
Overshoot (signal)
Encyclopedia

Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, control theory
Control theory
Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
, electronics
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
, and mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, overshoot is when a signal or function exceeds its target. It arises especially in the step response
Step response
The step response of a system in a given initial state consists of the time evolution of its outputs when its control inputs are Heaviside step functions. In electronic engineering and control theory, step response is the time behaviour of the outputs of a general system when its inputs change from...
of bandlimited
Bandlimited
Bandlimiting is the limiting of a deterministic or stochastic signal's Fourier transform or power spectral density to zero above a certain finite frequency...
systems such as low-pass filter
Low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
s. It is often followed by ringing, and at times conflated with this latter.
Definition
Maximum Overshoot (signal)Overshoot
Overshoot may refer to:* Overshoot , when a signal exceeds its steady state value* Overshoot , when a population exceeds the environment's carrying capacity* Overshoot , an aborted landing...
is defined in Katsuhiko Ogata's Discrete-time control systems as "the maximum peak value of the response curve measured from the desired response of the system."
Control theory
In control theoryControl theory
Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
, overshoot refers to an output exceeding its final, steady-state value. For a step input
Step response
The step response of a system in a given initial state consists of the time evolution of its outputs when its control inputs are Heaviside step functions. In electronic engineering and control theory, step response is the time behaviour of the outputs of a general system when its inputs change from...
, the percentage overshoot (PO) is the maximum value minus the step value divided by the step value. In the case of the unit step, the overshoot is just the maximum value of the step response minus one. Also see the definition of overshoot in an electronics context.
The percentage overshoot is a function of the Damping ratio
Damping ratio
[[Image:Damped spring.gif|right|frame|Underdamped [[spring–mass system]] with ζ 1 , and is referred to as overdamped.*Underdamped:If s is a complex number, then the solution is a decaying exponential combined with an oscillatory portion that looks like \exp...
ζ and is given by
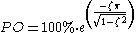
The damping ratio can also be found by
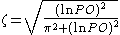
Electronics
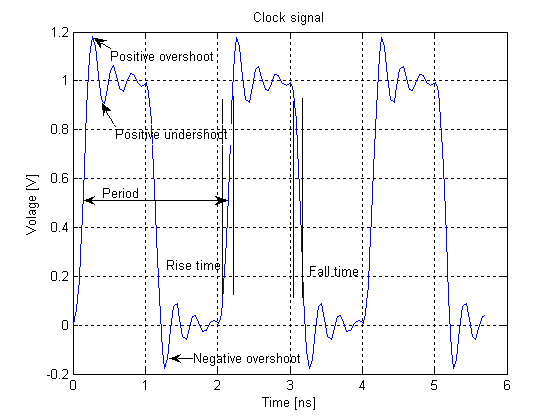
Usage: Overshoot occurs when the transitory values exceed final value. When they are lower than the final value, the phenomenon is called "undershoot".
A circuit
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
is designed to minimize risetime while containing distortion
Distortion
A distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
of the signal within acceptable limits.
- Overshoot represents a distortionDistortionA distortion is the alteration of the original shape of an object, image, sound, waveform or other form of information or representation. Distortion is usually unwanted, and often many methods are employed to minimize it in practice...
of the signal. - In circuit design, the goals of minimizing overshoot and of decreasing circuit risetime can conflict.
- The magnitude of overshoot depends on time through a phenomenon called "dampingDampingIn physics, damping is any effect that tends to reduce the amplitude of oscillations in an oscillatory system, particularly the harmonic oscillator.In mechanics, friction is one such damping effect...
." See illustration under step response. - Overshoot often is associated with settling timeSettling timeThe settling time of an amplifier or other output device is the time elapsed from the application of an ideal instantaneous step input to the time at which the amplifier output has entered and remained within a specified error band, usually symmetrical about the final value.Settling time includes a...
, how long it takes for the output to reach steady state; see step response.
Also see the definition of overshoot in a control theory context.
Mathematics
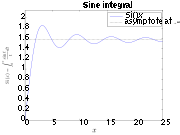
In the approximation of functions, overshoot is one term describing quality of approximation. When a function such as a square wave is represented by a summation of terms, for example, a Fourier series
Fourier series
In mathematics, a Fourier series decomposes periodic functions or periodic signals into the sum of a set of simple oscillating functions, namely sines and cosines...
or an expansion in orthogonal polynomials
Orthogonal polynomials
In mathematics, the classical orthogonal polynomials are the most widely used orthogonal polynomials, and consist of the Hermite polynomials, the Laguerre polynomials, the Jacobi polynomials together with their special cases the ultraspherical polynomials, the Chebyshev polynomials, and the...
, the approximation of the function by a truncated number of terms in the series can exhibit overshoot, undershoot and ringing. The more terms retained in the series, the less pronounced the departure of the approximation from the function it represents. However, though the period of the oscillations decreases, their amplitude does not; this is known as the Gibbs phenomenon
Gibbs phenomenon
In mathematics, the Gibbs phenomenon, named after the American physicist J. Willard Gibbs, is the peculiar manner in which the Fourier series of a piecewise continuously differentiable periodic function behaves at a jump discontinuity: the nth partial sum of the Fourier series has large...
. For the Fourier transform
Fourier transform
In mathematics, Fourier analysis is a subject area which grew from the study of Fourier series. The subject began with the study of the way general functions may be represented by sums of simpler trigonometric functions...
