Castilian Spanish
Encyclopedia
Castilian Spanish is a term related to the Spanish language
, but its exact meaning can vary even in that language. In English Castilian Spanish usually refers to the variety of European Spanish spoken in north and central Spain
or as the language standard for radio and TV speakers. The region where this variety of Spanish is spoken corresponds more or less to the Castilian historical region
.
The Spanish language term castellano (Castilian) may refer to the Spanish language as a whole, to the dialect
s spoken in central and northern Spain, or to the medieval language
which was a predecessor to modern Spanish.
The purpose of this article is to describe the features of the Spanish language spoken in central and northern Spain, especially in the way it contrasts with the Spanish varieties
in the Americas.
 The term Castilian Spanish can be used in English for the specific dialects of Spanish spoken in north and central Spain. Sometimes it is more loosely used to denote the Spanish spoken in all of Spain as compared to Spanish spoken in Latin America; however, there are several different dialects of Spanish
The term Castilian Spanish can be used in English for the specific dialects of Spanish spoken in north and central Spain. Sometimes it is more loosely used to denote the Spanish spoken in all of Spain as compared to Spanish spoken in Latin America; however, there are several different dialects of Spanish
as well as other official languages in Spain
.
For Spanish speakers in academic contexts, castellano refers to some dialects of the Spanish language as spoken in the historical region of Castile
, a former Kingdom
in what is now Spain. In general usage, however, castellano can refer to the language as a whole, as a synonym of español (Spanish).
(Royal Spanish Academy or RAE) defines Castilian Spanish as a standard language
, and many speakers accept RAE as the governing body of the language.
However, some traits of the Spanish spoken in Spain are exclusive to that country, and for this reason, courses of Spanish as a second language
often neglect them preferring Mexican Spanish
in the United States
and Canada
whilst European Spanish is taught in Europe
. While there is nothing comparable to American and British English spelling differences
, grammar
and to a lesser extent pronunciation can vary sometimes.
The most striking difference between dialects in central and northern Spain and American Spanish
is distinción (distinction), that is, the pronunciation of the letter z before all vowels, and of c only for e and i , as a voiceless dental fricative
/θ/, English th
in thing. Thus, in most variations of Spanish from Spain, cinco (five) is pronounced /ˈθinko/ as opposed to /ˈsinko/ in American Spanish, and similarly for zapato, cerdo, zorro, Zurbarán.
Additionally, all American
dialects drop the non-formal vosotros verb form for the second person plural, using ustedes in all contexts. In Spain, ustedes is used only in a formal context. Some other minor differences are:
in some American dialects, but to cart
in Spain. Sometimes there also appear gender differences: el PC (personal computer) in Castilian Spanish, la PC in American Spanish, due to the widespread use of the gallicism ordenador (from l'ordinateur in French) for computer in Castilian Spanish, which is masculine, instead of the Latin-American-preferred computadora, which is feminine, from the English word computer. Also, speakers of the second dialect tend to use words and polite-set expressions that, though recognized by the RAE
, aren't widely used nowadays (some of them even deemed as anachronisms) by speakers of Castilian Spanish. For example, enojarse and enfadarse are verbs with the same meaning (to become angry), enojarse being used much more in the Americas than in Spain, and enfadarse more in Spain than in the Americas.
1many of the vocabulary examples are used throughout Spain and not necessarily specific to just Castilian Spanish
2Latin American Spanish consists of several varieties spoken throughout the Americas. The examples may not represent all the dialect but are meant to show contrast
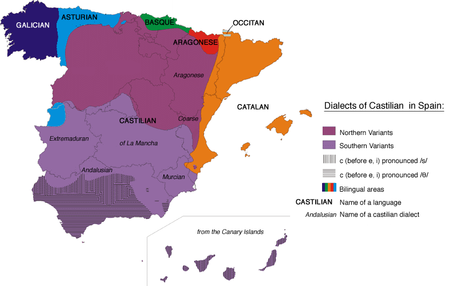
Inside Spain, there are many regional variations of Spanish, which can be divided roughly into four major dialectal areas:
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
, but its exact meaning can vary even in that language. In English Castilian Spanish usually refers to the variety of European Spanish spoken in north and central Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
or as the language standard for radio and TV speakers. The region where this variety of Spanish is spoken corresponds more or less to the Castilian historical region
Castile (historical region)
A former kingdom, Castile gradually merged with its neighbours to become the Crown of Castile and later the Kingdom of Spain when united with the Crown of Aragon and the Kingdom of Navarre...
