
Geology of the Pacific Northwest
Encyclopedia
The geology of the Pacific Northwest refers to the study of the composition (including rock
, minerals, and soils), structure, physical properties and the processes that shape the Pacific Northwest
region of the United States
and Canada
. The geology of the region produces much of the area's scenic beauty and also causes periodic catastrophes, such as volcano
es and earthquake
s.
There are at least five geologic province
s in the area: the Cascade Volcanoes
, the Columbia Plateau
, the North Cascades
, the Coast Mountains
, and the Insular Mountains
. The Cascade Volcanoes are an active volcanic region along the western side of the Pacific Northwest. The Columbia Plateau is a region of subdued geography that is inland of the Cascade Volcanoes, and the North Cascades are a mountainous region in the northwest corner of the United States, extending into Canada. The Coast Mountains and Insular Mountains are a strip of mountains along the coast of British Columbia, each with its own geological history.
The geology of the Pacific Northwest is vast, complex and confusing. Most of the region was formed about 200 million years ago as the North American Plate
started to drift westward during the rupture of Pangaea
. Since that date, the western edge of North America has grown westward as a succession of island arc
s and assorted ocean-floor rocks have been added along the continental margin
.
to Northern California
, roughly parallel to the Pacific coastline. Within this region, nearly 20 major volcanic centers lie in sequence like a string of explosive pearls.
 Although the largest volcanoes like Mount St. Helens
Although the largest volcanoes like Mount St. Helens
get the most
attention, the Cascade Volcanic Arc is really made up of a band of thousands of very
small, short-lived volcanoes that have built a platform of lava and
volcanic debris. Rising above this volcanic platform are a few strikingly large volcanoes that dominate the landscape.
The Cascade volcanoes define the Pacific Northwest section of the Ring of Fire
, an array of volcanoes that rim the Pacific Ocean. The Ring of Fire is also known for its frequent earthquakes. The volcanoes and earthquakes arise from a common source: subduction
.
Beneath the Cascade Volcanic Arc, a dense oceanic plate plunges beneath the North American Plate
; a process known as subduction. As the oceanic slab sinks deep into the Earth's interior beneath the
continental plate, high temperatures and pressures allow water molecules
locked in the minerals of solid rock to escape. The water vapor rises into the pliable mantle above the subducting plate, causing some of the mantle to melt. This newly formed magma rises toward the Earth's surface to erupt, forming a chain of volcanoes (the Cascade Volcanic Arc) above the subduction zone.
A close-up look at the Cascades reveals a more complicated picture than a simple subduction zone.
Not far off the coast of the North Pacific lies a spreading ridge;
a divergent plate boundary made up of a series of breaks in the oceanic crust where new ocean crust is created. On one side of the spreading ridge new Pacific Plate
crust is made, then moves away from the ridge. On the other side of the spreading ridge the Juan de Fuca
and Gorda Plate
s move eastward.
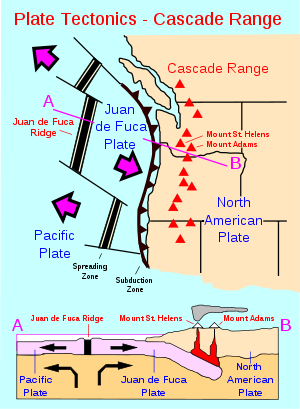 There are some unusual features at the Cascade subduction zone. Where the Juan de Fuca Plate sinks beneath the North American Plate there is no deep trench, seismicity (earthquakes) are fewer than expected, and there is evidence of a decline in volcanic activity over the past few million years. The probable explanation lies in the rate of convergence between the Juan de Fuca and North American Plates. These two plates converge at 3-4 centimeters per year at present. This is only about half the rate of convergence of 7 million years ago.
There are some unusual features at the Cascade subduction zone. Where the Juan de Fuca Plate sinks beneath the North American Plate there is no deep trench, seismicity (earthquakes) are fewer than expected, and there is evidence of a decline in volcanic activity over the past few million years. The probable explanation lies in the rate of convergence between the Juan de Fuca and North American Plates. These two plates converge at 3-4 centimeters per year at present. This is only about half the rate of convergence of 7 million years ago.
The small Juan de Fuca Plate and two platelets, the Explorer Plate
and Gorda Plate are the meager remnants of the much larger Farallon oceanic plate
. The Explorer Plate broke away from the Juan de Fuca about 4 million years ago and shows no evidence that it is still being subducted. The Gorda platelet split away between 18 and 5 million years ago and continues to sink beneath North America.
The Cascade Volcanic Arc made its first appearance 36 million years ago, but the major peaks that rise up from today's volcanic centers were born within the last 1.6 million years
. More than 3000 vents erupted during the most recent volcanic episode that began 5 million years ago. As long as subduction continues, new Cascade volcanoes will continue to rise.
 The Garibaldi Volcanic Belt
The Garibaldi Volcanic Belt
in southwestern British Columbia is the northern extension of the Cascade Volcanic Arc in the United States and contains the most explosive young volcanoes in Canada. Like the rest of the arc, it has its origins in the Cascadia subduction zone. Volcanoes of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt have been sporadically active over a time span of several millions of years. The northernmost member, Mount Meager
, was responsible for a major catastrophic eruption that occurred about 2,350 years ago. This eruption may have been close in size to that of the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens
. Ash from this eruption can be traced eastward to western Alberta
. It is also the most unstable volcanic massive in Canada, which has dumped clay
and rock several meters deep into the Pemberton Valley
at least three times during the past 7,300 years. Hot springs in the vicinity of Mount Cayley
and Mount Meager suggest that magmatic heat is still present. The long history of volcanism in the region, coupled with continued subduction
off the coast, suggests that volcanism has not yet ended in the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt. A few isolated volcanic centers northwest of Mount Meager such as the Franklin Glacier Volcano
and the Silverthrone Caldera
, which lie in the Pemberton Volcanic Belt
, may also be the product of Cascadia subduction, but geologic investigations have been very limited in this remote region. About 5-7 million years ago, the northern end of the Juan de Fuca Plate
broke off along the Nootka Fault
to form the Explorer Plate
, and there is no definitive consensus among geologist
s on the relation of the volcanoes north of that fault to the rest of the Cascade Arc. However, the Pemberton Volcanic Belt is usually merged with the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, making Mount Silverthrone the northernmost, but an uncertain Cascadia subduction-related volcano.
 The most active volcanic region of the northern Pacific Northwest is called the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province
The most active volcanic region of the northern Pacific Northwest is called the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province
(sometimes called the Stikine Volcanic Belt). It contains more than 100 young volcanoes and several eruptions known to have occurred within the last 400 years. The last eruptions within the volcanic belt
was about 150 years ago at The Volcano
in the Iskut-Unuk River Cones
volcanic field. The most voluminous and most persistent eruptive center within the belt and in Canada is the Level Mountain Range
. It is a large shield volcano
that covers an area of 1,800 km² southwest of Dease Lake and north of Telegraph Creek
. The broad dissected summit region consists of trachytic and rhyolitic lava dome
s and was considered to be dotted with several minor basalt
ic vents of postglacial age, although considered Holocene
activity to be uncertain. The Mount Edziza volcanic complex
is perhaps the most spectacular volcanic edifice in British Columbia
. It is the second largest persistent eruptive center within the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province and is flanked with numerous young satellite cone
s, including the young, well-preserved Eve Cone
. There are some indications that the Level Mountain Range and Mount Edziza volcanic complex may be between 11 and 9 million years old.
 The Anahim Volcanic Belt
The Anahim Volcanic Belt
is a volcanic belt that stretches from just north of Vancouver Island
to near Quesnel
. It is thought to have formed as a result of the North American Plate moving over a stationary hotspot
, similar to the hotspot feeding the Hawaiian Islands
, called the Anahim hotspot
. The youngest volcano
within the volcanic belt
is Nazko Cone
. It last erupted about 7,000 years ago, producing two small lava flow
s that traveled 1 km to the west, along with a blanket of volcanic ash
that extends several km to the north and east of the cone. The volcanic belt also contains three large shield volcanoes that were formed between 8 and 1 million years ago, called the Ilgachuz Range
, Rainbow Range
and the Itcha Range
.
The Chilcotin Group in southern British Columbia is a north-south range of volcanoes, thought to have formed as a result of back-arc extension
behind the Cascadia subduction zone
. The majority of the eruptions in this belt happened either 6 to 10 million years ago (Miocene
) or 2-3 million years ago (Pliocene
). However, there have been few eruptions in the Pleistocene
.
The Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field
in south-eastern British Columbia
consists of several small basalt
ic volcanoes and extensive lava
flows that have been active for the past 3 million years. It is within the Wells Gray Provincial Park
, which also includes the 465 feet (141.7 m)-high Helmcken Falls
. The origin of the volcanism is unknown, but is probably related to crustal
thinning. Some of the lava flows in the field are similar to those that erupted at Volcano Mountain
in the Yukon
, where olivine nephelinite
occurs. The last eruption in the field was about 400 years ago at Kostal Cone
.
Numerous seamount
s lie off British Columbia's coast and are related to hotspot
volcanism. The Bowie Seamount
located 180 kilometers west of the Queen Charlotte Islands
, is perhaps the shallowest seamount in Canada's Pacific waters. Because of its shallow depth, scientist
s believe it was an active volcanic island throughout the last ice age
. The Bowie Seamount is also the youngest seamount in the Kodiak-Bowie Seamount chain
.
is Canada's worst known geophysical disaster. The eruption produced a 22.5 km long lava flow, destroying the Nisga'a
village
s and the death of at least 2000 Nisga'a people by volcanic gas
es and poisonous smoke. The Nass River
valley was inundated by the lava flows and contain abundant tree molds and lava tube
s. The event coincided with the arrival of the first Europe
an explorers to penetrate the uncharted coastal waters of northern British Columbia
. Today, the basaltic lava deposits are a draw to tourists and are part of the Nisga'a Memorial Lava Beds Provincial Park
.
 The Pacific Northwest volcanoes continue to be a geologically active area. The most geologically recent volcanic eruptions include:
The Pacific Northwest volcanoes continue to be a geologically active area. The most geologically recent volcanic eruptions include:
 The Pacific Northwest is seismically active. The Juan de Fuca Plate
The Pacific Northwest is seismically active. The Juan de Fuca Plate
is capable of producing megathrust earthquake
s of moment magnitude
9: the last such earthquake was the 1700 Cascadia earthquake, which produced a tsunami
in Japan, and may have temporarily blocked the Columbia River
with the Bonneville Slide. More recently, in 2001, the Nisqually earthquake
(magnitude 6.8) struck 10 miles (16.1 km) northeast of Olympia, Washington
, causing some structural damage and panic.
In addition, eleven volcanoes in Canada have had seismic activity since 1975, including: the Silverthrone Caldera
, Mount Meager
, Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field
, Mount Garibaldi
, Mount Cayley
, Castle Rock
, The Volcano
, Mount Edziza volcanic complex
, Hoodoo Mountain
, Crow Lagoon
and Nazko Cone
.
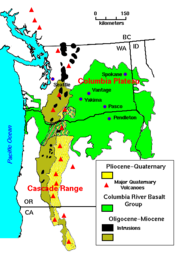
The Columbia Plateau province is enveloped by one of the world's largest
accumulations of lava. Over 500,000 km² of the Earth's surface is covered
by it. The topography here is dominated by geologically young lava flows
that inundated the countryside with amazing speed, all within the last 17
million years.
