canada, south along the...
. Geological
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
evidence indicates that great earthquakes may have occurred at least seven times in the last 3,500 years, suggesting a return time of 300 to 600 years. There is also evidence of accompanying tsunami
Tsunami
A tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
s with every earthquake, and one line of evidence for these earthquakes is tsunami damage, and through Japanese records of tsunamis.
The next rupture of the Cascadia Subduction Zone is anticipated to be capable of causing widespread destruction throughout the Pacific Northwest
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest is a region in northwestern North America, bounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains on the east. Definitions of the region vary and there is no commonly agreed upon boundary, even among Pacific Northwesterners. A common concept of the...
.
Other similar subduction zones in the world usually have such earthquakes every 100 to 200 years; the longer interval here may indicate unusually large stress buildup and subsequent unusually large earthquake slip.
San Andreas Fault connection
Studies of past earthquake traces on both the northern San Andreas FaultSan Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental strike-slip fault that runs a length of roughly through California in the United States. The fault's motion is right-lateral strike-slip...
and the southern Cascadia subduction zone indicate a correlation in time which may be evidence that quakes on the Cascadia subduction zone may have triggered most of the major quakes on the northern San Andreas during at least the past 3,000 years or so. The evidence also shows the rupture direction going from north to south in each of these time-correlated events. The 1906 San Francisco earthquake
1906 San Francisco earthquake
The San Francisco earthquake of 1906 was a major earthquake that struck San Francisco, California, and the coast of Northern California at 5:12 a.m. on Wednesday, April 18, 1906. The most widely accepted estimate for the magnitude of the earthquake is a moment magnitude of 7.9; however, other...
seems to have been a major exception to this correlation, however, as it was not preceded by a major Cascadia quake.
Forecasts of the next major earthquake
Recent findings concluded the Cascadia subduction zone was more hazardous than previously suggested. The feared next major earthquake has some geologists predicting a 10% to 14% probability that the Cascadia Subduction Zone will produce an event of magnitude 9 or higher in the next 50 years; however, the most recent studies suggest that this risk could be as high as 37% for earthquakes of magnitude 8 or higher. Geologists have also determined the Pacific Northwest is not prepared for such a colossal earthquake. The tsunamiTsunami
A tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
produced may reach heights of approximately 30 meters (100 ft).
Cascade Volcanic Arc
The Cascade Volcanic Arc is a continental volcanic arc that extends from northern CaliforniaCalifornia
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
to the coastal mountains of British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
. The arc consists of a series of Quaternary age stratovolcanoes that grew on top of pre-existing geologic materials that ranged from Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
volcanics to glacial ice
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
. The Cascade Volcanic arc is located approximately 100 km inland from the coast, and forms a north-to-south chain of peaks that average over 3,000 m (10,000 ft) in elevation. The major peaks from south to north include:
- Lassen PeakLassen PeakLassen Peak is the southernmost active volcano in the Cascade Range. It is part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc which is an arc that stretches from northern California to southwestern British Columbia...
and Mt. Shasta (California) - Crater LakeCrater LakeCrater Lake is a caldera lake located in the south-central region of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and famous for its deep blue color and water clarity. The lake partly fills a nearly deep caldera that was formed around 7,700 years agoby the...
(Mazama), Three SistersThree Sisters (Oregon)The Three Sisters are three volcanic peaks of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the Cascade Range in Oregon, each of which exceeds in elevation. They are the third, fourth, and fifth highest peaks in the state of Oregon and are located in the Three Sisters Wilderness, about southwest from the nearest...
, Mt. Jefferson, Mt. Hood (Oregon) - Mt. AdamsMount Adams (Washington)Mount Adams is a potentially activestratovolcano in the Cascade Range and the second-highest mountain in the U.S. state of Washington.Adams is a member of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, and is one of the arc's largest volcanoes,...
, Mt. St. Helens, Mt. Rainier, Glacier PeakGlacier PeakGlacier Peak is the most isolated of the five major stratovolcanoes of the Cascade Volcanic Arc in Washington...