.
The Spanish language term castellano (Castilian) may refer to the Spanish language as a whole, to the dialect
Dialect
The term dialect is used in two distinct ways, even by linguists. One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors,...
s spoken in central and northern Spain, or to the medieval language
Old Spanish language
Old Spanish, also known as Old Castilian or Mediaeval Spanish , is an early form of the Spanish language that was spoken on the Iberian Peninsula from the tenth century until roughly the beginning of the fifteenth century, before a consonantic readjustment gave rise to the evolution of modern...
which was a predecessor to modern Spanish.
The purpose of this article is to describe the features of the Spanish language spoken in central and northern Spain, especially in the way it contrasts with the Spanish varieties
Spanish dialects and varieties
Spanish dialects and varieties are the regional variants of the Spanish language, some of which are quite divergent from one another, especially in pronunciation and vocabulary, and less so in grammar....
in the Americas.
Terminology

Spanish dialects and varieties
Spanish dialects and varieties are the regional variants of the Spanish language, some of which are quite divergent from one another, especially in pronunciation and vocabulary, and less so in grammar....
as well as other official languages in Spain
Languages of Spain
The languages of Spain are the languages spoken or once spoken in Spain. Romance languages are the most widely spoken in Spain, of which Spanish is the country's official language...
.
For Spanish speakers in academic contexts, castellano refers to some dialects of the Spanish language as spoken in the historical region of Castile
Castile (historical region)
A former kingdom, Castile gradually merged with its neighbours to become the Crown of Castile and later the Kingdom of Spain when united with the Crown of Aragon and the Kingdom of Navarre...
, a former Kingdom
Kingdom of Castile
Kingdom of Castile was one of the medieval kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula. It emerged as a political autonomous entity in the 9th century. It was called County of Castile and was held in vassalage from the Kingdom of León. Its name comes from the host of castles constructed in the region...
in what is now Spain. In general usage, however, castellano can refer to the language as a whole, as a synonym of español (Spanish).
Accent particularities
The Real Academia EspañolaReal Academia Española
The Royal Spanish Academy is the official royal institution responsible for regulating the Spanish language. It is based in Madrid, Spain, but is affiliated with national language academies in twenty-one other hispanophone nations through the Association of Spanish Language Academies...
(Royal Spanish Academy or RAE) defines Castilian Spanish as a standard language
Standard language
A standard language is a language variety used by a group of people in their public discourse. Alternatively, varieties become standard by undergoing a process of standardization, during which it is organized for description in grammars and dictionaries and encoded in such reference works...
, and many speakers accept RAE as the governing body of the language.
However, some traits of the Spanish spoken in Spain are exclusive to that country, and for this reason, courses of Spanish as a second language
Second language
A second language or L2 is any language learned after the first language or mother tongue. Some languages, often called auxiliary languages, are used primarily as second languages or lingua francas ....
often neglect them preferring Mexican Spanish
Mexican Spanish
Mexican Spanish is a version of the Spanish language, as spoken in Mexico and in various places of Canada and the United States of America, where there are communities of Mexican origin....
in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
whilst European Spanish is taught in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. While there is nothing comparable to American and British English spelling differences
American and British English spelling differences
One of the ways in which American English and British English differ is in spelling.-Historical origins:In the early 18th century, English spelling was not standardized. Differences became noticeable after the publishing of influential dictionaries...