Over 170,000 cubic kilometers of basaltic lava, known as the Columbia River
basalts, covers the western part of the province. These tremendous flows
erupted between 17-6 million years ago. Most of the lava flooded out in the
first 1.5 million years: an extraordinarily short time for such an
outpouring of molten rock.
The Snake River Plain
stretches across Oregon, through northern Nevada,
southern Idaho, and ends at the Yellowstone Plateau in Wyoming. Looking
like a great spoon scooped out the Earth surface, the smooth topography of
this province forms a striking contrast with the strong mountainous fabric
around it.
The Snake River Plain lies in a distinct depression. At the western end,
the base has dropped down along normal faults, forming a graben
structure. Although there is extensive faulting at the eastern end, the
structure is not as clear.
 Like the Columbia River region, volcanic eruptions dominate the story of
Like the Columbia River region, volcanic eruptions dominate the story of
the Snake River Plain in the eastern part of the Columbia Plateau
Province. The earliest Snake River Plain eruptions began about 15 million
years ago, just as the tremendous early eruptions of Columbia River Basalt
were ending. But most of the Snake River Plain volcanic rock is less than a
few million years old, Pliocene
age (5-1.6 million years ago) and
younger.
In the west, the Columbia River Basalts are just that:almost exclusively
black basalt
. Not so in the Snake River Plain, where relatively quiet
eruptions of soupy black basalt lava flows alternated with tremendous
explosive eruptions of rhyolite
, a light-colored volcanic rock.
Cinder cones
dot the landscape of the Snake River
Plain. Some are aligned along vents, the fissures that fed flows and
cone-building eruptions. Calderas, great pits formed by explosive
volcanism, and low shield volcanoes, and rhyolite hills are also part of
the landscape here, but many are obscured by later lava flows.
Evidence suggests that some concentrated heat source is melting rock
beneath the Columbia Plateau Province. At the base of the lithosphere (the
layer of crust and upper mantle that forms Earth's moving tectonic
plates). In an effort to figure out why this area, far from a plate
boundary, had such an enormous outpouring of lava, scientists established
hardening dates for many of the individual lava flows. They found that the
youngest volcanic rocks were clustered near the Yellowstone Plateau, and
that the farther west they went, the older the lavas.
Although scientists are still gathering evidence, a probable explanation is
that a hot spot, an extremely hot plume of deep mantle
material, is rising to the surface beneath the Columbia Plateau Province. Geologists know that
beneath Hawaii
and Iceland
, a temperature instability develops (for reasons
not yet well understood) at the boundary between the core and mantle. The
concentrated heat triggers a plume hundreds of kilometers in diameter that
ascends directly through to the surface of the Earth.
When the hot plume arrives at the base of the lithosphere
, some of the
lighter rock of the lithosphere rapidly melts. It is this molten
lithosphere that becomes the basalt lavas that gush onto the surface to
form the Columbia River and Snake River Plain basalts.
The track of this hot spot starts in the west and sweeps up to Yellowstone National Park
. The steaming fumaroles and explosive geyser
s are ample
evidence of a concentration of heat beneath the surface. The hotspot is
probably quite stationary, but the North American plate is moving over it,
creating a superb record of the rate and direction of plate motion.
time (about one million years ago), cooling temperatures provided conditions favorable for the creation of continental glacier
s. Over the centuries, as snowfall exceeded melting and evaporation, a great accumulation of snow covered part of the continent, forming extensive ice fields. This vast continental ice sheet reached a thickness of about 4000 feet (1,219.2 m) in some areas. Sufficient pressure on the ice caused it to flow outward as a glacier. The glacier moved south out of Canada
, damming rivers and creating lakes in Washington, Idaho and Montana.
The ice blocked the Clark Fork River, forming the huge Glacial Lake Missoula
. The lake measured about 7 770 km² (297.3 sq mi) and contained about 2100 cubic kilometers (500 cubic miles), half the volume of Lake Michigan
.
 Glacial Lake Missoula eventually broke through the ice dam, allowing a tremendous volume of water to rush across northern Idaho and into eastern Washington. Such catastrophic floods raced across the southward-dipping plateau a number of times, etching the coulees which characterize this region, now known as the channeled scablands
Glacial Lake Missoula eventually broke through the ice dam, allowing a tremendous volume of water to rush across northern Idaho and into eastern Washington. Such catastrophic floods raced across the southward-dipping plateau a number of times, etching the coulees which characterize this region, now known as the channeled scablands
.
As the floods in this vicinity raced southward, two major cascades formed along their course. The larger cataract was that of the Upper Coulee, where the river roared over an 800 feet (243.8 m) waterfall. The eroding power of the water plucked pieces of basalt from the precipice, causing the falls to retreat 20 miles (32.2 km) and self-destruct by cutting through to the Columbia River valley near what is now the Grand Coulee Dam.
The other major cataract is now known as Dry Falls
. It started near Soap Lake in Washington State, where less resistant basalt layers gave way before the great erosive power of this tremendous torrent and waterfalls developed. As in the Upper Coulee, the raging river yanked chunks of rock from the face of the falls and the falls eventually retreated to their present location. Dry Falls is three and one-half miles wide, with a drop of more than 400 feet (121.9 m). By way of comparison, Niagara Falls
, one mile (1.6 km) wide with a drop of only 165 feet (50.3 m), would be dwarfed by Dry Falls.
, a mountain chain stretching more than 12000 miles (19,312.1 km) from
Tierra del Fuego
to the Alaska Peninsula
, and second only to the
Alpine-Himalayan chain in height. Although only a small part
of the Cordillera, mile for mile, the North Cascade Range is steeper and
wetter than most other ranges in the conterminous United States.
In geology, the range has more in common with the Coast Ranges of British
Columbia and Alaska than it does with its Cordilleran cousins in the Rocky
Mountains or Sierra Nevada. Although the peaks of the North Cascades do not
reach great elevations (high peaks are generally in the 7,000 to 8000 feet (2,438.4 m)
range), their overall relief, that is, the relatively uninterrupted
vertical distance from valley bottom to mountain top, is commonly 4,000 to
6,000 feet.
Rocks of the North Cascades record at least 400 million years of history:
time enough to have collected a jumble of different rocks. The range is a
geologic mosaic made up of volcanic island arc
s, deep ocean sediments,
basaltic ocean floor, parts of old continents, submarine fans, and
even pieces of the deep subcrustal mantle
of the earth. The disparate
pieces of the North Cascade mosaic were born far from one another but
subsequently drifted together, carried along by the tectonic plates that
make up the Earth's outer shell. Over time, the moving plates eventually
accreted the various pieces of the mosaic onto the western side of North
America.
As if this mosaic of unrelated pieces were not complex enough, some of the
assembled pieces were uplift
ed, eroded
by stream
s, and then
locally buried in their own eroded debris; other pieces were forced deep
into the Earth to be heated and squeezed, almost beyond recognition, and
then raised again to view.
About 35 million years ago, a volcanic arc grew across this complex mosaic
of old terrane
s. Volcanoes erupted to cover the older rocks with lava and
ash. Large masses of molten rock invaded the older rocks from below. The
volcanic arc is still active today, decorating the skyline with the cones
of Mount Baker
and Glacier Peak
.
 The deep canyons and sharp peaks of today's North Cascades scene are
The deep canyons and sharp peaks of today's North Cascades scene are
products of profound erosion. Running water has etched out the grain of the
range, landslides have softened the abrupt edges, homegrown glaciers have
scoured the peaks and high valleys and, during the Ice Age
, the
Cordilleran Ice Sheet
overrode almost all the range and rearranged
courses of streams. Erosion has written and still writes it own history in
the mountains, but it has also revealed the complex mosaic of the
bedrock.
are the western range of the North American mainland cordillera, covering the Alaska Panhandle
and most of costal British Columbia. The range is approximately 1600 km (994 mi) long and 200 km (124 mi) wide.
Most of the Coast Mountains are composed of granite
, which is part of the Coast Plutonic Complex. This is the single largest contiguous granite outcropping in the world, which extends approximately 1800 km (1,118 mi) in length. It is a large batholith
complex. Its formation is related to subduction
of the Kula
and Farallon
tectonic plates along the continental margin
during the Jurassic
-to-Eocene
periods. The plutonic complex is built on unusual island arc
fragments, oceanic plateau
s and continental margin assemblages accreted between the Triassic
and the Cretaceous
periods. In addition, the Garibaldi
, Meager
, Cayley
and Silverthrone
areas are of recent volcanic origin.
 The Coast Mountains consist of a single uplifted mass. During the Pliocene
The Coast Mountains consist of a single uplifted mass. During the Pliocene
period the Coast Mountains did not exist and a level peneplain extended to the sea. This mass was uplifted during the Miocene
period. Rivers such as the Klinaklini River
and Homathko River
predate this uplift and due to erosion
occurring faster than uplift, have continued to flow right up to the present day, directly across the axis of the range. The mountains flanking the Homathko River are the highest in the Coast Mountains, and include Mount Waddington
west of the river in the Waddington Range
and Mount Queen Bess
east of the river, adjacent to the Homathko Icefield
.
The Pacific Ranges
in southwestern British Columbia are the southernmost subdivision of the Coast Mountains. It has been characterized by rapid rates of uplift over the past 4 million years unlike the North Cascades and has led to relatively high rates of erosion.
on the coast of British Columbia is not yet fully emerged above sea level
, and Vancouver Island
and the Queen Charlotte Islands
are just the higher elevations of the range, which was in fact fully exposed during the last ice age
when the continental shelf
in this area was a broad coastal plain
. Although the Coast Mountains
are commonly considered to be the westernmost range of the American cordillera
, the Insular Mountains are the true westernmost range. Through the most recent ice age
about 18,000 years ago, ice
enclosed nearly all of the mountain
s. Glacier
s that ran down to the Pacific Ocean
sharpened the valley
faces and eroded
their bottoms.
 The Insular Mountains were formed when a large island arc
The Insular Mountains were formed when a large island arc
, called the Insular Islands
, collided against North America during the Mid-Cretaceous
period. The mountains are made of turbidite
and pillow lava
s unlike the plutons of the Coast Plutonic Complex that make the Coast Mountains. The Insular Mountains have much seismic activity
, with the Juan de Fuca Plate
subducting at the Cascadia subduction zone
and the Pacific Plate
sliding along the Queen Charlotte Fault
. Large earthquakes have led to collapsing mountains, landslide
s, and the development of fissure
s. Flood basalt
s on Vancouver Island form a geologic formation
called the Karmutsen Formation
, which is perhaps the thickest accreted section of an oceanic plateau
worldwide, exposing up to 6000 m (19,685 ft) of basal sediment-sill
complexes, basalt
ic to picritic pillow lavas, pillow breccia
, and thick, massive basalt flows.
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock or stone is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids.The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock. In general rocks are of three types, namely, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic...
, minerals, and soils), structure, physical properties and the processes that shape the Pacific Northwest
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest is a region in northwestern North America, bounded by the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains on the east. Definitions of the region vary and there is no commonly agreed upon boundary, even among Pacific Northwesterners. A common concept of the...
region of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
. The geology of the region produces much of the area's scenic beauty and also causes periodic catastrophes, such as volcano
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
es and earthquake
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
s.
There are at least five geologic province
Geologic province
A geologic or geomorphic province is a spatial entity with common geologic or geomorphic attributes. A province may include a single dominant structural element such as a basin or a fold belt, or a number of contiguous related elements...
s in the area: the Cascade Volcanoes
Cascade Volcanoes
The Cascade Volcanoes are a number of volcanoes in a volcanic arc in western North America, extending from southwestern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California, a distance of well over 700 mi ...
