
Circular uniform distribution
Encyclopedia
In probability theory
and directional statistics, a circular uniform distribution is a probability distribution on the unit circle whose density is uniform for all angles.
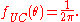
In terms of the circular variable the circular moments of the circular uniform distribution all zero, except for
the circular moments of the circular uniform distribution all zero, except for 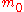 :
:
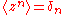
where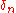 is the Kronecker delta symbol.
is the Kronecker delta symbol.
The mean angle is undefined, and the length of the mean resultant is zero.
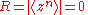
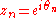 drawn from a circular uniform distribution is defined as:
drawn from a circular uniform distribution is defined as:
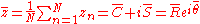
where the average sine and cosine are:

and the average resultant length is:
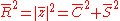
and the mean angle is:

The sample mean for the circular uniform distribution will be concentrated about zero, becoming more concentrated as N increases. The distribution of the sample mean for the uniform distribution is given by:
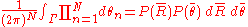
where consists of intervals of
consists of intervals of  in the variables, subject to the constraint that
in the variables, subject to the constraint that 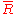 and
and 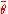 are constant, or, alternatively, that
are constant, or, alternatively, that 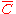 and
and 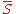 are constant. The distribution of the angle
are constant. The distribution of the angle is uniform
is uniform
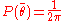
and the distribution of is given by:
is given by:

where is the Bessel function
is the Bessel function
of order zero. There is no known general analytic solution for the above integral, and it is difficult to evaluate due to the large number of oscillations in the integrand. A 10,000 point Monte Carlo simulation of the distribution of the mean for N=3 is shown in the figure.
For certain special cases, the above integral can be evaluated:
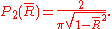
For large N, the distribution of the mean can be determined from the central limit theorem for directional statistics
. Since the angles are uniformly distributed, the individual sines and cosines of the angles will be distributed as:
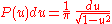
where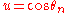 or
or 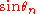 . It follows that they will have zero mean and a variance of 1/2. By the central limit theorem, in the limit of large N,
. It follows that they will have zero mean and a variance of 1/2. By the central limit theorem, in the limit of large N,  and
and  , being the sum of a large number of i.i.d's, will be normally distributed with mean zero and variance
, being the sum of a large number of i.i.d's, will be normally distributed with mean zero and variance  . The mean resultant length
. The mean resultant length 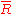 , being the square root of the sum of two normally distributed variables, will be Chi-distributed with two degrees of freedom (i.e.Rayleigh-distributed) and variance
, being the square root of the sum of two normally distributed variables, will be Chi-distributed with two degrees of freedom (i.e.Rayleigh-distributed) and variance 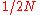 :
:
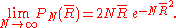

where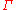 is any interval of length
is any interval of length  . This is the maximum entropy any circular distribution may have.
. This is the maximum entropy any circular distribution may have.
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
and directional statistics, a circular uniform distribution is a probability distribution on the unit circle whose density is uniform for all angles.
Description
The pdf of the circular uniform distribution is: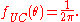
In terms of the circular variable
 the circular moments of the circular uniform distribution all zero, except for
the circular moments of the circular uniform distribution all zero, except for 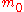 :
: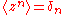
where
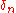 is the Kronecker delta symbol.
is the Kronecker delta symbol.The mean angle is undefined, and the length of the mean resultant is zero.
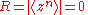
Distribution of the mean
The sample mean of a set of N measurements drawn from a circular uniform distribution is defined as:
drawn from a circular uniform distribution is defined as: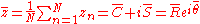
where the average sine and cosine are:

and the average resultant length is:
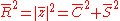
and the mean angle is:

The sample mean for the circular uniform distribution will be concentrated about zero, becoming more concentrated as N increases. The distribution of the sample mean for the uniform distribution is given by:
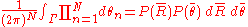
where
 consists of intervals of
consists of intervals of  in the variables, subject to the constraint that
in the variables, subject to the constraint that  and
and  are constant, or, alternatively, that
are constant, or, alternatively, that  and
and  are constant. The distribution of the angle
are constant. The distribution of the angle is uniform
is uniform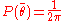
and the distribution of
 is given by:
is given by:
where
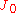 is the Bessel function
is the Bessel functionBessel function
In mathematics, Bessel functions, first defined by the mathematician Daniel Bernoulli and generalized by Friedrich Bessel, are canonical solutions y of Bessel's differential equation:...
of order zero. There is no known general analytic solution for the above integral, and it is difficult to evaluate due to the large number of oscillations in the integrand. A 10,000 point Monte Carlo simulation of the distribution of the mean for N=3 is shown in the figure.
For certain special cases, the above integral can be evaluated:
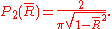
For large N, the distribution of the mean can be determined from the central limit theorem for directional statistics
Central limit theorem for directional statistics
In probability theory, the central limit theorem states conditions under which the mean of a sufficiently large number of independent random variables, each with finite mean and variance, will be approximately normally distributed....
. Since the angles are uniformly distributed, the individual sines and cosines of the angles will be distributed as:
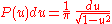
where
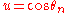 or
or  . It follows that they will have zero mean and a variance of 1/2. By the central limit theorem, in the limit of large N,
. It follows that they will have zero mean and a variance of 1/2. By the central limit theorem, in the limit of large N,  and
and  , being the sum of a large number of i.i.d's, will be normally distributed with mean zero and variance
, being the sum of a large number of i.i.d's, will be normally distributed with mean zero and variance  . The mean resultant length
. The mean resultant length  , being the square root of the sum of two normally distributed variables, will be Chi-distributed with two degrees of freedom (i.e.Rayleigh-distributed) and variance
, being the square root of the sum of two normally distributed variables, will be Chi-distributed with two degrees of freedom (i.e.Rayleigh-distributed) and variance 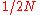 :
: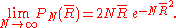
Entropy
The differential information entropy of the uniform distribution is simply
where
 is any interval of length
is any interval of length  . This is the maximum entropy any circular distribution may have.
. This is the maximum entropy any circular distribution may have.