, grammar
Spanish grammar
Spanish grammar is the grammar of the Spanish language , which is a Romance language that originated in north central Spain and is spoken today throughout Spain, some twenty countries in the Americas, and Equatorial Guinea....
and to a lesser extent pronunciation can vary sometimes.
The most striking difference between dialects in central and northern Spain and American Spanish
American Spanish
Spanish language in the Americas, also known as American Spanish, refers to the Spanish spoken in the Americas, as opposed to European Spanish. Linguistically, this grouping is somewhat arbitrary, akin to having a term for "overseas British" encompassing variants spoken in the US, Canada, India,...
is distinción (distinction), that is, the pronunciation of the letter z before all vowels, and of c only for e and i , as a voiceless dental fricative
Voiceless dental fricative
The voiceless dental non-sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It is familiar to English speakers as the 'th' in thing. Though rather rare as a phoneme in the world's inventory of languages, it is encountered in some of the most widespread and influential...
/θ/, English th
Pronunciation of English th
In English, the digraph ⟨th⟩ represents in most cases one of two different phonemes: the voiced dental fricative and the voiceless dental fricative...
in thing. Thus, in most variations of Spanish from Spain, cinco (five) is pronounced /ˈθinko/ as opposed to /ˈsinko/ in American Spanish, and similarly for zapato, cerdo, zorro, Zurbarán.
Additionally, all American
New World
The New World is one of the names used for the Western Hemisphere, specifically America and sometimes Oceania . The term originated in the late 15th century, when America had been recently discovered by European explorers, expanding the geographical horizon of the people of the European middle...
dialects drop the non-formal vosotros verb form for the second person plural, using ustedes in all contexts. In Spain, ustedes is used only in a formal context. Some other minor differences are:
- The widespread use of "le" instead "la" and "lo" as direct object, especially referring to men.
- In the past, the sounds for "y" and "ll" were phonologically different in most European SpanishPeninsular SpanishPeninsular Spanish, also known as European Spanish, refers to the varieties of the Spanish language spoken in the Iberian Peninsula, as opposed to the Spanish spoken in the Americas and in the Canary Islands....
subvarieties, compared with only a few dialects in Latin America, but that difference is now disappearing in all Peninsular SpanishPeninsular SpanishPeninsular Spanish, also known as European Spanish, refers to the varieties of the Spanish language spoken in the Iberian Peninsula, as opposed to the Spanish spoken in the Americas and in the Canary Islands....
dialects, including the standard (that is, Castilian Spanish). A distinct phoneme for "ll" is still heard in the speech of older speakers in rural areas throughout Spain, but most Spanish-speaking adults and youngsters merge "ll" and "y". In Latin America "ll" remains different from "y" in traditional dialects along the Andes range, especially in Peru highlands, all Bolivia and also in Paraguay. In the PhilippinesPhilippinesThe Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, speakers of Spanish employ the distinctionDistinction*Distinction may refer to:* Distinction is a social force that places different values on different individuals....
between "ll" /ʎ/ and "y" /j/. - In most Latin America usted is used more often than in mainland Spain, however in Latin America, this tendency is less common among young people, especially in Caribbean dialects.
- In Castilian Spanish, the letter j as well as the letter g before the letters i and e are pronounced as a stronger velar fricative /x/ and very often the friction is uvular χ, while in Latin America they are generally guttural as well, but not as strong and the uvular realizations of European Spanish are not reported . In the CaribbeanCaribbean SpanishCaribbean Spanish is the general name of the Spanish dialects spoken in the Caribbean region. It closely resembles the Spanish spoken in the Canary Islands and Andalusia....
, including all Colombia, Venezuela, the Canary Islands and most Western AndalusianAndalusian SpanishThe Andalusian varieties of Spanish are spoken in Andalusia, Ceuta, Melilla and Gibraltar. They include perhaps the most distinct of the southern variants of peninsular Spanish, differing in many respects from northern varieties, and also from Standard Spanish...
it is pronounced as h.