, the Columbia Plateau
Columbia Plateau
The Columbia Plateau is a geologic and geographic region that lies across parts of the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is a wide flood basalt plateau between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains, cut through by the Columbia River...
, the North Cascades
North Cascades
The North Cascades are a section of the Cascade Range of western North America. They span the border between the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington and are officially named in Canada as the Cascade Mountains...
, the Coast Mountains
Coast Mountains
The Coast Mountains are a major mountain range, in the Pacific Coast Ranges, of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the Coast of British Columbia. They are so-named because of their proximity to the sea coast, and are often...
, and the Insular Mountains
Insular Mountains
The Insular Mountains are a range of mountains in the Pacific Coast Ranges on the coast of British Columbia, Canada, comprising the Vancouver Island Ranges and Queen Charlotte Mountains. The Insular Mountains are rugged, particularly on Vancouver Island where peaks in Strathcona Provincial Park...
. The Cascade Volcanoes are an active volcanic region along the western side of the Pacific Northwest. The Columbia Plateau is a region of subdued geography that is inland of the Cascade Volcanoes, and the North Cascades are a mountainous region in the northwest corner of the United States, extending into Canada. The Coast Mountains and Insular Mountains are a strip of mountains along the coast of British Columbia, each with its own geological history.
The geology of the Pacific Northwest is vast, complex and confusing. Most of the region was formed about 200 million years ago as the North American Plate
North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Greenland, Cuba, Bahamas, and parts of Siberia, Japan and Iceland. It extends eastward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and westward to the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. The plate includes both continental and oceanic crust...
started to drift westward during the rupture of Pangaea
Pangaea
Pangaea, Pangæa, or Pangea is hypothesized as a supercontinent that existed during the Paleozoic and Mesozoic eras about 250 million years ago, before the component continents were separated into their current configuration....
. Since that date, the western edge of North America has grown westward as a succession of island arc
Volcanic arc
A volcanic arc is a chain of volcanoes positioned in an arc shape as seen from above. Offshore volcanoes form islands, resulting in a volcanic island arc. Generally they result from the subduction of an oceanic tectonic plate under another tectonic plate, and often parallel an oceanic trench...
s and assorted ocean-floor rocks have been added along the continental margin
Continental margin
The continental margin is the zone of the ocean floor that separates the thin oceanic crust from thick continental crust. Continental margins constitute about 28% of the oceanic area....
.
The Cascade Volcanoes
The Cascades Province forms an arc-shaped band extending from southwestern British ColumbiaBritish Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
to Northern California
Northern California
Northern California is the northern portion of the U.S. state of California. The San Francisco Bay Area , and Sacramento as well as its metropolitan area are the main population centers...
, roughly parallel to the Pacific coastline. Within this region, nearly 20 major volcanic centers lie in sequence like a string of explosive pearls.

Mount St. Helens
Mount St. Helens is an active stratovolcano located in Skamania County, Washington, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is south of Seattle, Washington and northeast of Portland, Oregon. Mount St. Helens takes its English name from the British diplomat Lord St Helens, a...
get the most
attention, the Cascade Volcanic Arc is really made up of a band of thousands of very
small, short-lived volcanoes that have built a platform of lava and
volcanic debris. Rising above this volcanic platform are a few strikingly large volcanoes that dominate the landscape.
The Cascade volcanoes define the Pacific Northwest section of the Ring of Fire
Pacific Ring of Fire
The Pacific Ring of Fire is an area where large numbers of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur in the basin of the Pacific Ocean. In a horseshoe shape, it is associated with a nearly continuous series of oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, and volcanic belts and/or plate movements...
, an array of volcanoes that rim the Pacific Ocean. The Ring of Fire is also known for its frequent earthquakes. The volcanoes and earthquakes arise from a common source: subduction
Subduction
In geology, subduction is the process that takes place at convergent boundaries by which one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate, sinking into the Earth's mantle, as the plates converge. These 3D regions of mantle downwellings are known as "Subduction Zones"...
.
Beneath the Cascade Volcanic Arc, a dense oceanic plate plunges beneath the North American Plate
North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Greenland, Cuba, Bahamas, and parts of Siberia, Japan and Iceland. It extends eastward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and westward to the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. The plate includes both continental and oceanic crust...
; a process known as subduction. As the oceanic slab sinks deep into the Earth's interior beneath the
continental plate, high temperatures and pressures allow water molecules
locked in the minerals of solid rock to escape. The water vapor rises into the pliable mantle above the subducting plate, causing some of the mantle to melt. This newly formed magma rises toward the Earth's surface to erupt, forming a chain of volcanoes (the Cascade Volcanic Arc) above the subduction zone.
A close-up look at the Cascades reveals a more complicated picture than a simple subduction zone.
Not far off the coast of the North Pacific lies a spreading ridge;
a divergent plate boundary made up of a series of breaks in the oceanic crust where new ocean crust is created. On one side of the spreading ridge new Pacific Plate
Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At 103 million square kilometres, it is the largest tectonic plate....
crust is made, then moves away from the ridge. On the other side of the spreading ridge the Juan de Fuca
Juan de Fuca Plate
The Juan de Fuca Plate, named after the explorer of the same name, is a tectonic plate, generated from the Juan de Fuca Ridge, and subducting under the northerly portion of the western side of the North American Plate at the Cascadia subduction zone...
and Gorda Plate
Gorda Plate
The Gorda Plate, located beneath the Pacific Ocean off the coast of northern California, is one of the northern remnants of the Farallon Plate. It is sometimes referred to as simply the southernmost portion of the neighboring Juan de Fuca Plate, another Farallon remnant.Unlike most tectonic...
s move eastward.

The small Juan de Fuca Plate and two platelets, the Explorer Plate
Explorer Plate
The Explorer Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Vancouver Island, Canada.The eastern boundary of the Explorer Plate is being slowly subducted under the North American Plate, to which it may eventually accrete owing to the slow rate of subduction...
and Gorda Plate are the meager remnants of the much larger Farallon oceanic plate
Farallon Plate
The Farallon Plate was an ancient oceanic plate, which began subducting under the west coast of the North American Plate— then located in modern Utah— as Pangaea broke apart during the Jurassic Period...
. The Explorer Plate broke away from the Juan de Fuca about 4 million years ago and shows no evidence that it is still being subducted. The Gorda platelet split away between 18 and 5 million years ago and continues to sink beneath North America.
The Cascade Volcanic Arc made its first appearance 36 million years ago, but the major peaks that rise up from today's volcanic centers were born within the last 1.6 million years
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
. More than 3000 vents erupted during the most recent volcanic episode that began 5 million years ago. As long as subduction continues, new Cascade volcanoes will continue to rise.
Volcanism outside the Cascades

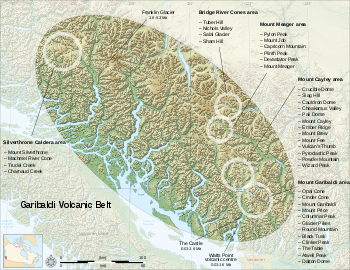
Garibaldi Volcanic Belt
The Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, also called the Canadian Cascade Arc, is a northwest-southeast trending volcanic chain in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains that extends from Watts Point in the south to the Ha-Iltzuk Icefield in the north. This chain of volcanoes is located in southwestern...
in southwestern British Columbia is the northern extension of the Cascade Volcanic Arc in the United States and contains the most explosive young volcanoes in Canada. Like the rest of the arc, it has its origins in the Cascadia subduction zone. Volcanoes of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt have been sporadically active over a time span of several millions of years. The northernmost member, Mount Meager
Mount Meager
Mount Meager, originally known as Meager Mountain, is a complex volcano in the Sea-to-Sky Corridor of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located north of Vancouver at the northern end of the Pemberton Valley. Part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc of western North America, its summit is above...
, was responsible for a major catastrophic eruption that occurred about 2,350 years ago. This eruption may have been close in size to that of the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens
1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens
The 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens, a stratovolcano located in Washington state, in the United States, was a major volcanic eruption. The eruption was the only significant one to occur in the contiguous 48 U.S. states since the 1915 eruption of Lassen Peak in California...
. Ash from this eruption can be traced eastward to western Alberta
Alberta
Alberta is a province of Canada. It had an estimated population of 3.7 million in 2010 making it the most populous of Canada's three prairie provinces...
. It is also the most unstable volcanic massive in Canada, which has dumped clay
Clay
Clay is a general term including many combinations of one or more clay minerals with traces of metal oxides and organic matter. Geologic clay deposits are mostly composed of phyllosilicate minerals containing variable amounts of water trapped in the mineral structure.- Formation :Clay minerals...
and rock several meters deep into the Pemberton Valley
Pemberton Valley
The Pemberton Valley is a valley flanking the Lillooet River upstream from Lillooet Lake, including the communities of Mount Currie, Pemberton, British Columbia and the agricultural district surrounding them and flanking the river as far upstream as the Pemberton Meadows area...
at least three times during the past 7,300 years. Hot springs in the vicinity of Mount Cayley
Mount Cayley
Mount Cayley is a potentially active stratovolcano in Squamish-Lillooet Regional District of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Located north of Squamish and west of Whistler in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains, it rises above the Squamish River to the west and above the Cheakamus...
and Mount Meager suggest that magmatic heat is still present. The long history of volcanism in the region, coupled with continued subduction
Subduction
In geology, subduction is the process that takes place at convergent boundaries by which one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate, sinking into the Earth's mantle, as the plates converge. These 3D regions of mantle downwellings are known as "Subduction Zones"...
off the coast, suggests that volcanism has not yet ended in the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt. A few isolated volcanic centers northwest of Mount Meager such as the Franklin Glacier Volcano
Franklin Glacier Volcano
Franklin Glacier Volcano is a deeply eroded and huge long and wide caldera complex in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, located east-southeast of the Silverthrone Caldera in the Hoodoo Creek and Franklin Glacier area on the northwest flank of the Waddington Massif of the Pacific Ranges...
and the Silverthrone Caldera
Silverthrone Caldera
The Silverthrone Caldera is a potentially active caldera complex in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, located over northwest of the city of Vancouver and about west of Mount Waddington in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. The caldera is one of the largest of the few calderas in...
, which lie in the Pemberton Volcanic Belt
Pemberton Volcanic Belt
The Pemberton Volcanic Belt is an eroded Oligocene volcanic belt at a low angle near Mount Meager, British Columbia, Canada. The Garibaldi and Pemberton volcanic belts appear to merge into a single belt, although the Pemberton is older than the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt...
, may also be the product of Cascadia subduction, but geologic investigations have been very limited in this remote region. About 5-7 million years ago, the northern end of the Juan de Fuca Plate
Juan de Fuca Plate
The Juan de Fuca Plate, named after the explorer of the same name, is a tectonic plate, generated from the Juan de Fuca Ridge, and subducting under the northerly portion of the western side of the North American Plate at the Cascadia subduction zone...
broke off along the Nootka Fault
Nootka Fault
The Nootka Fault is an active transform fault running southwest from Nootka Island, near Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada.-Geology:...
to form the Explorer Plate
Explorer Plate
The Explorer Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate beneath the Pacific Ocean off the west coast of Vancouver Island, Canada.The eastern boundary of the Explorer Plate is being slowly subducted under the North American Plate, to which it may eventually accrete owing to the slow rate of subduction...
, and there is no definitive consensus among geologist
Geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid and liquid matter that constitutes the Earth as well as the processes and history that has shaped it. Geologists usually engage in studying geology. Geologists, studying more of an applied science than a theoretical one, must approach Geology using...
s on the relation of the volcanoes north of that fault to the rest of the Cascade Arc. However, the Pemberton Volcanic Belt is usually merged with the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, making Mount Silverthrone the northernmost, but an uncertain Cascadia subduction-related volcano.