, Mt. Baker (Washington) - Mt. Garibaldi and Mt. MeagerMount MeagerMount Meager, originally known as Meager Mountain, is a complex volcano in the Sea-to-Sky Corridor of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located north of Vancouver at the northern end of the Pemberton Valley. Part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc of western North America, its summit is above...
(British Columbia)
The most active volcanoes in the chain include Mt. St. Helens, Mt. Baker, Lassen Peak, and Mt. Hood. St. Helens captured worldwide attention when it erupted catastrophically in 1980. St. Helens continues to rumble, albeit more quietly, emitting occasional steam plumes and experiencing small earthquakes, both signs of continuing magmatic activity. Most of the volcanoes have a main, central vent from which the most recent eruptions have occurred. The peaks are composed of layers of solidified andesitic
Andesite
Andesite is an extrusive igneous, volcanic rock, of intermediate composition, with aphanitic to porphyritic texture. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between basalt and dacite. The mineral assemblage is typically dominated by plagioclase plus pyroxene and/or hornblende. Magnetite,...
to dacitic
Dacite
Dacite is an igneous, volcanic rock. It has an aphanitic to porphyritic texture and is intermediate in composition between andesite and rhyolite. The relative proportions of feldspars and quartz in dacite, and in many other volcanic rocks, are illustrated in the QAPF diagram...
magma
Magma
Magma is a mixture of molten rock, volatiles and solids that is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and is expected to exist on other terrestrial planets. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and dissolved gas and sometimes also gas bubbles. Magma often collects in...
, and the more siliceous (and explosive) rhyolite
Rhyolite
This page is about a volcanic rock. For the ghost town see Rhyolite, Nevada, and for the satellite system, see Rhyolite/Aquacade.Rhyolite is an igneous, volcanic rock, of felsic composition . It may have any texture from glassy to aphanitic to porphyritic...
.
The volcanoes within the subduction zone include:
- Silverthrone CalderaSilverthrone CalderaThe Silverthrone Caldera is a potentially active caldera complex in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, located over northwest of the city of Vancouver and about west of Mount Waddington in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. The caldera is one of the largest of the few calderas in...
- Mount MeagerMount MeagerMount Meager, originally known as Meager Mountain, is a complex volcano in the Sea-to-Sky Corridor of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located north of Vancouver at the northern end of the Pemberton Valley. Part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc of western North America, its summit is above...
- Mount CayleyMount CayleyMount Cayley is a potentially active stratovolcano in Squamish-Lillooet Regional District of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Located north of Squamish and west of Whistler in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains, it rises above the Squamish River to the west and above the Cheakamus...
- Mount GaribaldiMount GaribaldiMount Garibaldi is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Sea to Sky Country of British Columbia, north of Vancouver, Canada. Located in the southernmost Coast Mountains, it is one of the most recognized peaks in the South Coast region, as well as British Columbia's best known volcano...
- Mount BakerMount BakerMount Baker , also known as Koma Kulshan or simply Kulshan, is an active glaciated andesitic stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the North Cascades of Washington State in the United States. It is the second-most active volcano in the range after Mount Saint Helens...
- Glacier PeakGlacier PeakGlacier Peak is the most isolated of the five major stratovolcanoes of the Cascade Volcanic Arc in Washington...
- Mount RainierMount RainierMount Rainier is a massive stratovolcano located southeast of Seattle in the state of Washington, United States. It is the most topographically prominent mountain in the contiguous United States and the Cascade Volcanic Arc, with a summit elevation of . Mt. Rainier is considered one of the most...
- Mount St. HelensMount St. HelensMount St. Helens is an active stratovolcano located in Skamania County, Washington, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is south of Seattle, Washington and northeast of Portland, Oregon. Mount St. Helens takes its English name from the British diplomat Lord St Helens, a...
- Mount AdamsMount Adams (Washington)Mount Adams is a potentially activestratovolcano in the Cascade Range and the second-highest mountain in the U.S. state of Washington.Adams is a member of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, and is one of the arc's largest volcanoes,...