Vocabulary
The meaning of certain words may differ greatly between both dialects of the language: carro refers to carAutomobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
in some American dialects, but to cart
Cart
A cart is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by one or a pair of draught animals. A handcart is pulled or pushed by one or more people...
in Spain. Sometimes there also appear gender differences: el PC (personal computer) in Castilian Spanish, la PC in American Spanish, due to the widespread use of the gallicism ordenador (from l'ordinateur in French) for computer in Castilian Spanish, which is masculine, instead of the Latin-American-preferred computadora, which is feminine, from the English word computer. Also, speakers of the second dialect tend to use words and polite-set expressions that, though recognized by the RAE
Real Academia Española
The Royal Spanish Academy is the official royal institution responsible for regulating the Spanish language. It is based in Madrid, Spain, but is affiliated with national language academies in twenty-one other hispanophone nations through the Association of Spanish Language Academies...
, aren't widely used nowadays (some of them even deemed as anachronisms) by speakers of Castilian Spanish. For example, enojarse and enfadarse are verbs with the same meaning (to become angry), enojarse being used much more in the Americas than in Spain, and enfadarse more in Spain than in the Americas.
| Castilian Spanish1 | Latin American Spanish2 | English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
|---|---|---|
| vale | de acuerdo/oqué | okay |
| gafas | anteojos/lentes | eyeglasses/spectacles |
| melocotón | durazno | peach |
| patata | papa | potato |
| judía, alubia | chícharo/frijol/habichuela | bean |
| jersey | chaleco/suéter | jumper/sweater |
| coche | auto/carro | car |
| conducir | manejar | to drive |
| estacionar/aparcar | parquear/estacionar | to park |
| ordenador | computadora | computer |
| zumo | jugo | juice |
| chulo/guay | chévere/chido/piola | cool (slang) |
| tío | tipo | dude/bloke (slang) |
1many of the vocabulary examples are used throughout Spain and not necessarily specific to just Castilian Spanish
2Latin American Spanish consists of several varieties spoken throughout the Americas. The examples may not represent all the dialect but are meant to show contrast
Inside Spain, there are many regional variations of Spanish, which can be divided roughly into four major dialectal areas:
- Northern Spanish (northern coast, Ebro and Duero valleys). This dialect is sometimes called Castilian Spanish, but in fact it excludes quite a large area in the historical region of CastileCastile (historical region)A former kingdom, Castile gradually merged with its neighbours to become the Crown of Castile and later the Kingdom of Spain when united with the Crown of Aragon and the Kingdom of Navarre...
and includes areas not in it. - Transitional area between North and South (ExtremaduraExtremaduraExtremadura is an autonomous community of western Spain whose capital city is Mérida. Its component provinces are Cáceres and Badajoz. It is bordered by Portugal to the west...
, MurciaMurcia-History:It is widely believed that Murcia's name is derived from the Latin words of Myrtea or Murtea, meaning land of Myrtle , although it may also be a derivation of the word Murtia, which would mean Murtius Village...
, MadridMadrid (autonomous community)The Community of Madrid is one of the seventeen autonomous communities of Spain. It is located at the center of the country, the Iberian Peninsula, and the Castilian Central Plateau . The community is also conterminous with the province of Madrid and contains the capital of Spain, which is also...
, La ManchaLa ManchaLa Mancha is a natural and historical region or greater comarca located on an arid, fertile, elevated plateau of central Spain, south of Madrid, stretching between the Montes de Toledo and the western spurs of the Serrania de Cuenca. It is bounded on the south by the Sierra Morena and on the north...
). - Andalusian SpanishAndalusian SpanishThe Andalusian varieties of Spanish are spoken in Andalusia, Ceuta, Melilla and Gibraltar. They include perhaps the most distinct of the southern variants of peninsular Spanish, differing in many respects from northern varieties, and also from Standard Spanish...
- Canarian SpanishCanarian SpanishCanarian Spanish is a variant of standard Spanish spoken in the Canary Islands by the Canarian people, and in the southeastern section of Louisiana in Isleño communities that emigrated to the Americas as early as the 18th century...