Northern Cordilleran volcanic province
The Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province , formerly known as the Stikine Volcanic Belt, is a geologic province defined by the occurrence of Miocene to Holocene volcanoes in the Pacific Northwest of North America...
(sometimes called the Stikine Volcanic Belt). It contains more than 100 young volcanoes and several eruptions known to have occurred within the last 400 years. The last eruptions within the volcanic belt
Volcanic belt
A volcanic belt is a large volcanically active region. Other terms are used for smaller areas of activity, such as volcanic fields. Volcanic belts are found above zones of unusually high temperature where magma is created by partial melting of solid material in the Earth's crust and upper mantle....
was about 150 years ago at The Volcano
The Volcano (British Columbia)
The Volcano, also known as Lava Fork volcano, is a small cinder cone in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains in northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located approximately northwest of the small community of Stewart near the head of Lava Fork...
in the Iskut-Unuk River Cones
Iskut-Unuk River Cones
The Iskut-Unuk River Cones are a group of eight small basaltic centres at the southern end of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains. The lava flows date back 70,000 years, but the subaerial vents produced cinder cones and lava flows that were...
volcanic field. The most voluminous and most persistent eruptive center within the belt and in Canada is the Level Mountain Range
Level Mountain Range
The Level Mountain Range, also known as Level Mountain, is a mountain range in Cassiar Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located just northeast of Callison Ranch, southwest of Dease Lake and about north of Mount Edziza. It consists of a massive shield volcano and lies on the Nahlin...
. It is a large shield volcano
Shield volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano usually built almost entirely of fluid lava flows. They are named for their large size and low profile, resembling a warrior's shield. This is caused by the highly fluid lava they erupt, which travels farther than lava erupted from more explosive volcanoes...
that covers an area of 1,800 km² southwest of Dease Lake and north of Telegraph Creek
Telegraph Creek, British Columbia
Telegraph Creek is a small community located off Highway 37 in Northern British Columbia at the confluence of the Stikine River and Telegraph Creek. The only permanent settlement on the Stikine River, it is home to approximately 350 members of the Tahltan First Nation, as well as another 50...
. The broad dissected summit region consists of trachytic and rhyolitic lava dome
Lava dome
|250px|thumb|right|Image of the [[rhyolitic]] lava dome of [[Chaitén Volcano]] during its 2008–2009 eruption.In volcanology, a lava dome is a roughly circular mound-shaped protrusion resulting from the slow extrusion of viscous lava from a volcano...
s and was considered to be dotted with several minor basalt
Basalt
Basalt is a common extrusive volcanic rock. It is usually grey to black and fine-grained due to rapid cooling of lava at the surface of a planet. It may be porphyritic containing larger crystals in a fine matrix, or vesicular, or frothy scoria. Unweathered basalt is black or grey...
ic vents of postglacial age, although considered Holocene
Holocene
The Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"...
activity to be uncertain. The Mount Edziza volcanic complex
Mount Edziza volcanic complex
The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a large and potentially active north-south trending complex volcano in Stikine Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located southeast of the small community of Telegraph Creek...
is perhaps the most spectacular volcanic edifice in British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
. It is the second largest persistent eruptive center within the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province and is flanked with numerous young satellite cone
Satellite cone
A parasitic cone is the cone-shaped accumulation of volcanic material not part of the central vent of a volcano. One forms by eruptions from fractures on the flank of the volcano. These fractures occur because of the flank of the volcano is unstable...
s, including the young, well-preserved Eve Cone
Eve Cone
Eve Cone is a well-preserved black cinder cone on the Big Raven Plateau, British Columbia, Canada. It is one of the 30 cinder cones on the flanks of the massive shield volcano of Mount Edziza that formed in the year 700, making it one of the most recent eruptions on the Big Raven Plateau and in...
. There are some indications that the Level Mountain Range and Mount Edziza volcanic complex may be between 11 and 9 million years old.

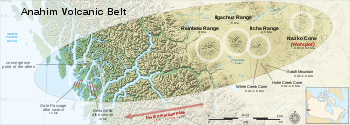
Anahim Volcanic Belt
The Anahim Volcanic Belt is a long volcanic belt, stretching from just north of Vancouver Island to near Quesnel, British Columbia, Canada. The Anahim Volcanic Belt has had three main magmatic episodes: 15–13 Ma, 9–6 Ma, and 3–1 Ma. The volcanoes generally become younger eastward at a rate of to ...
is a volcanic belt that stretches from just north of Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is a large island in British Columbia, Canada. It is one of several North American locations named after George Vancouver, the British Royal Navy officer who explored the Pacific Northwest coast of North America between 1791 and 1794...
to near Quesnel
Quesnel, British Columbia
-Demographics:Quesnel had a population of 9,326 people in 2006, which was a decrease of 7.1% from the 2001 census count. The median household income in 2005 for Quesnel was $54,044, which is slightly above the British Columbia provincial average of $52,709....
. It is thought to have formed as a result of the North American Plate moving over a stationary hotspot
Hotspot (geology)
The places known as hotspots or hot spots in geology are volcanic regions thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the mantle elsewhere. They may be on, near to, or far from tectonic plate boundaries. There are two hypotheses to explain them...
, similar to the hotspot feeding the Hawaiian Islands
Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, numerous smaller islets, and undersea seamounts in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some 1,500 miles from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost Kure Atoll...
, called the Anahim hotspot
Anahim hotspot
The Anahim hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in central British Columbia, Canada. It is situated on the Interior Plateau, a large region that lies between the Cariboo and Monashee Mountains to the east, and the Hazelton Mountains, Coast Mountains and Cascade Range to the west...
. The youngest volcano
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
within the volcanic belt
Volcanic belt
A volcanic belt is a large volcanically active region. Other terms are used for smaller areas of activity, such as volcanic fields. Volcanic belts are found above zones of unusually high temperature where magma is created by partial melting of solid material in the Earth's crust and upper mantle....
is Nazko Cone
Nazko Cone
Nazko Cone is a small potentially active basaltic cinder cone in central British Columbia, Canada, located 75 km west of Quesnel and 150 kilometers southwest of Prince George. It is considered the easternmost volcano in the Anahim Volcanic Belt. The small tree-covered cone rises 120 m above...
. It last erupted about 7,000 years ago, producing two small lava flow
Lava
Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at...
s that traveled 1 km to the west, along with a blanket of volcanic ash
Volcanic ash
Volcanic ash consists of small tephra, which are bits of pulverized rock and glass created by volcanic eruptions, less than in diameter. There are three mechanisms of volcanic ash formation: gas release under decompression causing magmatic eruptions; thermal contraction from chilling on contact...
that extends several km to the north and east of the cone. The volcanic belt also contains three large shield volcanoes that were formed between 8 and 1 million years ago, called the Ilgachuz Range
Ilgachuz Range
The Ilgachuz Range is a name given to an extinct shield volcano in British Columbia, Canada. It is not a mountain range in the normal sense, because it was formed as a single volcano that has been eroded for the past 5 million years. It lies on the Chilcotin Plateau, located some north-northwest...
, Rainbow Range
Rainbow Range (Coast Mountains)
The Rainbow Range, formerly known as the Rainbow Mountains, is a mountain range in British Columbia, Canada, located northwest of Anahim Lake...
and the Itcha Range
Itcha Range
The Itcha Range is a mountain range on the Chilcotin Plateau of the West-Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. The range is located 25 miles northeast of Anahim Lake...
.
The Chilcotin Group in southern British Columbia is a north-south range of volcanoes, thought to have formed as a result of back-arc extension
Back-arc basin
Back-arc basins are geologic features, submarine basins associated with island arcs and subduction zones.They are found at some convergent plate boundaries, presently concentrated in the Western Pacific ocean. Most of them result from tensional forces caused by oceanic trench rollback and the...
behind the Cascadia subduction zone
Cascadia subduction zone
The Cascadia subduction zone is a subduction zone, a type of convergent plate boundary that stretches from northern Vancouver Island to northern California. It is a very long sloping fault that separates the Juan de Fuca and North America plates.New ocean floor is being created offshore of...
. The majority of the eruptions in this belt happened either 6 to 10 million years ago (Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
) or 2-3 million years ago (Pliocene
Pliocene
The Pliocene Epoch is the period in the geologic timescale that extends from 5.332 million to 2.588 million years before present. It is the second and youngest epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch...
). However, there have been few eruptions in the Pleistocene
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
.
The Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field
The Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, also called the Clearwater Cone Group, is a potentially active monogenetic volcanic field in east-central British Columbia, Canada, located approximately north of Kamloops. It is situated in the Cariboo Mountains of the Columbia Mountains and on the...
in south-eastern British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
consists of several small basalt
Basalt
Basalt is a common extrusive volcanic rock. It is usually grey to black and fine-grained due to rapid cooling of lava at the surface of a planet. It may be porphyritic containing larger crystals in a fine matrix, or vesicular, or frothy scoria. Unweathered basalt is black or grey...
ic volcanoes and extensive lava
Lava
Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at...
flows that have been active for the past 3 million years. It is within the Wells Gray Provincial Park
Wells Gray Provincial Park
Wells Gray Provincial Park is a large wilderness park located in east-central British Columbia, Canada. The park protects most of the southern, and highest, regions of the Cariboo Mountains and covers 5,250 square kilometres...
, which also includes the 465 feet (141.7 m)-high Helmcken Falls
Helmcken Falls
Helmcken Falls is a waterfall on the Murtle River within Wells Gray Provincial Park in British Columbia, Canada. The protection of Helmcken Falls was one of the reasons for the creation of Wells Gray Provincial Park in 1939....
. The origin of the volcanism is unknown, but is probably related to crustal
Crust (geology)
In geology, the crust is the outermost solid shell of a rocky planet or natural satellite, which is chemically distinct from the underlying mantle...
thinning. Some of the lava flows in the field are similar to those that erupted at Volcano Mountain
Volcano Mountain
Volcano Mountain is an active cinder cone in central Yukon Territory, Canada, located a short distance north of Fort Selkirk, near the confluence of the Pelly and Yukon Rivers...
in the Yukon
Yukon
Yukon is the westernmost and smallest of Canada's three federal territories. It was named after the Yukon River. The word Yukon means "Great River" in Gwich’in....
, where olivine nephelinite
Lava
Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at...
occurs. The last eruption in the field was about 400 years ago at Kostal Cone
Kostal Cone
Kostal Cone, also called Kostal Volcano, is a young cinder cone in Wells Gray Provincial Park in east-central British Columbia, Canada. It rises from the northeast shore of Kostal Lake in the Cariboo Mountains...
.
Numerous seamount
Seamount
A seamount is a mountain rising from the ocean seafloor that does not reach to the water's surface , and thus is not an island. These are typically formed from extinct volcanoes, that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from a seafloor of depth. They are defined by oceanographers as...
s lie off British Columbia's coast and are related to hotspot
Hotspot (geology)
The places known as hotspots or hot spots in geology are volcanic regions thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the mantle elsewhere. They may be on, near to, or far from tectonic plate boundaries. There are two hypotheses to explain them...
volcanism. The Bowie Seamount
Bowie Seamount
Bowie Seamount is a large submarine volcano in the northeastern Pacific Ocean, located west of Haida Gwaii, British Columbia, Canada.The seamount is named after William Bowie of the Coast & Geodetic Survey....
located 180 kilometers west of the Queen Charlotte Islands
Queen Charlotte Islands
Haida Gwaii , formerly the Queen Charlotte Islands, is an archipelago on the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada. Haida Gwaii consists of two main islands: Graham Island in the north, and Moresby Island in the south, along with approximately 150 smaller islands with a total landmass of...
