
Chatham Rise
Encyclopedia
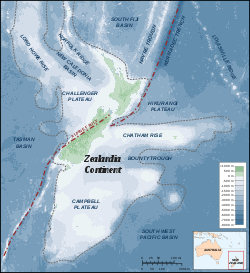
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
, forming part of the Zealandia
Zealandia (continent)
Zealandia , also known as Tasmantis or the New Zealand continent, is a nearly submerged continental fragment that sank after breaking away from Australia 60–85 million years ago, having separated from Antarctica between 85 and 130 million years ago...
continent. It stretches for some 1000 kilometres (621.4 mi) from near the South Island
South Island
The South Island is the larger of the two major islands of New Zealand, the other being the more populous North Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south and east by the Pacific Ocean...
in the west, to the Chatham Islands
Chatham Islands
The Chatham Islands are an archipelago and New Zealand territory in the Pacific Ocean consisting of about ten islands within a radius, the largest of which are Chatham Island and Pitt Island. Their name in the indigenous language, Moriori, means Misty Sun...
in the east. It is New Zealand's most productive and important fishing
Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch wild fish. Fish are normally caught in the wild. Techniques for catching fish include hand gathering, spearing, netting, angling and trapping....
ground.
Relative to the rest of the Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
waters around New Zealand, the Chatham Rise is relatively shallow, no more than 1000 metres (3,280.8 ft) deep at any point. This shallowness is made more remarkable by the depth of the ocean immediately to the north and south. To the northeast, the Hikurangi Trench
Hikurangi Trench
The Hikurangi Trench is a linear deep in the Pacific Ocean off the east coast of the North Island of New Zealand, lying between the southern end of the Cook Strait and the Chatham Rise. Though much shallower, it is the southward continuation of the Kermadec Trench and forms part of the...
, an extension of the much deeper Kermadec Trench
Kermadec Trench
The Kermadec trench is one of Earth's deepest oceanic trenches, reaching a depth of . Formed by the subduction of the Pacific Plate under the Indo-Australian Plate, it runs over a thousand kilometres parallel with and to the east of the Kermadec Ridge and island arc, from near the northeastern tip...
, drops to below 3000 m (9,842.5 ft) close to the New Zealand coast, and further from the coast the Rise borders on the Hikurangi Plateau
Hikurangi Plateau
Hikurangi Plateau is an Early Cretaceous basaltic oceanic plateau in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The portion of the plateau exposed on the seafloor has an area of 350,000 km2, and including the portions subducted beneath the...
. To the south, similar depths are achieved in the Bounty Trough. Past the eastern end of the rise, the sea floor drops away to the abyssal plain
Abyssal plain
An abyssal plain is an underwater plain on the deep ocean floor, usually found at depths between 3000 and 6000 metres. Lying generally between the foot of a continental rise and a mid-ocean ridge, abyssal plains cover more than 50% of the Earth’s surface. They are among the flattest, smoothest...
.
Geology
Geologically and tectonically, the Chatham Rise can be thought of as an extension of the eastern South Island. It was largely dry land at the end of the CretaceousCretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
(65.5 million years ago) and formed a large peninsula
Peninsula
A peninsula is a piece of land that is bordered by water on three sides but connected to mainland. In many Germanic and Celtic languages and also in Baltic, Slavic and Hungarian, peninsulas are called "half-islands"....
extending from New Zealand to the Chatham Islands at that time. This was characterized by a volcanic landscape. Fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s found on the Chatham Islands characterize the flora
Flora
Flora is the plant life occurring in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring or indigenous—native plant life. The corresponding term for animals is fauna.-Etymology:...
and fauna
Fauna
Fauna or faunæ is all of the animal life of any particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is flora.Zoologists and paleontologists use fauna to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the "Sonoran Desert fauna" or the "Burgess shale fauna"...
of the Chatham Rise in the late Mesozoic
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic era is an interval of geological time from about 250 million years ago to about 65 million years ago. It is often referred to as the age of reptiles because reptiles, namely dinosaurs, were the dominant terrestrial and marine vertebrates of the time...
; it had forests dominated by gymnosperm
Gymnosperm
The gymnosperms are a group of seed-bearing plants that includes conifers, cycads, Ginkgo, and Gnetales. The term "gymnosperm" comes from the Greek word gymnospermos , meaning "naked seeds", after the unenclosed condition of their seeds...
s (such as Araucaria
Araucaria
Araucaria is a genus of evergreen coniferous trees in the family Araucariaceae. There are 19 extant species in the genus, with a highly disjunct distribution in New Caledonia , Norfolk Island, eastern Australia, New Guinea, Argentina, Chile, and southern Brazil.-Description:Araucaria are mainly...
, Mataia and Podocarpus
Podocarpus
Podocarpus is a genus of conifers, the most numerous and widely distributed of the podocarp family Podocarpaceae. The 105 species of Podocarpus are evergreen shrubs or trees from 1-25 m in height...
) and Lycopodiopsida
Lycopodiopsida
Lycopodiopsida is a class of plants often loosely grouped as the fern allies. Traditionally the group included not only the clubmosses and firmosses, but also the spikemosses and the quillworts...