- Mount HoodMount HoodMount Hood, called Wy'east by the Multnomah tribe, is a stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc of northern Oregon. It was formed by a subduction zone and rests in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States...
- Mount JeffersonMount Jefferson (Oregon)Mount Jefferson is a stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc, part of the Cascade Range, and is the second highest mountain in Oregon. Situated in the far northeastern corner of Linn County on the Jefferson County line, about east of Corvallis, Mount Jefferson is in a rugged wilderness and is...
- Three SistersThree Sisters (Oregon)The Three Sisters are three volcanic peaks of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the Cascade Range in Oregon, each of which exceeds in elevation. They are the third, fourth, and fifth highest peaks in the state of Oregon and are located in the Three Sisters Wilderness, about southwest from the nearest...
- Newberry VolcanoNewberry VolcanoNewberry Volcano is a large potentially active shield volcano located east of the Cascade Range and about southeast of Bend, Oregon. It is not a typical shield volcano. In addition to erupting basaltic lavas, it also has erupted andesitic and even rhyolitic lava.The volcano is in diameter and...
- Mount MazamaMount MazamaMount Mazama is a destroyed stratovolcano in the Oregon part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the Cascade Range. The volcano's collapsed caldera holds Crater Lake, and the entire mountain is located within Crater Lake National Park....
- Mount McLoughlinMount McLoughlinMount McLoughlin is a steep-sided lava cone built on top of a shield volcano in the Cascade Range of southern Oregon and within the Sky Lakes Wilderness area. It is one of the volcanic peaks in the Cascade Volcanic Arc. The mountain is north of Mount Shasta, south of Crater Lake, and west of Upper...
- Medicine Lake VolcanoMedicine Lake VolcanoMedicine Lake Volcano is a large shield volcano in northeastern California about northeast of Mount Shasta. The volcano is located in a zone of east-west crustal extension east of the main axis of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the Cascade Range. The thick shield is from east to west and from...
- Mount ShastaMount ShastaMount Shasta is located at the southern end of the Cascade Range in Siskiyou County, California and at is the second highest peak in the Cascades and the fifth highest in California...
- Lassen PeakLassen PeakLassen Peak is the southernmost active volcano in the Cascade Range. It is part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc which is an arc that stretches from northern California to southwestern British Columbia...
- Black ButteBlack Butte (Oregon)Black Butte is a cinder cone butte located in Deschutes National Forest, northwest of the town of Sisters, Oregon. An extinct volcano, it is composed of basaltic andesite. The cone rises over the surrounding plateau. Black Butte is a striking feature just north of US Highway 20, which descends...
See also
Related topics- Cascadia (disambiguation)
- 1700 Cascadia earthquake
- Cascade RangeCascade RangeThe Cascade Range is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, and the notable volcanoes known as the High Cascades...
- Cascade VolcanoesCascade VolcanoesThe Cascade Volcanoes are a number of volcanoes in a volcanic arc in western North America, extending from southwestern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California, a distance of well over 700 mi ...
- Geology of the Pacific NorthwestGeology of the Pacific NorthwestThe geology of the Pacific Northwest refers to the study of the composition , structure, physical properties and the processes that shape the Pacific Northwest region of the United States and Canada...
- North Cascades National ParkNorth Cascades National ParkNorth Cascades National Park is a U.S. National Park located in the state of Washington. The park is the largest of the three National Park Service units that comprise the North Cascades National Park Service Complex. Several national wilderness areas and British Columbia parkland adjoin the...
General
- Plate tectonicsPlate tectonicsPlate tectonics is a scientific theory that describes the large scale motions of Earth's lithosphere...
- Subduction zone
External links
- "Cascadia Peril '09" at dailywireless.org
- "Cascadia Peril 09 Tests Disaster Preparedness" at Clatsop County Oregon (Department News Release)
- Perilous Situation
- 9.0 Shakemap Scenario