, is perhaps the shallowest seamount in Canada's Pacific waters. Because of its shallow depth, scientist
Scientist
A scientist in a broad sense is one engaging in a systematic activity to acquire knowledge. In a more restricted sense, a scientist is an individual who uses the scientific method. The person may be an expert in one or more areas of science. This article focuses on the more restricted use of the word...
s believe it was an active volcanic island throughout the last ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
. The Bowie Seamount is also the youngest seamount in the Kodiak-Bowie Seamount chain
Kodiak-Bowie Seamount chain
The Kodiak–Bowie Seamount chain, also called the Pratt–Welker Seamount chain, is a seamount chain in southeastern Gulf of Alaska stretching from the Aleutian Trench in the north to Bowie Seamount, the youngest volcano in the chain, which lies west of the Queen Charlotte Islands,...
.
Volcanic disasters
The last eruption of the Tseax ConeTseax Cone
The Tseax Cone , also called the Tseax River Cone or alternately the Aiyansh Volcano, is a young cinder cone and adjacent lava flows associated with the Nass Ranges and the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province...
is Canada's worst known geophysical disaster. The eruption produced a 22.5 km long lava flow, destroying the Nisga'a
Nisga'a
The Nisga’a , often formerly spelled Nishga and spelled in the Nisga’a language as Nisga’a, are an Indigenous nation or First Nation in Canada. They live in the Nass River valley of northwestern British Columbia. Their name comes from a combination of two Nisga’a words: Nisk’-"top lip" and...
village
Village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet with the population ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand , Though often located in rural areas, the term urban village is also applied to certain urban neighbourhoods, such as the West Village in Manhattan, New...
s and the death of at least 2000 Nisga'a people by volcanic gas
Volcanic gas
|250px|thumb|right|Image of the [[rhyolitic]] [[lava dome]] of [[Chaitén Volcano]] during its 2008-2010 eruption.Volcanic gases include a variety of substances given off by active volcanoes...
es and poisonous smoke. The Nass River
Nass River
The Nass River is a river in northern British Columbia, Canada. It flows from the Coast Mountains southwest to Nass Bay, a sidewater of Portland Inlet, which connects to the North Pacific Ocean via the Dixon Entrance...
valley was inundated by the lava flows and contain abundant tree molds and lava tube
Lava tube
Lava tubes are natural conduits through which lava travels beneath the surface of a lava flow, expelled by a volcano during an eruption. They can be actively draining lava from a source, or can be extinct, meaning the lava flow has ceased and the rock has cooled and left a long, cave-like...
s. The event coincided with the arrival of the first Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
an explorers to penetrate the uncharted coastal waters of northern British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
. Today, the basaltic lava deposits are a draw to tourists and are part of the Nisga'a Memorial Lava Beds Provincial Park
Nisga'a Memorial Lava Beds Provincial Park
Nisga'a Memorial Lava Bed Provincial Park is a provincial park in the Nass River valley in northwestern British Columbia, Canada, about 80 kilometres north of Terrace, and near the Nisga'a Villages of Gitlakdamix and Gitwinksihlkw.The park was established by Order in Council on April 29, 1992,...
.
Recent volcanic activity

- Level Mountain RangeLevel Mountain RangeThe Level Mountain Range, also known as Level Mountain, is a mountain range in Cassiar Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located just northeast of Callison Ranch, southwest of Dease Lake and about north of Mount Edziza. It consists of a massive shield volcano and lies on the Nahlin...
, Canada's most voluminous and most persistent eruptive center, might have erupted in the HoloceneHoloceneThe Holocene is a geological epoch which began at the end of the Pleistocene and continues to the present. The Holocene is part of the Quaternary period. Its name comes from the Greek words and , meaning "entirely recent"...
. - Nazko ConeNazko ConeNazko Cone is a small potentially active basaltic cinder cone in central British Columbia, Canada, located 75 km west of Quesnel and 150 kilometers southwest of Prince George. It is considered the easternmost volcano in the Anahim Volcanic Belt. The small tree-covered cone rises 120 m above...
, the youngest volcano in the Anahim Volcanic BeltAnahim Volcanic BeltThe Anahim Volcanic Belt is a long volcanic belt, stretching from just north of Vancouver Island to near Quesnel, British Columbia, Canada. The Anahim Volcanic Belt has had three main magmatic episodes: 15–13 Ma, 9–6 Ma, and 3–1 Ma. The volcanoes generally become younger eastward at a rate of to ...
, erupted 7200 BPBefore PresentBefore Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
. - Hoodoo MountainHoodoo MountainHoodoo Mountain is a potentially active flat-topped stratovolcano in the Stikine Country of northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located northeast of Wrangell, Alaska on the north side of the lower Iskut River and east of its junction with the Stikine River...
erupted 7050 BPBefore PresentBefore Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
. - Lava ButteLava ButteLava Butte is a cinder cone located in central Oregon, USA, just west of US Highway 97 between the towns of Bend, Oregon, and Sunriver, Oregon. It is part of a system of small cinder cones on the northwest flank of Newberry Volcano, a massive shield volcano which rises to the southeast...
, OregonOregonOregon is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located on the Pacific coast, with Washington to the north, California to the south, Nevada on the southeast and Idaho to the east. The Columbia and Snake rivers delineate much of Oregon's northern and eastern...
erupted about 7,000 years ago. - Mount MazamaMount MazamaMount Mazama is a destroyed stratovolcano in the Oregon part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the Cascade Range. The volcano's collapsed caldera holds Crater Lake, and the entire mountain is located within Crater Lake National Park....
, which erupted catastrophically in 5670 BC to form Crater LakeCrater LakeCrater Lake is a caldera lake located in the south-central region of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and famous for its deep blue color and water clarity. The lake partly fills a nearly deep caldera that was formed around 7,700 years agoby the...
. - Mount MeagerMount MeagerMount Meager, originally known as Meager Mountain, is a complex volcano in the Sea-to-Sky Corridor of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located north of Vancouver at the northern end of the Pemberton Valley. Part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc of western North America, its summit is above...
erupted about 2350 BPBefore PresentBefore Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
, sending an ash columnEruption columnAn eruption column consists of hot volcanic ash emitted during an explosive volcanic eruption. The ash forms a column rising many kilometres into the air above the peak of the volcano. In the most explosive eruptions, the eruption column may rise over 40 km, penetrating the stratosphere...
20 km high into the stratosphereStratosphereThe stratosphere is the second major layer of Earth's atmosphere, just above the troposphere, and below the mesosphere. It is stratified in temperature, with warmer layers higher up and cooler layers farther down. This is in contrast to the troposphere near the Earth's surface, which is cooler...
. - Mount Edziza volcanic complexMount Edziza volcanic complexThe Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a large and potentially active north-south trending complex volcano in Stikine Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located southeast of the small community of Telegraph Creek...
, Canada's second largest eruptive center, erupted about 1340 BPBefore PresentBefore Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
. - Medicine Lake VolcanoMedicine Lake VolcanoMedicine Lake Volcano is a large shield volcano in northeastern California about northeast of Mount Shasta. The volcano is located in a zone of east-west crustal extension east of the main axis of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the Cascade Range. The thick shield is from east to west and from...
erupted about 1000 BPBefore PresentBefore Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
. - Silverthrone CalderaSilverthrone CalderaThe Silverthrone Caldera is a potentially active caldera complex in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, located over northwest of the city of Vancouver and about west of Mount Waddington in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. The caldera is one of the largest of the few calderas in...
might have eruptions younger than 1000 AD - Kostal ConeKostal ConeKostal Cone, also called Kostal Volcano, is a young cinder cone in Wells Gray Provincial Park in east-central British Columbia, Canada. It rises from the northeast shore of Kostal Lake in the Cariboo Mountains...
in the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic fieldWells Gray-Clearwater volcanic fieldThe Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, also called the Clearwater Cone Group, is a potentially active monogenetic volcanic field in east-central British Columbia, Canada, located approximately north of Kamloops. It is situated in the Cariboo Mountains of the Columbia Mountains and on the...
might have erupted and formed in 1500 based on tree-ring dating. - Glacier PeakGlacier PeakGlacier Peak is the most isolated of the five major stratovolcanoes of the Cascade Volcanic Arc in Washington...
erupted in the 17th or 18th century. - Tseax ConeTseax ConeThe Tseax Cone , also called the Tseax River Cone or alternately the Aiyansh Volcano, is a young cinder cone and adjacent lava flows associated with the Nass Ranges and the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province...
erupted in the 18th century. - Mount HoodMount HoodMount Hood, called Wy'east by the Multnomah tribe, is a stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc of northern Oregon. It was formed by a subduction zone and rests in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States...
erupted in 1781-82; fumaroleFumaroleA fumarole is an opening in a planet's crust, often in the neighborhood of volcanoes, which emits steam and gases such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, hydrochloric acid, and hydrogen sulfide. The steam is created when superheated water turns to steam as its pressure drops when it emerges from...
s on the summit still spew sulfurSulfurSulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
ous gas. - Mount ShastaMount ShastaMount Shasta is located at the southern end of the Cascade Range in Siskiyou County, California and at is the second highest peak in the Cascades and the fifth highest in California...
erupted in 1786. - The VolcanoThe Volcano (British Columbia)The Volcano, also known as Lava Fork volcano, is a small cinder cone in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains in northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located approximately northwest of the small community of Stewart near the head of Lava Fork...
erupted about 150 BPBefore PresentBefore Present years is a time scale used in archaeology, geology, and other scientific disciplines to specify when events in the past occurred. Because the "present" time changes, standard practice is to use AD 1950 as the origin of the age scale, reflecting the fact that radiocarbon...
, producing a 22.5 km long lava flow. - Mount RainierMount RainierMount Rainier is a massive stratovolcano located southeast of Seattle in the state of Washington, United States. It is the most topographically prominent mountain in the contiguous United States and the Cascade Volcanic Arc, with a summit elevation of . Mt. Rainier is considered one of the most...
erupted 1854. - Mount BakerMount BakerMount Baker , also known as Koma Kulshan or simply Kulshan, is an active glaciated andesitic stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the North Cascades of Washington State in the United States. It is the second-most active volcano in the range after Mount Saint Helens...
erupted in 1880; fumaroles still occur at its summit. - Ruby MountainRuby MountainRuby Mountain is a cinder cone in Stikine Region, British Columbia, Canada, located 23 km northeast of Atlin and south of Mount Barham. A recent collapse on the volcanoes eastern side created a large landslide which dissects this side of Ruby Mountain...
might have erupted in 1898. - Lassen PeakLassen PeakLassen Peak is the southernmost active volcano in the Cascade Range. It is part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc which is an arc that stretches from northern California to southwestern British Columbia...
erupted in 1914-5. - Mount St. HelensMount St. HelensMount St. Helens is an active stratovolcano located in Skamania County, Washington, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is south of Seattle, Washington and northeast of Portland, Oregon. Mount St. Helens takes its English name from the British diplomat Lord St Helens, a...
erupted in 1980, killing 57 people. (see 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens1980 eruption of Mount St. HelensThe 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens, a stratovolcano located in Washington state, in the United States, was a major volcanic eruption. The eruption was the only significant one to occur in the contiguous 48 U.S. states since the 1915 eruption of Lassen Peak in California...
).
