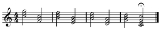
Circle progression
Encyclopedia
In music
, the circle progression is a chord progression
named for the circle of fifths
, along which it travels. It is "undoubtedly the most common and the strongest of all harmonic progressions" and consists of "adjacent roots
in ascending fourth or descending fifth relationship", with movement by ascending perfect fourth
being equivalent to movement by descending perfect fifth
due to inversion
.
The circle progression is commonly a circle through the diatonic chords, chords of the diatonic scale
, by fifths, including one progression by diminished fifth (in C: between F and B) and one diminished chord
(in C: B):
I-IV-viio-iii-vi-ii-V-I
Shorter common progressions may be derived by selecting certain specific chords from the series completing a circle from the tonic
through all seven diatonic chords, such as the primary triad
s book-ending the progression:
I- V-I = I-V-I
I-IV- V-I = I-IV-V-I
The ii-V-I turnaround lies at the end of the circle progression, as does the vi-ii-V-I progression of root movement by descending fifths, which establishes tonality and also strengthens the key
through the contrast of minor and major
.
Music
Music is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
, the circle progression is a chord progression
Chord progression
A chord progression is a series of musical chords, or chord changes that "aims for a definite goal" of establishing a tonality founded on a key, root or tonic chord. In other words, the succession of root relationships...
named for the circle of fifths
Circle of fifths
In music theory, the circle of fifths shows the relationships among the 12 tones of the chromatic scale, their corresponding key signatures, and the associated major and minor keys...
, along which it travels. It is "undoubtedly the most common and the strongest of all harmonic progressions" and consists of "adjacent roots
Root (chord)
In music theory, the root of a chord is the note or pitch upon which a triadic chord is built. For example, the root of the major triad C-E-G is C....
in ascending fourth or descending fifth relationship", with movement by ascending perfect fourth
Perfect fourth
In classical music from Western culture, a fourth is a musical interval encompassing four staff positions , and the perfect fourth is a fourth spanning five semitones. For example, the ascending interval from C to the next F is a perfect fourth, as the note F lies five semitones above C, and there...
being equivalent to movement by descending perfect fifth
Perfect fifth
In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is a musical interval encompassing five staff positions , and the perfect fifth is a fifth spanning seven semitones, or in meantone, four diatonic semitones and three chromatic semitones...
due to inversion
Inversion (music)
In music theory, the word inversion has several meanings. There are inverted chords, inverted melodies, inverted intervals, and inverted voices...
.
The circle progression is commonly a circle through the diatonic chords, chords of the diatonic scale
Diatonic scale
In music theory, a diatonic scale is a seven note, octave-repeating musical scale comprising five whole steps and two half steps for each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole steps...
, by fifths, including one progression by diminished fifth (in C: between F and B) and one diminished chord
Diminished chord
A diminished triad chord or diminished chord is a triad consisting of two minor thirds above the root — if built on C, a diminished chord would have a C, an E and a G. It resembles a minor triad with a lowered fifth....
(in C: B):
I-IV-viio-iii-vi-ii-V-I
Shorter common progressions may be derived by selecting certain specific chords from the series completing a circle from the tonic
Tonic (music)
In music, the tonic is the first scale degree of the diatonic scale and the tonal center or final resolution tone. The triad formed on the tonic note, the tonic chord, is thus the most significant chord...
through all seven diatonic chords, such as the primary triad
Primary triad
In music, a primary triad is a one of the three triads, or three note chord built from thirds, most important in tonal and diatonic music, as opposed to an auxiliary triad or secondary triad....
s book-ending the progression:
I- V-I = I-V-I
I-IV- V-I = I-IV-V-I
The ii-V-I turnaround lies at the end of the circle progression, as does the vi-ii-V-I progression of root movement by descending fifths, which establishes tonality and also strengthens the key
Key (music)
In music theory, the term key is used in many different and sometimes contradictory ways. A common use is to speak of music as being "in" a specific key, such as in the key of C major or in the key of F-sharp. Sometimes the terms "major" or "minor" are appended, as in the key of A minor or in the...
through the contrast of minor and major
Major and minor
In Western music, the adjectives major and minor can describe a musical composition, movement, section, scale, key, chord, or interval.Major and minor are frequently referred to in the titles of classical compositions, especially in reference to the key of a piece.-Intervals and chords:With regard...
.

