
Clipping (signal processing)
Encyclopedia
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
that limits a signal once it exceeds a threshold. Clipping may occur when a signal is recorded by a sensor
Sensor
A sensor is a device that measures a physical quantity and converts it into a signal which can be read by an observer or by an instrument. For example, a mercury-in-glass thermometer converts the measured temperature into expansion and contraction of a liquid which can be read on a calibrated...
that has constraints on the range of data it can measure, it can occur when a signal is digitized, or it can occur any other time an analog
Analog signal
An analog or analogue signal is any continuous signal for which the time varying feature of the signal is a representation of some other time varying quantity, i.e., analogous to another time varying signal. It differs from a digital signal in terms of small fluctuations in the signal which are...
or digital signal
Digital signal
A digital signal is a physical signal that is a representation of a sequence of discrete values , for example of an arbitrary bit stream, or of a digitized analog signal...
is transformed, particularly in the presence of gain
Gain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
or overshoot
Overshoot (signal)
In signal processing, control theory, electronics, and mathematics, overshoot is when a signal or function exceeds its target. It arises especially in the step response of bandlimited systems such as low-pass filters...
and undershoot.
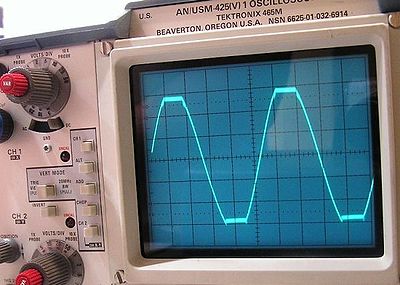
Clipping may be described as hard, in cases where the signal is strictly limited at the threshold, producing a flat cutoff; or it may be described as soft, in cases where the clipped signal continues to follow the original at a reduced gain. Hard clipping results in many high frequency harmonics; soft clipping results in fewer higher order harmonics and intermodulation distortion components.
Audio

In the audio domain, clipping may be heard as general distortion or as pops.
Because the clipped waveform has more area underneath it than the smaller unclipped waveform, the amplifier produces more power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
than its rated (sine wave
Sine wave
The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields...
) output when it is clipping. This extra power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
can damage any part of the loudspeaker
Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
, including the woofer
Woofer
Woofer is the term commonly used for a loudspeaker driver designed to produce low frequency sounds, typically from around 40 hertz up to about a kilohertz or higher. The name is from the onomatopoeic English word for a dog's bark, "woof"...
, or the tweeter
Tweeter
A tweeter is a loudspeaker designed to produce high audio frequencies, typically from around 2,000 Hz to 20,000 Hz . Some tweeters can manage response up to 65 kHz...
, by causing over-excursion, or by overheating the voice coil. It may cause damage to the amplifier's power supply
Power supply
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy...
or simply blow a fuse
Fuse (electrical)
In electronics and electrical engineering, a fuse is a type of low resistance resistor that acts as a sacrificial device to provide overcurrent protection, of either the load or source circuit...
.
In the frequency domain
Frequency domain
In electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, frequency domain is a term used to describe the domain for analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time....
, clipping produces strong harmonics in the high frequency range (as the clipped waveform comes closer to a squarewave). The extra high frequency weighting of the signal could make tweeter
Tweeter
A tweeter is a loudspeaker designed to produce high audio frequencies, typically from around 2,000 Hz to 20,000 Hz . Some tweeters can manage response up to 65 kHz...
damage more likely than if the signal was not clipped. However most loudspeakers are designed to handle signals like cymbal crashes that have even more high frequency weighting than amplifier clipping produces, so damage attributable to this characteristic is rare.
Many electric guitar
Electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that uses the principle of direct electromagnetic induction to convert vibrations of its metal strings into electric audio signals. The signal generated by an electric guitar is too weak to drive a loudspeaker, so it is amplified before sending it to a loudspeaker...
players
Guitarist
A guitarist is a musician who plays the guitar. Guitarists may play a variety of instruments such as classical guitars, acoustic guitars, electric guitars, and bass guitars. Some guitarists accompany themselves on the guitar while singing.- Versatility :The guitarist controls an extremely...
intentionally overdrive their amplifiers (or insert a "fuzz box") to cause clipping in order to get a desired sound (see guitar distortion).
Some audiophiles believe that the clipping behavior of vacuum tube
Vacuum tube
In electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
s with little or no negative feedback
Negative feedback
Negative feedback occurs when the output of a system acts to oppose changes to the input of the system, with the result that the changes are attenuated. If the overall feedback of the system is negative, then the system will tend to be stable.- Overview :...
is superior to that of transistors, in that vacuum tubes clip more gradually than transistors (i.e. soft clipping, and mostly even harmonics), resulting in harmonic distortion that is generally less objectionable. In general though, the distortion associated with clipping is unwanted, and is visible on an oscilloscope
Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope is a type of electronic test instrument that allows observation of constantly varying signal voltages, usually as a two-dimensional graph of one or more electrical potential differences using the vertical or 'Y' axis, plotted as a function of time,...
even if it is inaudible. Even in a transistorised amplifier with hard clipping, the gain of the transistor will be reducing (leading to nonlinear distortion) as the output current increases and the voltage across the transistor reduces close to the saturation voltage (for bipolar transistors), and so "full power" for the purposes of measuring distortion in amplifiers is usually taken as a few percent below clipping.