Seismic activity

Juan de Fuca Plate
The Juan de Fuca Plate, named after the explorer of the same name, is a tectonic plate, generated from the Juan de Fuca Ridge, and subducting under the northerly portion of the western side of the North American Plate at the Cascadia subduction zone...
is capable of producing megathrust earthquake
Megathrust earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at subduction zones at destructive plate boundaries , where one tectonic plate is forced under another. Due to the shallow dip of the plate boundary, which causes large sections to get stuck, these earthquakes are among the world's largest, with moment magnitudes ...
s of moment magnitude
Moment magnitude scale
The moment magnitude scale is used by seismologists to measure the size of earthquakes in terms of the energy released. The magnitude is based on the seismic moment of the earthquake, which is equal to the rigidity of the Earth multiplied by the average amount of slip on the fault and the size of...
9: the last such earthquake was the 1700 Cascadia earthquake, which produced a tsunami
Tsunami
A tsunami is a series of water waves caused by the displacement of a large volume of a body of water, typically an ocean or a large lake...
in Japan, and may have temporarily blocked the Columbia River
Columbia River
The Columbia River is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state...
with the Bonneville Slide. More recently, in 2001, the Nisqually earthquake
Nisqually earthquake
The Nisqually earthquake was an intraslab earthquake, occurring at 10:54 a.m. PST . on February 28, 2001, and was one of the largest recorded earthquakes in Washington state history. The quake measured 6.8 on the MMS and lasted approximately 45 seconds. The epicenter of the earthquake was Anderson...
(magnitude 6.8) struck 10 miles (16.1 km) northeast of Olympia, Washington
Olympia, Washington
Olympia is the capital city of the U.S. state of Washington and the county seat of Thurston County. It was incorporated on January 28, 1859. The population was 46,478 at the 2010 census...
, causing some structural damage and panic.
In addition, eleven volcanoes in Canada have had seismic activity since 1975, including: the Silverthrone Caldera
Silverthrone Caldera
The Silverthrone Caldera is a potentially active caldera complex in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, located over northwest of the city of Vancouver and about west of Mount Waddington in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. The caldera is one of the largest of the few calderas in...
, Mount Meager
Mount Meager
Mount Meager, originally known as Meager Mountain, is a complex volcano in the Sea-to-Sky Corridor of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located north of Vancouver at the northern end of the Pemberton Valley. Part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc of western North America, its summit is above...
, Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field
The Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, also called the Clearwater Cone Group, is a potentially active monogenetic volcanic field in east-central British Columbia, Canada, located approximately north of Kamloops. It is situated in the Cariboo Mountains of the Columbia Mountains and on the...
, Mount Garibaldi
Mount Garibaldi
Mount Garibaldi is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Sea to Sky Country of British Columbia, north of Vancouver, Canada. Located in the southernmost Coast Mountains, it is one of the most recognized peaks in the South Coast region, as well as British Columbia's best known volcano...
, Mount Cayley
Mount Cayley
Mount Cayley is a potentially active stratovolcano in Squamish-Lillooet Regional District of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Located north of Squamish and west of Whistler in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains, it rises above the Squamish River to the west and above the Cheakamus...
, Castle Rock
Castle Rock (volcano)
Castle Rock is a volcanic neck located west of Iskut and 8 km northwest of Tuktsayda Mountain in British Columbia, Canada. It is part of the Pacific Ring of Fire that includes over 160 active volcanoes and is in the Klastline Group, Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province and last erupted in...
, The Volcano
The Volcano (British Columbia)
The Volcano, also known as Lava Fork volcano, is a small cinder cone in the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains in northwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located approximately northwest of the small community of Stewart near the head of Lava Fork...
, Mount Edziza volcanic complex
Mount Edziza volcanic complex
The Mount Edziza volcanic complex is a large and potentially active north-south trending complex volcano in Stikine Country, northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located southeast of the small community of Telegraph Creek...
, Hoodoo Mountain
Hoodoo Mountain
Hoodoo Mountain is a potentially active flat-topped stratovolcano in the Stikine Country of northwestern British Columbia, Canada, located northeast of Wrangell, Alaska on the north side of the lower Iskut River and east of its junction with the Stikine River...
, Crow Lagoon
Crow Lagoon
Crow Lagoon is a little-known volcanic center located north of Prince Rupert, British Columbia, Canada. There are beds of thick, basaltic tephra that are of Holocene age....
and Nazko Cone
Nazko Cone
Nazko Cone is a small potentially active basaltic cinder cone in central British Columbia, Canada, located 75 km west of Quesnel and 150 kilometers southwest of Prince George. It is considered the easternmost volcano in the Anahim Volcanic Belt. The small tree-covered cone rises 120 m above...
.
Columbia Plateau

The Columbia Plateau province is enveloped by one of the world's largest
accumulations of lava. Over 500,000 km² of the Earth's surface is covered
by it. The topography here is dominated by geologically young lava flows
that inundated the countryside with amazing speed, all within the last 17
million years.
Over 170,000 cubic kilometers of basaltic lava, known as the Columbia River
Columbia River
The Columbia River is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada, flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state...
basalts, covers the western part of the province. These tremendous flows
erupted between 17-6 million years ago. Most of the lava flooded out in the
first 1.5 million years: an extraordinarily short time for such an
outpouring of molten rock.
The Snake River Plain
Snake River Plain
The Snake River Plain is a geologic feature located primarily within the state of Idaho in the United States of America. It stretches about westward from northwest of the state of Wyoming to the Idaho-Oregon border. The plain is a wide flat bow-shaped depression, and covers about a quarter of Idaho...
stretches across Oregon, through northern Nevada,
southern Idaho, and ends at the Yellowstone Plateau in Wyoming. Looking
like a great spoon scooped out the Earth surface, the smooth topography of
this province forms a striking contrast with the strong mountainous fabric
around it.
The Snake River Plain lies in a distinct depression. At the western end,
the base has dropped down along normal faults, forming a graben
Graben
In geology, a graben is a depressed block of land bordered by parallel faults. Graben is German for ditch. Graben is used for both the singular and plural....
structure. Although there is extensive faulting at the eastern end, the
structure is not as clear.

the Snake River Plain in the eastern part of the Columbia Plateau
Province. The earliest Snake River Plain eruptions began about 15 million
years ago, just as the tremendous early eruptions of Columbia River Basalt
were ending. But most of the Snake River Plain volcanic rock is less than a
few million years old, Pliocene
Pliocene
The Pliocene Epoch is the period in the geologic timescale that extends from 5.332 million to 2.588 million years before present. It is the second and youngest epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch...
age (5-1.6 million years ago) and
younger.
In the west, the Columbia River Basalts are just that:almost exclusively
black basalt
Basalt
Basalt is a common extrusive volcanic rock. It is usually grey to black and fine-grained due to rapid cooling of lava at the surface of a planet. It may be porphyritic containing larger crystals in a fine matrix, or vesicular, or frothy scoria. Unweathered basalt is black or grey...
. Not so in the Snake River Plain, where relatively quiet
eruptions of soupy black basalt lava flows alternated with tremendous
explosive eruptions of rhyolite
Rhyolite
This page is about a volcanic rock. For the ghost town see Rhyolite, Nevada, and for the satellite system, see Rhyolite/Aquacade.Rhyolite is an igneous, volcanic rock, of felsic composition . It may have any texture from glassy to aphanitic to porphyritic...
, a light-colored volcanic rock.
Cinder cones
Volcanic cone
Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic formations. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and size of the fragments ejected during the eruption...
dot the landscape of the Snake River
Plain. Some are aligned along vents, the fissures that fed flows and
cone-building eruptions. Calderas, great pits formed by explosive
volcanism, and low shield volcanoes, and rhyolite hills are also part of
the landscape here, but many are obscured by later lava flows.
Evidence suggests that some concentrated heat source is melting rock
beneath the Columbia Plateau Province. At the base of the lithosphere (the
layer of crust and upper mantle that forms Earth's moving tectonic
plates). In an effort to figure out why this area, far from a plate
boundary, had such an enormous outpouring of lava, scientists established
hardening dates for many of the individual lava flows. They found that the
youngest volcanic rocks were clustered near the Yellowstone Plateau, and
that the farther west they went, the older the lavas.
Although scientists are still gathering evidence, a probable explanation is
that a hot spot, an extremely hot plume of deep mantle
Mantle (geology)
The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of the Earth, similar to the other terrestrial planets, is chemically divided into layers. The mantle is a highly viscous layer between the crust and the outer core....
material, is rising to the surface beneath the Columbia Plateau Province. Geologists know that
beneath Hawaii
Hawaii
Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of...
and Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
, a temperature instability develops (for reasons
not yet well understood) at the boundary between the core and mantle. The
concentrated heat triggers a plume hundreds of kilometers in diameter that
ascends directly through to the surface of the Earth.
When the hot plume arrives at the base of the lithosphere
Lithosphere
The lithosphere is the rigid outermost shell of a rocky planet. On Earth, it comprises the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater.- Earth's lithosphere :...
, some of the
lighter rock of the lithosphere rapidly melts. It is this molten
lithosphere that becomes the basalt lavas that gush onto the surface to
form the Columbia River and Snake River Plain basalts.
The track of this hot spot starts in the west and sweeps up to Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park, established by the U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Ulysses S. Grant on March 1, 1872, is a national park located primarily in the U.S. state of Wyoming, although it also extends into Montana and Idaho...
. The steaming fumaroles and explosive geyser
Geyser
A geyser is a spring characterized by intermittent discharge of water ejected turbulently and accompanied by a vapour phase . The word geyser comes from Geysir, the name of an erupting spring at Haukadalur, Iceland; that name, in turn, comes from the Icelandic verb geysa, "to gush", the verb...
s are ample
evidence of a concentration of heat beneath the surface. The hotspot is
probably quite stationary, but the North American plate is moving over it,
creating a superb record of the rate and direction of plate motion.
The Ice Age floods
With the beginning of the PleistocenePleistocene
The Pleistocene is the epoch from 2,588,000 to 11,700 years BP that spans the world's recent period of repeated glaciations. The name pleistocene is derived from the Greek and ....
time (about one million years ago), cooling temperatures provided conditions favorable for the creation of continental glacier
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
s. Over the centuries, as snowfall exceeded melting and evaporation, a great accumulation of snow covered part of the continent, forming extensive ice fields. This vast continental ice sheet reached a thickness of about 4000 feet (1,219.2 m) in some areas. Sufficient pressure on the ice caused it to flow outward as a glacier. The glacier moved south out of Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, damming rivers and creating lakes in Washington, Idaho and Montana.
The ice blocked the Clark Fork River, forming the huge Glacial Lake Missoula
Glacial Lake Missoula
Glacial Lake Missoula was a prehistoric proglacial lake in western Montana that existed periodically at the end of the last ice age between 15,000 and 13,000 years ago...
. The lake measured about 7 770 km² (297.3 sq mi) and contained about 2100 cubic kilometers (500 cubic miles), half the volume of Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan
Lake Michigan is one of the five Great Lakes of North America and the only one located entirely within the United States. It is the second largest of the Great Lakes by volume and the third largest by surface area, after Lake Superior and Lake Huron...
.

Channeled scablands
The Channeled Scablands are a unique geological erosion feature in the U.S. state of Washington. They were created by the cataclysmic Missoula Floods that swept periodically across eastern Washington and down the Columbia River Plateau during the Pleistocene epoch. Geologist J Harlen Bretz coined...
.
