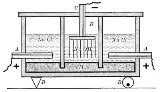
Castner-Kellner process
Overview
Electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a method of using a direct electric current to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction...
on an aqueous alkali
Alkali
In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or alkaline earth metal element. Some authors also define an alkali as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7. The adjective alkaline is commonly used in English as a synonym for base,...
chloride
Chloride
The chloride ion is formed when the element chlorine, a halogen, picks up one electron to form an anion Cl−. The salts of hydrochloric acid HCl contain chloride ions and can also be called chlorides. The chloride ion, and its salts such as sodium chloride, are very soluble in water...
solution (usually sodium chloride
Sodium chloride
Sodium chloride, also known as salt, common salt, table salt or halite, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaCl. Sodium chloride is the salt most responsible for the salinity of the ocean and of the extracellular fluid of many multicellular organisms...
solution) to produce the corresponding alkali hydroxide
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carrying a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, as a ligand, a nucleophile, and a...
, invented by American Hamilton Castner
Hamilton Castner
Hamilton Young Castner was an American industrial chemist.-Biography:He was born in Brooklyn, New York and educated at the Brooklyn Polytechnic Institute, then at the Columbia University School of Mines. He left without a degree and in 1879 joined his brother, E. B. Castner, as a consulting chemist...
and Austrian Karl Kellner in the 1890s.
The apparatus shown is divided into two types of cells separated by slate
Slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade regional metamorphism. The result is a foliated rock in which the foliation may not correspond to the original sedimentary layering...
walls. The first type, shown on the right and left of the diagram, uses an electrolyte of sodium chloride solution, a graphite
Graphite
The mineral graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon. It was named by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1789 from the Ancient Greek γράφω , "to draw/write", for its use in pencils, where it is commonly called lead . Unlike diamond , graphite is an electrical conductor, a semimetal...
anode
Anode
An anode is an electrode through which electric current flows into a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: ACID ....
(A), and a mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
cathode
Cathode
A cathode is an electrode through which electric current flows out of a polarized electrical device. Mnemonic: CCD .Cathode polarity is not always negative...
(M).
Unanswered Questions