Images

Saturation (color theory)
In colorimetry and color theory, colorfulness, chroma, and saturation are related but distinct concepts referring to the perceived intensity of a specific color. Colorfulness is the degree of difference between a color and gray. Chroma is the colorfulness relative to the brightness of another color...
(washed-out) bright areas that turn to pure white if all color components
Channel (digital image)
Color digital images are made of pixels, and pixels are made of combinations of primary colors. A channel in this context is the grayscale image of the same size as a color image, made of just one of these primary colors. For instance, an image from a standard digital camera will have a red, green...
clip.
Analog circuitry
A circuit designer may intentionally use a clipperClipper (electronics)
In electronics, a clipper is a device designed to prevent the output of a circuit from exceeding a predetermined voltage level without distorting the remaining part of the applied waveform....
or clamper
Clamper (electronics)
A clamper is an electronic circuit that prevents a signal from exceeding a certain defined magnitude by shifting its DC value. The clamper does not restrict the peak-to-peak excursion of the signal, but moves it up or down by a fixed value...
to keep a signal within a desired range.
When an amplifier is pushed to create a signal with more power than it can support, it will amplify the signal only up to its maximum capacity, at which point the signal will be amplified no further.
- An integrated circuitIntegrated circuitAn integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
or discrete solid stateSolid state (electronics)Solid-state electronics are those circuits or devices built entirely from solid materials and in which the electrons, or other charge carriers, are confined entirely within the solid material...
amplifier cannot give an output voltage larger than the voltage it is powered by (commonly a 24- or 30-volt spread for operational amplifiers used in line level equipment). - A vacuum tubeVacuum tubeIn electronics, a vacuum tube, electron tube , or thermionic valve , reduced to simply "tube" or "valve" in everyday parlance, is a device that relies on the flow of electric current through a vacuum...
can only move a limited number of electrons in an amount of time, dependent on its size, temperature, and metals. - A transformer (most commonly used between stages in tube equipment) will clip when its ferromagnetic core becomes electromagnetically saturated.
Digital processing
In digital signal processingDigital signal processing
Digital signal processing is concerned with the representation of discrete time signals by a sequence of numbers or symbols and the processing of these signals. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing...
, clipping occurs when the signal is restricted by the range of a chosen representation. For example in a system using 16-bit signed
Signed-digit representation
Signed-digit representation of numbers indicates that digits can be prefixed with a − sign to indicate that they are negative.Signed-digit representation can be used in low-level software and hardware to accomplish fast addition of integers because it can eliminate carries...
integers, 32767 is the largest positive value that can be represented, and if during processing the amplitude of the signal is doubled, sample values of 32000 should become 64000, but instead they are truncated to the maximum, 32767. Clipping is preferable to the alternative in digital systems — wrapping — which occurs if the digital hardware is allowed to "overflow
Arithmetic overflow
The term arithmetic overflow or simply overflow has the following meanings.# In a computer, the condition that occurs when a calculation produces a result that is greater in magnitude than that which a given register or storage location can store or represent.# In a computer, the amount by which a...
", ignoring the most significant bit
Most significant bit
In computing, the most significant bit is the bit position in a binary number having the greatest value...
s of the magnitude, and sometimes even the sign of the sample value, resulting in gross distortion of the signal.
The incidence of clipping may be greatly reduced by using floating point numbers instead of integers. However, floating point numbers are usually less efficient to use, sometimes result in a loss of precision
Accuracy and precision
In the fields of science, engineering, industry and statistics, the accuracy of a measurement system is the degree of closeness of measurements of a quantity to that quantity's actual value. The precision of a measurement system, also called reproducibility or repeatability, is the degree to which...
, and they can still clip if a number is extremely large or small.
Avoiding clipping
Clipping can be detected by viewing the signal (on an oscilloscope, for example), and observing that the tops and bottoms of waves aren't smooth anymore. When working with images, some tools can highlight all pixelPixel
In digital imaging, a pixel, or pel, is a single point in a raster image, or the smallest addressable screen element in a display device; it is the smallest unit of picture that can be represented or controlled....
s that are pure white, allowing the user to identify larger groups of white pixels and decide if too much clipping has occurred.
To avoid clipping, the signal can be dynamically reduced using a limiter
Limiter
In electronics, a limiter is a circuit that allows signals below a specified input power to pass unaffected while attenuating the peaks of stronger signals that exceed this input power....
. If not done carefully, this can still cause undesirable distortion, but it prevents any data from being completely lost.