As the floods in this vicinity raced southward, two major cascades formed along their course. The larger cataract was that of the Upper Coulee, where the river roared over an 800 feet (243.8 m) waterfall. The eroding power of the water plucked pieces of basalt from the precipice, causing the falls to retreat 20 miles (32.2 km) and self-destruct by cutting through to the Columbia River valley near what is now the Grand Coulee Dam.
The other major cataract is now known as Dry Falls
Dry Falls
Dry Falls is a 3.5 mile long scalloped precipice in central Washington, on the opposite side of the Upper Grand Coulee from the Columbia River, and at the head of the Lower Grand Coulee. Ten times the size of Niagara, Dry Falls is thought to be the greatest known waterfall that ever existed...
. It started near Soap Lake in Washington State, where less resistant basalt layers gave way before the great erosive power of this tremendous torrent and waterfalls developed. As in the Upper Coulee, the raging river yanked chunks of rock from the face of the falls and the falls eventually retreated to their present location. Dry Falls is three and one-half miles wide, with a drop of more than 400 feet (121.9 m). By way of comparison, Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls
The Niagara Falls, located on the Niagara River draining Lake Erie into Lake Ontario, is the collective name for the Horseshoe Falls and the adjacent American Falls along with the comparatively small Bridal Veil Falls, which combined form the highest flow rate of any waterfalls in the world and has...
, one mile (1.6 km) wide with a drop of only 165 feet (50.3 m), would be dwarfed by Dry Falls.
The North Cascades
The North Cascade Range in Washington is part of the American cordilleraAmerican cordillera
The American Cordillera is a cordillera that consists of an essentially continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America and Antarctica. From north to south, this sequence of overlapping and parallel ranges begins with the...
, a mountain chain stretching more than 12000 miles (19,312.1 km) from
Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of a main island Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego divided between Chile and Argentina with an area of , and a group of smaller islands including Cape...
to the Alaska Peninsula
Alaska Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. The peninsula separates the Pacific Ocean from Bristol Bay, an arm of the Bering Sea....
, and second only to the
Alpine-Himalayan chain in height. Although only a small part
of the Cordillera, mile for mile, the North Cascade Range is steeper and
wetter than most other ranges in the conterminous United States.
In geology, the range has more in common with the Coast Ranges of British
Columbia and Alaska than it does with its Cordilleran cousins in the Rocky
Mountains or Sierra Nevada. Although the peaks of the North Cascades do not
reach great elevations (high peaks are generally in the 7,000 to 8000 feet (2,438.4 m)
range), their overall relief, that is, the relatively uninterrupted
vertical distance from valley bottom to mountain top, is commonly 4,000 to
6,000 feet.
Rocks of the North Cascades record at least 400 million years of history:
time enough to have collected a jumble of different rocks. The range is a
geologic mosaic made up of volcanic island arc
Island arc
An island arc is a type of archipelago composed of a chain of volcanoes which alignment is arc-shaped, and which are situated parallel and close to a boundary between two converging tectonic plates....
s, deep ocean sediments,
basaltic ocean floor, parts of old continents, submarine fans, and
even pieces of the deep subcrustal mantle
Mantle (geology)
The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of the Earth, similar to the other terrestrial planets, is chemically divided into layers. The mantle is a highly viscous layer between the crust and the outer core....
of the earth. The disparate
pieces of the North Cascade mosaic were born far from one another but
subsequently drifted together, carried along by the tectonic plates that
make up the Earth's outer shell. Over time, the moving plates eventually
accreted the various pieces of the mosaic onto the western side of North
America.
As if this mosaic of unrelated pieces were not complex enough, some of the
assembled pieces were uplift
Tectonic uplift
Tectonic uplift is a geological process most often caused by plate tectonics which increases elevation. The opposite of uplift is subsidence, which results in a decrease in elevation. Uplift may be orogenic or isostatic.-Orogenic uplift:...
ed, eroded
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
by stream
Stream
A stream is a body of water with a current, confined within a bed and stream banks. Depending on its locale or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to as a branch, brook, beck, burn, creek, "crick", gill , kill, lick, rill, river, syke, bayou, rivulet, streamage, wash, run or...
s, and then
locally buried in their own eroded debris; other pieces were forced deep
into the Earth to be heated and squeezed, almost beyond recognition, and
then raised again to view.
About 35 million years ago, a volcanic arc grew across this complex mosaic
of old terrane
Terrane
A terrane in geology is short-hand term for a tectonostratigraphic terrane, which is a fragment of crustal material formed on, or broken off from, one tectonic plate and accreted or "sutured" to crust lying on another plate...
s. Volcanoes erupted to cover the older rocks with lava and
ash. Large masses of molten rock invaded the older rocks from below. The
volcanic arc is still active today, decorating the skyline with the cones
of Mount Baker
Mount Baker
Mount Baker , also known as Koma Kulshan or simply Kulshan, is an active glaciated andesitic stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the North Cascades of Washington State in the United States. It is the second-most active volcano in the range after Mount Saint Helens...
and Glacier Peak
Glacier Peak
Glacier Peak is the most isolated of the five major stratovolcanoes of the Cascade Volcanic Arc in Washington...
.

products of profound erosion. Running water has etched out the grain of the
range, landslides have softened the abrupt edges, homegrown glaciers have
scoured the peaks and high valleys and, during the Ice Age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
, the
Cordilleran Ice Sheet
Cordilleran Ice Sheet
The Cordilleran ice sheet was a major ice sheet that covered, during glacial periods of the Quaternary, a large area of North America. This included the following areas:*Western Montana*The Idaho Panhandle...
overrode almost all the range and rearranged
courses of streams. Erosion has written and still writes it own history in
the mountains, but it has also revealed the complex mosaic of the
bedrock.
Coast Mountains
The Coast MountainsCoast Mountains
The Coast Mountains are a major mountain range, in the Pacific Coast Ranges, of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the Coast of British Columbia. They are so-named because of their proximity to the sea coast, and are often...
are the western range of the North American mainland cordillera, covering the Alaska Panhandle
Alaska Panhandle
Southeast Alaska, sometimes referred to as the Alaska Panhandle, is the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Alaska, which lies west of the northern half of the Canadian province of British Columbia. The majority of Southeast Alaska's area is part of the Tongass National Forest, the United...
and most of costal British Columbia. The range is approximately 1600 km (994 mi) long and 200 km (124 mi) wide.
Most of the Coast Mountains are composed of granite
Granite
Granite is a common and widely occurring type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock. Granite usually has a medium- to coarse-grained texture. Occasionally some individual crystals are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic...
, which is part of the Coast Plutonic Complex. This is the single largest contiguous granite outcropping in the world, which extends approximately 1800 km (1,118 mi) in length. It is a large batholith
Batholith
A batholith is a large emplacement of igneous intrusive rock that forms from cooled magma deep in the Earth's crust...
complex. Its formation is related to subduction
Subduction
In geology, subduction is the process that takes place at convergent boundaries by which one tectonic plate moves under another tectonic plate, sinking into the Earth's mantle, as the plates converge. These 3D regions of mantle downwellings are known as "Subduction Zones"...
of the Kula
Kula Plate
The Kula Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate under the northern Pacific Ocean south of the Near Islands segment of the Aleutian Islands. It is subducting under the North American Plate at the Aleutian Trench and is surrounded by the Pacific Plate...
and Farallon
Farallon Plate
The Farallon Plate was an ancient oceanic plate, which began subducting under the west coast of the North American Plate— then located in modern Utah— as Pangaea broke apart during the Jurassic Period...
tectonic plates along the continental margin
Continental margin
The continental margin is the zone of the ocean floor that separates the thin oceanic crust from thick continental crust. Continental margins constitute about 28% of the oceanic area....
during the Jurassic
Jurassic
The Jurassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about Mya to Mya, that is, from the end of the Triassic to the beginning of the Cretaceous. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic era, also known as the age of reptiles. The start of the period is marked by...
-to-Eocene
Eocene
The Eocene Epoch, lasting from about 56 to 34 million years ago , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Palaeocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the...
periods. The plutonic complex is built on unusual island arc
Volcanic arc
A volcanic arc is a chain of volcanoes positioned in an arc shape as seen from above. Offshore volcanoes form islands, resulting in a volcanic island arc. Generally they result from the subduction of an oceanic tectonic plate under another tectonic plate, and often parallel an oceanic trench...
fragments, oceanic plateau
Oceanic plateau
An oceanic plateau is a large, relatively flat submarine region that rises well above the level of the ambient seabed. While many oceanic plateaus are composed of continental crust, and often form a step interrupting the continental slope, some plateaus are undersea remnants of large igneous...
s and continental margin assemblages accreted between the Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
and the Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
periods. In addition, the Garibaldi
Mount Garibaldi
Mount Garibaldi is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Sea to Sky Country of British Columbia, north of Vancouver, Canada. Located in the southernmost Coast Mountains, it is one of the most recognized peaks in the South Coast region, as well as British Columbia's best known volcano...
, Meager
Mount Meager
Mount Meager, originally known as Meager Mountain, is a complex volcano in the Sea-to-Sky Corridor of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is located north of Vancouver at the northern end of the Pemberton Valley. Part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc of western North America, its summit is above...
, Cayley
Mount Cayley
Mount Cayley is a potentially active stratovolcano in Squamish-Lillooet Regional District of southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Located north of Squamish and west of Whistler in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains, it rises above the Squamish River to the west and above the Cheakamus...
and Silverthrone
Silverthrone Caldera
The Silverthrone Caldera is a potentially active caldera complex in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, located over northwest of the city of Vancouver and about west of Mount Waddington in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. The caldera is one of the largest of the few calderas in...
areas are of recent volcanic origin.

Pliocene
The Pliocene Epoch is the period in the geologic timescale that extends from 5.332 million to 2.588 million years before present. It is the second and youngest epoch of the Neogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Pliocene follows the Miocene Epoch and is followed by the Pleistocene Epoch...
period the Coast Mountains did not exist and a level peneplain extended to the sea. This mass was uplifted during the Miocene
Miocene
The Miocene is a geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about . The Miocene was named by Sir Charles Lyell. Its name comes from the Greek words and and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern sea invertebrates than the Pliocene. The Miocene follows the Oligocene...
period. Rivers such as the Klinaklini River
Klinaklini River
The Klinaklini River is one of the major rivers of the Pacific Ranges section of the Coast Mountains in British Columbia. It begins in the northern basins of the Pantheon Range to the north of Mount Waddington and briefly heads northeast onto the Chilcotin Plateau before bending around...
and Homathko River
Homathko River
The Homathko River is one of the major rivers of the southern Coast Mountains of British Columbia, and one of the few rivers that penetrates the range from the Chilcotin Plateau to the coastal inlets, entering the sea at the head of Bute Inlet adjacent to the mouth of the Southgate River, just to...
predate this uplift and due to erosion
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
occurring faster than uplift, have continued to flow right up to the present day, directly across the axis of the range. The mountains flanking the Homathko River are the highest in the Coast Mountains, and include Mount Waddington
Mount Waddington
Mount Waddington, once known as Mystery Mountain, is the highest peak in the Coast Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. Although Mount Fairweather and Mount Quincy Adams, which straddle the US border between Alaska and British Columbia are taller, Mount Waddington is the highest peak that lies...
west of the river in the Waddington Range
Waddington Range
The Waddington Range is a subrange of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. It is only about 4000 km² in area, relatively small in area within the expanse of the range, but it is the highest area of the Pacific Ranges and of the Coast Mountains, being...
and Mount Queen Bess
Mount Queen Bess
Mount Queen Bess is one of the principal summits of the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains of southern British Columbia. It stands west of Chilko Lake and to the south of Tatlayoko Lake, and crowns a peak-studded ridge to the north of the Homathko Icefield....
east of the river, adjacent to the Homathko Icefield
Homathko Icefield
The Homathko Icefield is an icefield in British Columbia, Canada. Officially named the Homathko Snowfield from 1950 until the current name was adopted in 1976, it is one of the largest icefields in the southern half of the Coast Mountains, with an area of over...