(clubmosses). Some angiosperms were also present. Dinosaur
Dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of animals of the clade and superorder Dinosauria. They were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates for over 160 million years, from the late Triassic period until the end of the Cretaceous , when the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event led to the extinction of...
s such as theropods dwelt on the peninsula and probably evolved into numerous endemic forms (Stilwell et al. 2006).
Commercial fishing
The Chatham Rise is New Zealand's most productive and important commercial fishing groundFishery
Generally, a fishery is an entity engaged in raising or harvesting fish which is determined by some authority to be a fishery. According to the FAO, a fishery is typically defined in terms of the "people involved, species or type of fish, area of water or seabed, method of fishing, class of boats,...
. Warm subtropical surface waters from the north and cold subantarctic
Subantarctic
The Subantarctic is a region in the southern hemisphere, located immediately north of the Antarctic region. This translates roughly to a latitude of between 46° – 60° south of the Equator. The subantarctic region includes many islands in the southern parts of the Indian Ocean, Atlantic Ocean and...
surface waters from the south meet in the vicinity of the Chatham Rise to create a subtropical front
Subtropical Front
Subtropical Front is a term used in Oceanography to describe a boundary between water systems based on temperature and salinity.- Northern Subtropical Front :A subtropical front in the Pacific Ocean lying between 25 and 30 degrees north latitude....
. Nutrient rich waters from the south mix with warm northern waters and create ideal conditions for plankton
Plankton
Plankton are any drifting organisms that inhabit the pelagic zone of oceans, seas, or bodies of fresh water. That is, plankton are defined by their ecological niche rather than phylogenetic or taxonomic classification...
and the animals that feed on them. The fishing grounds near the subtropical front and particularly the Chatham Rise provide 60 percent of New Zealand’s fish catch
Fishing industry in New Zealand
As with other countries, New Zealand’s 200 nautical mile exclusive economic zone gives its fishing industry special fishing rights. It covers 4.1 million square kilometres. This is the sixth largest zone in the world, and is fourteen times the land area of New Zealand itself.The zone has a rich and...
. Because the Chatham Rise is relatively shallow, it is accessible to both midwater trawling and bottom trawling
Bottom trawling
Bottom trawling is trawling along the sea floor. It is also often referred to as "dragging".The scientific community divides bottom trawling into benthic trawling and demersal trawling...
. Species include the main hoki
Blue grenadier
The blue grenadier, hoki, blue hake, New Zealand whiptail, whiptail or whiptail hake, Macruronus novaezelandiae, is a merluccid hake of the family Merlucciidae found around southern Australia and New Zealand at depths of between . Its length is between...
, hake
Merlucciidae
Merlucciidae is a family of cod-like fish, including most hakes.They are native to the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, being common in southern waters off Tasmania and New Zealand....
, ling
Pink cusk-eel
The pink cusk-eel, Genypterus blacodes, is a cusk eel of the genus Genypterus, found in southern Australia, Chile, Brazil, South Africa and around New Zealand except the east coast of Northland, in depths of a few metres to 1000 metres...
, silver warehou
Silver warehou
The silver warehou, Seriolella punctata, is a medusafish of the family Centrolophidae found in the southern Indian and southern Pacific oceans, at depths of between 100 and 650 m...
, squid
Squid
Squid are cephalopods of the order Teuthida, which comprises around 300 species. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, a mantle, and arms. Squid, like cuttlefish, have eight arms arranged in pairs and two, usually longer, tentacles...
, orange roughy
Orange roughy
The orange roughy, red roughy, or deep sea perch, Hoplostethus atlanticus, is a relatively large deep-sea fish belonging to the slimehead family . The Marine Conservation Society has categorized orange roughy as vulnerable to exploitation...
and deep sea (oreo) dory
Black oreo
The black oreo, Allocyttus niger, is an oreo of the family Oreosomatidae, found around Australia and New Zealand between latitudes of between 43°S and 55°S at depths of between 560 and 1,300 m. Its length is up to 47 cm....
fisheries.
The traditional approach to fisheries management
Fisheries management
Fisheries management draws on fisheries science in order to find ways to protect fishery resources so sustainable exploitation is possible. Modern fisheries management is often referred to as a governmental system of appropriate management rules based on defined objectives and a mix of management...
has been to focus on a single species - determining how many can be caught before the breeding population is affected to the point of harming the species fishery. There is a current trend towards ecosystem based fisheries. Removing any fish affects other marine life up and down the food chain
Food chain
A food web depicts feeding connections in an ecological community. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one of two categories called trophic levels: 1) the autotrophs, and 2) the heterotrophs...
, such as marine life that eat the fish, and the marine life eating the marine life that eat the fish. Scientists from NIWA
National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research
The National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research or NIWA , is a Crown Research Institute of New Zealand. Established in 1992, NIWA conducts commercial and non-commercial research across a broad range of disciplines in the environmental sciences...
are examining over 40,000 fish stomachs to see what different species are eating across the Chatham Rise. These studies, combined with other studies on marine mammals and sea birds and with relevant ocean and climate studies, will show how the different parts fit together in the Chatham Rise ecosystem.