, this can be modeled by approximating a step function
Step function
In mathematics, a function on the real numbers is called a step function if it can be written as a finite linear combination of indicator functions of intervals...
by the integral up to a certain frequency, which yields the sine integral. This can be interpreted as convolution with the sinc function; in signal processing terms, this is a low-pass filter
Low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
.
Signal processing


.svg.png)
Signal processing
Signal processing is an area of systems engineering, electrical engineering and applied mathematics that deals with operations on or analysis of signals, in either discrete or continuous time...
, overshoot is when the output of a filter
Filter (signal processing)
In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes from a signal some unwanted component or feature. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal...
has a higher maximum value than the input, specifically for the step response
Step response
The step response of a system in a given initial state consists of the time evolution of its outputs when its control inputs are Heaviside step functions. In electronic engineering and control theory, step response is the time behaviour of the outputs of a general system when its inputs change from...
, and frequently yields the related phenomenon of ringing artifacts
Ringing artifacts
In signal processing, particularly digital image processing, ringing artifacts are artifacts that appear as spurious signals near sharp transitions in a signal. Visually, they appear as bands or "ghosts" near edges; audibly, they appear as "echos" near transients, particularly sounds from...
.
This occurs for instance in using the sinc filter
Sinc filter
In signal processing, a sinc filter is an idealized filter that removes all frequency components above a given bandwidth, leaves the low frequencies alone, and has linear phase...
as an ideal (brick-wall) low-pass filter
Low-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
. The step response can be interpreted as the convolution
Convolution
In mathematics and, in particular, functional analysis, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions f and g, producing a third function that is typically viewed as a modified version of one of the original functions. Convolution is similar to cross-correlation...
with the impulse response
Impulse response
In signal processing, the impulse response, or impulse response function , of a dynamic system is its output when presented with a brief input signal, called an impulse. More generally, an impulse response refers to the reaction of any dynamic system in response to some external change...
, which is a sinc function.
The overshoot and undershoot can be understood in this way: kernels are generally normalized to have integral 1, so they send constant functions to constant functions – otherwise they have gain
Gain
In electronics, gain is a measure of the ability of a circuit to increase the power or amplitude of a signal from the input to the output. It is usually defined as the mean ratio of the signal output of a system to the signal input of the same system. It may also be defined on a logarithmic scale,...
. The value of a convolution at a point is a linear combination
Linear combination
In mathematics, a linear combination is an expression constructed from a set of terms by multiplying each term by a constant and adding the results...
of the input signal, with coefficients (weights) the values of the kernel. If a kernel is non-negative, such as for a Gaussian kernel, then the value of the filtered signal will be a convex combination
Convex combination
In convex geometry, a convex combination is a linear combination of points where all coefficients are non-negative and sum up to 1....
of the input values (the coefficients (the kernel) integrate to 1, and are non-negative), and will thus fall between the minimum and maximum of the input signal – it will not undershoot or overshoot. If, on the other hand, the kernel assumes negative values, such as the sinc function, then the value of the filtered signal will instead be an affine combination of the input values, and may fall outside of the minimum and maximum of the input signal, resulting in undershoot and overshoot.
Overshoot is often undesirable, particularly if it causes clipping
Clipping (signal processing)
Clipping is a form of distortion that limits a signal once it exceeds a threshold. Clipping may occur when a signal is recorded by a sensor that has constraints on the range of data it can measure, it can occur when a signal is digitized, or it can occur any other time an analog or digital signal...
, but is sometimes desirable in image sharpening, due to increasing acutance
Acutance
In photography, acutance is the edge contrast of an image. Acutance is related to the amplitude of the derivative of brightness with respect to space...
(perceived sharpness).
Related concepts
A closely related phenomenon is ringing, when, following overshoot, a signal then falls below its steady-state value, and then may bounce back above, taking some time to settle close to its steady-state value; this latter time is called the settle time.In ecology
Ecology
Ecology is the scientific study of the relations that living organisms have with respect to each other and their natural environment. Variables of interest to ecologists include the composition, distribution, amount , number, and changing states of organisms within and among ecosystems...
, overshoot
Overshoot (ecology)
In ecology, overshoot occurs when a population exceeds the long term carrying capacity of its environment. The consequence of overshoot is called a crash or die-off. An attempt to apply this concept to human experience is Overshoot: The Ecological Basis of Revolutionary Change, by William R....
is the analogous concept, where a population exceeds the carrying capacity of a system.
See also
- Step responseStep responseThe step response of a system in a given initial state consists of the time evolution of its outputs when its control inputs are Heaviside step functions. In electronic engineering and control theory, step response is the time behaviour of the outputs of a general system when its inputs change from...
- Ringing (signal)Ringing (signal)In electronics, signal processing, and video, ringing is unwanted oscillation of a signal, particularly in the step response...
- Settle time
- DampingDampingIn physics, damping is any effect that tends to reduce the amplitude of oscillations in an oscillatory system, particularly the harmonic oscillator.In mechanics, friction is one such damping effect...
- OvermodulationOvermodulationOvermodulation is the condition that prevails in telecommunication when the instantaneous level of the modulating signal exceeds the value necessary to produce 100% modulation of the carrier. In the sense of this definition, it is almost always considered a fault condition. In layman's terms, the...
- Integral windupIntegral windupIntegral windup refers to the situation in a PID controller where a large change in setpoint occurs and the integral terms accumulates a significant error during the rise , thus overshooting and continuing to increase as this accumulated error is unwound...