.
The Pacific Ranges
Pacific Ranges
The Pacific Ranges are the southernmost subdivision of the Coast Mountains portion of the Pacific Cordillera. Located entirely within British Columbia, Canada, they run northwest from the lower stretches of the Fraser River to Bella Coola, north of which are the Kitimat Ranges.The Pacific Ranges...
in southwestern British Columbia are the southernmost subdivision of the Coast Mountains. It has been characterized by rapid rates of uplift over the past 4 million years unlike the North Cascades and has led to relatively high rates of erosion.
Insular Mountains
The Insular MountainsInsular Mountains
The Insular Mountains are a range of mountains in the Pacific Coast Ranges on the coast of British Columbia, Canada, comprising the Vancouver Island Ranges and Queen Charlotte Mountains. The Insular Mountains are rugged, particularly on Vancouver Island where peaks in Strathcona Provincial Park...
on the coast of British Columbia is not yet fully emerged above sea level
Sea level
Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation...
, and Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island
Vancouver Island is a large island in British Columbia, Canada. It is one of several North American locations named after George Vancouver, the British Royal Navy officer who explored the Pacific Northwest coast of North America between 1791 and 1794...
and the Queen Charlotte Islands
Queen Charlotte Islands
Haida Gwaii , formerly the Queen Charlotte Islands, is an archipelago on the North Coast of British Columbia, Canada. Haida Gwaii consists of two main islands: Graham Island in the north, and Moresby Island in the south, along with approximately 150 smaller islands with a total landmass of...
are just the higher elevations of the range, which was in fact fully exposed during the last ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
when the continental shelf
Continental shelf
The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain. Much of the shelf was exposed during glacial periods, but is now submerged under relatively shallow seas and gulfs, and was similarly submerged during other interglacial periods. The continental margin,...
in this area was a broad coastal plain
Coastal plain
A coastal plain is an area of flat, low-lying land adjacent to a seacoast and separated from the interior by other features. One of the world's longest coastal plains is located in eastern South America. The southwestern coastal plain of North America is notable for its species diversity...
. Although the Coast Mountains
Coast Mountains
The Coast Mountains are a major mountain range, in the Pacific Coast Ranges, of western North America, extending from southwestern Yukon through the Alaska Panhandle and virtually all of the Coast of British Columbia. They are so-named because of their proximity to the sea coast, and are often...
are commonly considered to be the westernmost range of the American cordillera
American cordillera
The American Cordillera is a cordillera that consists of an essentially continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America and Antarctica. From north to south, this sequence of overlapping and parallel ranges begins with the...
, the Insular Mountains are the true westernmost range. Through the most recent ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
about 18,000 years ago, ice
Ice
Ice is water frozen into the solid state. Usually ice is the phase known as ice Ih, which is the most abundant of the varying solid phases on the Earth's surface. It can appear transparent or opaque bluish-white color, depending on the presence of impurities or air inclusions...
enclosed nearly all of the mountain
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
s. Glacier
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
s that ran down to the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
sharpened the valley
Valley
In geology, a valley or dale is a depression with predominant extent in one direction. A very deep river valley may be called a canyon or gorge.The terms U-shaped and V-shaped are descriptive terms of geography to characterize the form of valleys...
faces and eroded
Erosion
Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere...
their bottoms.

Volcanic arc
A volcanic arc is a chain of volcanoes positioned in an arc shape as seen from above. Offshore volcanoes form islands, resulting in a volcanic island arc. Generally they result from the subduction of an oceanic tectonic plate under another tectonic plate, and often parallel an oceanic trench...
, called the Insular Islands
Insular Islands
The Insular Islands were a giant chain of active volcanic islands somewhere in the Pacific Ocean during the Cretaceous time that rode on top a microplate called the Insular Plate, beginning around 130 million years ago. The Insular Islands were surrounded by two prehistoric oceans; the Panthalassa...
, collided against North America during the Mid-Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
period. The mountains are made of turbidite
Turbidite
Turbidite geological formations have their origins in turbidity current deposits, which are deposits from a form of underwater avalanche that are responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean.-The ideal turbidite sequence:...
and pillow lava
Pillow lava
Pillow lavas are lavas that contain characteristic pillow-shaped structures that are attributed to the extrusion of the lava under water, or subaqueous extrusion. Pillow lavas in volcanic rock are characterized by thick sequences of discontinuous pillow-shaped masses, commonly up to one metre in...
s unlike the plutons of the Coast Plutonic Complex that make the Coast Mountains. The Insular Mountains have much seismic activity
Earthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
, with the Juan de Fuca Plate
Juan de Fuca Plate
The Juan de Fuca Plate, named after the explorer of the same name, is a tectonic plate, generated from the Juan de Fuca Ridge, and subducting under the northerly portion of the western side of the North American Plate at the Cascadia subduction zone...
subducting at the Cascadia subduction zone
Cascadia subduction zone
The Cascadia subduction zone is a subduction zone, a type of convergent plate boundary that stretches from northern Vancouver Island to northern California. It is a very long sloping fault that separates the Juan de Fuca and North America plates.New ocean floor is being created offshore of...
and the Pacific Plate
Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At 103 million square kilometres, it is the largest tectonic plate....
sliding along the Queen Charlotte Fault
Queen Charlotte Fault
The Queen Charlotte Fault is an active transform fault, located between the North American Plate and the Pacific Plate, Canada's equivalent of the San Andreas Fault. The Queen Charlotte Fault forms a triple junction on its south with the Cascadia subduction zone and the Explorer Ridge...
. Large earthquakes have led to collapsing mountains, landslide
Landslide
A landslide or landslip is a geological phenomenon which includes a wide range of ground movement, such as rockfalls, deep failure of slopes and shallow debris flows, which can occur in offshore, coastal and onshore environments...
s, and the development of fissure
Fissure
In anatomy, a fissure is a groove, natural division, deep furrow, elongated cleft, or tear in various parts of the body.-Brain:...
s. Flood basalt
Flood basalt
A flood basalt or trap basalt is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that coats large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Flood basalts have occurred on continental scales in prehistory, creating great plateaus and mountain ranges...
s on Vancouver Island form a geologic formation
Geologic formation
A formation or geological formation is the fundamental unit of lithostratigraphy. A formation consists of a certain number of rock strata that have a comparable lithology, facies or other similar properties...
called the Karmutsen Formation
Karmutsen Formation
The Karmutsen Formation is a Late Triassic volcanic sequence of tholeiitic pillow basalts and breccias on Vancouver Island, British Columbia, Canada. It is perhaps the thickest accreted section of an oceanic plateau worldwide, exposing up to 6000 m of basal sediment-sill complexes, basaltic to...
, which is perhaps the thickest accreted section of an oceanic plateau
Oceanic plateau
An oceanic plateau is a large, relatively flat submarine region that rises well above the level of the ambient seabed. While many oceanic plateaus are composed of continental crust, and often form a step interrupting the continental slope, some plateaus are undersea remnants of large igneous...
worldwide, exposing up to 6000 m (19,685 ft) of basal sediment-sill
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or even along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. The term sill is synonymous with concordant intrusive sheet...
complexes, basalt
Basalt
Basalt is a common extrusive volcanic rock. It is usually grey to black and fine-grained due to rapid cooling of lava at the surface of a planet. It may be porphyritic containing larger crystals in a fine matrix, or vesicular, or frothy scoria. Unweathered basalt is black or grey...
ic to picritic pillow lavas, pillow breccia
Breccia
Breccia is a rock composed of broken fragments of minerals or rock cemented together by a fine-grained matrix, that can be either similar to or different from the composition of the fragments....
, and thick, massive basalt flows.
See also
- Geology of North America
- Beaverhead craterBeaverhead craterBeaverhead is an impact structure in central Idaho and western Montana in the United States.Estimated at in diameter, it is one of the largest impact craters on Earth...
, IdahoIdahoIdaho is a state in the Rocky Mountain area of the United States. The state's largest city and capital is Boise. Residents are called "Idahoans". Idaho was admitted to the Union on July 3, 1890, as the 43rd state.... - Cascade RangeCascade RangeThe Cascade Range is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, and the notable volcanoes known as the High Cascades...
- Cascade VolcanoesCascade VolcanoesThe Cascade Volcanoes are a number of volcanoes in a volcanic arc in western North America, extending from southwestern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California, a distance of well over 700 mi ...
- Cascadia subduction zoneCascadia subduction zoneThe Cascadia subduction zone is a subduction zone, a type of convergent plate boundary that stretches from northern Vancouver Island to northern California. It is a very long sloping fault that separates the Juan de Fuca and North America plates.New ocean floor is being created offshore of...
- Challis ArcChallis ArcThe Challis Arc was an Eocene volcanic arc that stretched from southwestern British Columbia through Washington to Idaho, United States. The arc formed 57 million years ago as a result of subduction of the eastern block of the Kula Plate ending 37 million years ago...
- Columbia River Basalt GroupColumbia River Basalt GroupThe Columbia River Basalt Group is a large igneous province that lies across parts of the Western United States. It is found in the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Nevada, and California...
- Fort Rock
- Garibaldi Volcanic BeltGaribaldi Volcanic BeltThe Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, also called the Canadian Cascade Arc, is a northwest-southeast trending volcanic chain in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains that extends from Watts Point in the south to the Ha-Iltzuk Icefield in the north. This chain of volcanoes is located in southwestern...
- Geology of British ColumbiaGeology of British ColumbiaThe geology of British Columbia is a function of its location on the leading edge of the North American continent. The mountainous physiography and the diversity of rock types and ages hint at the complex geology, which is still undergoing revision despite a century of exploration and mapping.The...
- Geology of the Lassen volcanic areaGeology of the Lassen volcanic areaThe geology of the Lassen volcanic area presents a record of sedimentation and volcanic activity in the area in and around Lassen Volcanic National Park in Northern California, U.S. The park is located in the southernmost part of the Cascade Mountain Range in the Pacific Northwest region of the...
- Hole-in-the-GroundHole-in-the-GroundHole-in-the-Ground is a large maar in the Fort Rock Basin of Lake County, central Oregon, northeast of Crater Lake, near Oregon Route 31....
- List of volcanoes in Canada
- Olympic-Wallowa LineamentOlympic-Wallowa LineamentThe Olympic-Wallowa lineament – first reported by cartographer Erwin Raisz in 1945 on a relief map of the continental United States – is a physiographic feature of unknown origin in the state of Washington running approximately from the town of Port Angeles, on the Olympic Peninsula...
- Puget Sound faultsPuget Sound faultsThe Puget Sound faults under the heavily populated Puget Sound region of Washington state form a regional complex of interrelated seismogenic geologic faults...
- Volcanism in CanadaVolcanism in CanadaVolcanism of Canada has produced lava flows, lava plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes, and maars, along with examples of more less common volcanic forms such as tuyas and subglacial mounds...
External links
- Burke Museum web site Geologic history of Washington.
- Evolution of the Pacific Northwest Good text on the geology of Cascadia.
- One link on Northwest geology
- Reducing Earthquake Losses Throughout the United States: Averting Surprises in the Pacific Northwest (USGS)
- USGS site on earthquakes
- On the eruption of Mt. Meager

